Devices and methods for selecting apoptosis-signaling resistant cells, and uses thereof
a technology of apoptosis signaling and resistant cells, applied in the direction of drug compositions, separation processes, immunological disorders, etc., can solve the problems of life-threatening situations, loss of some beneficial stem cells, and negative selection of stem cell populations, so as to improve the clinical outcome of hematopoietic stem cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Ex Vivo Exposure of Umbilical Cord Blood Cells to Death Ligands
Apoptotic Activity of Death Receptor Activation In Vitro
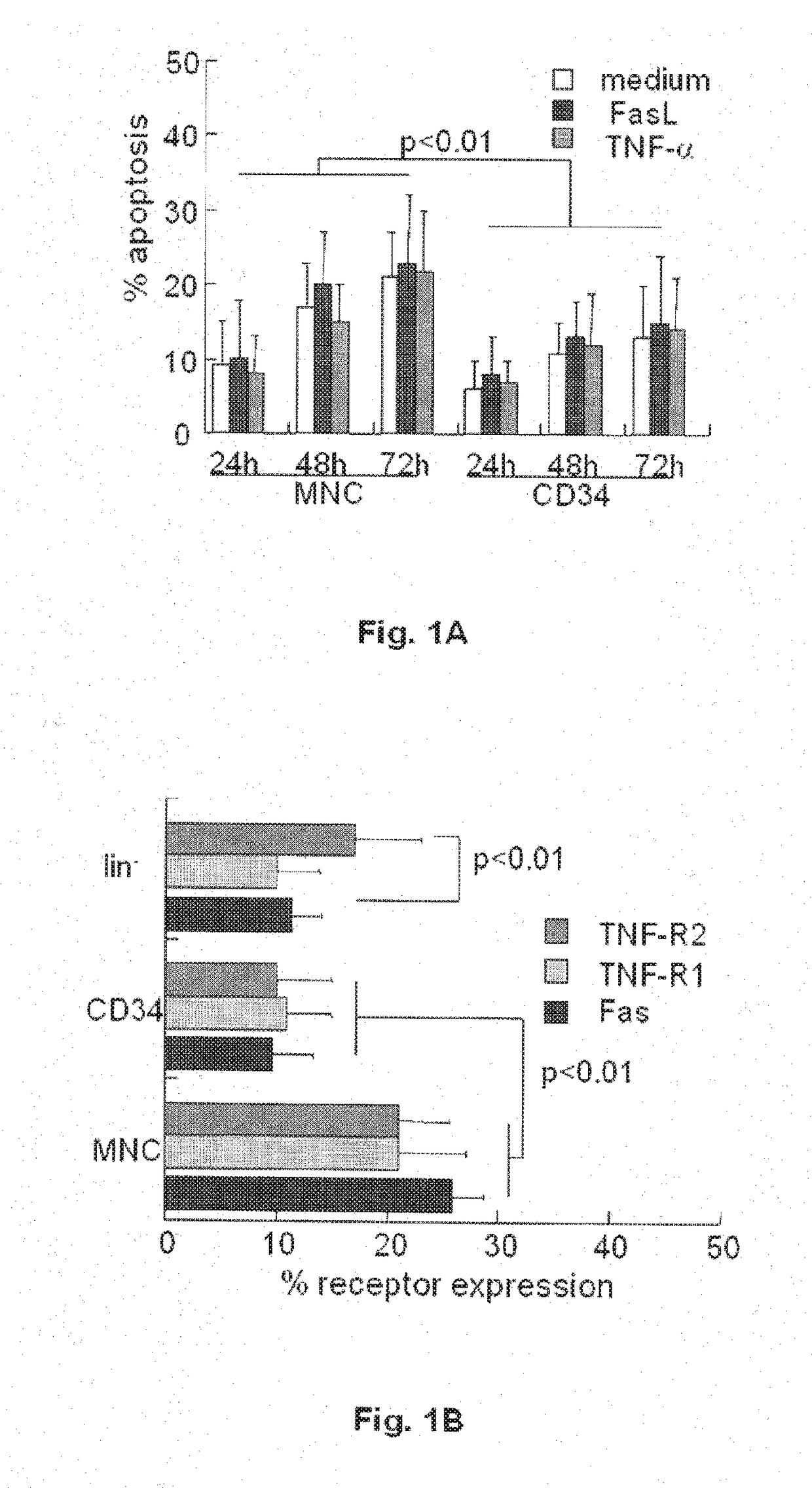
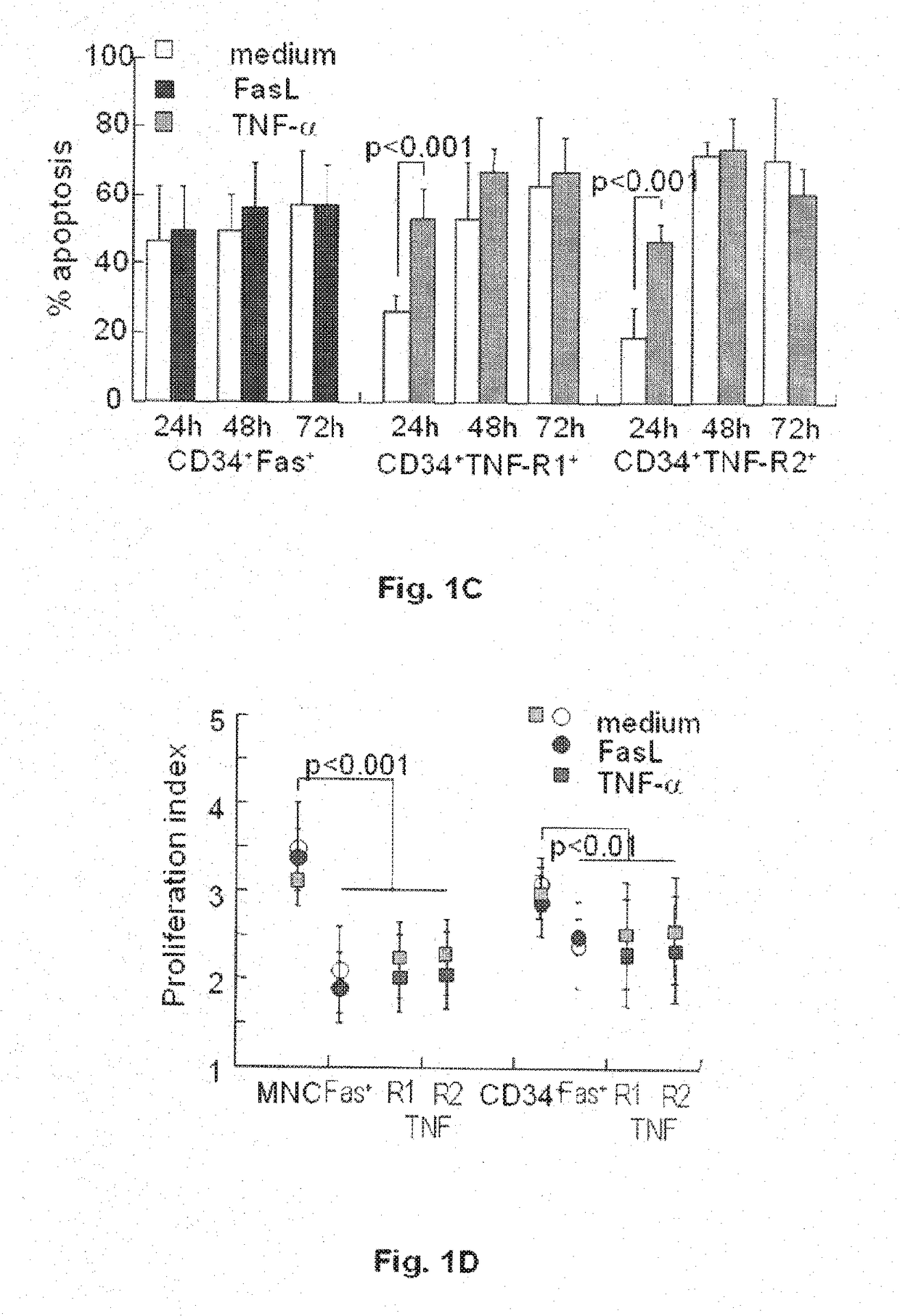
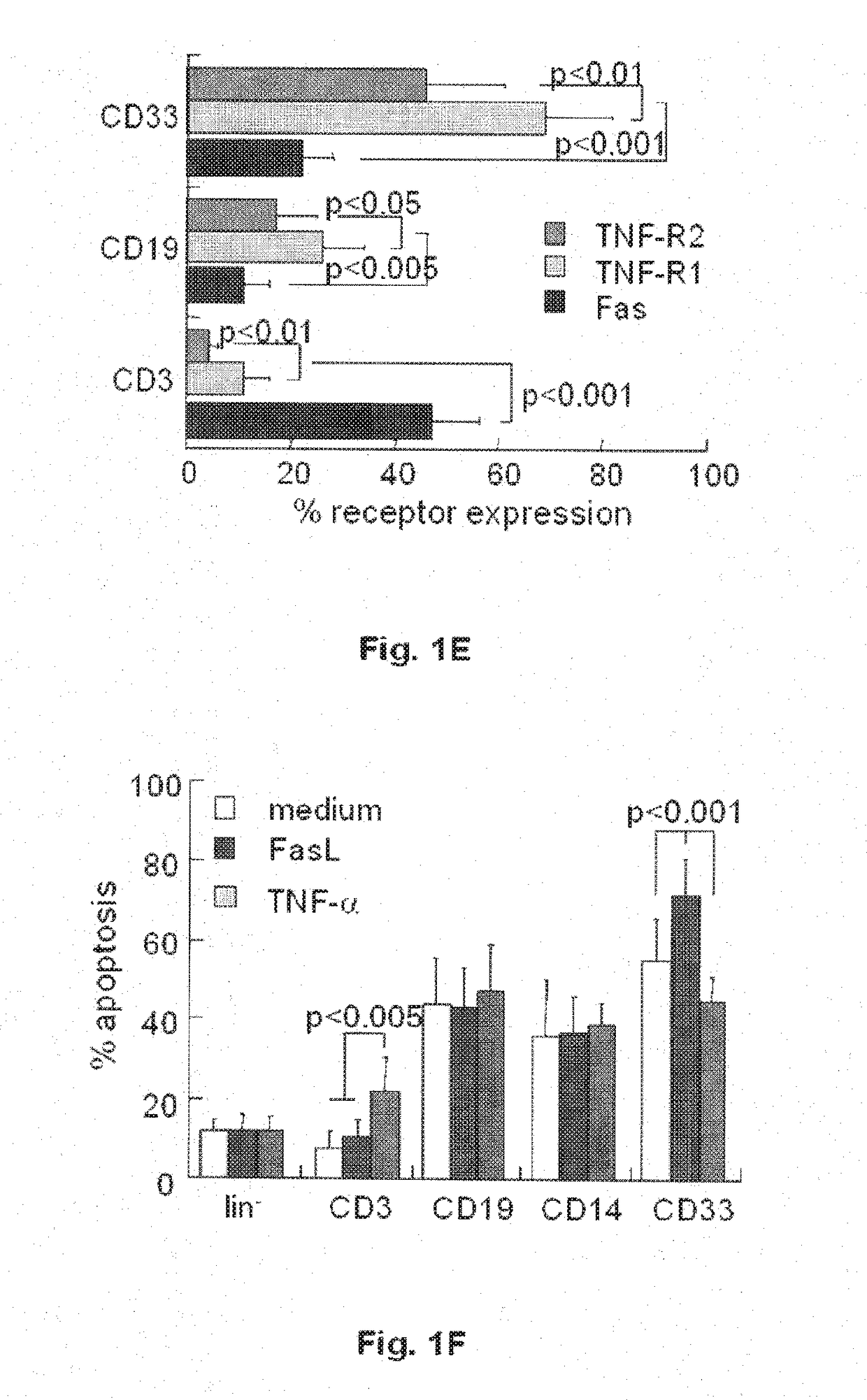
[0136]The primary activity of the TNF superfamily is transduction of apoptotic signals. Fresh umbilical cord blood (UCB) obtained from term deliveries upon informed consent were exposed to FasL and TNF-α for various periods of time in liquid culture without supplementation of growth factors. Gated CD34+ progenitors within the bulk UCB cultures displayed reduced rates of apoptosis, with increasing susceptibility as a function of time (FIG. 1A), however apoptotic cell death is not enhanced by exposure