Synthetic combinatorial aav capsid library for targeted gene therapy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
AAV Vector Library Construction
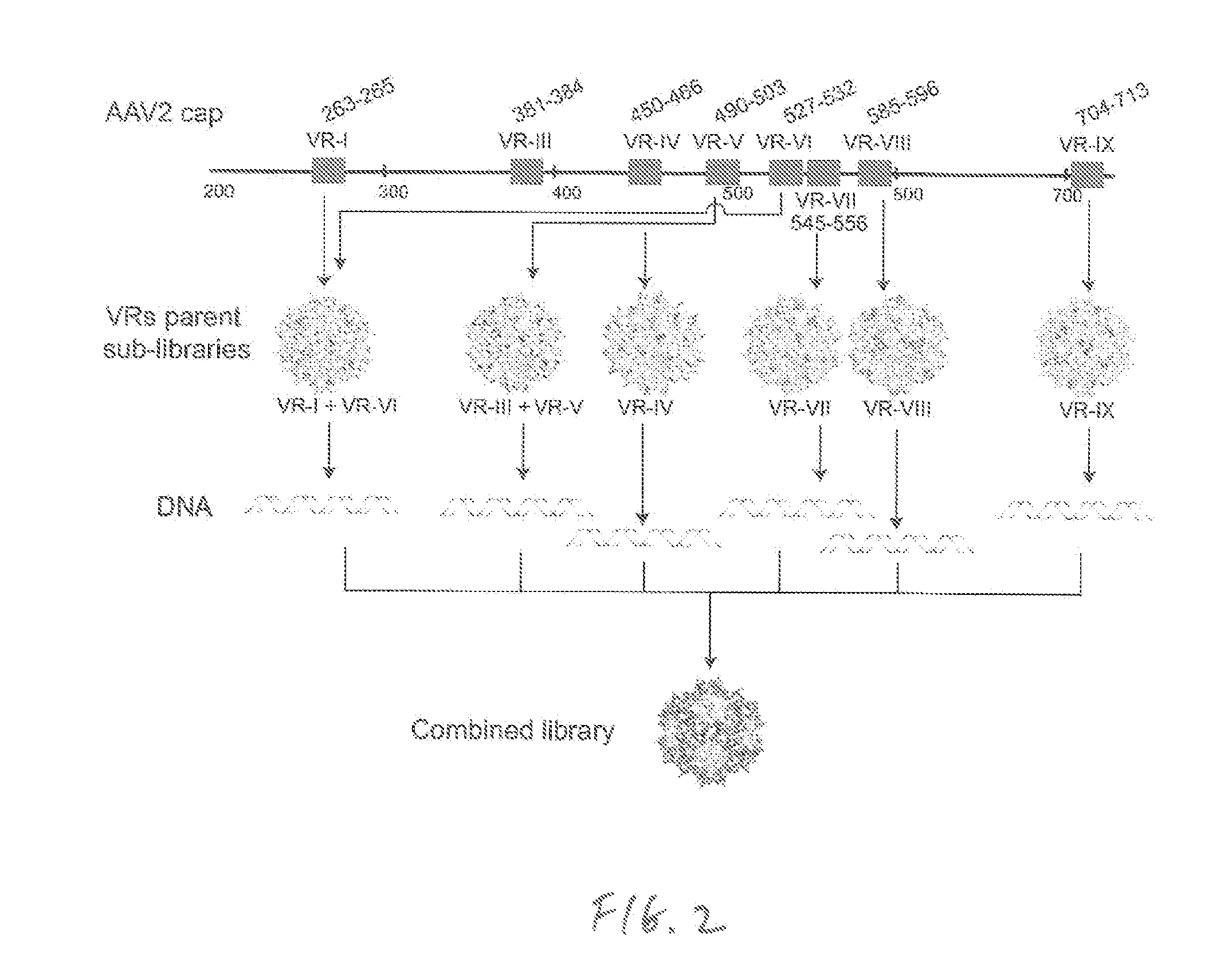
[0149]Methodologies to improve existing AAV vectors for gene therapy include either rational approaches or directed evolution to derive capsid variants characterized by superior transduction efficiencies in targeted tissues. In the present invention, both approaches were integrated in one unified design strategy of “virtual family shuffling” to derive a combinatorial capsid library whereby only variable regions on the surface of the capsid are modified. Individual sub-libraries were first assembled in order to pre-select compatible amino acid residues within restricted surface-exposed regions to minimize the generation of dead-end variants. Subsequently, the successful families were interbred to derive a combined library of about 1×108 complexity. Next-Gen sequencing of the packaged viral DNA revealed capsid surface areas susceptible to directed evolution thus providing guidance for future designs. The utility of the library in gene therapy application...
example 2
Integrating Combinatorial and Rational Approaches to Derive Novel Aav Variants
[0154]AAV is a single-stranded DNA virus belonging to the Parvoviridae family (Muzyczka and Berns, 2001). AAV-derived vectors are promising tools for human gene therapy applications because of their absence of pathogenicity, episomal localization and stable transgene expression (Wu et al., 2006). However, significant limitations to the clinical use of AAV are its promiscuity and its susceptibility to neutralization by human antibodies (Louis-Jeune et al., 2013). Both of these limitations are determined by the nature of amino acid residues exposed at the surface of the capsid. Two main strategies are generally employed to improve AAV vectors: 1) mutagenizing capsid residues to facilitate binding, entry, and / or intracellular trafficking through a rational approach based on the knowledge of virus biology (Wu et al., 2000; Zhong et al., 2008; Lochrie et al., 2005; Aslanidi et al., 2012; Li et al., 2012; Gabrie...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com