Polynucleotides encoding mature AHASL proteins for creating imidazolinone-tolerant plants
A polynucleotide and protein technology, applied in the field of plant molecular biology, can solve problems such as nucleotide and amino acid sequences that have not been reported
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0120] Example 1: The large AHASL subunit is encoded by 3 genes
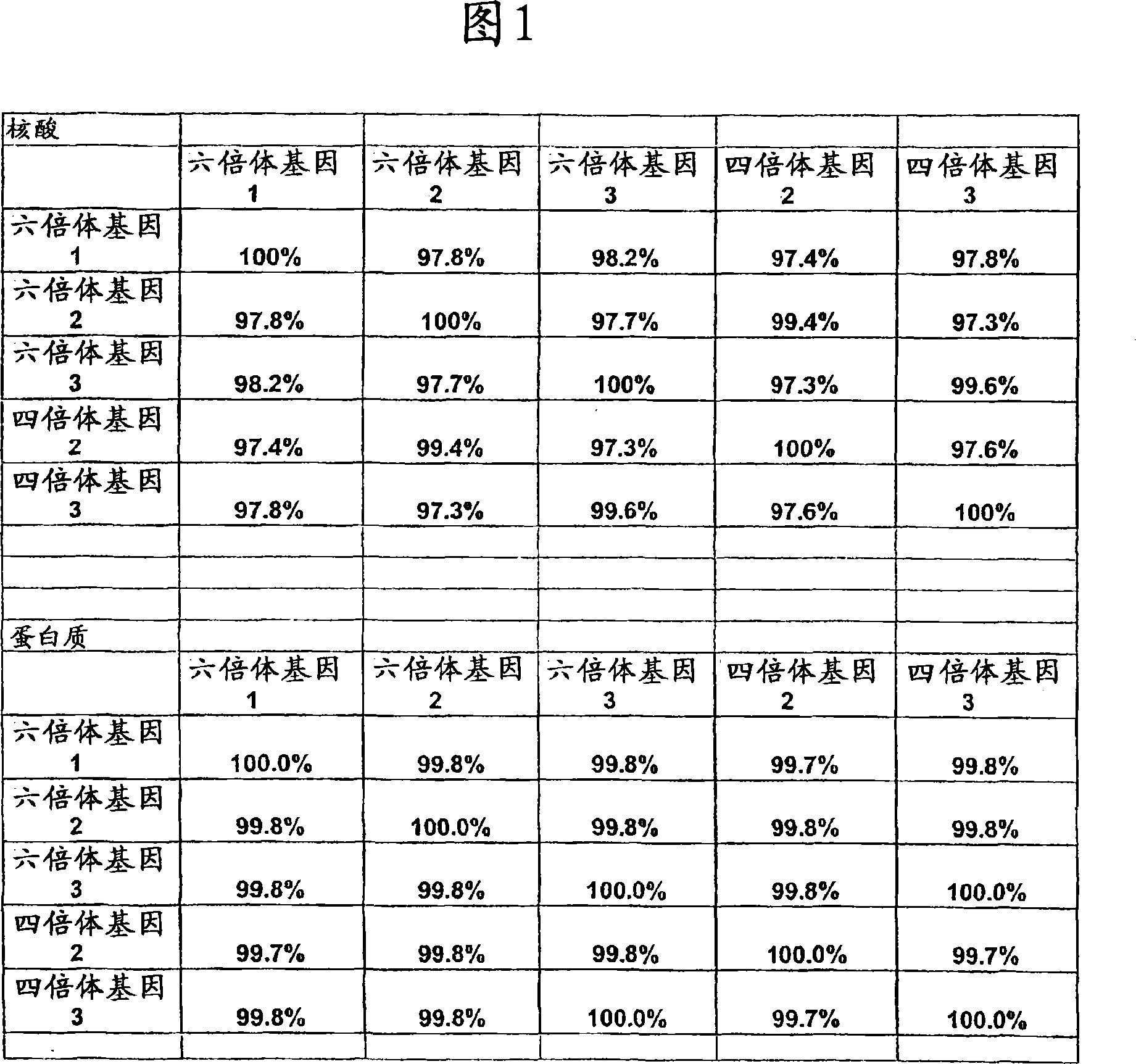
[0121] During the course of the wheat mutagenesis program, thousands of independently derived lines were analyzed through herbicide spray assays. In order to understand the molecular basis of tolerance, efforts were made to identify active genes in wheat. By designing degenerate PCR primers based on previously cloned AHASL nucleotide molecules, the AHASL gene was cloned from wild-type and imidazolinone-resistant wheat plants. The cloned PCR products were divided into 3 closely related groups, indicating that there are 3 AHASL genes in hexaploid wheat. This is consistent with having one AHASL gene per diploid genome. Subsequent EST data analysis showed that there were only 3 active copies of AHASL. In addition, only 3 independently isolated resistance genes (Pozniak and Hucl, in press) were found. The nearly full-length sequence of wheat AHASL gene has been determined by RACE-PCR. The nucleotide and amino acid sequen...
