Apparatus for irritating animal cell and recording its physiological signal and its production and using method
A technology of animal cells and physiological signals, applied in the methods of stress-stimulating the growth of microorganisms, biochemical cleaning devices, biochemical equipment and methods, etc. Problems such as normal growth and difficulty in controlling the growth direction of neurites
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1, manufacture device of the present invention
[0032] On one side surface of a square glass substrate with a thickness of 350 micrometers, a layer of gold with a thickness of 300 nanometers and a measurement microelectrode with a pattern required for design is processed with conventional photolithography, and the power electrode (patterned with a polymer) partially connected) and leads.
[0033] Apply electricity to the powered electrode, and polymerize a layer of polyaniline conductive polymer with a thickness of 100 nanometers on the gold surface connected to the powered electrode by electrochemical polymerization to form the required pattern.
[0034] A layer of isolation layer is formed on the surface by spin coating, and the desired structure is formed by photolithography.
[0035] After the above steps, the device of the present invention for stimulating animal cells and recording their physiological signals can be obtained.
[0036] In this embodim...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2, structure of the present invention
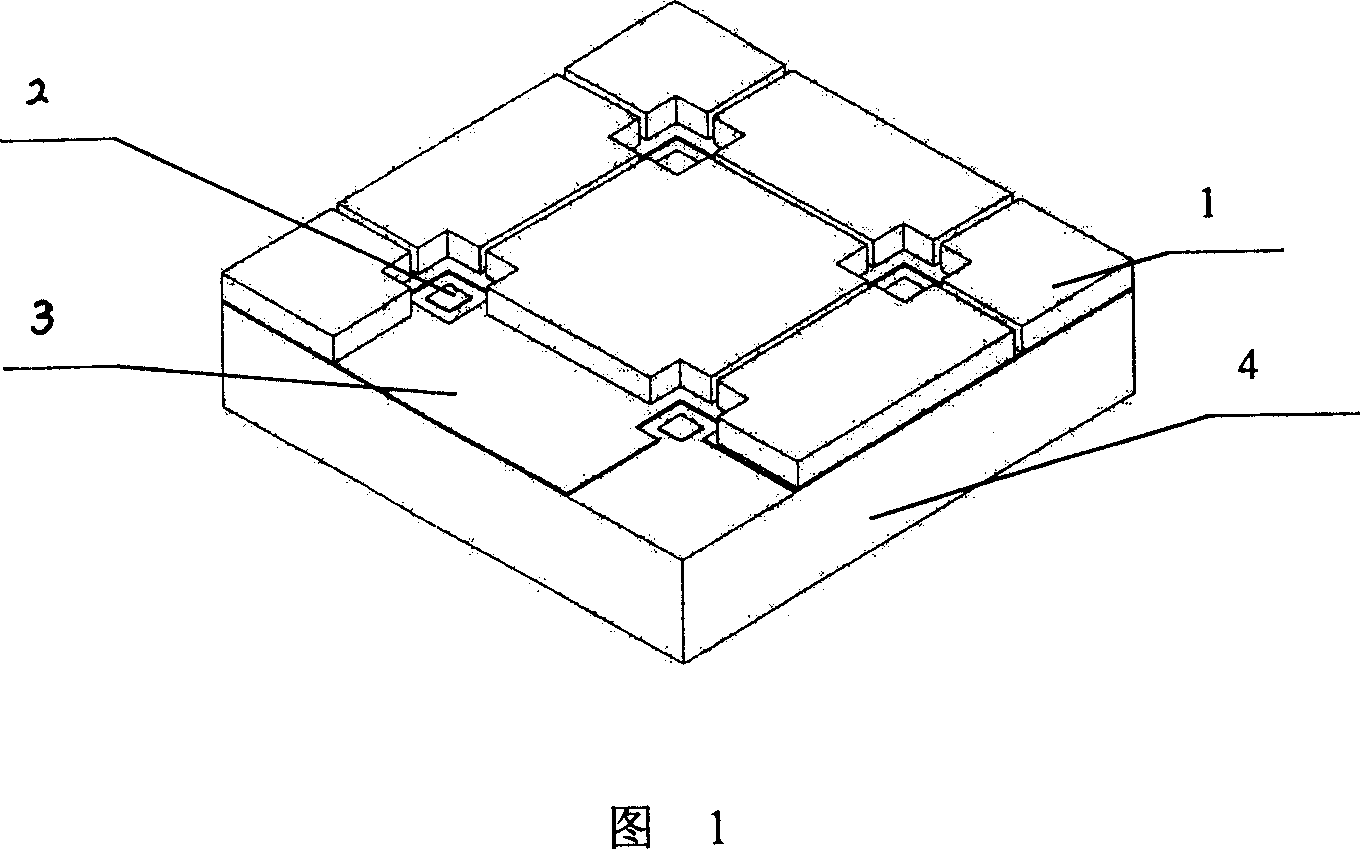
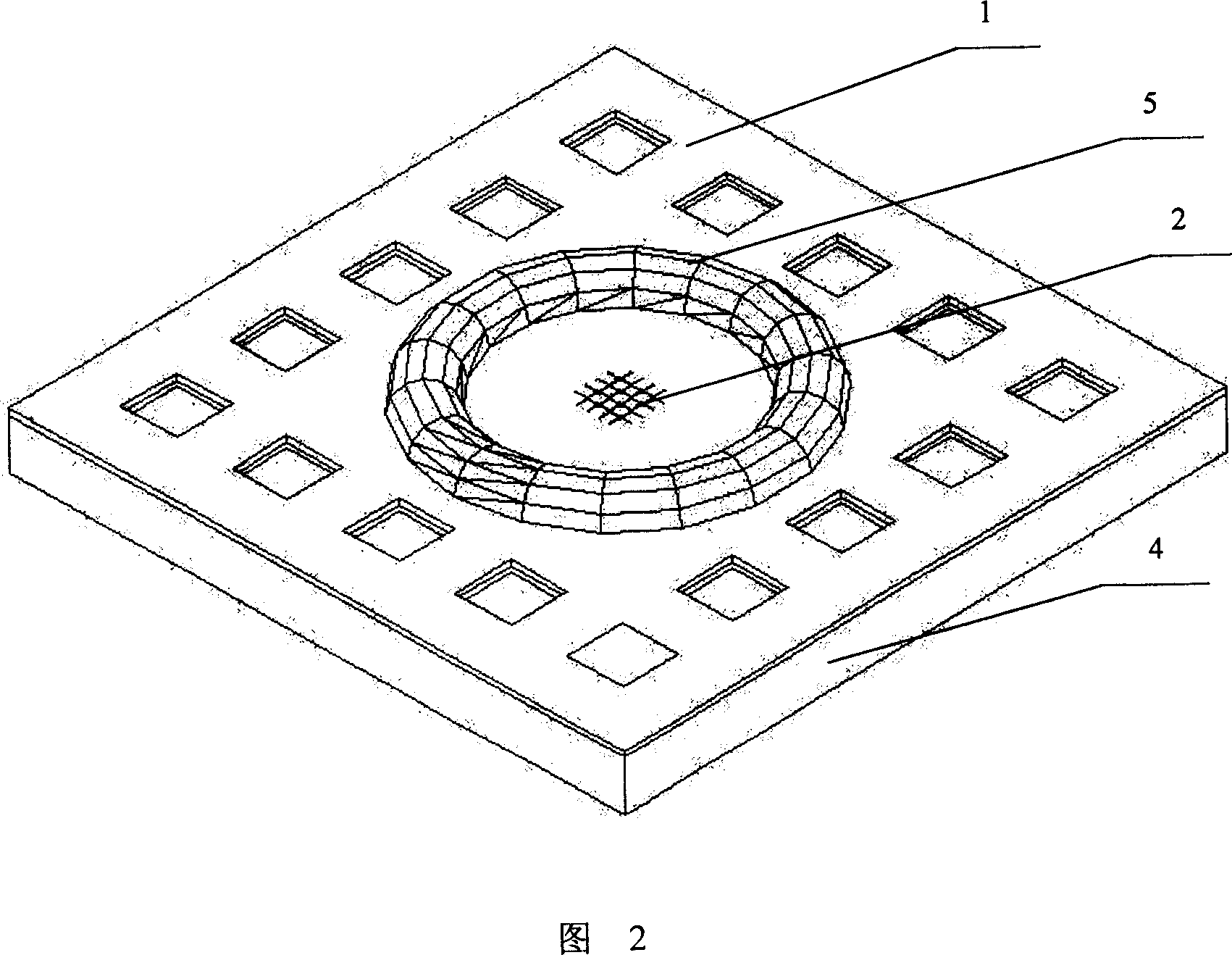
[0038] As shown in Fig. 1, Fig. 2, Fig. 3, the device of the present invention that stimulates animal cells and records its physiological signals includes a square silicon substrate 4 with a thickness of 400 microns; Object layer 3, two electrode lead-out ends (not shown) on the conducting polymer layer 3; Be located at 16 platinum microelectrodes 2 with a thickness of 60 nanometers on the substrate 4, each microelectrode 2 is provided with an output end ( Not shown in the figure); There is a distance of 25 microns between the conductive polymer layer 3 and the microelectrode 2; the part other than the conductive polymer layer 3 on the substrate 4 and the non-cell body growth and microelectrode measurement is provided with polyimide isolation Material layer 1, the thickness of which is 10 microns, forms grooves with a width of 3-7 microns to prevent cells from escaping.
