Wavelength detector, wavelength stabilization laser device, and image display device
a wavelength stabilization laser and wavelength detection technology, applied in the direction of optical radiation measurement, interferometric spectrometry, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of more likely changes in the mode of laser light, device complexity, and error in wavelength detection of laser light, so as to achieve high color reproducibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
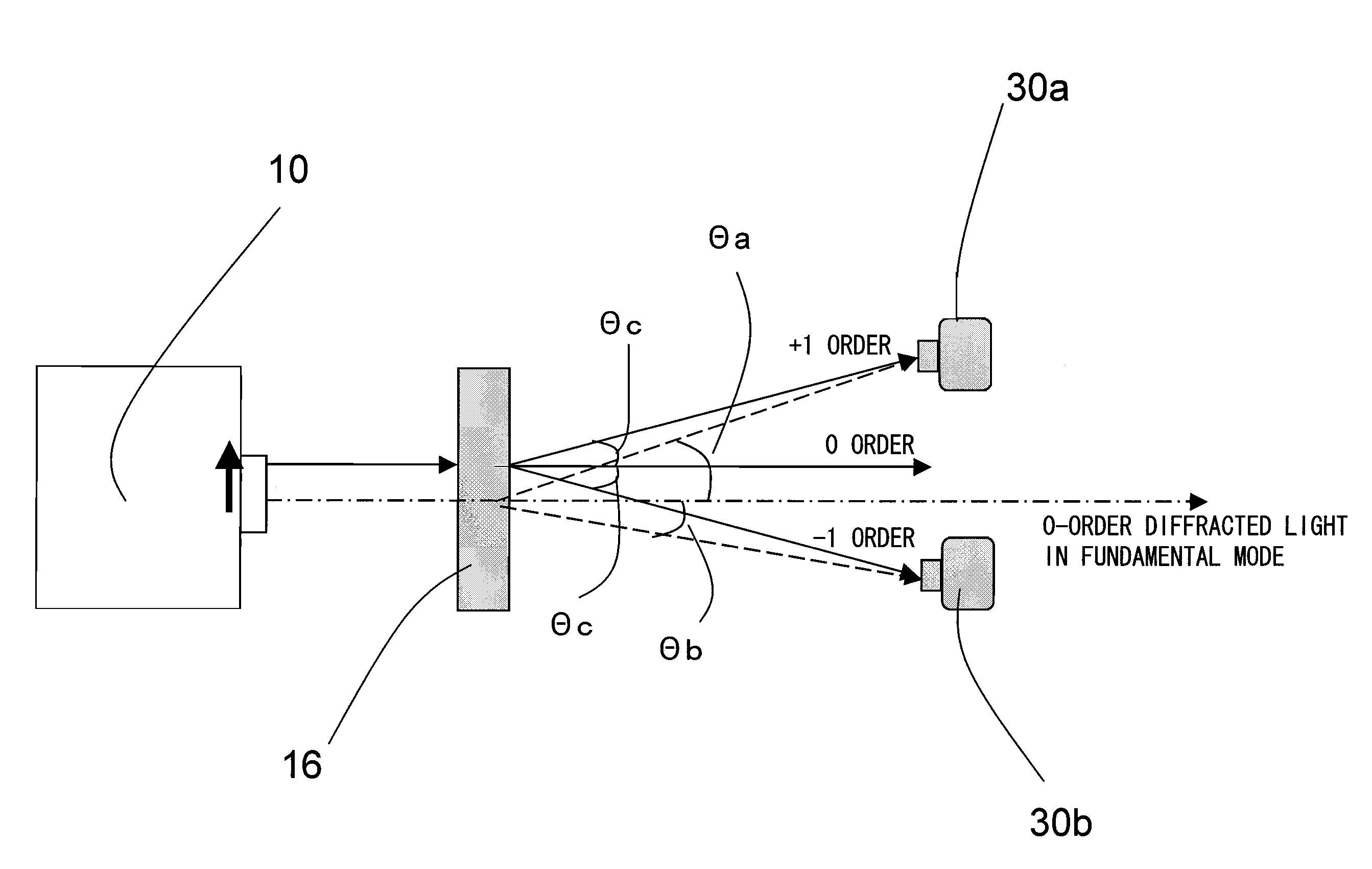
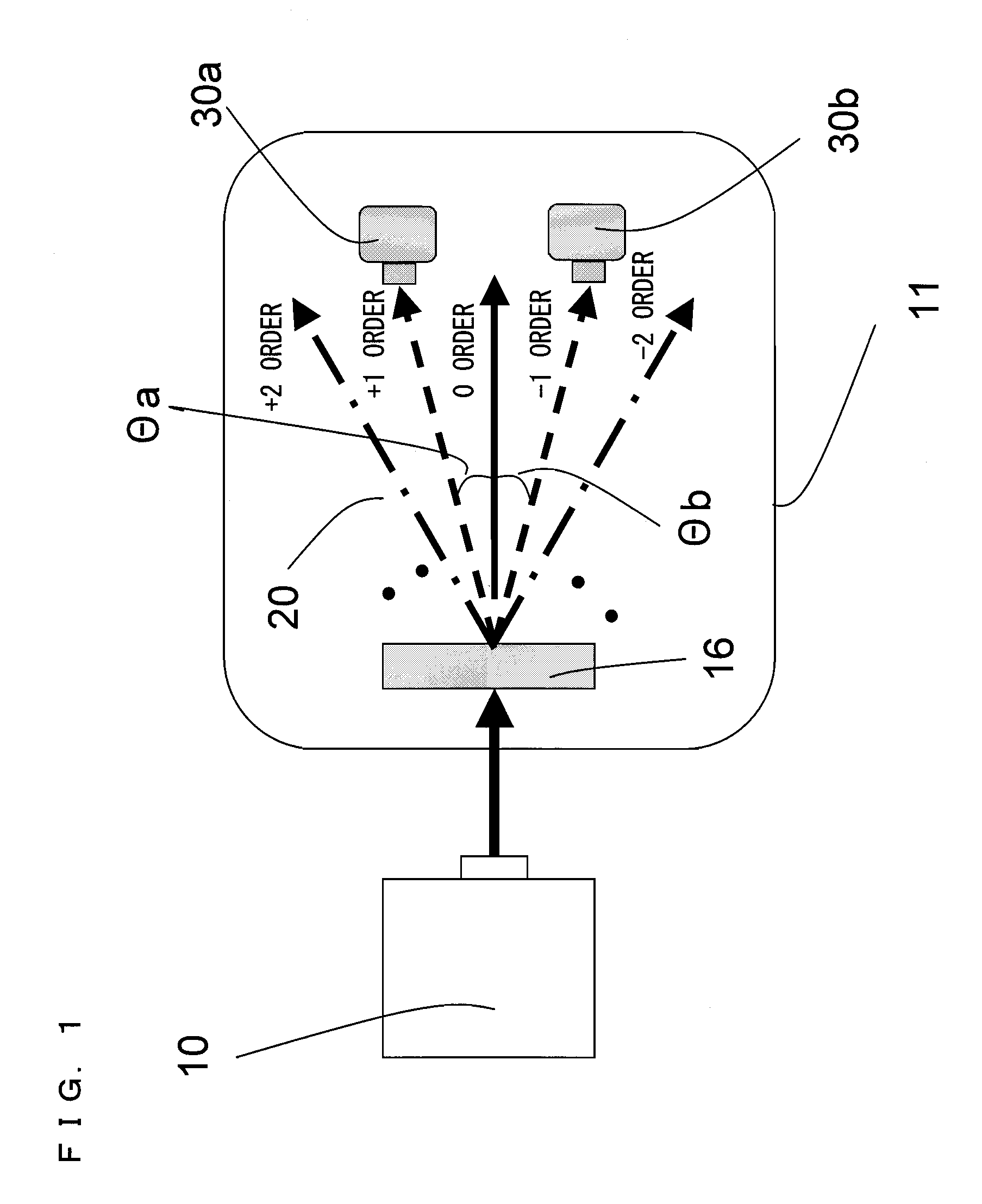
[0060]FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing an example structure of a wavelength detector 11 according to a first embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 1, the wavelength detector 11 includes a diffraction grating 16 for diffracting a laser light emerging from a laser light source 10, and also includes at least two photodetectors 30a and 30b which measure a +n-order diffracted light and a −n-order diffracted light, respectively (n is an integer equal to or greater than 1). The laser light emerging from the laser light source 10 is incident on the wavelength detector 11 provided in the light path of the laser light. In the wavelength detector 11, the laser light incident thereon is diffracted by the diffraction grating 16, and the diffracted laser lights interfere with one another and thus generate ±n-order diffracted lights 20. Light incidence surfaces of the photodetectors 30a and 30b which measure the diffracted lights 20 are each designed to be equal to or smaller...
