Boundary acoustic wave device
A technology of acoustic wave devices and boundaries, applied in the direction of electrical components, impedance networks, etc., can solve problems that are difficult to meet the boundary acoustic wave performance and characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
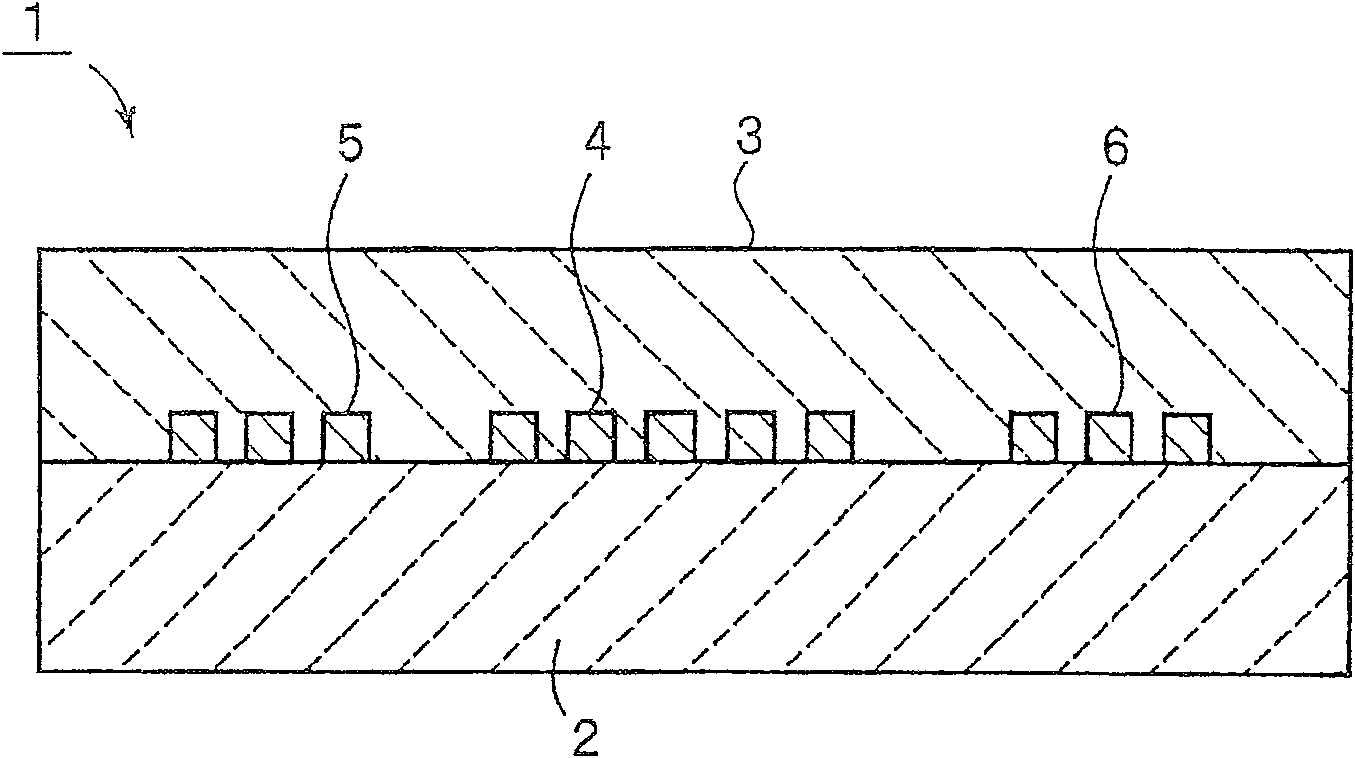
[0157] As piezoelectric material 2, LiNbO with Euler angles (0°, 90°, 0°) was prepared 3 substrate, i.e., the Y-directed plated X-propagated LiNbO 3 substrate. By utilizing LiNbO 3 substrate, which can obtain excellent piezoelectric properties. In addition, as a material for forming the dielectric substance 3, SiO 2 . SiO can be easily formed by 2 thin film formation, due to the LiNbO having shifted 3 Positive temperature coefficient of frequency TCF of negative TCF, SiO 2 The temperature characteristics can be improved.
