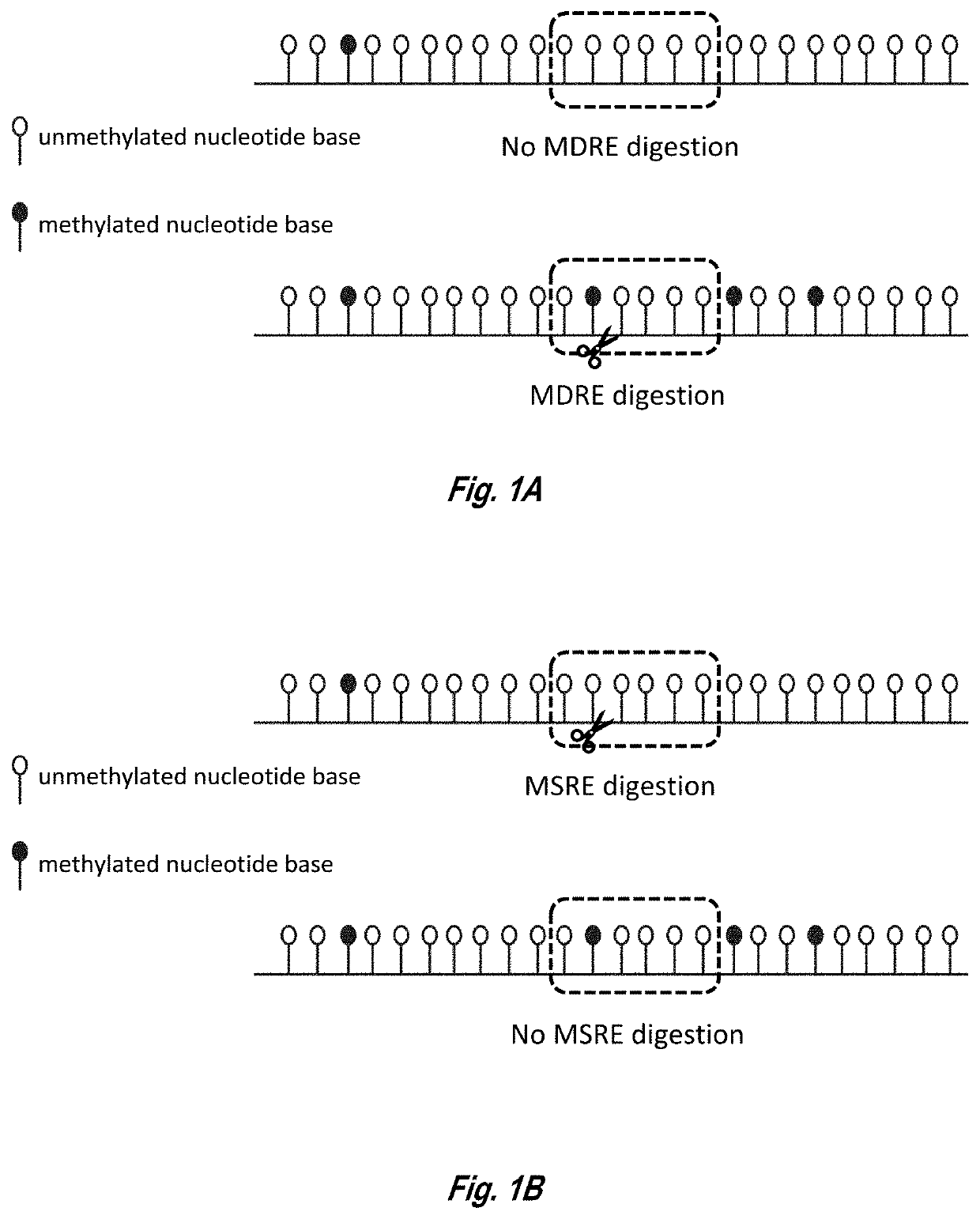
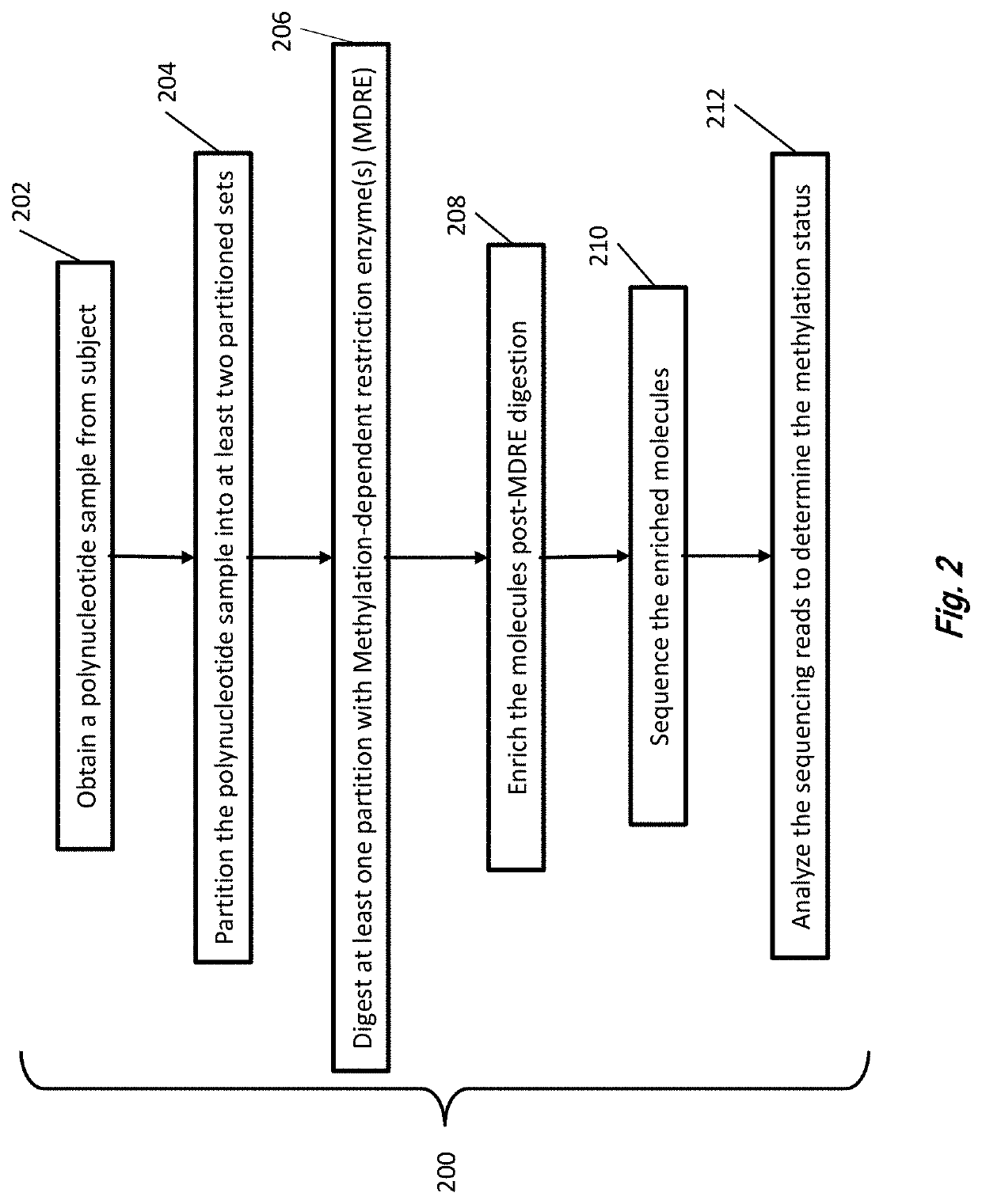
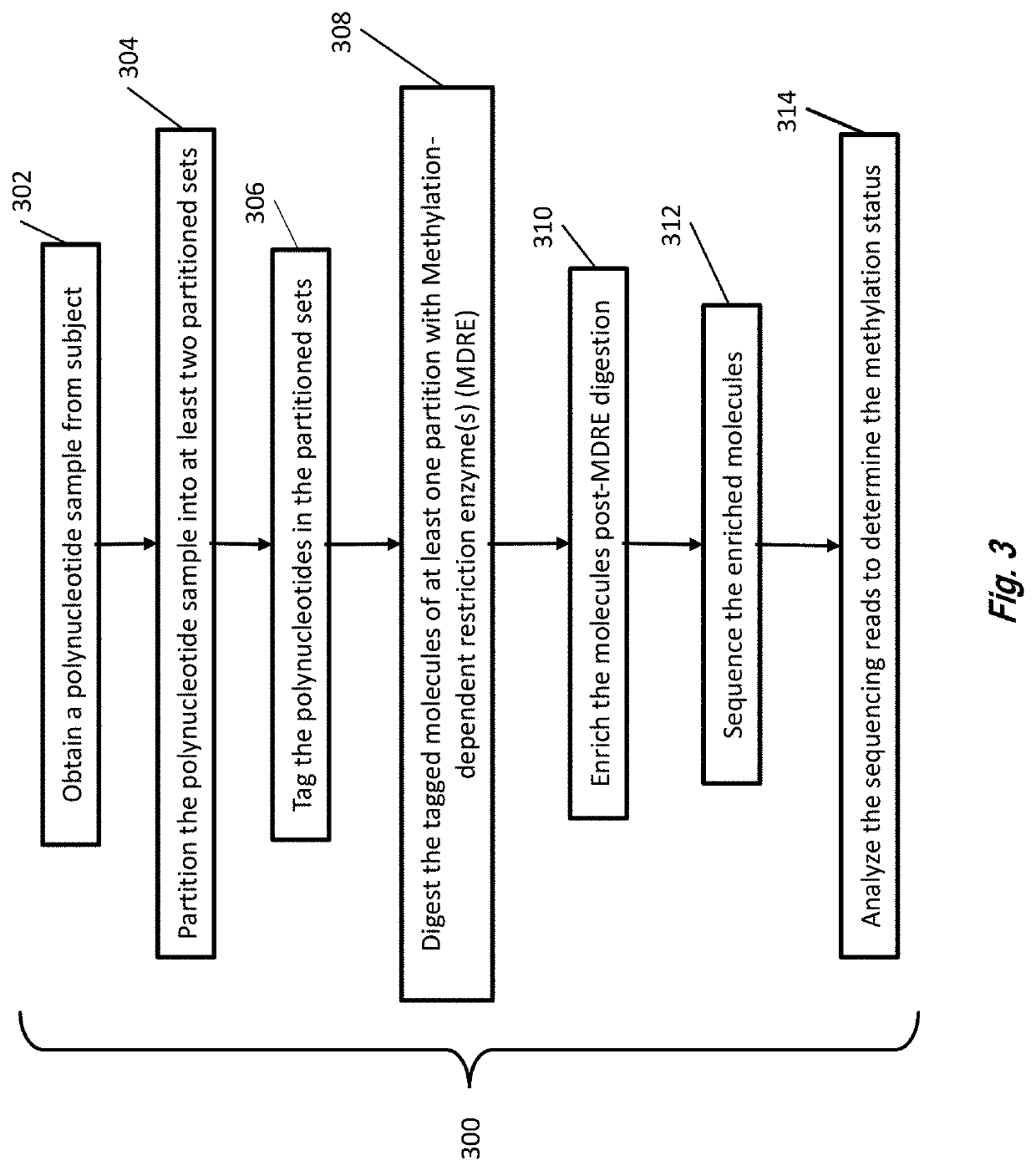
Analysis of methylated DNA comprising methylation-sensitive or methylation-dependent restrictions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
of cfDNA to Detect the Presence / Absence of Tumor
[0494]A set of patient samples are analyzed by a blood-based NGS assay at Guardant Health (Redwood City, Calif., USA) to detect the presence / absence of cancer. cfDNA is extracted from the plasma of these patients. cfDNA of the patient samples is then combined with methyl binding domain (MBD) buffers and magnetic beads conjugated with an MBD protein and incubated overnight. Methylated cfDNA (if present, in the cfDNA sample) is bound to the MBD protein during this incubation. Non-methylated or less methylated DNA is washed away from the beads with buffers containing increasing concentrations of salt. Finally, a high salt buffer is used to wash the heavily methylated DNA away from the MBD protein. These washes result in three partitions (hypomethylated, residual methylation and hypermethylated partitions) of increasingly methylated cfDNA.
