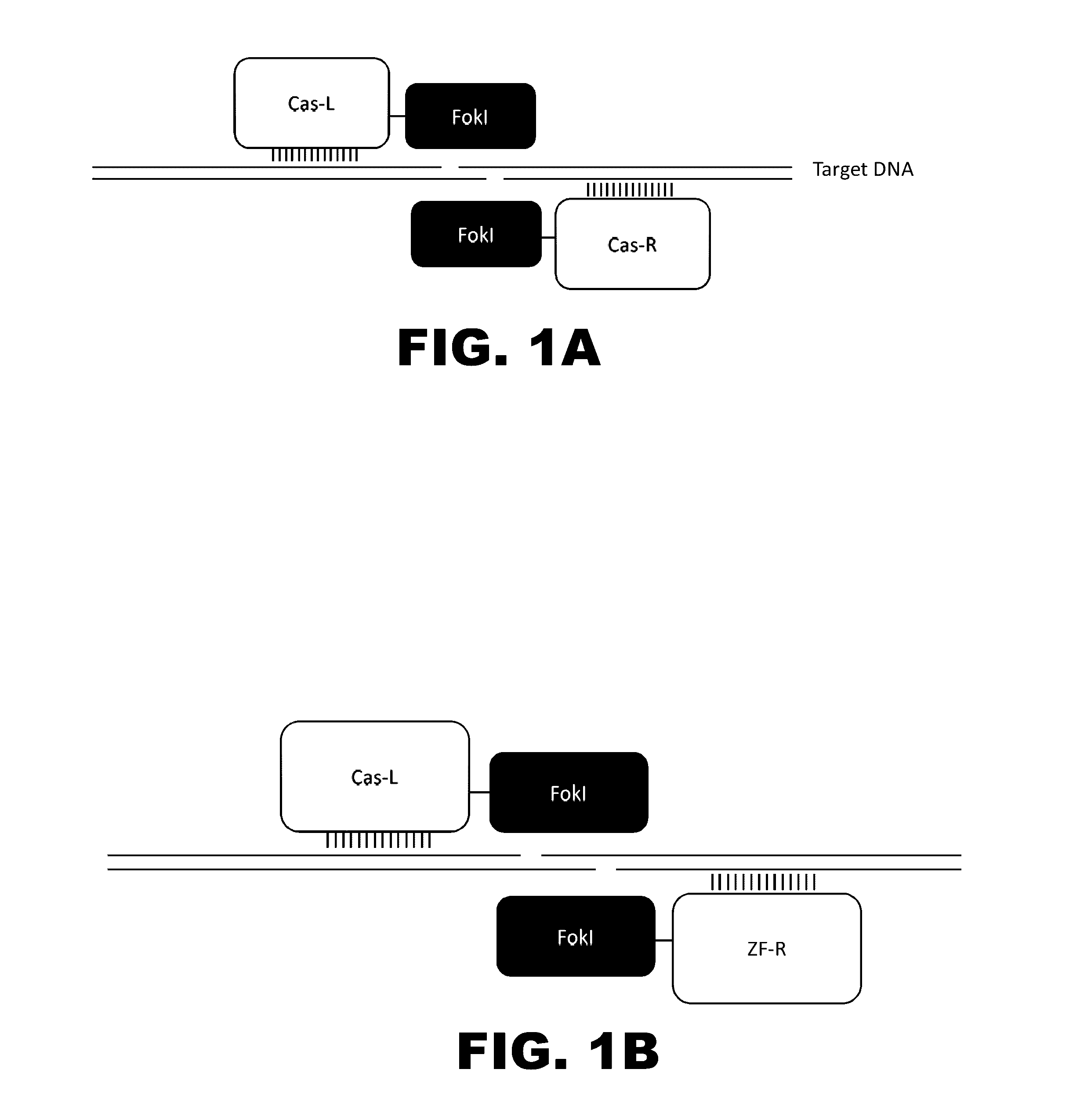
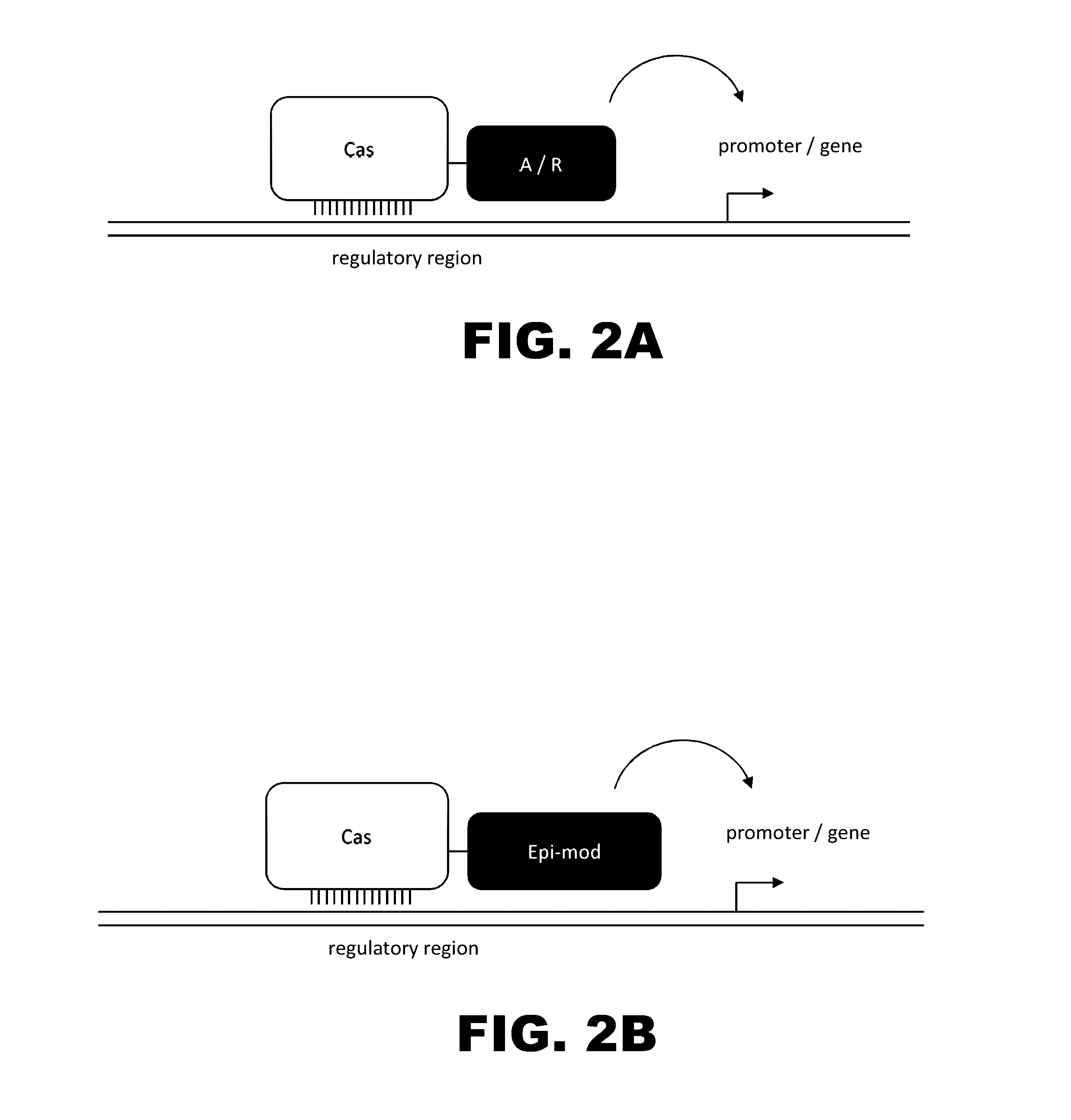
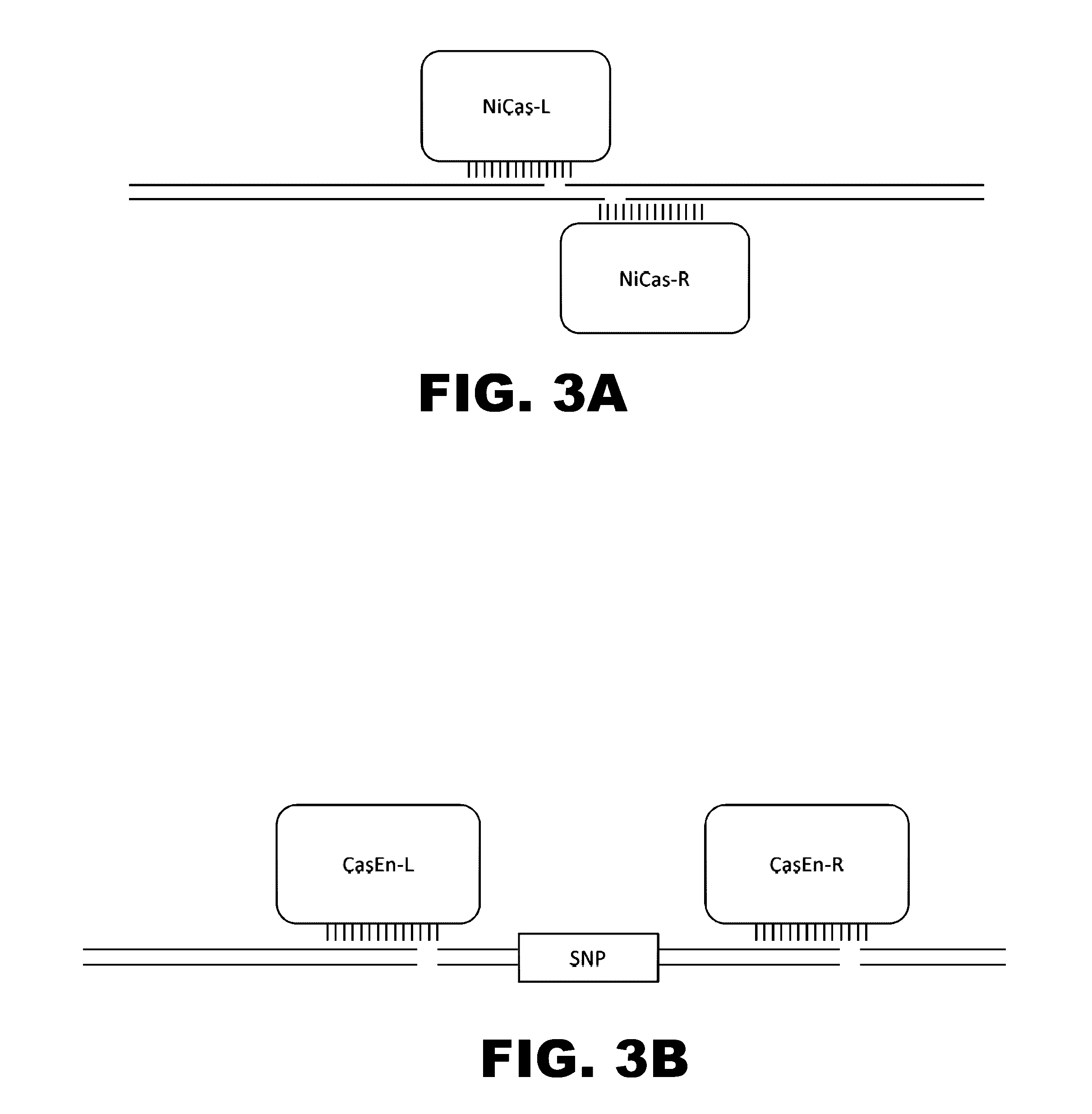
Crispr-based genome modification and regulation
a genome modification and regulation technology, applied in the direction of peptides/protein ingredients, enzyme stabilisation, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of high cost and time-consuming preparation of custom-designed nucleases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Modification of Cas9 Gene for Mammalian Expression
[0161]A Cas9 gene from Streptococcus pyogenes strain MGAS15252 (Accession number YP_005388840.1) was optimized with Homo sapiens codon preference to enhance its translation in mammalian cells. The Cas9 gene also was modified by adding a nuclear localization signal PKKKRKV (SEQ ID NO:1) at the C terminus for targeting the protein into the nuclei of mammalian cells. Table 1 presents the modified Cas9 amino acid sequence, with the nuclear localization sequence underlined. Table 2 presents the codon optimized, modified Cas9 DNA sequence.