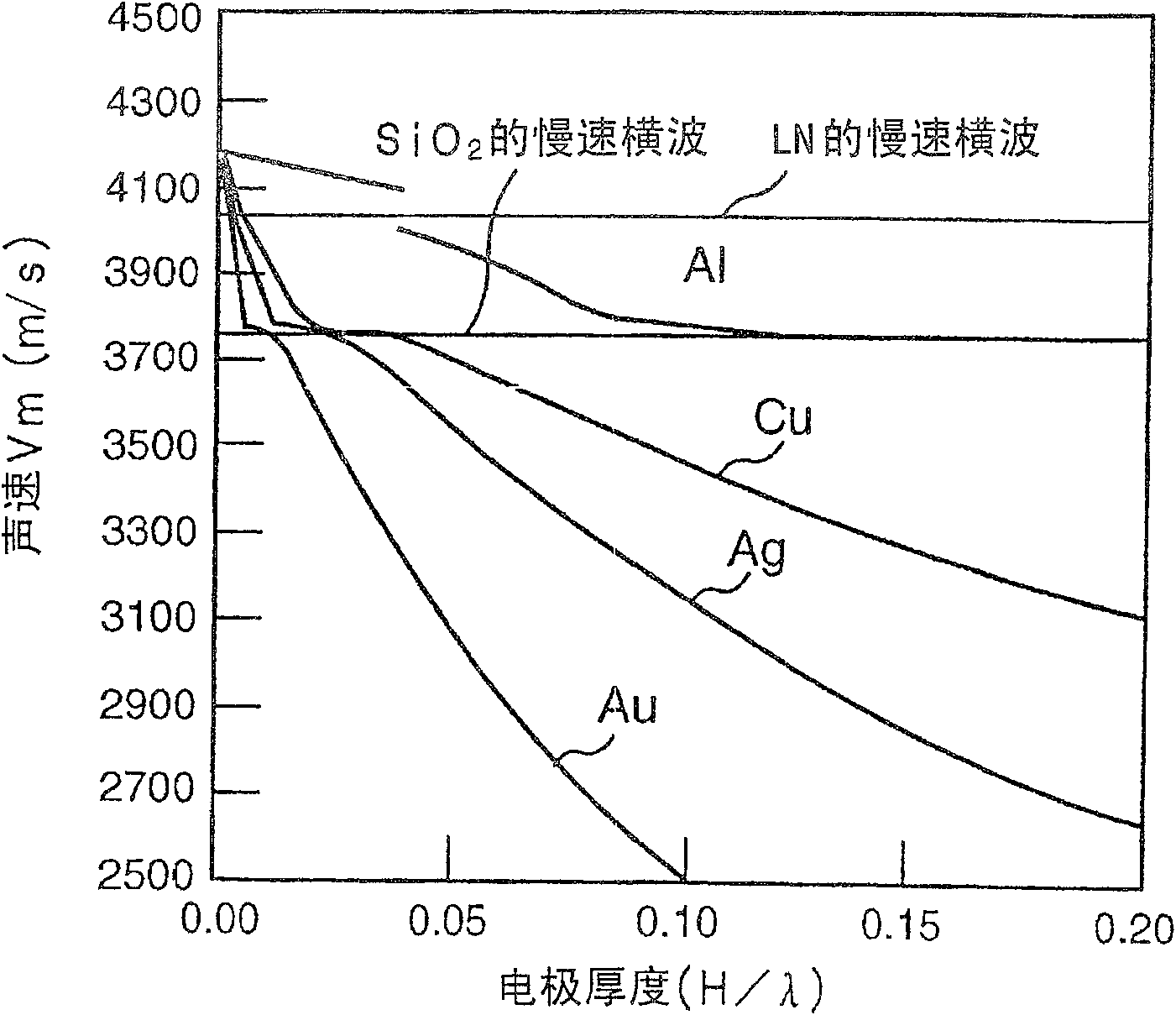
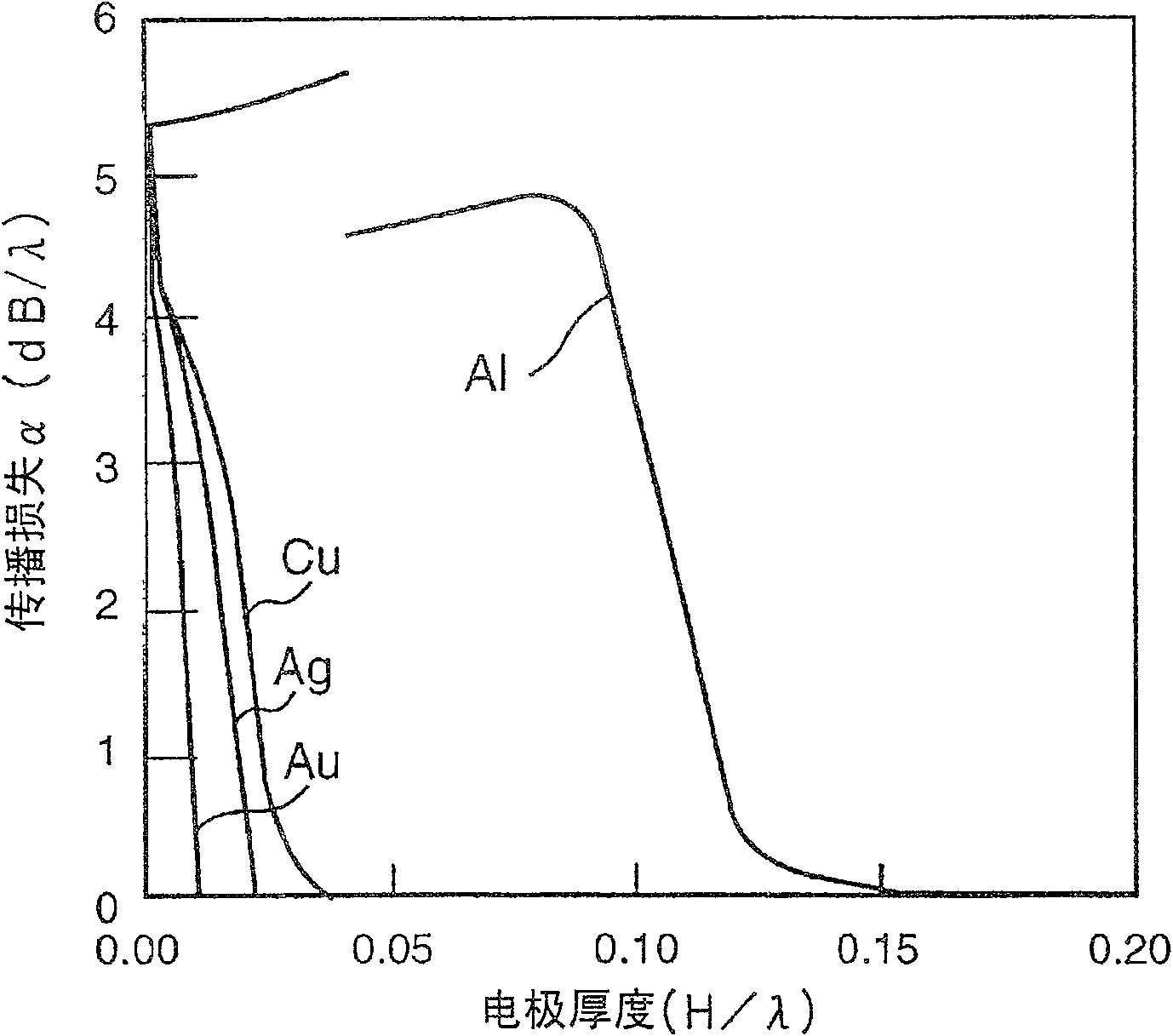
[0158] By using various electrode materials with different densities, an electrode was formed between the piezoelectric substance 2 and the dielectric substance 3, and the relationship between the electrode thickness and the sound velocity V, the electromechanical coefficient k 2 , the relationship between propagation loss α, frequency temperature coefficient TCF and power flow angle PFA. Figures 2 to 6 Results are shown.
[0159] By based on "A m...
example 2
[0182] Based on the results obtained in Example 1 above, experimentally formed figure 1 Boundary acoustic wave resonators shown and having the structures shown in Table 3 below. Figure 9 The frequency characteristics of the boundary acoustic wave resonator thus formed are shown in .
[0183] table 3
[0184] project
detail
structure
SiO 2 / Au / LiNbO 3
SiO 2 thickness
7.5λ
Au thickness
0.035λ
IDT, reflector period λ
3.2μm
IDT configuration
Ordinary single strap, 50 pieces, open
Length 25λ
reflector configuration
Ordinary single strap, 40 pieces, open
Length 25λ
[0185] In the above boundary acoustic resonator, the impedance ratio, that is, the ratio of the impedance at the antiresonance point to the impedance at the resonance point is 45.6dB, and the difference between the resonance frequency and the antiresonance frequency is 8.1%; therefore, it is preferred the ...
example 3
[0189] As in the case of the SH-type boundary acoustic wave, the above-mentioned spurious signal response generated around the antiresonant frequency in Example 2 is limited to the SiO 2 and LiNbO 3 The Stoneley wave response around the electrode at the boundary between them. Since the sound velocity of the Stoneley wave is lower than that of the SH-type boundary acoustic wave in many cases, even when the thickness of the electrode is small compared with the case of the SH-type boundary acoustic wave, the Stoneley wave is expressed as a boundary acoustic wave.
[0190] For example, when cutting X propagation in Y direction (represented by Euler angles (0°, 90°, 0°)) LiNbO 3 SiO with a sufficiently large thickness is formed on the substrate 2 film so as not to excite surface acoustic waves such as Rayleigh waves or first leaky waves, and the Au electrodes are placed on the LiNbO 3 Substrate and SiO 2 Between films, the SH-type boundary acoustic wave has a large attenuation ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com