Light-emitting device with increased quantum efficiency
A technology of light-emitting devices and light-emitting layers, which is applied in the fields of electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, etc., can solve problems such as loss and quantum efficiency decline, and achieve the effect of precise adjustment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
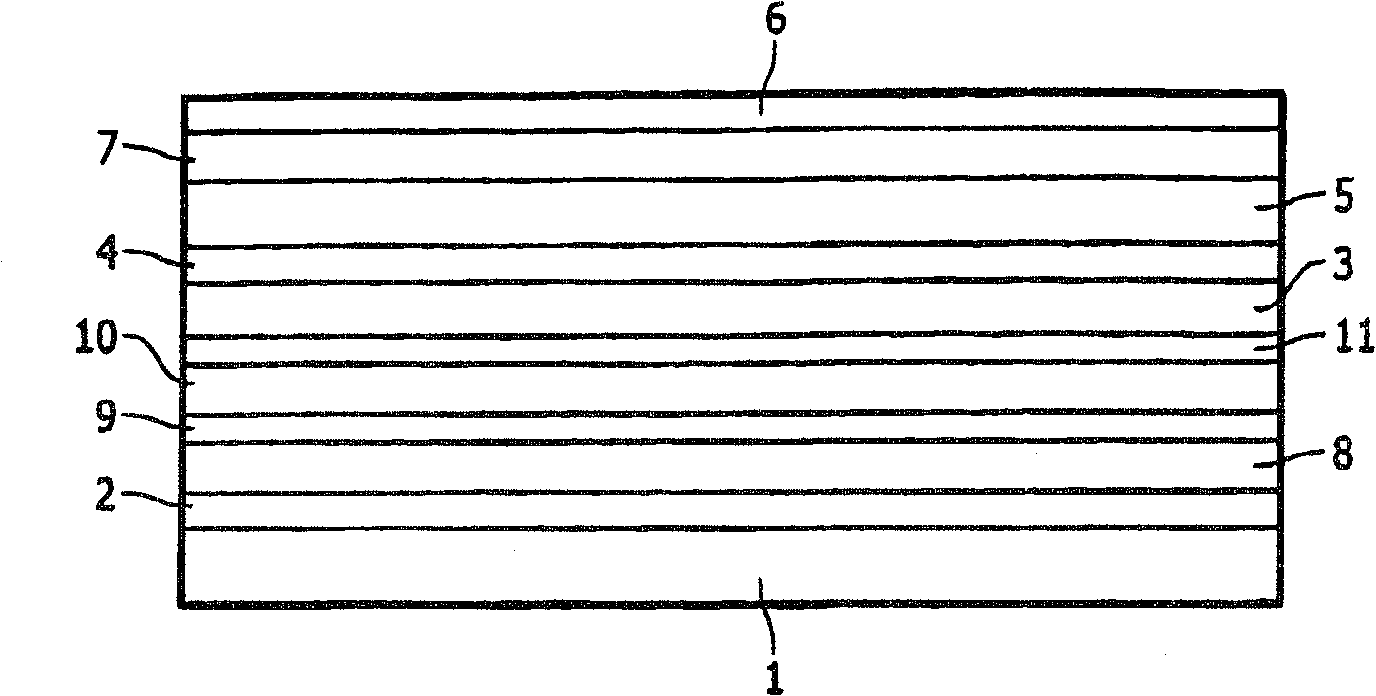
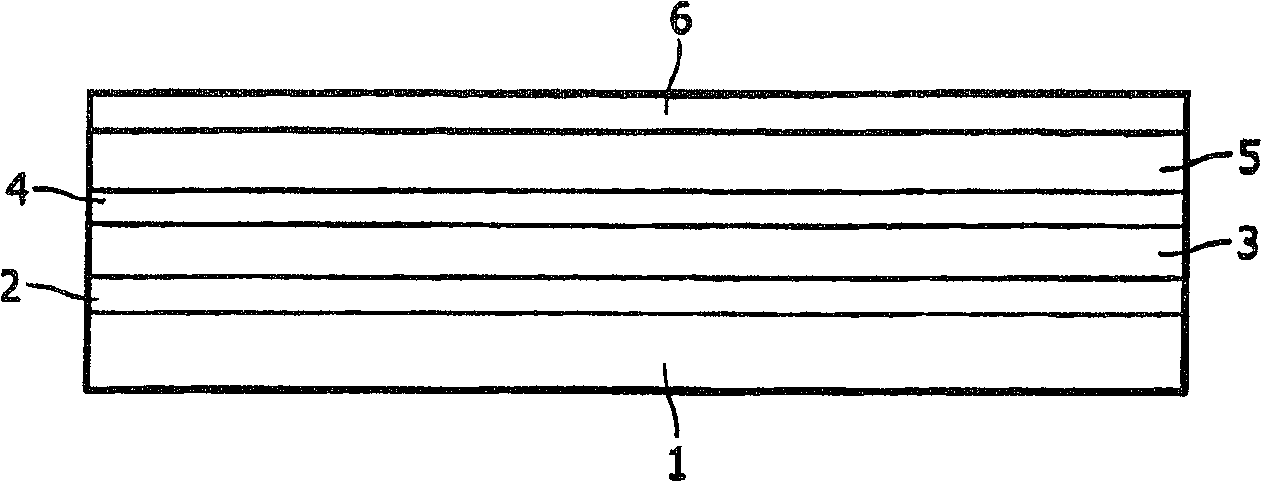
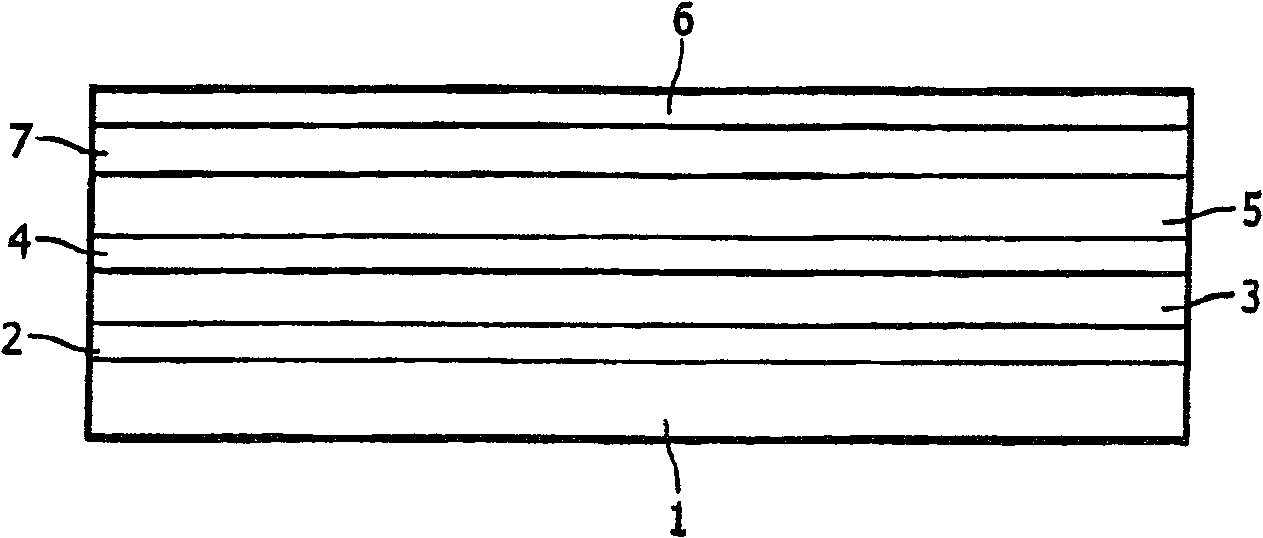
[0040] On a transparent substrate 1 made of glass, ITO with a layer thickness of 150 nm was applied as anode 2 . α-NPD with a layer thickness of 30 nm was applied as first hole-transport layer 3 on the anode 2 by spin coating. A BCP first hole-blocking layer 4 with a layer thickness of 1 nm is applied on the hole-transport layer 3 . On the first hole blocking layer 4 is applied an emitting layer 5, i.e. Ir(ppy) embedded in TCTA 3 . The layer thickness of the light emitting layer 5 was 30 nm. A 10 nm-thick second hole-blocking layer 7 of BCP is applied on the emitting layer 5 . Alq was applied with a layer thickness of 40 nm on the second hole blocking layer 7 3 as the electron transport layer 12. A 151.5-nm-thick cathode 6 consisting of a 1.5-nm-thick lithium benzoate first layer and a 150-nm-thick aluminum second layer is applied to the electron-transport layer 12 .
[0041] Compared with the light emitting device without the first hole blocking layer 4, the quantum eff...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com