second embodiment
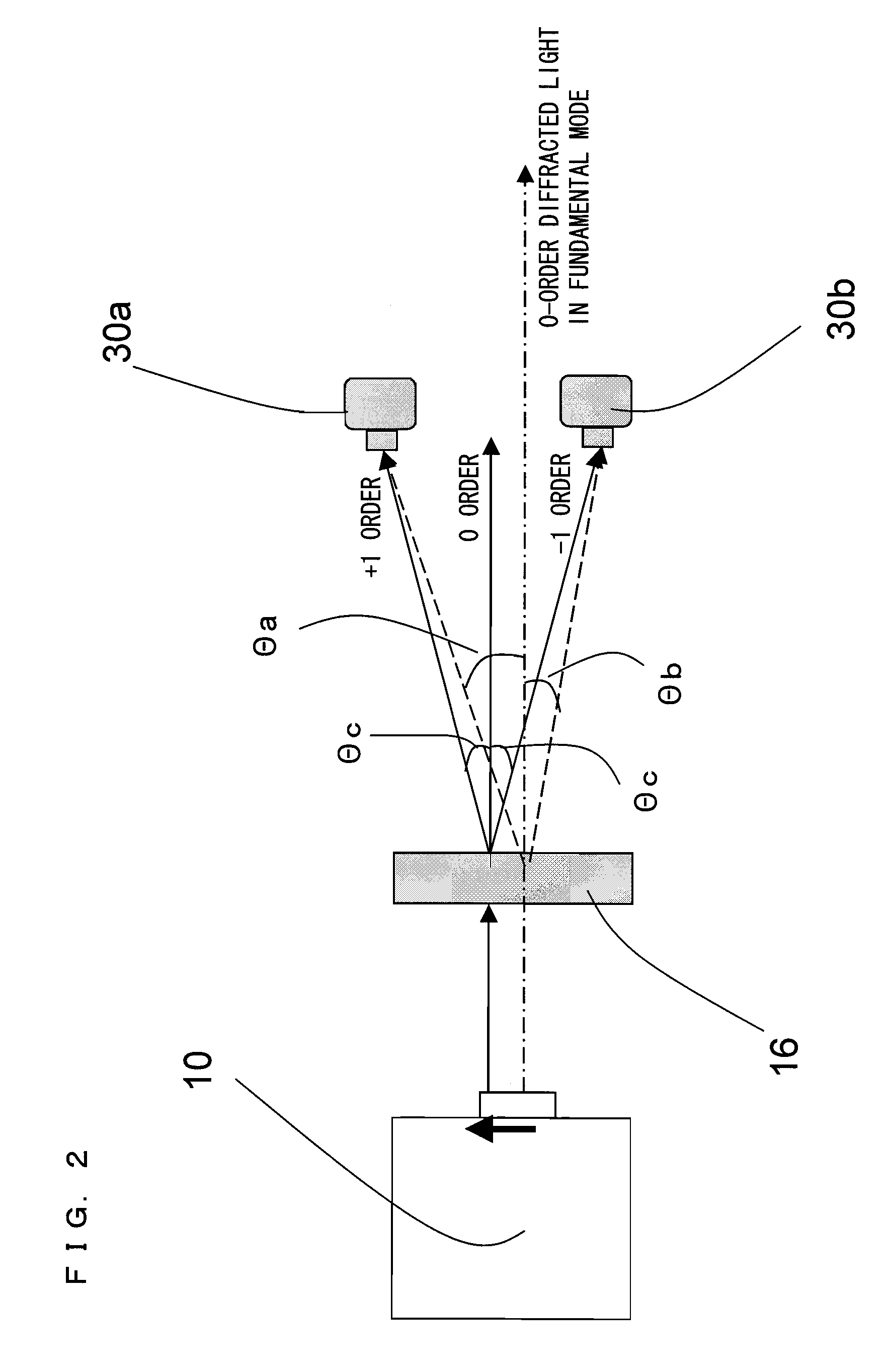
[0068]FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram showing an example structure of a wavelength detector 12 according to a second embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 3, the wavelength detector 12 includes a diffraction grating 16 for diffracting a laser light emerging from a laser light source 10, and also includes at least two photodetectors 40a and 40b which measure a +n-order diffracted light and a −n-order diffracted light, respectively. The laser light emerging from the laser light source 10 is incident on the wavelength detector 12 provided in the light path of the laser light. In the wavelength detector 12, the laser light incident thereon is diffracted by the diffraction grating 16, and the diffracted laser lights interfere with one another and thus generate ±n-order diffracted lights 20. In this example, the photodetectors 40a and 40b measure a +1-order diffracted light and a −1-order diffracted light, respectively.
[0069]As shown in FIG. 3, on light incidence surfaces 4...
third embodiment
[0082]FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram showing an example structure of a wavelength detector 13 according to a third embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 7, the wavelength detector 13 includes a diffraction grating 16 for diffracting a laser light emerging from a laser light source 10, and also includes at least two photodetectors 50a and 50b which measure a +n-order diffracted light and a −n-order diffracted light, respectively. The laser light emerging from the laser light source 10 is incident on the wavelength detector 13 provided in the light path of the laser light. In the wavelength detector 13, the laser light incident thereon is diffracted by the diffraction grating 16, and the diffracted laser lights interfere with one another and thus generate ±n-order diffracted lights 20. In this example, the photodetectors 50a and 50b measure a +1-order diffracted light and a −1-order diffracted light, respectively.
[0083]Referring to FIG. 7, a beam spot 52a is the beam s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com