Safe identification and association of wireless sensors
A wireless sensor and sensor technology, applied in the direction of sensors, human identification, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems such as error-prone and manual intervention, and achieve the effect of reducing the possibility of crosstalk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
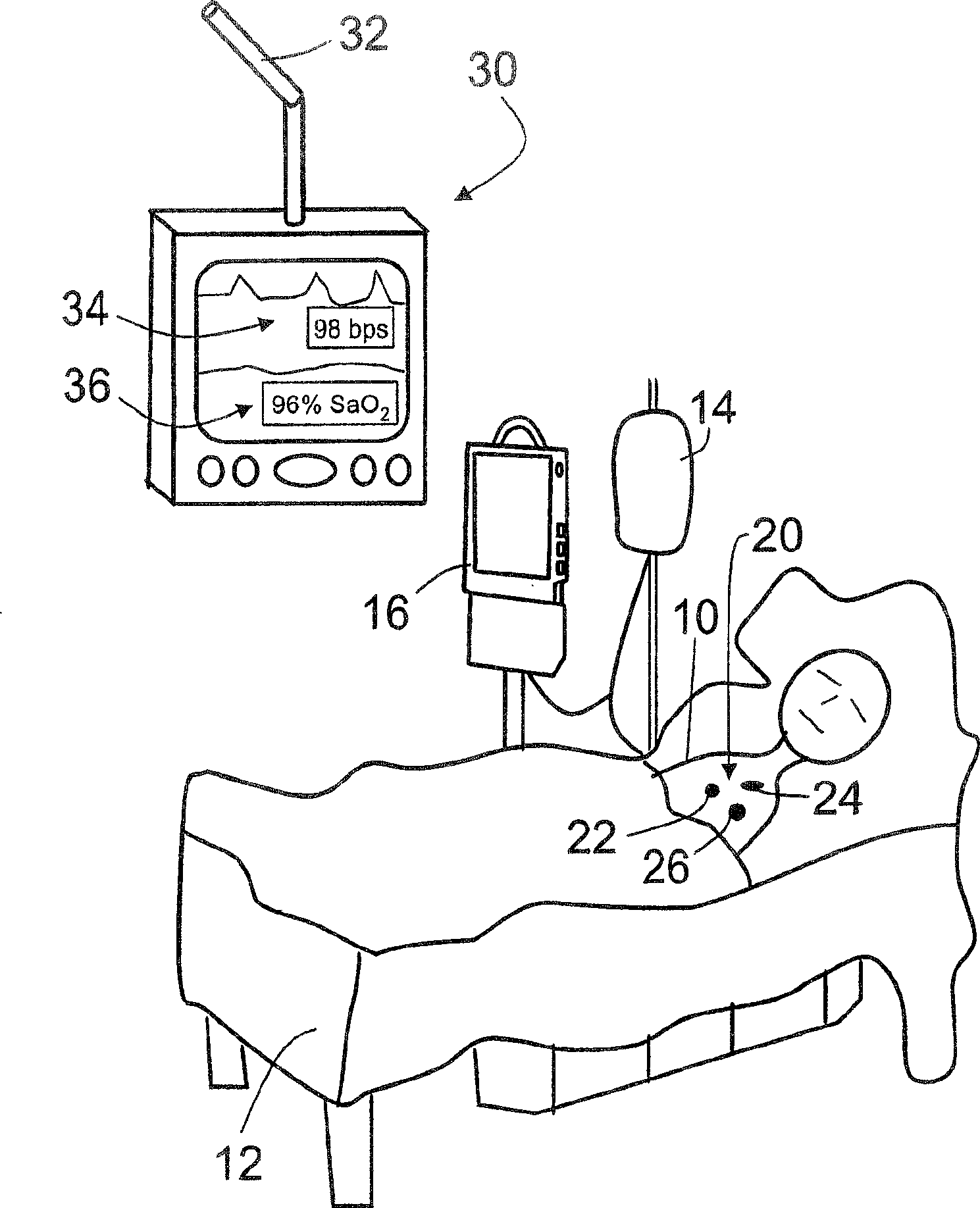
[0022] refer to figure 1 , a medical patient 10 is lying on a bed 12 . A patient 10 is shown receiving intravenous fluid from an intravenous fluid tank 14 controlled by an intravenous flow monitor 16 . Such intravenous fluid therapy is an illustrative example; in general, patient 10 may receive additional or other therapy, may receive medication from, for example, an automatic dispenser (e.g., an infusion pump), or may receive no therapy at all or medication.
