Starch compositions and methods for use in papermaking
a technology of starch and composition, applied in the field of improved starch composition, can solve the problems of not all retained microparticles on the web, papermaking systems are not all alike, and can show significant variation, so as to improve drainage and retention, improve performance, and improve the effect of drainage and retention
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
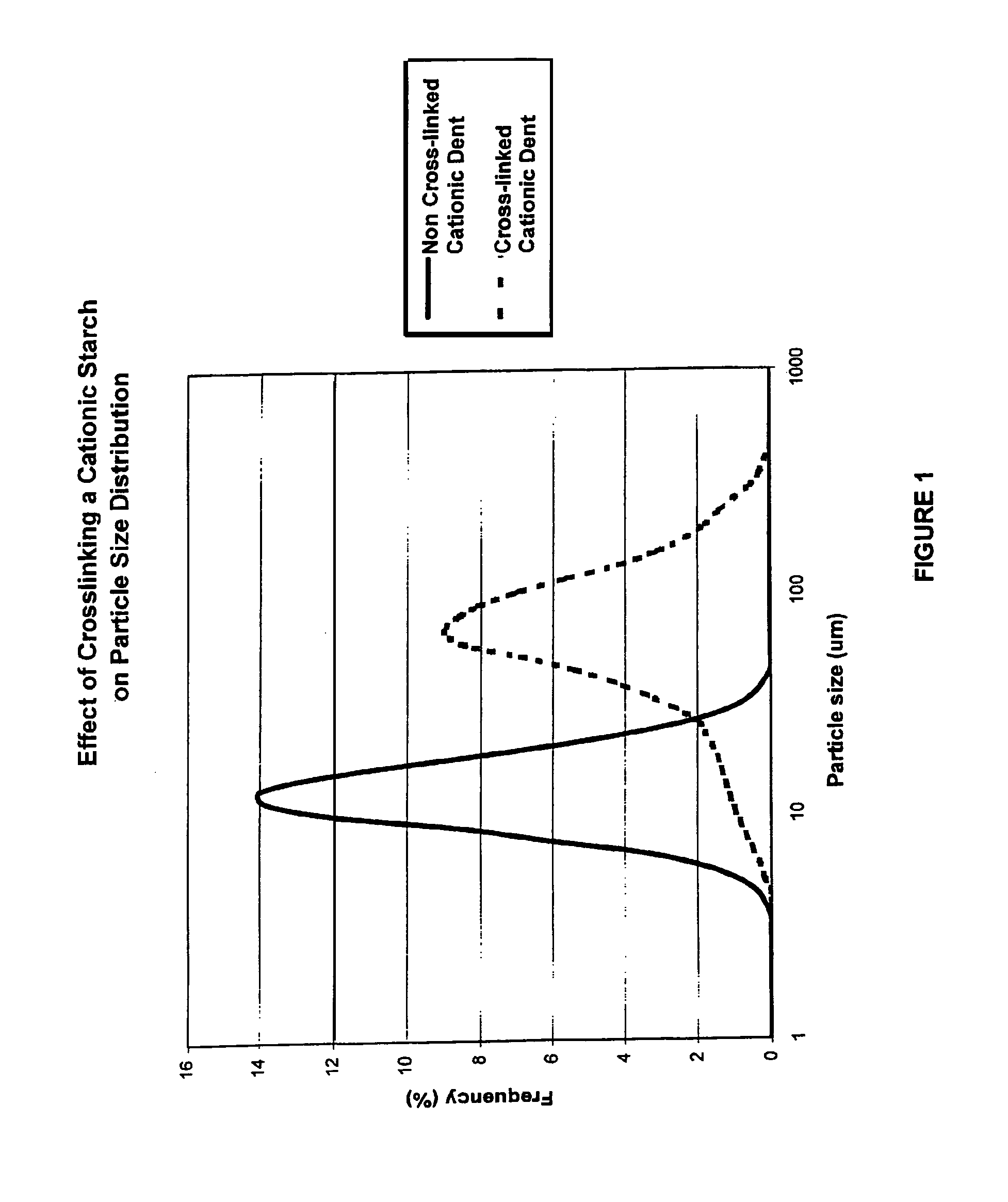
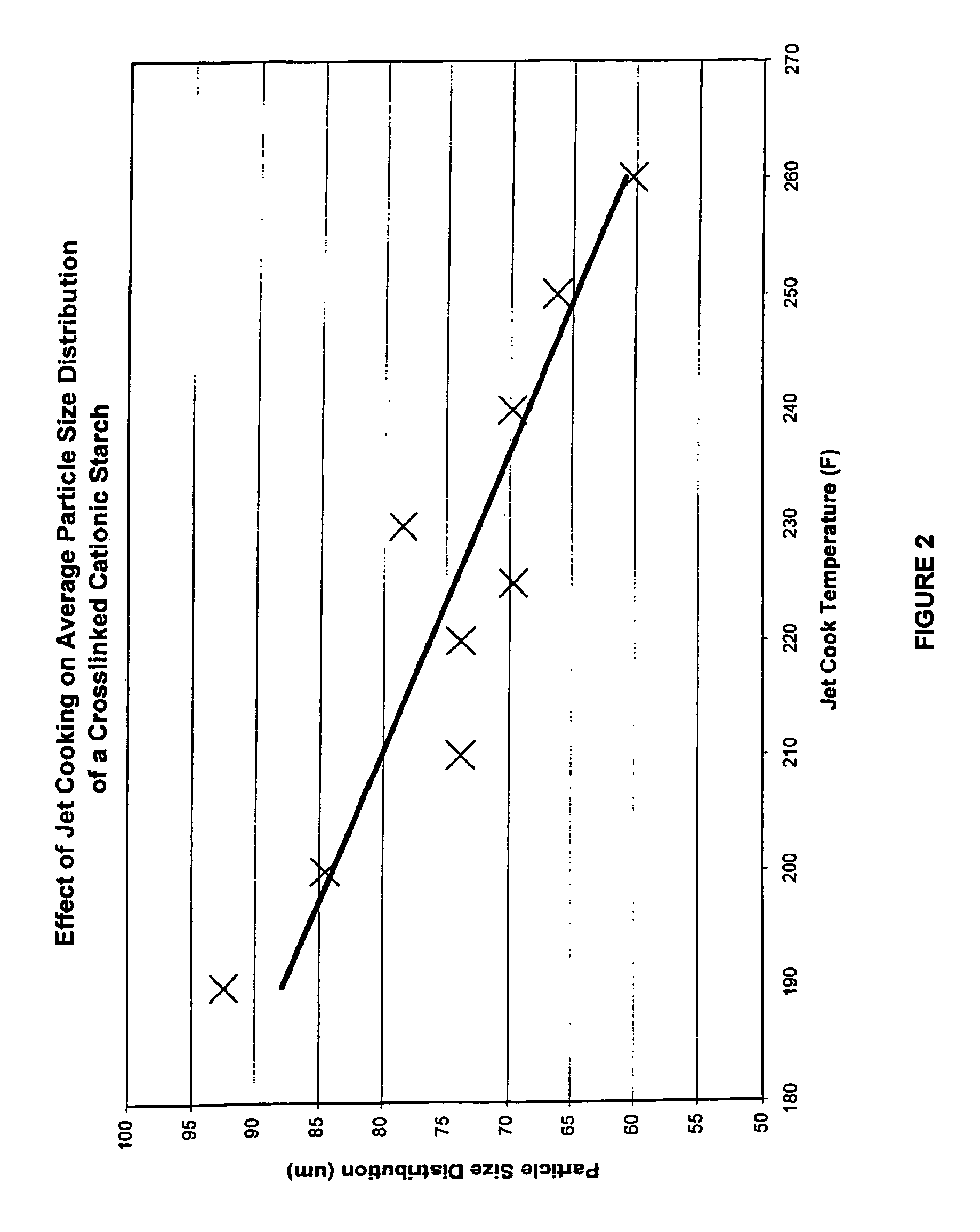
