Strong magnetic field vacuum annealing method for eliminating bulky Widmansttten structure in hypoeutectoid steel
A technology of Widmanstatten structure and hypoeutectoid steel, which is applied in the field of high magnetic field vacuum annealing to eliminate the coarse Widmanstatten structure in hypoeutectoid steel, can solve the problems such as the difficulty of eliminating Widmanstatten structure, and achieve the improvement of mechanical properties and plastic deformation effect of ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
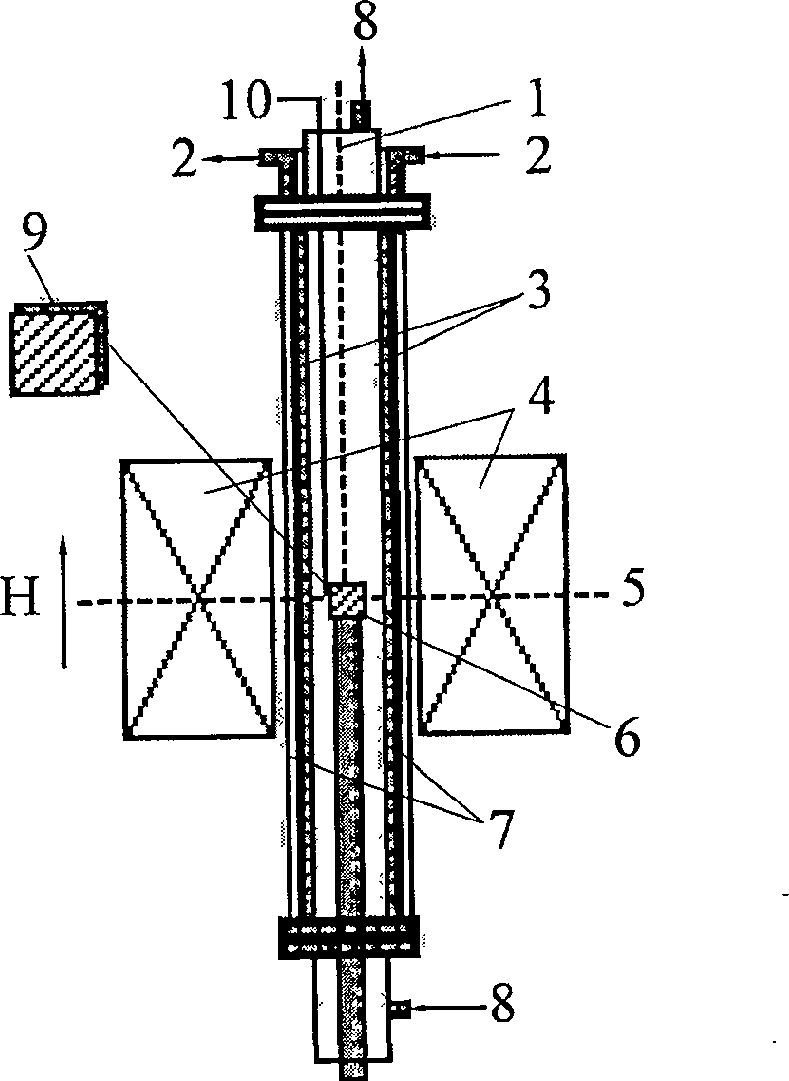
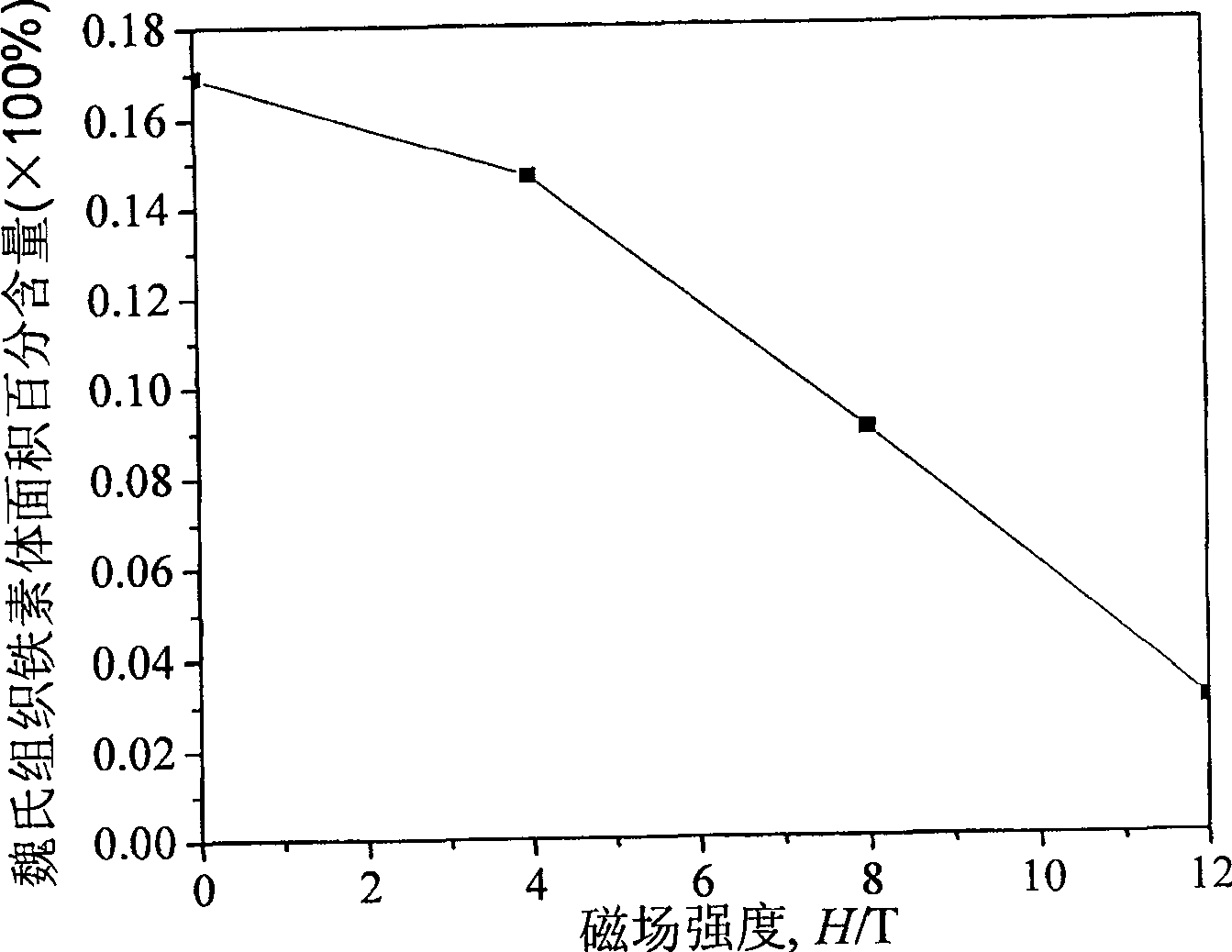
[0024] The material is high-purity Fe—0.52C alloy, the chemical composition is shown in Table 1, and its Ae is calculated by using Thermo—calc thermal analysis software. 3The temperature is 1037K. The heat treatment process is to heat the sample to 1067K, keep it warm for 5min, cool to 873K at 0.5K / min, and cool to room temperature with the furnace. During the heat treatment, 0T, 4T, 8T and 12T strong magnetic fields are applied respectively. The strong magnetic field generating device is a JMTD-12T100 superconducting direct current constant strong magnetic field generating device, which can generate a maximum magnetic field strength of 12T. The size of the sample is 7mm×7mm×1mm. After the heat-treated sample is ground, polished and corroded with 3% nital solution, the microstructure is observed with an Olympus optical microscope. The metallographic observation surface is a section parallel to the direction of magnetic field application, and the direction indicated by the arr...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The material is high-purity Fe-0.52C alloy, chemical composition and Ae 3 Temperature is identical with embodiment 1. The heat treatment process is to heat the sample to 1067K, hold it for 5min, cool it to 873K at different cooling rates (0.5K / min, 2K / min, 5K / min), and cool it to room temperature with the furnace. magnetic field. The strong magnetic field generating device, the sample size and the sample processing and microstructure observation after heat treatment are all the same as in Example 1.
