Modified cross-section fiber
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
(Production of Modified Cross-Section Fiber)
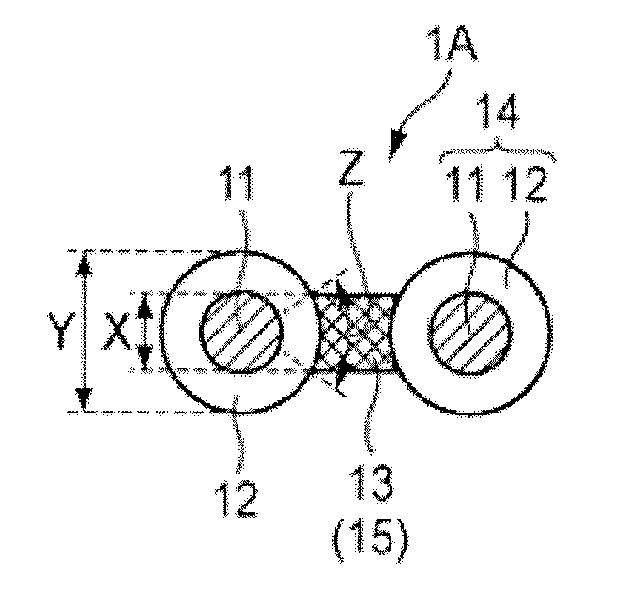
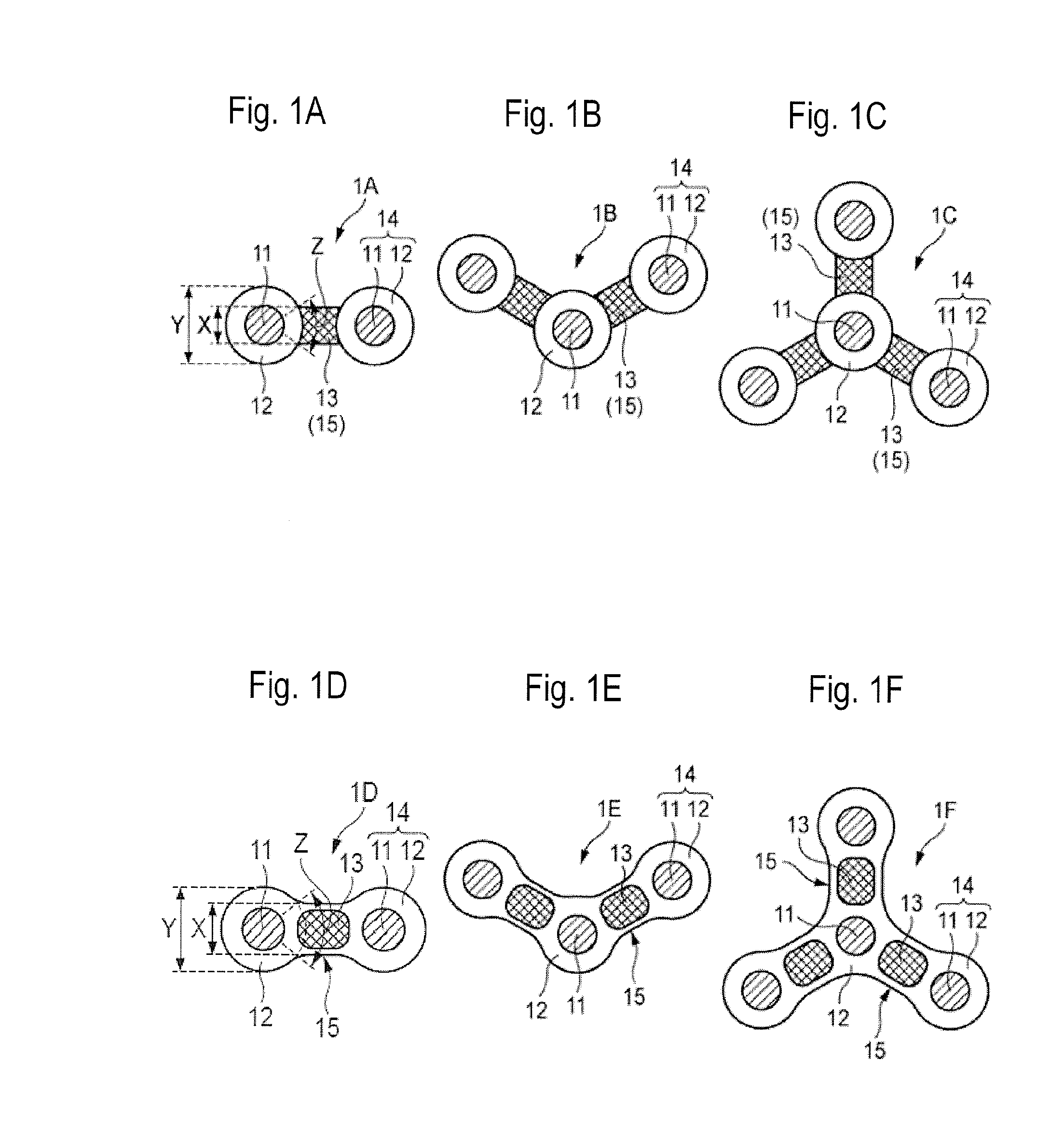
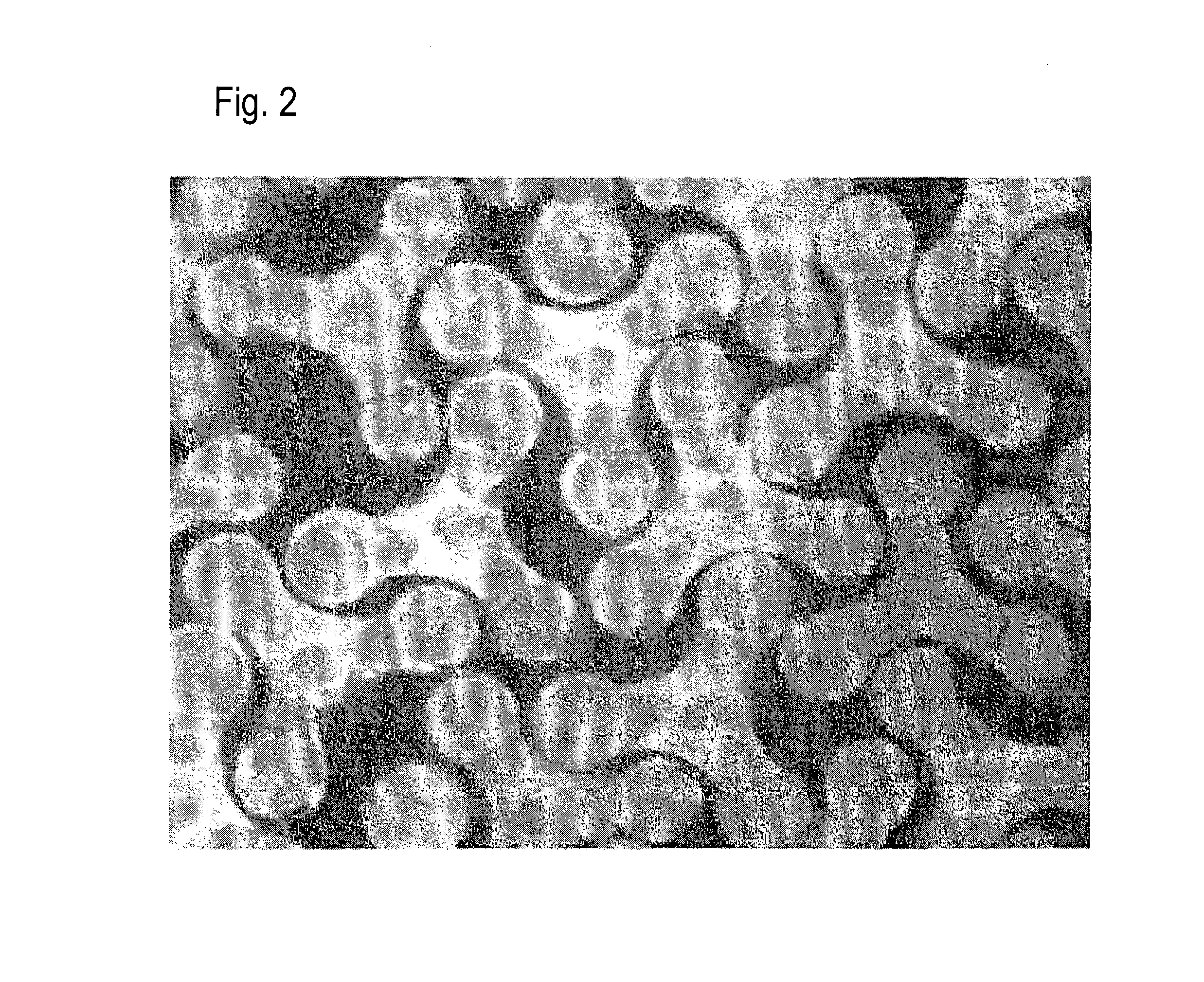
[0080]The first thermoplastic resin (PP), the second thermoplastic resin (PE) and the third thermoplastic resin (PP) were used to spin a modified cross-section fiber shown in FIG. 1(f) through a spinneret for the modified cross-section fiber at 50 / 50 in a volume ratio of (the first thermoplastic resin and the third thermoplastic resin) to the second thermoplastic resin. The modified cross-section fiber having a fineness of 9.5 dtex and having a cross-sectional shape shown in FIG. 2 was obtained.
[0081]On the occasion, as a surfactant, a fiber treating agent containing an alkyl phosphate K salt as a main component was brought into contact with a spun fiber using an oiling roll, and was deposited onto the fiber.
[0082]The resultant unstretched fiber was stretched 6 times using a stretching machine by setting a stretching temperature at 90° C., and the fiber was cut using a cutter into a short fiber.
[0083]As shown in FIG. 3, in the fiber after ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com