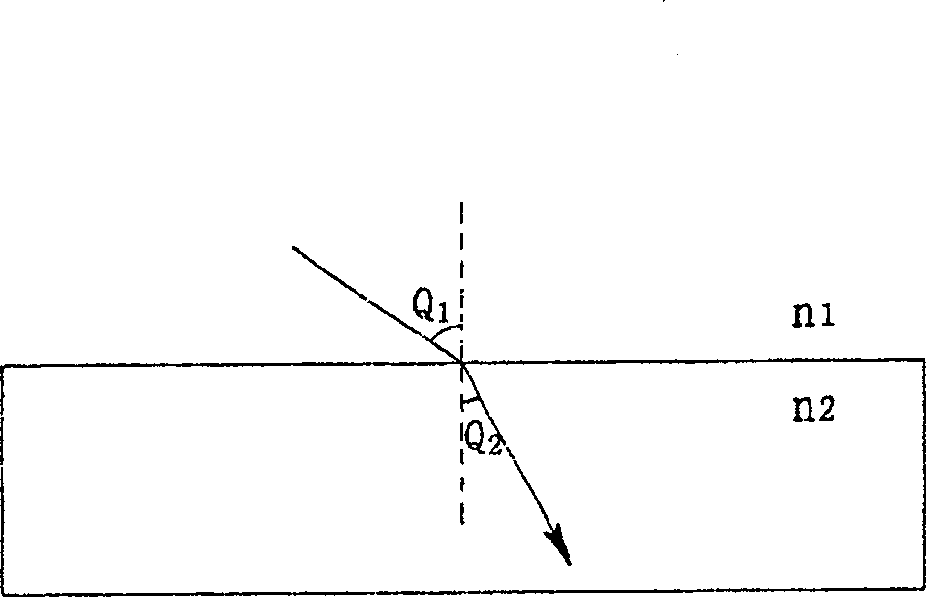
Preparation method of light emitting device
A technology for light-emitting devices and thin films, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of difficult epitaxial layers, high system costs, and poor yield of nano-structured devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] The following will describe in detail in conjunction with the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings.
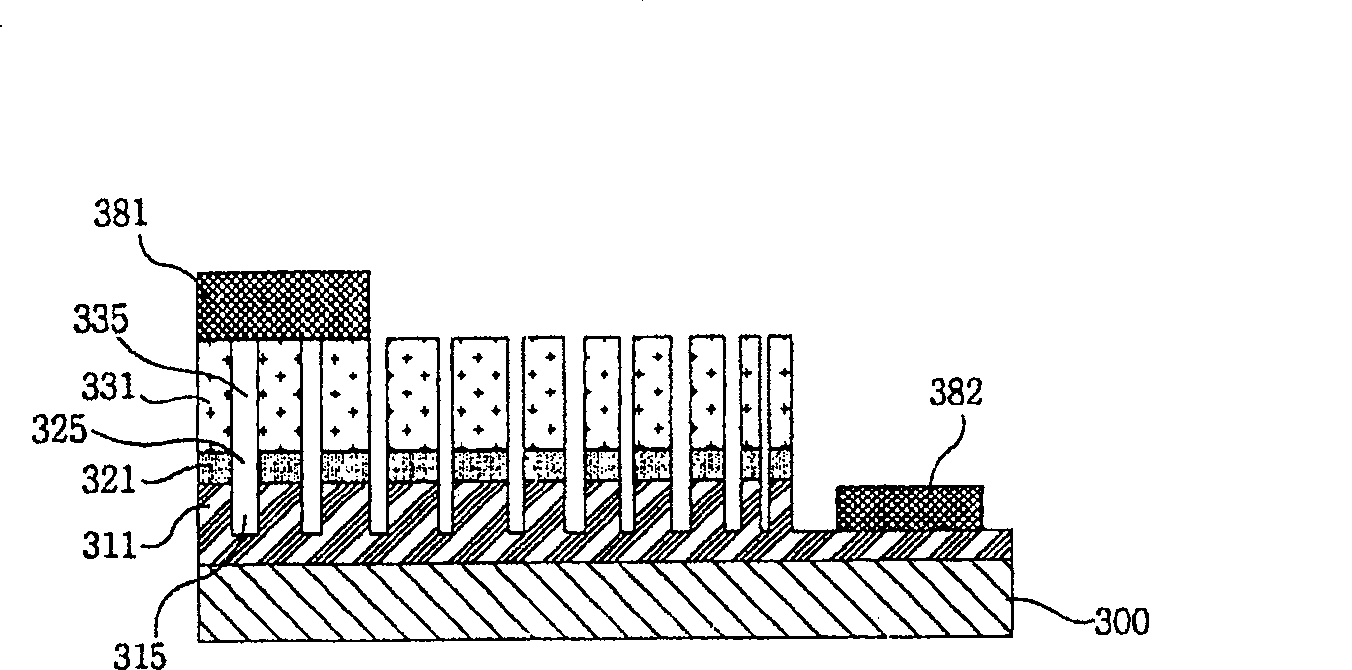
[0039] Figure 3a and 3b is a schematic sectional view of a light emitting device according to the present invention. refer to Figure 3a, the light emitting device comprises: a substrate (300); a first layer (311) having a first polarity formed on the substrate (300), a part of the first layer (311) is removed and a plurality of nanogrooves (315) are formed In the region where the first layer (311) is not removed; an active layer (321) formed on the unremoved first layer (311); formed on the active layer (321) and having a a second layer (331) of opposite polarity to the layer (311); a first electrode (381) formed on the second layer (331); and a second electrode formed on the removed first layer (311) (382).
[0040] The second layer (331) may further include a transparent electrode thereon, and the first electrode may ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com