[0495]Optionally, the cfDNA molecules in the hypermethylated partition are subjected to enzymatic modi...
example 2
of Methylation at Single Nucleotide Resolution in cfDNA Samples from Healthy Subjects and Subjects with Early-Stage Colorectal Cancer
[0501]Samples of cfDNA from healthy subjects and subjects with early-stage colorectal cancer were analyzed as follows. cfDNA was partitioned using MBD to provide a hypermethylated partition, an intermediate partition, and a hypomethylated partition. The partitioned DNA of each partition was ligated to adapters and subjected to an EM-seq conversion procedure whereby unmodified cytosines, but not mC and hmC, undergo deamination, although in an alternative procedure the partitioned DNA of the hypomethylated partition could be contacted with a methylation-dependent nuclease as described herein. Following such deamination, the partitions were prepared for sequencing and subjected to whole-genome sequencing. Each partition was sequenced separately, although in an alternative procedure the partitions could be differentially tagged (e.g., after partitioning an...
example 3
of Technical Noise by Digestion of Nonspecifically Partitioned DNA
[0503]A pool of cfDNA from two healthy normal samples was combined, from which 18.6 ng was used as input to a MBD-partitioning assay described herein. To a subset of the samples, cfDNA from a colorectal cancer sample (CRC) with 0.5% MAF (mutant allele fraction) was added, resulting in a diluted CRC sample with 0.16% MAF. Three sets of normal samples and diluted CRC samples were used in the assay. The three sets of samples were then partitioned using MBD protein into three partitions (hyper, residual and hypo partitions). Following cleanup, the cfDNA molecules in each partition was ligated with partition-specific adapters comprising molecular barcodes. The molecular barcodes use in hyper and residual partition are selected such that they do not have MSRE recognition sites, so they are not digested in the downstream processing (irrespective of cfDNA methylation state). Post-ligation, ligation cleanups were performed. Fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com