Method and system for automatically manufacturing shoes
a technology of automatic manufacturing and manufacturing method, applied in the direction of soles, other domestic articles, uppers, etc., can solve the problems of complex and labor-intensive production methods of the prior art, and the overall production of shoes is still very complex and labor-intensive, and achieve the effect of facilitating the automation of the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
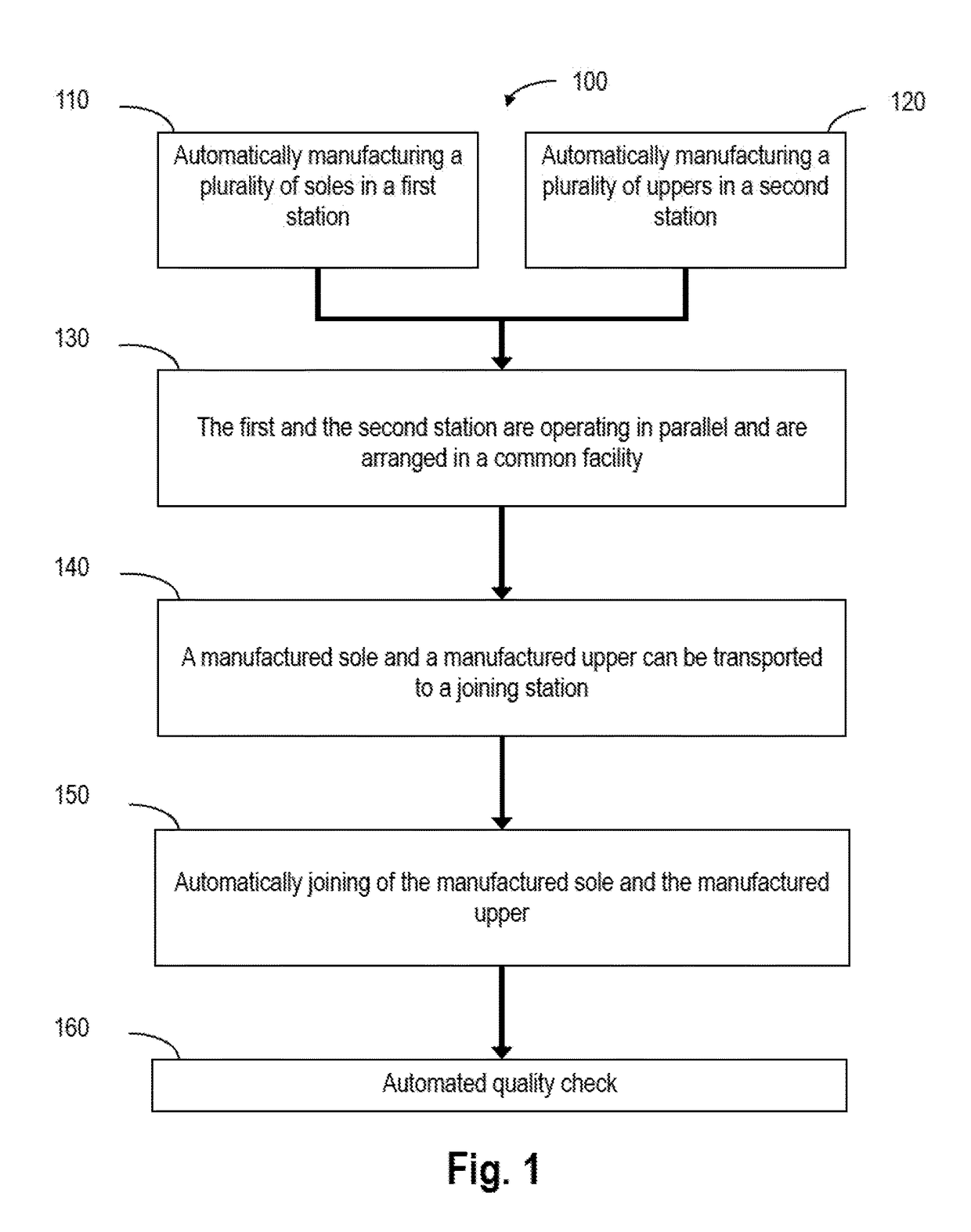
embodiment 1
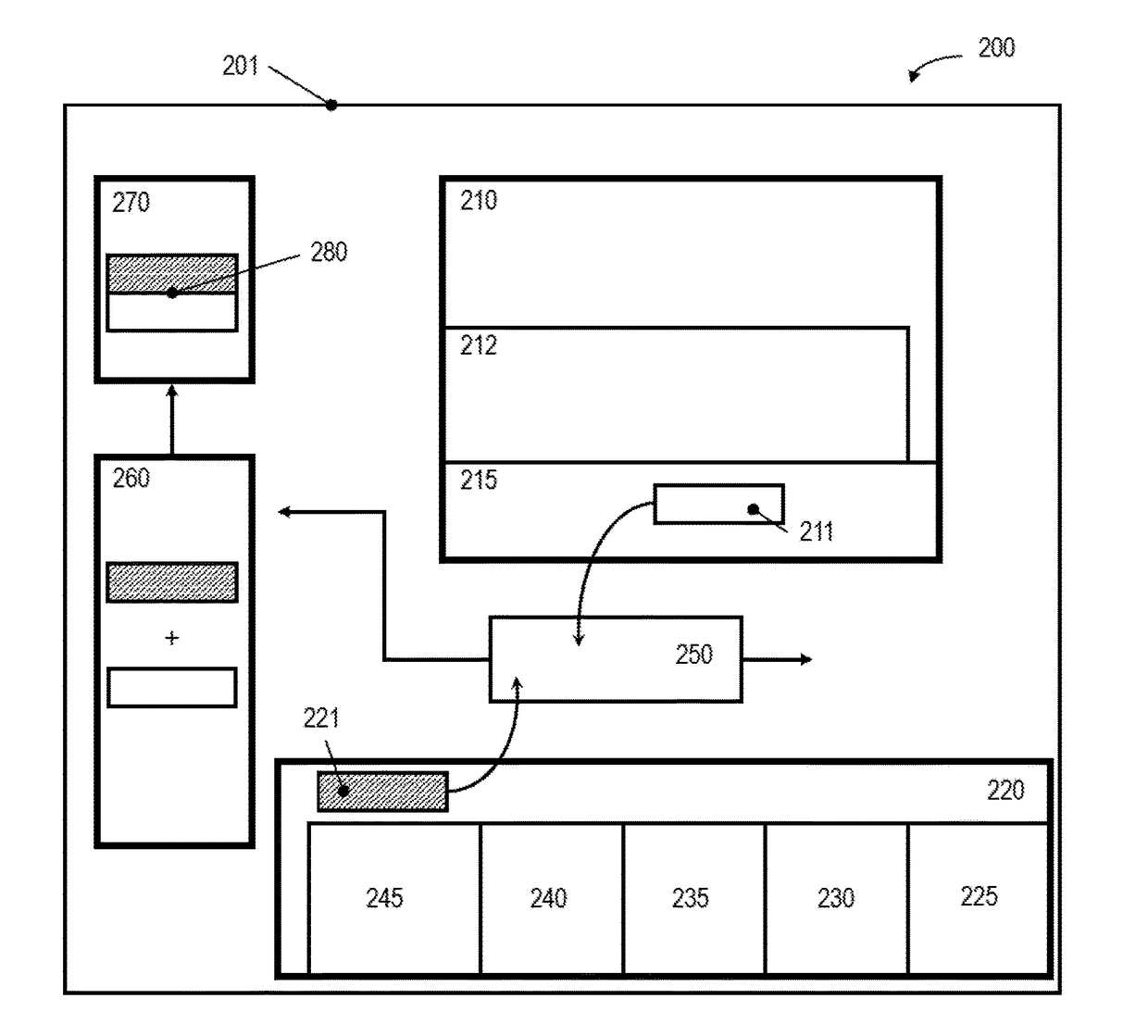
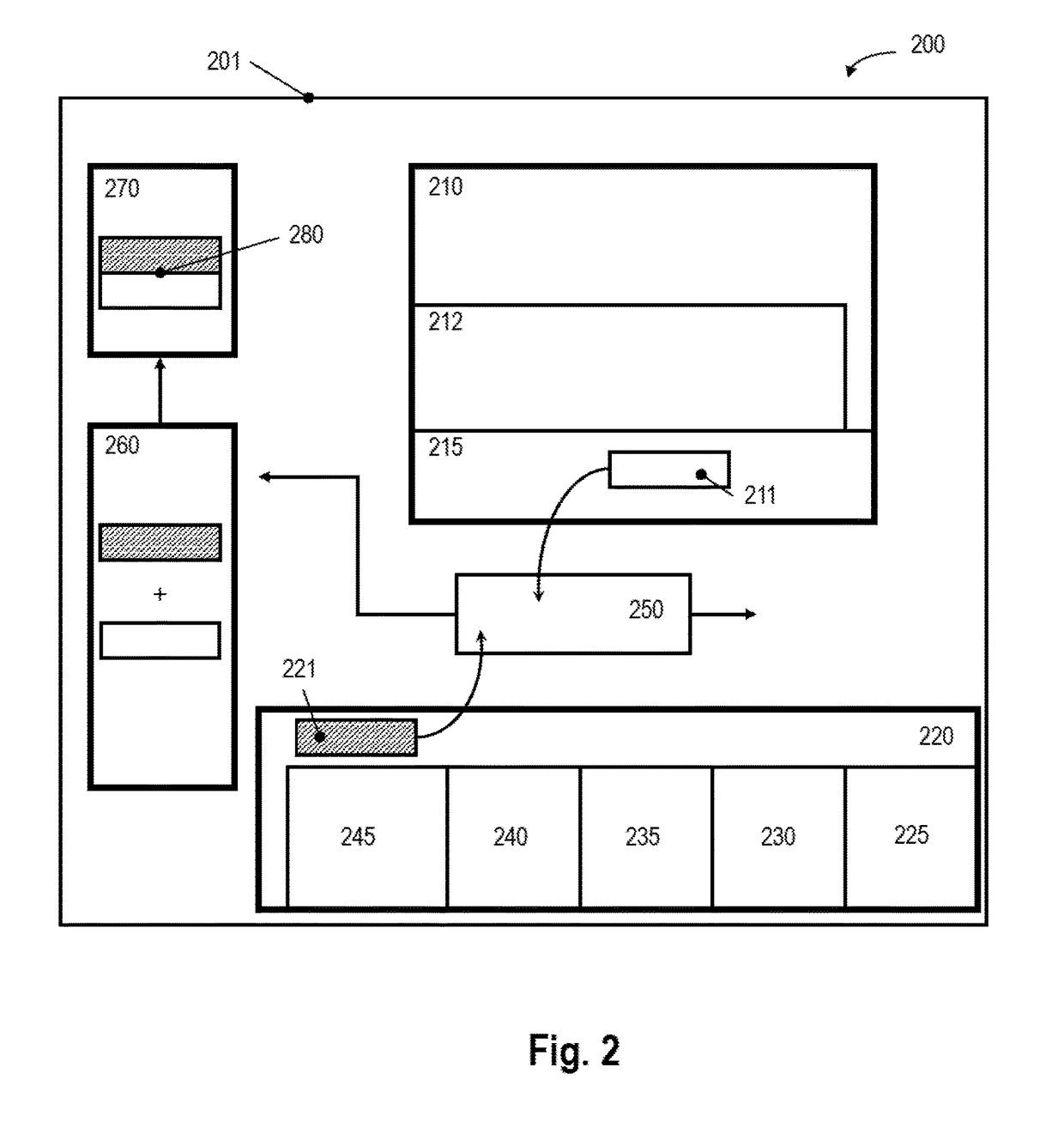
[0083]2. Method according to the preceding embodiment 1, wherein a first number of soles manufactured in step a. corresponds to a second number of uppers manufactured in step b.
embodiment 2
[0084]3. Method according to the preceding embodiment 2, wherein the correspondence between the first number and the second number takes a percentage of defective soles and / or defective uppers into account.
[0085]4. Method according to one of the preceding embodiments 1-3, wherein the automatic manufacture of the plurality of soles in the first station comprises molding individual soles from a plurality of particles.
[0086]5. Method according to one of the preceding embodiments 1-4, further comprising an automated quality check of the manufactured soles.
embodiment 5
[0087]6. Method , wherein the automated quality check involves an automated measurement of the weight and / or the size of the manufactured sole.
[0088]7. Method according to one of the preceding embodiments 1-6, wherein the joining station automatically joins a manufactured sole and a manufactured upper by means of applying heat.
[0089]8. Method according to the preceding embodiment 7, wherein the step of automatically joining is performed without an adhesive, preferably by directly welding the material of the upper onto the material of the sole.
[0090]9. Method according to one of the preceding embodiments 1-8, wherein the step b. comprises reinforcing a manufactured upper by selectively placing at least one patch onto an upper material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com