to death ligands of the TNF family. It has been previously suggested that insensitivity to apoptotic signaling is caused by low-level expression of the receptors in hematopoietic progenitors. The analysis revealed lower expression of the Fas and TNF receptors in gated CD34+ and isolated lin− progenitors than in the bulk UCB population (FIG. 1B). More focused evaluation o...
example 2
Ex Vivo Exposure of Mobilized Peripheral Blood Cells to Death Ligands
[0145]APOPTOTIC activity of death receptor activation in vitro
[0146]A prevalent source of hematopoietic progenitors for transplantation is peripheral blood following mobilization with granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) or antagonists of c-kit and CXCR4. The mobilized mononuclear cells are subsequently collected from peripheral blood by apheresis, containing a substantial number of CD34+ progenitors. Cells harvested from the peripheral blood are generally activated, therefore the periods of exposure to death ligands for selective depletion are significantly shorter. An additional difference from data presented for UCB cells is the use of cryopreserved mPB samples, the thawing of which is associated with apoptotic death of 15-25% of the cells. Fas is expressed in ˜25% of CD34+ progenitors (FIG. 6A) and considerable fractions of B lymphocytes and myeloid cells (50-65%, FIG. 6B). The TNF receptors are expres...
example 3
Pretransplant Depletion of T Cells Prevents Lethal GvHD
Prevention of Lethal GvHD by Ex Vivo Selective Depletion of Host-Sensitized T Cells
[0151]Both physical depletion of T cells from donor inoculum and FasL-mediated elimination of host-reactive T cells reliably prevent GVHD. Haploidentical murine transplants (parent to child) represent the extreme risk of GvHD, characterized by high levels of mortality. In first stage experiments were recapitulated using depletion of T cells by apoptotic signals following sensitization to host antigens. Antigen-specific sensitization in vitro for 2-3 days causes T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated stimulation of responsive T cells who concomitantly upregulate Fas and its cognate ligand, resulting in execution of the apoptotic cascade in parallel to downregulation of protective antiapoptotic mechanisms. To compare this procedure to tested approach using brief exposure to apoptotic ligands ex vivo without prolonged incubation, the donors were pre-immunize...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com