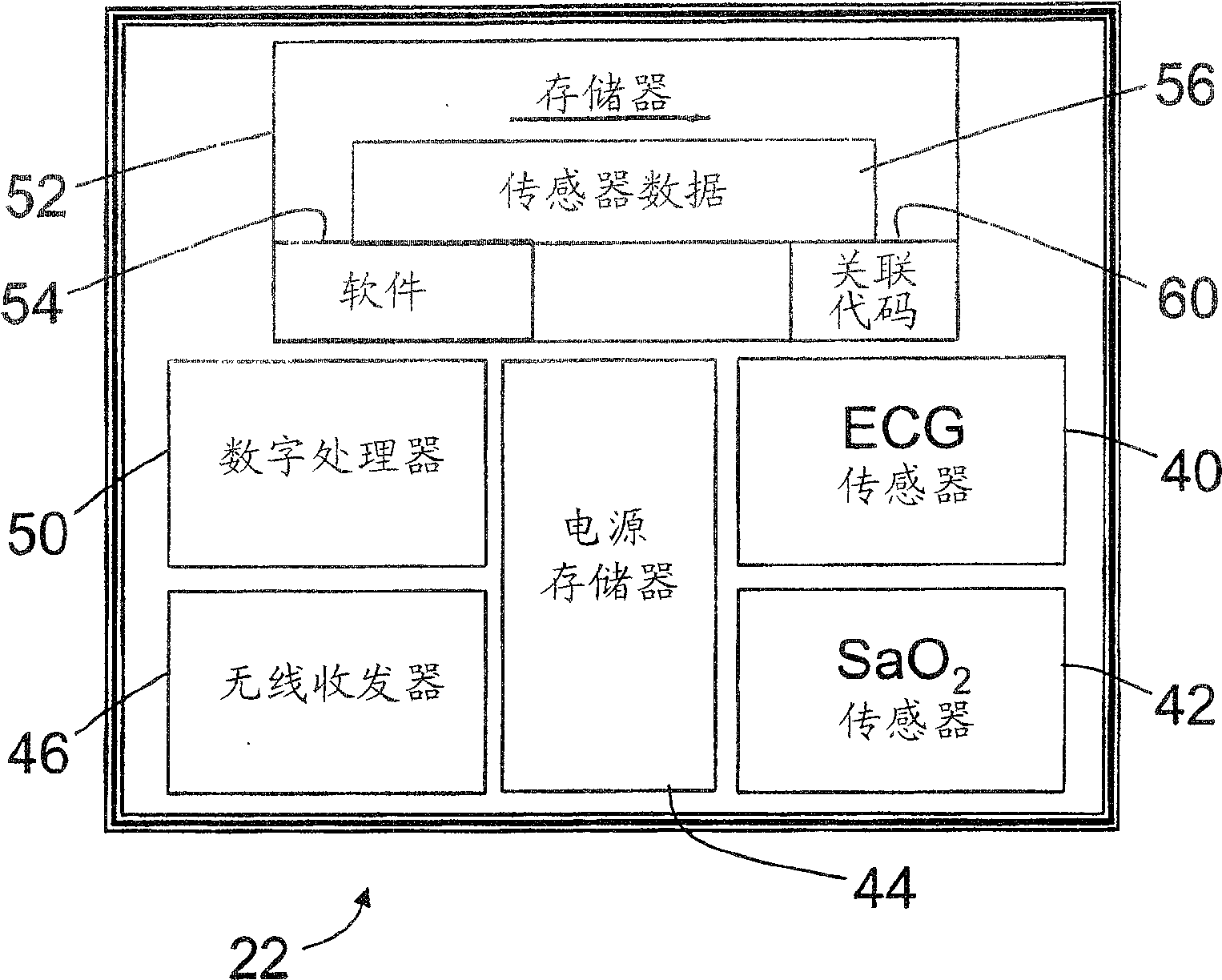
[0023] The patient 10 is monitored via a wireless sensor network 20 which, in the illustrated embodiment, includes three sensor nodes 22 , 24 , 26 . More generally, the sensor network may include substantially any number of sensor nodes. The sensor nodes 22 , 24 , 26 communicate wirelessly with an external monitor 30 . In the illustrated embodiment, the external monitor 30 is mounted on a ceiling (not shown) by an articulated mounting arm 32, and displays: (i) electrocardiogram (ECG) data 34; and (ii) blood oxygen s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com