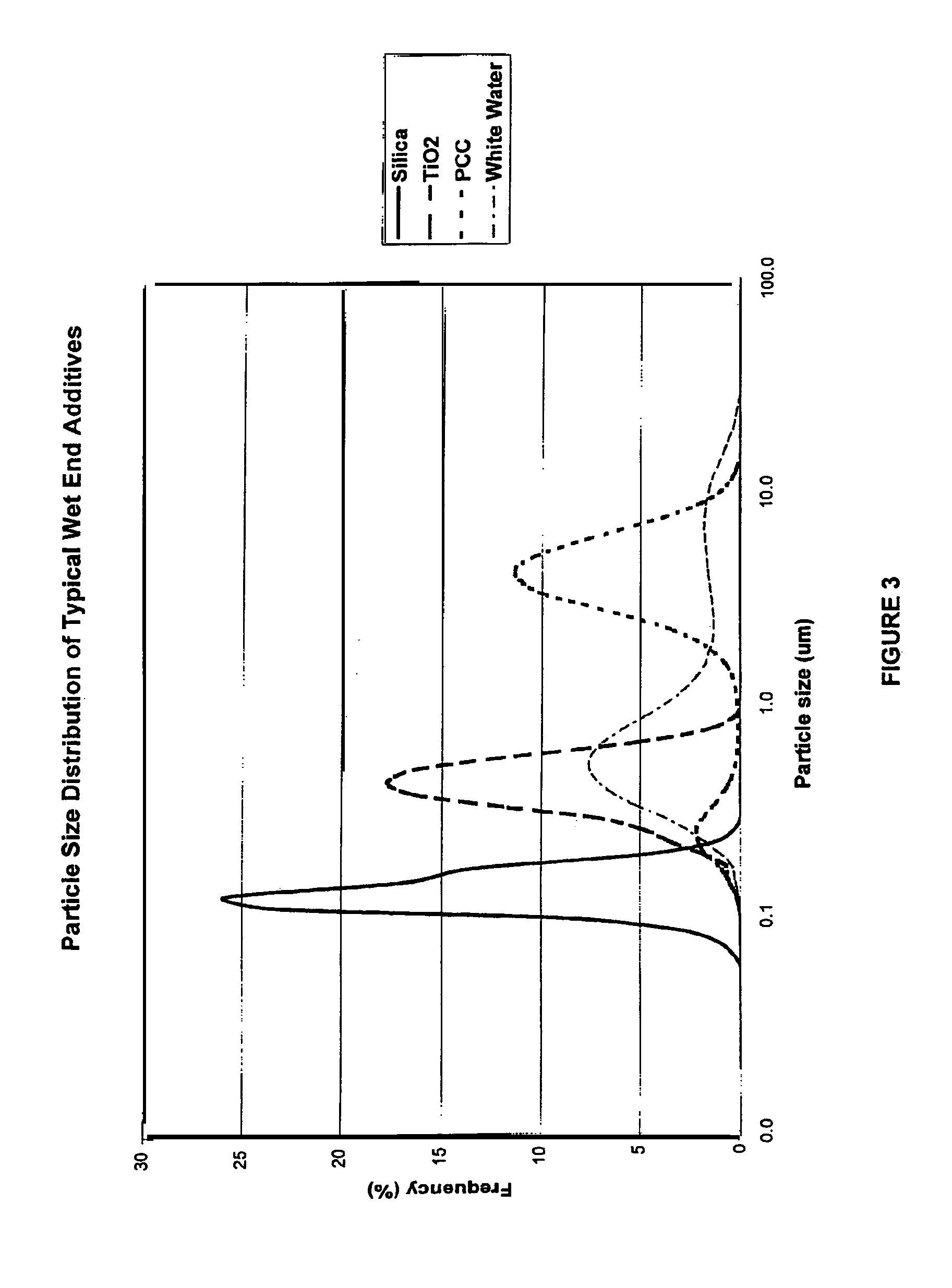
[0030]The present disclosure relates to starches, including cationic crosslinked starches, and to the use of those starches in papermaking. More particularly, the present disclosure is directed to cationized crosslinked starch and to use of the starch in the wet end system of a paper machine. The starch is adapted for customization to various wet end conditions, and allows for modification to correspond to variations in the wet end of the papermaking machine.
[0031]According to an aspect of the disclosure, a cationic starch which has been crosslinked after cationization is added to paper pulp or furnish during paper manufacture. The starch is cooked prior to addition at the wet end of the papermaking machine and the cooking parameters are adjusted in order to improve the properties of the wet end furnish, such as particle retention and drainage of the furnish. In this manner the properties of the starch are customized so as to conform to the specific conditions of the wet end of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com