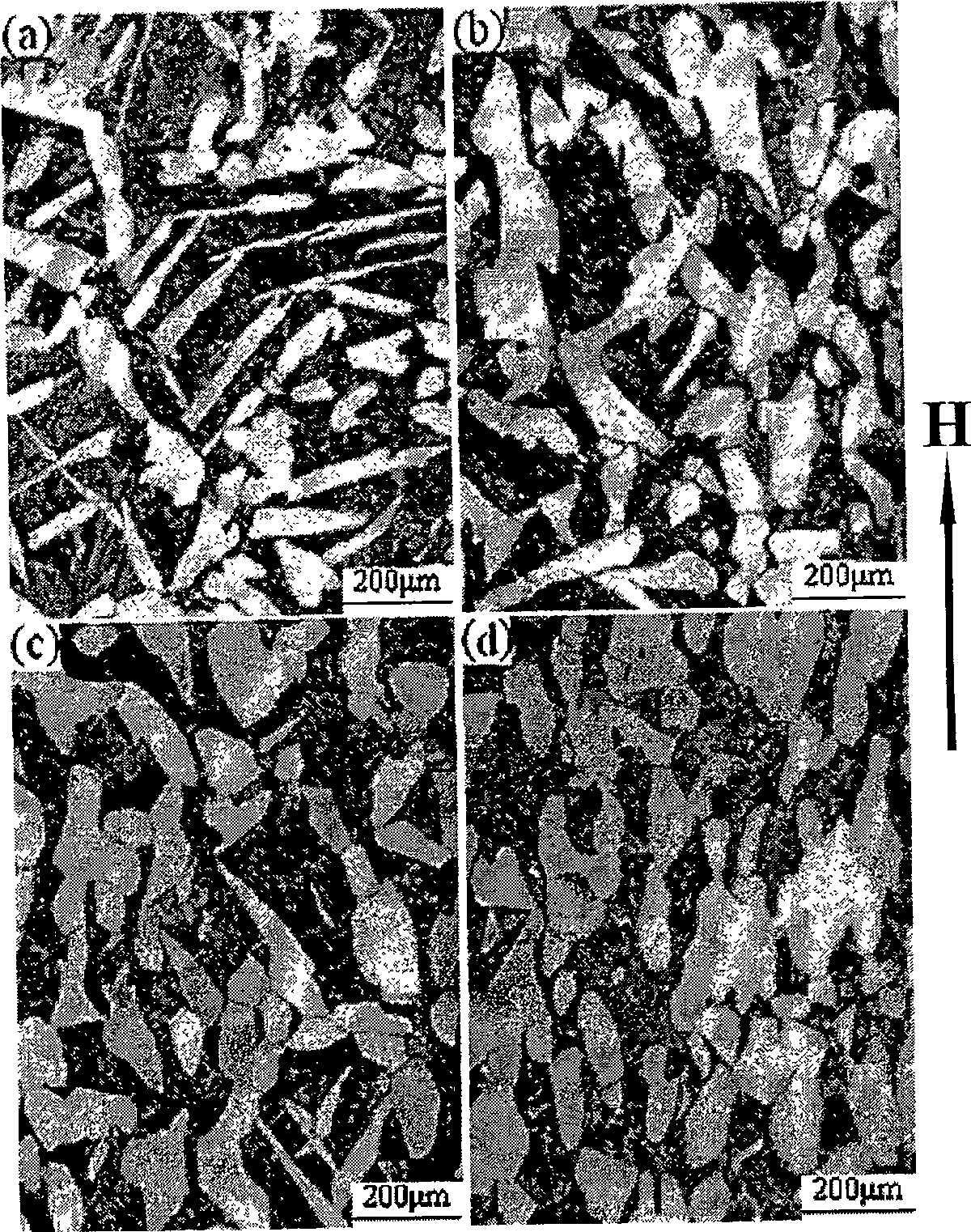
[0031] Figure 4 It is the microstructure of high-purity Fe-0.52C alloy after heat treatment with different cooling rates (0.5K / min, 2K / min, 5K / min) under non-magnetic field and 12T magnetic field. Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that the non-magnetic field heat-treated samples ( Figure 4 (a), (b), (c)) in the microstructure, the pro-eutectoid ferrite is needle-like Widmanstatten ferrite and a small amount of equiaxed ferrite. Among them, the distribution of ferr...
Embodiment 3
[0033] The material is high-purity Fe-0.36C alloy, and its chemical composition is shown in Table 2. Ae 3 The temperature is 1069K. The heat treatment process is to heat the sample to 1099K, keep it warm for 5min, cool to 873K at a cooling rate of 0.5K / min, and cool to room temperature with the furnace. During the heat treatment process, 0T and 12T strong magnetic fields are applied respectively. The strong magnetic field generating device, the sample size and the sample processing and microstructure observation after heat treatment are the same as in Example 1.
[0034] Table 2. Chemical composition of Fe—0.36C alloy (mass%).
[0035]
[0036] Figure 5 shown as Figure 5 . The microstructure of Fe—0.36C alloy under the condition of 0T or 12T magnetic field, after 1099K, 5min austenitization, cooling to 873K at a cooling rate of 0.5K / min, and then furnace cooling to room temperature. Similar to the Fe-0.52C alloy, the magnetic field is 0T after heat treatment ( Figu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com