Process for the Preparation of Polyolefin Fibers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0139]0.52 g of a UHMWPE (commercialized by Ticona under the name GUR® 4113; a linear polyethylene in powder form with a molecular weight of approximately 3.9 MM g / mol calculated using Margolies' equation (Mv (kdalton)=53.7IV1.49), an intrinsic viscosity (IV in dl / g) of about 17.90 dl / g as measured according to ISO 1628-3, and a molecular weight distribution ranging from 7 to 9 measured as described above) were mixed with 10 g nonan-2-ol. The mixture was placed in an oven at 180° C. and regularly mixed. A gel was progressively formed.
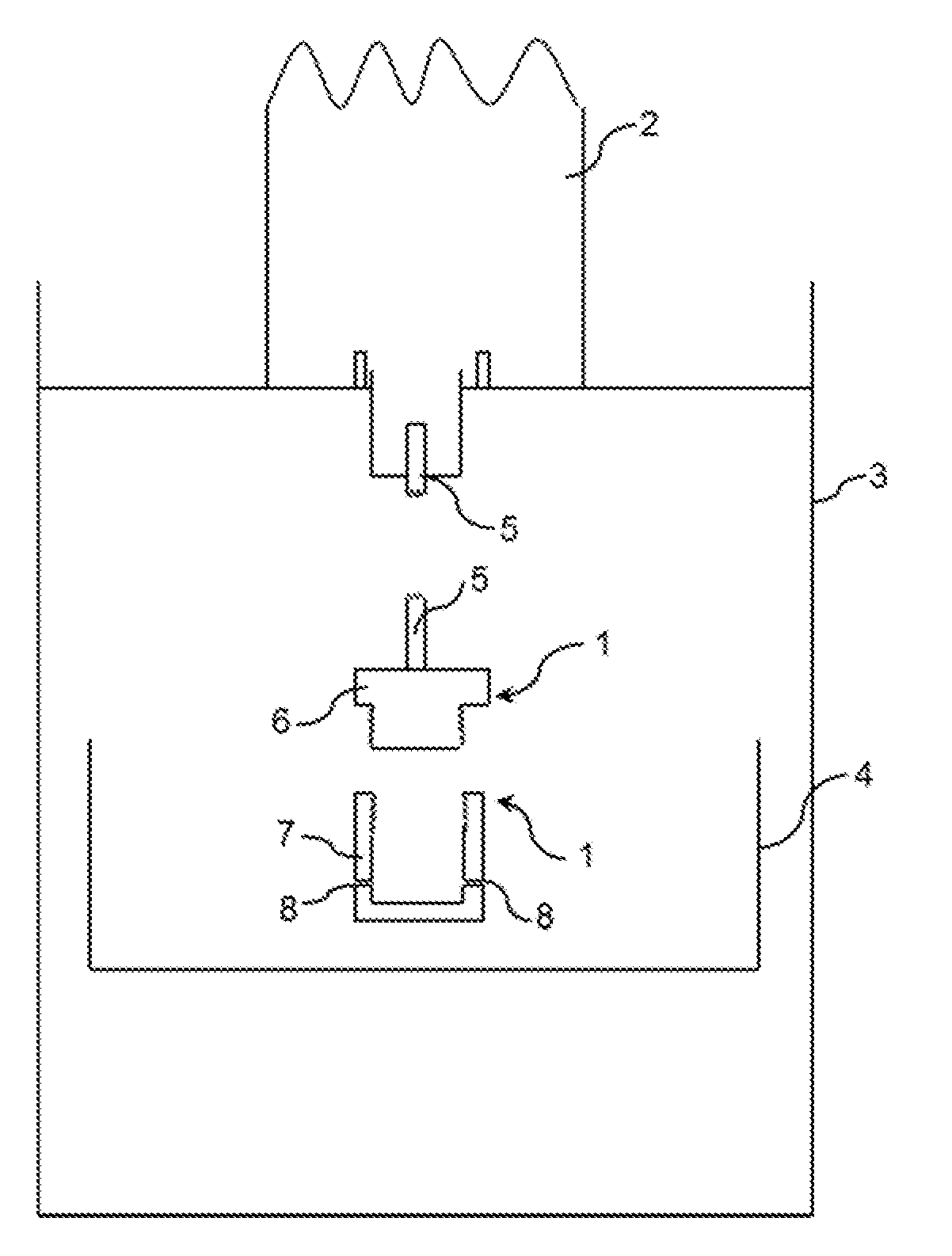
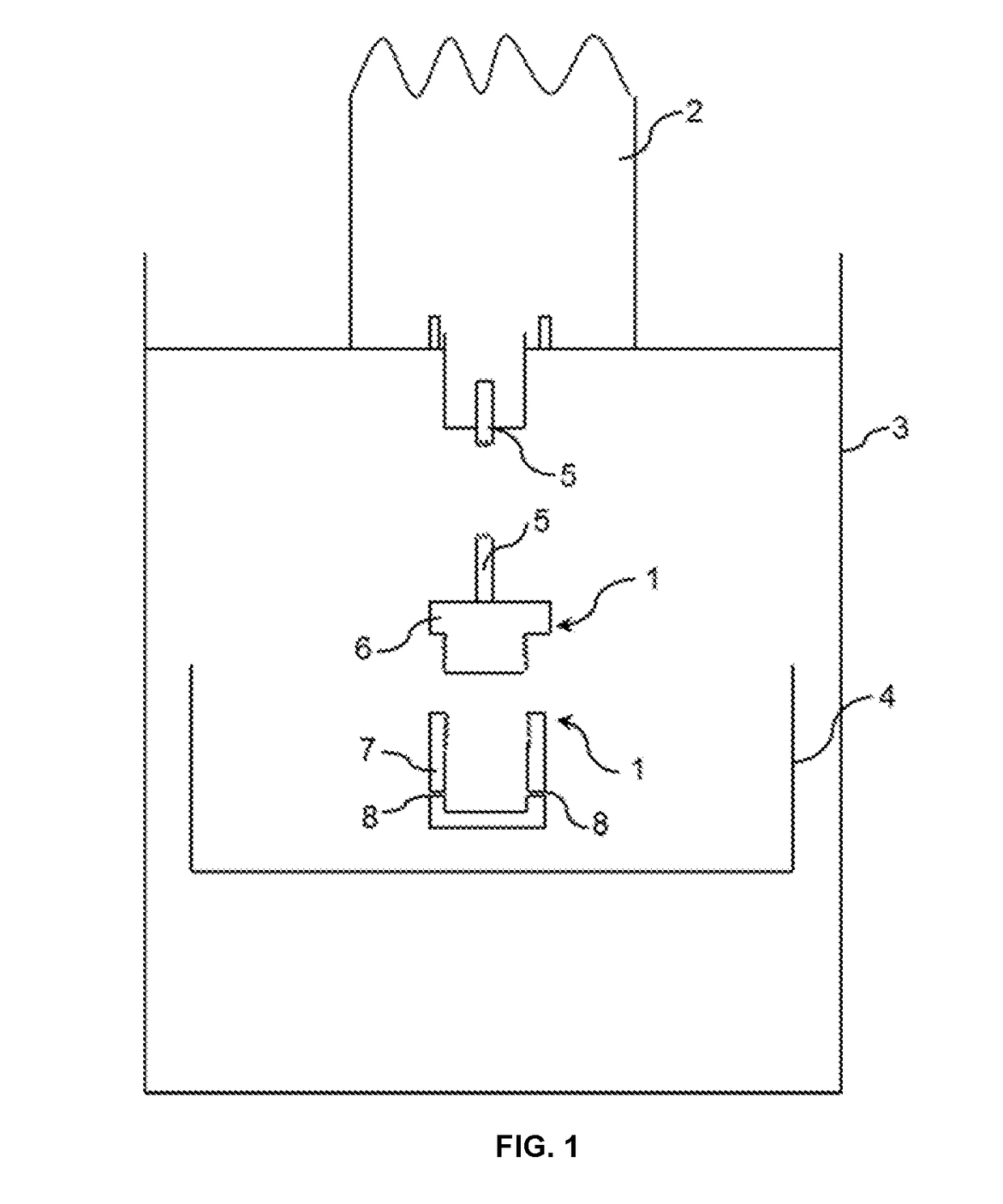
[0140]Once a homogenous gel was formed, a part of the hot gel was rapidly placed in the fiber producing device as described above and represented in FIG. 1. Then rotation of the spinneret was imposed at 16 000 RPM. The fibers were then collected on the collector 4.
[0141]Mean measured diameter of the produced fibers was 3.5 μm.
example 2
[0142]The procedure described in example 1 has been reproduced but the imposed rotation speed of the spinneret was 22 000 RPM. The mean measured diameter of the produced fibers was 0.9 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com