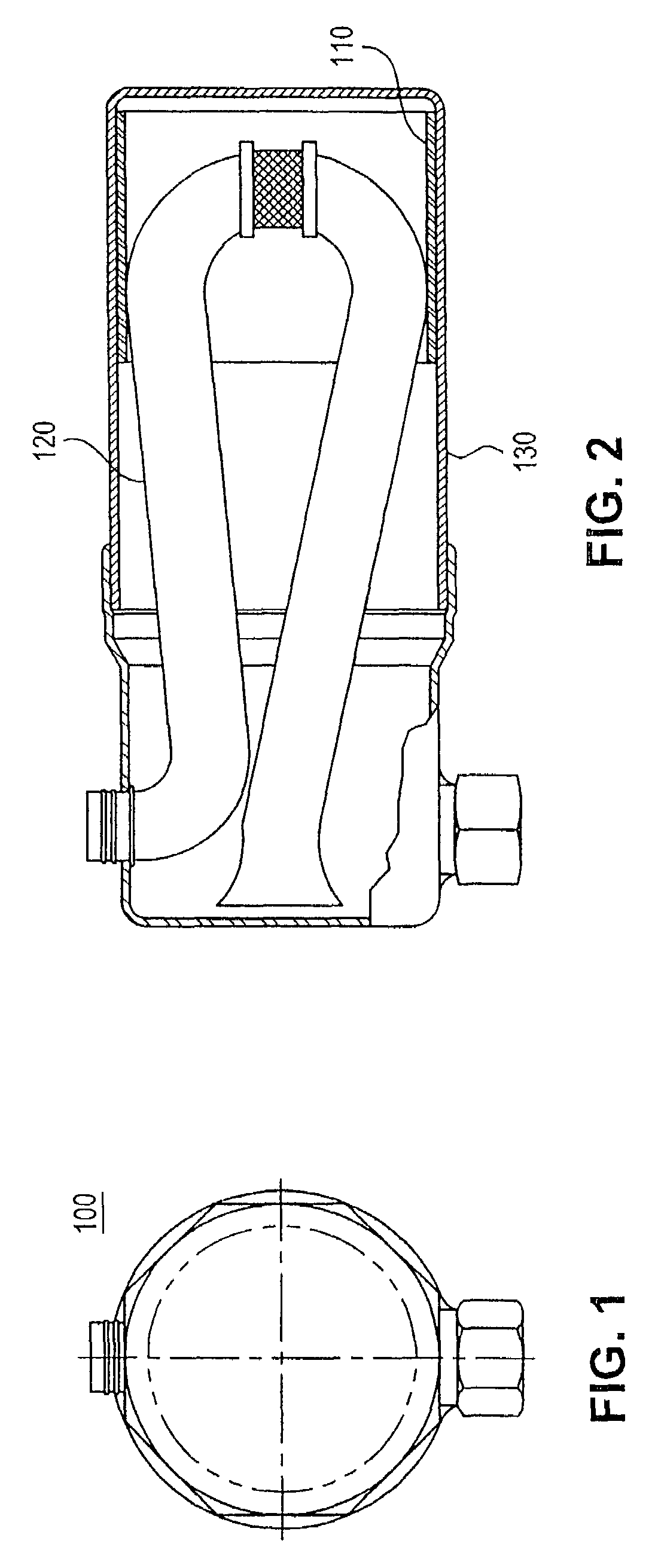
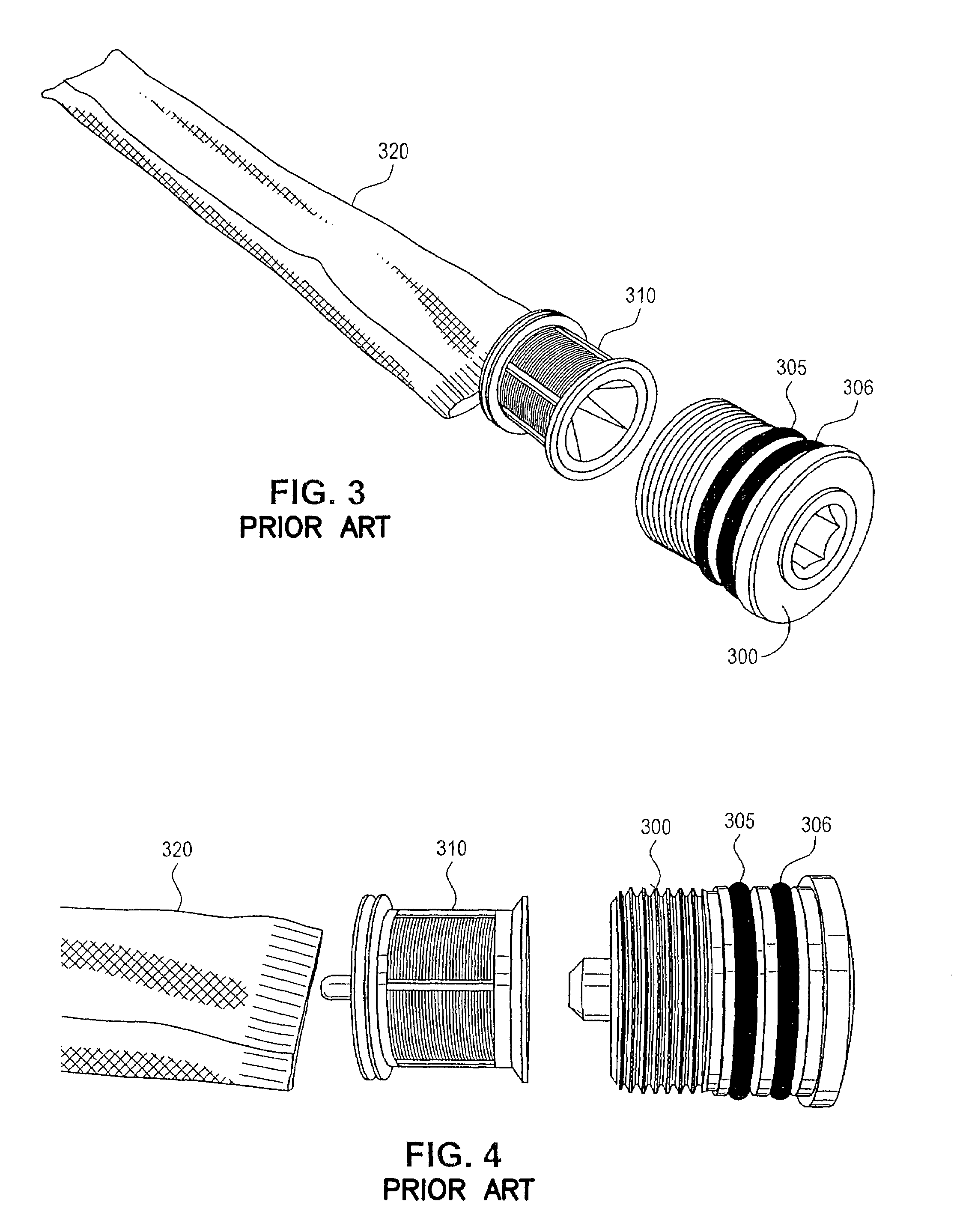
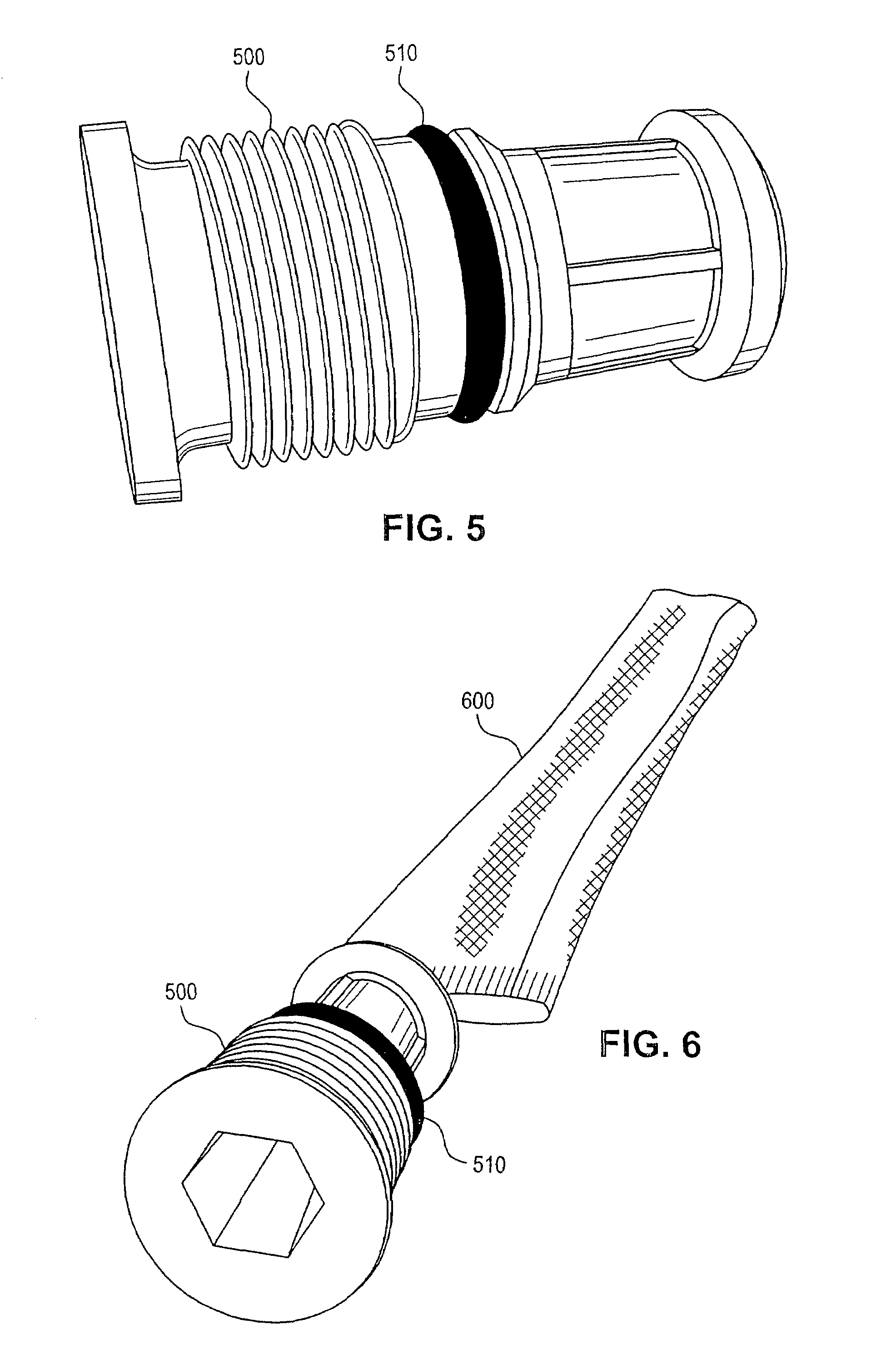
Resin bonded sorbent
a sorbent and resin technology, applied in the field of resin bonded sorbent, can solve the problems of degrading or reducing the strength of the molded object fabricated therewith, and achieve the effect of high moisture adsorption properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0041]Test samples of resin bonded sorbents were prepared according to the claimed invention employing the following protocols. The resins are procured from a supplier in pellet form (most common is cylindrical (0.03-0.12 inch diameter×0.06-0.25 inch long), other forms included tear drop format (0.06-0.19 inch). The ratio of molecular sieve to the resin is determined by weight of the components. The resin was premixed in a poly bag by hand (5-15 min). The pre-blend was emptied into the hopper of a Brabender single screw extruder. Action from the screw further blends and melts the resin and molecular sieve as it travels through the extruder barrel. The