[0039] As shown in Figure 2, a small culture ca...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Embodiment 3, utilize the device of the present invention to carry out the research of neural network in vitro
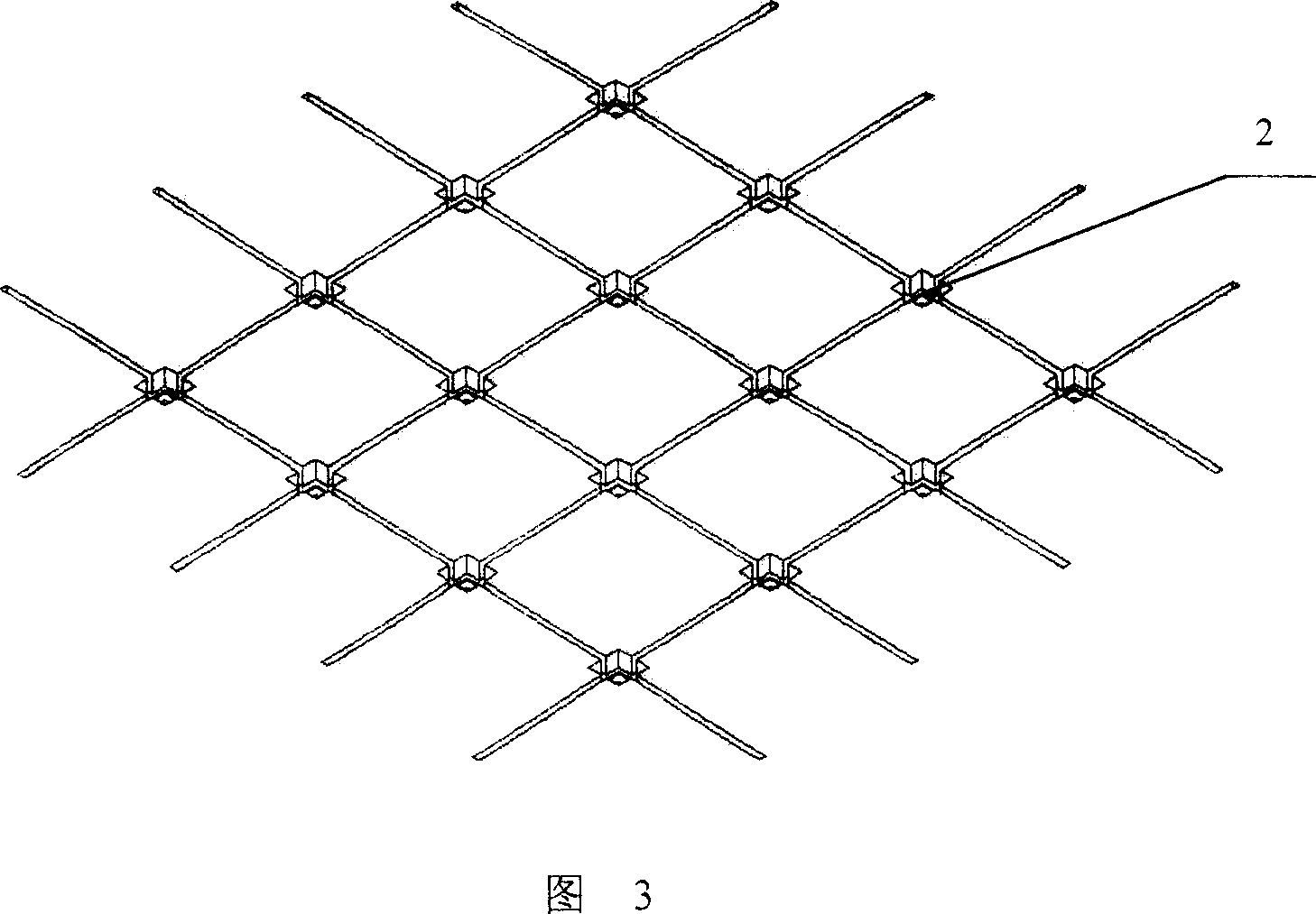
[0043] As shown in Figure 4, the nerve cells 7 are placed on the device of the present invention, the conductive polymer 3 is intermittently energized, the electrical stimulation can be direct current or alternating current, and the stimulation frequency is 1-10 6 Hz; the physiological signal generated in the tested cell is measured by the microelectrode 2 .
[0044] By intermittently energizing the nerve cells (constant voltage 100mV), after culturing for several days, compare the growth of the cells in the energized group and the control group, such as cell body size, process length and other indicators. In addition, by giving stimulation to cells such as electrical and chemical signals, microelectrodes are used to measure changes in the outer membrane potential of cells to study the responses of cells to various stimuli.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com