Thrombotic episode risk assays using oxidized phospholipids
a technology of phospholipids and thrombosis, which is applied in the field of diagnostic blood clotting assays, can solve the problems of not having a sufficient affinity for procoagulant phospholipids to be anticoagulants, no adequate monitoring technique has been developed for such a treatment, and no adequate technique has been developed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Method Of Preparing Non-Oxidized And Oxidized Phospholipid Reagents
[0022]A reagent useful in the assay of the present invention was prepared comprising 40% PE, 20% PS and 40% PC. The individual phospholipids derived from bovine brain (and therefore comprised of naturally-occurring fatty acids) were obtained from Avanti Polar Lipids, Inc. They were tested using the Klein spectrophotometric assay and found to be less than 1% oxidized. The lipids were mixed in the weight proportions indicated, dried under argon and lyophilized 3 hours to remove organic solvents. They were then reconstituted under argon, suspended by vortex in 0.15 M NaCl, 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.5 or 0.15 M NaCl, 20 mM Tris HCl, pH 7.4 to 5 mg / ml total lipid. Buffers were treated with Chelex 100 resin (BioRad) and saturated with argon before use. Other reagents with different compositions of phospholipids may be made in a similar manner by varying the proportions of phospholipids used.
[0023]Liposomes were prepared by extrusi...
example 2
Determination of Baseline Clotting Values in The Absence of APC And Comparison To Values In The Presence of APC
[0025]Coagulation assays were performed as one stage clotting assays using the ST4 coagulation instrument (Diagnostica Stago, Parsippany, NJ). For assays in which APC and / or immunoglobulin (normal or patient sample) were omitted, volumes were made up with buffer (0.1 M NaCl, 0.02 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 1 mg / ml gelatin).
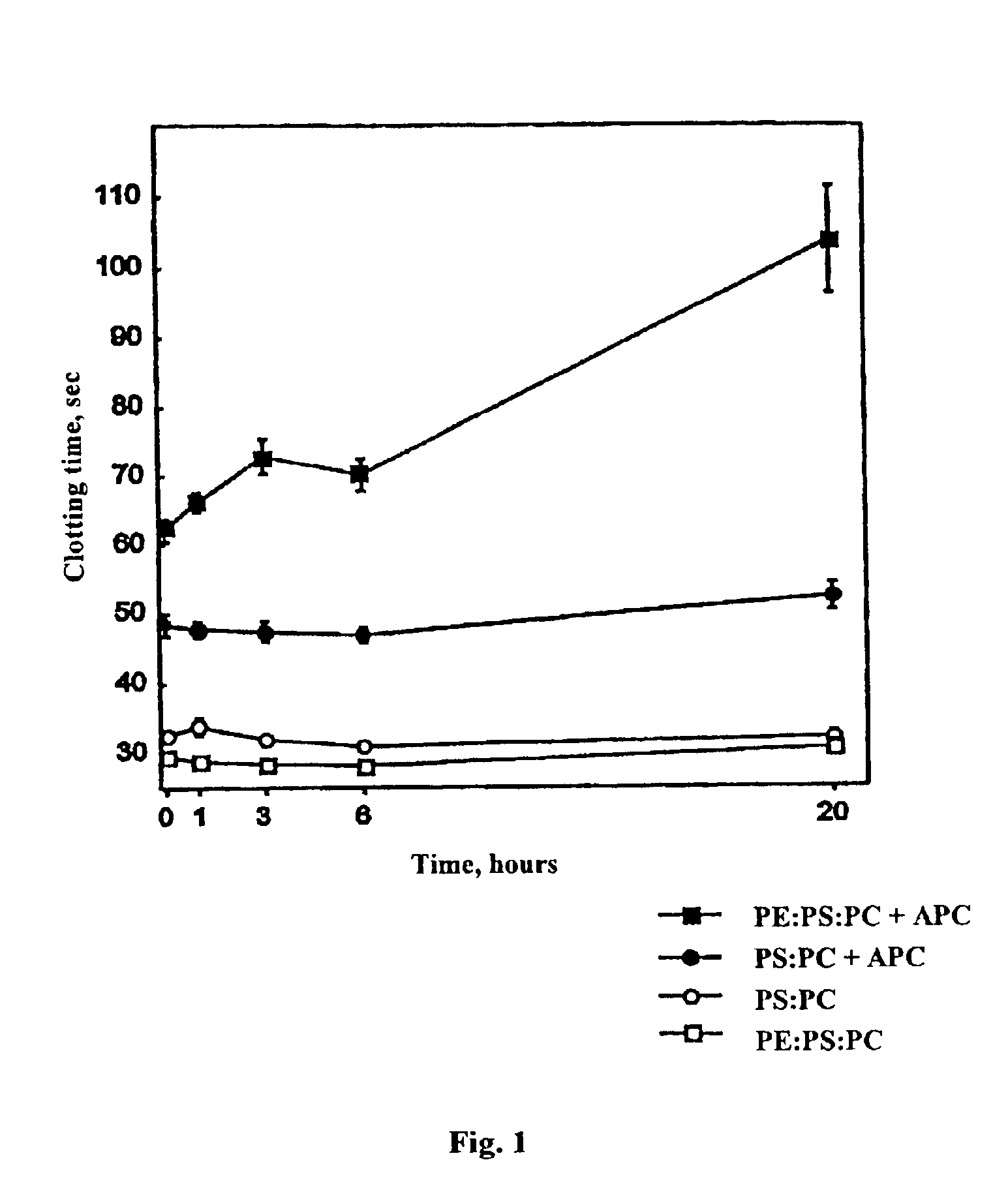
[0026]The effect of lipid oxidation on coagulation assays in the presence or absence of APC was determined as a function of time of oxidation of the phospholipid (FIG. 1). Pooled normal plasma (50 μl) was placed in the reaction vessels and the following reagents added to the final concentrations indicated in parentheses: Factor X-activating enzyme from Russell's viper venom (prepared as per C. T. Esmon, Dissertation, Washington University, St. Louis, 1973) or obtained from American Diagnostica, Greenwich, CN) (0.1-0.15 nM, sufficient to yield a 30 sec clotting t...
example 3
Evaluation of Normal Plasma-Derived IgG Compared to IgG from Plasma of Patents with Diagnosed Clotting Disorders
[0030]Patients used in this study are described in Table I. Patients 1-7 were evaluated as follows. Double centrifuged citrated plasma was used for all coagulation assays and prepared according to the method of Sletnes, K. E., Gravem, K., and Wisloff, F. 1992. “Preparation of plasma for the detection of lupus anticoagulants and antiphospholipid antibodies.” Thromb. Res. 66;43-53. The presence or apparent absence of lupus anticoagulant was determined by a prolonged clotting time with a commercial PTT reagent (StaclotR LA, Diagnostica Stago) in a 50:50 mixture of test plasma and normal plasma. Plasma with clotting times exceeding the 95th percentile of a previously established control population underwent additional testing. The diagnosis was confirmed by normalization or significant correction of the clotting time (≧8 seconds) in the presence of hexagonal (II) phase phospho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com