TABLE 1Modified Cas9 Amino Acid SequenceMDKKYSIGLDIGTNSVGWAVITDDYKVPSKKFKVLGNTDRHSIKKNLIGALLFGSGETAEATRLKRTARRRYTRRKNRICYLQEIFSNEMAKVDDSFFHRLEESFLVEEDKKHERHPIFGNIVDEVAYHEKYPTIYHLRKKLADSTDKADLRLIYLALAHMIKFRGHFLIEGDLNPDNSDVDKLFIQLVQIYNQLFEENPINASRVDAKAILSARLSKSRRLENLIAQLPGEKRNGLFGNLIALSLGLTPNFKSNFDLAEDAKLQLSKDTYDDDLDNLLAQIGDQYADLFLAAKNLSDAILLSDILRVNSEITKAPLSASMIKRYDEHHQDLTLLKALVRQQLPEKYKEIFFDQSKNGYAGYIDGGAS...
example 2
Targeting Cas9
[0163]The adeno-associated virus integration site 1 (AAVS1) locus was used as a target for Cas9-mediated human genome modification. The human AAVS1 locus is located in intron 1 (4427 bp) of protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 12C (PPP1R12C). Table 3 presents the first exon (shaded gray) and the first intron of PPP1R12C. The underlined sequence within the intron is the targeted modification site (i.e., AAVS1 locus).
TABLE 3 First Exon and Intron of PPP1R12C (5′-3′)(SEQ ID NO:11)GCCCGGCGTCTCCCGGGGCCAGGTCCACCCTCTGCTGCGCCACCTGGGGCATCCTCCTTCCCCGTTGCCAGTCTCGATCCGCCCCGTCGTTCCTGGCCCTGGGCTTTGCCACCCTATGCTGACACCCCGTCCCAGTCCCCCTTACCATTCCCCTTCGACCACCCCACTTCCGAATTGGAGCCGCTTCAACTGGCCCTGGGCTTAGCCACTCTGTGCTGACCACTCTGCCCCAGGCCTCCTTACCATTCCCCTTCGACCTACTCTCTTCCGCATTGGAGTCGCTTTAACTGGCCCTGGCTTTGGCAGCCTGTGCTGACCCATGCAGTCCTCCTTACCATCCCTCCCTCGACTTCCCCTCTTCCGATGTTGAGCCCCTCCAGCCGGTCCTGGACTTTGTCTCCTTCCCTGCCCTGCCCTCTCCTGAACCTGAGCCAGCTCCCATAGCTCAGTCTGGTCTATCTGCCTGGCCCTGGCCATTGTCACTTTGCGCTGCCCT...
example 3
Preparation of Donor Polynucleotide to Monitor Genome Modification
[0165]Targeted integration of a GFP protein into the N terminus of PPP1R12C was used to monitor Cas9-mediated genome modification. To mediate integration by homologous recombination a donor polynucleotide was prepared. The AAVS1-GFP DNA donor contained a 5′ (1185 bp) AAVS1 locus homologous arm, an RNA splicing receptor, a turbo GFP coding sequence, a 3′ transcription terminator, and a 3′ (1217 bp) AAVS1 locus homologous arm. Table 5 presents the sequences of the RNA splicing receptor and the GFP coding sequence followed by the 3′ transcription terminator. Plasmid DNA was prepared by using GenElute Endotoxin-Free Plasmid Maxiprep Kit (Sigma).
TABLE 5Sequences in the AAVS1-GFP DNA donor sequenceSEQ ID5′-3′ SequenceNO:RNA splicingCTGACCTCTTCTCTTCCTCCCACAG15receptorGFP codingGCCACCATGGACTACAAAGACGATGACGACAAGGTCGACT16sequence andCTAGAGCTGCAGAGAGCGACGAGAGCGGCCTGCCCGCCAtranscriptionTGGAGATCGAGTGCCGCATCACCGGCACCCTGAACGGCGtermi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| nucleic acid | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| fluorescence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com