resin bonded sorbent then exits through the single strand die (1 circular hole) at the end of the extruder forming one strand of molten material. The nylon based resin was heated above 262° C. The strand was then cooled by air. The strands were broken into pieces. The pieces were placed in a hopper of an injection molding machine and p...
example 2
[0048]Further experiments were performed using compositions comprising polypropylene, namely Huntsman Polypropylene 6106. This resin was also compatible with refrigerants, as well as with compressor lubricant. It was compounded in a similar fashion as nylon in Example 1, namely: 60% polypropylene resin and 40% molecular sieve Type 4A. The resin was heated above 174° C. The compounded resin had similar advantageous mechanical properties compared to the pure resin, and performs, structurally, close to that of a glass reinforced resin. Its properties are summarized in Table II. The values were determined by the same ASTM standards as provided in Table I.
[0049]
TABLE IIProperties of Reinforced PolypropyleneMaterial:Molecular SieveGlass BeadGlass FiberReinforcedReinforcedReinforcedProperty:PP NeatPolypropylenePolypropylenePolypropyleneLoading (%)037.541.939.4Hardness - Shore D66.874.665.675.4Tensile Modulus (psi)131242228023159321342977Tensile Displacement0.3300.1370.2740.222@ Max Load (i...
example 3
[0052]As may be seen in Table III, melt flow was reduced with sorbent reinforced nylon compared with nylon neat (pure polymer) or glass bead reinforced nylon. Nevertheless it was in a workable range and was higher than polypropylene. Melt flow of sorbent reinforced polypropylene was improved relative to polypropylene neat or glass reinforced polypropylene.
[0053]
TABLE IIIMelt Flow Properties of Sorbent Reinforced PolymersMelt Flow Index(g / 10 min)Molecular SieveGlass Bead(ASTM D 1238)NeatReinforcedReinforcedNylon56.314.755.5Polypropylene5.37.32.1
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mechanical properties | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mechanical bonding | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystallinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com