Flow structure of controlling liquid continuously flowing in micro-pipeline
A micro-pipeline and liquid technology, applied in gas/liquid distribution and storage, pipeline systems, mechanical equipment, etc., to achieve the effect of convenient bubble-free fusion and reliable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
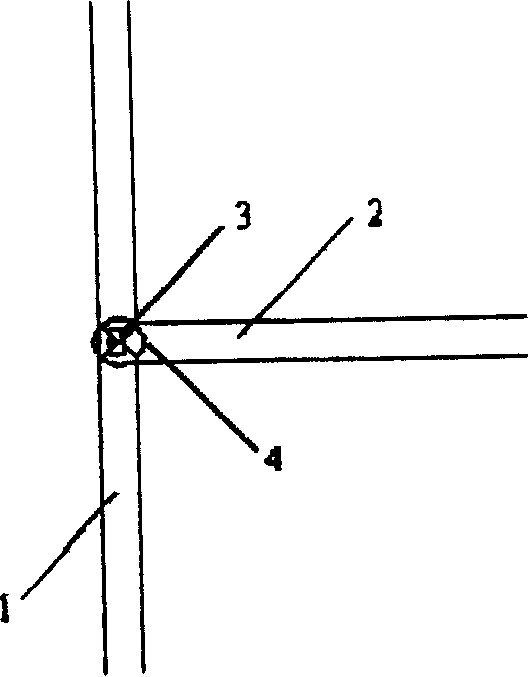
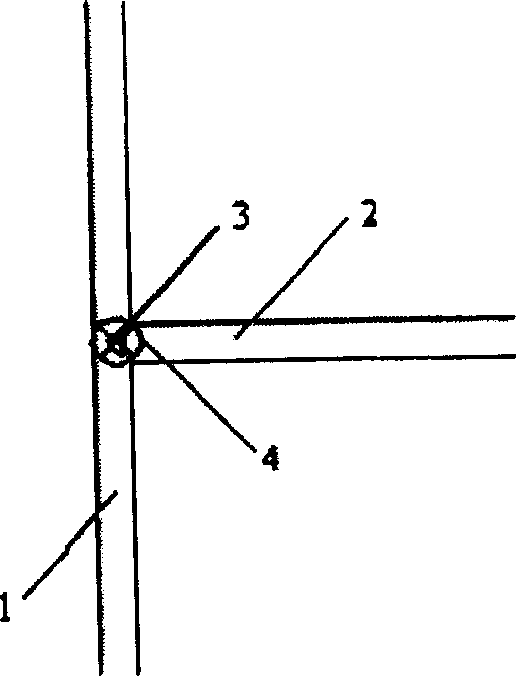
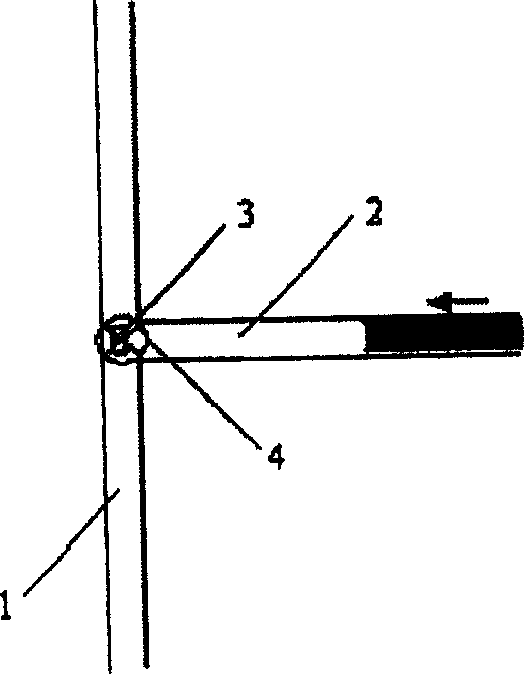
[0024] Such as figure 1 Shown, the structure of the present invention comprises a main micropipe 1, an auxiliary micropipe 2 communicated with the main micropipe 1, and a bluff body 3 is set at the confluence area of the auxiliary micropipe 2 and the main micropipe 1, which can effectively To reduce the area of the flow path, the shape of the bluff body 3 can be a rectangle or a triangle (such as figure 2 shown), other shapes are also possible. The inlet ends of the main micropipe 1 and the auxiliary micropipe 2 are respectively provided with a driving device (not shown in the figure) that provides a driving force. The driving force generated by the device. Such as figure 1 As shown, a sensor 4 can also be arranged in the confluence area for monitoring the inflow and outflow of liquid.
[0025] The fabrication of the above-mentioned structure can adopt the usual method of making chips. First, the grooves forming the micropipes 1 and 2 and the baffle body 3 are made on...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Such as Figure 8 As shown, this embodiment includes a main micropipe 1 and an auxiliary micropipe 2 , and when the auxiliary micropipe 2 approaches the confluence area with the main micropipe 1 , it branches to form a bypass micropipe 5 . Auxiliary micropipe 2 and main micropipe 1 form a confluence region a at point a, and a bluff body 3 is set in confluence region a; bypass micropipe 5 and main micropipe 1 form another confluence region b at point b, and A bluff body 3 ′ is arranged in the confluence region b, and after the two liquids merge in the confluence region b, they continue to extend to form a common downstream micropipe 6 .
[0041] The basic working principle of this embodiment is: drive the first stream of liquid into the auxiliary micropipe 2, and when it is blocked by the first bluff body 3 in the first confluence area a, it can still flow in the bypass micropipe 5 Continue to flow until the signal generated by the sensor 4 completely removes the drivin...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Such as Figure 9 As shown, the present embodiment includes a main micropipe 1, an auxiliary micropipe 2 and a bypass micropipe 7 branched from the auxiliary micropipe 2, and the confluence region of the main micropipe 1 and the auxiliary micropipe 2 is provided with a blocking body 3. In this embodiment, the main micropipe 1 is used as an exhaust pipe, and the bypass micropipe 7 is used as a fusion pipe. The inlet end of the bypass pipe 7 is very close to the confluence area of the main micropipe 1 and the auxiliary micropipe 2 .
[0045] This embodiment has the function of exhaust connection. When working, the liquid enters from the auxiliary micro-pipe 2 and is blocked by the choke body 3. At the same time, it automatically enters the bypass micro-pipe 7. At this time, part of the liquid will stay in a small section of pipeline between the bluff body 3 and the inlet of the bypass micropipe 7. If this section of pipeline is too long, when the liquid tail enters the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com