Embodiment 2
[0122] Example 2: Wheat AHASL gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 6
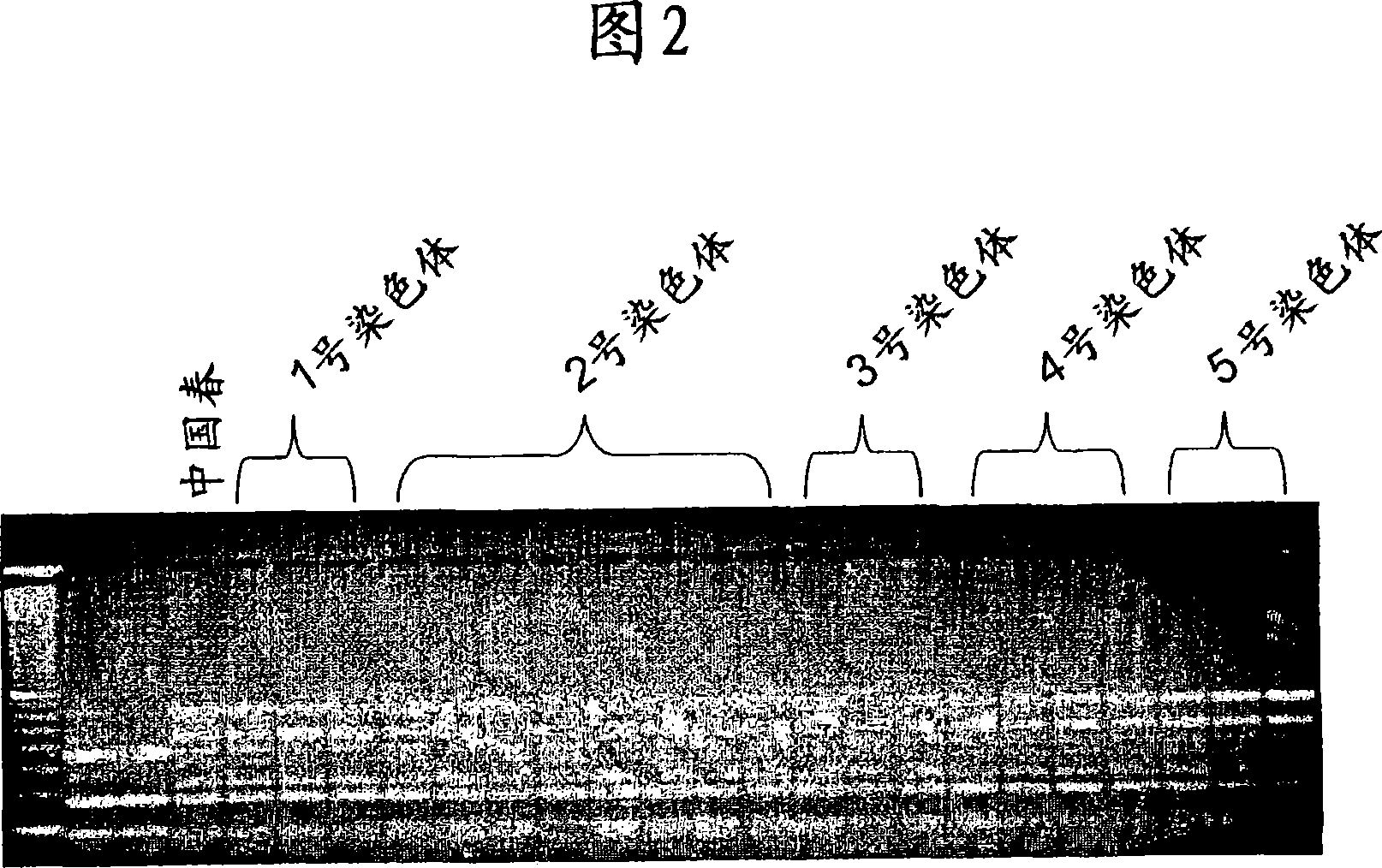
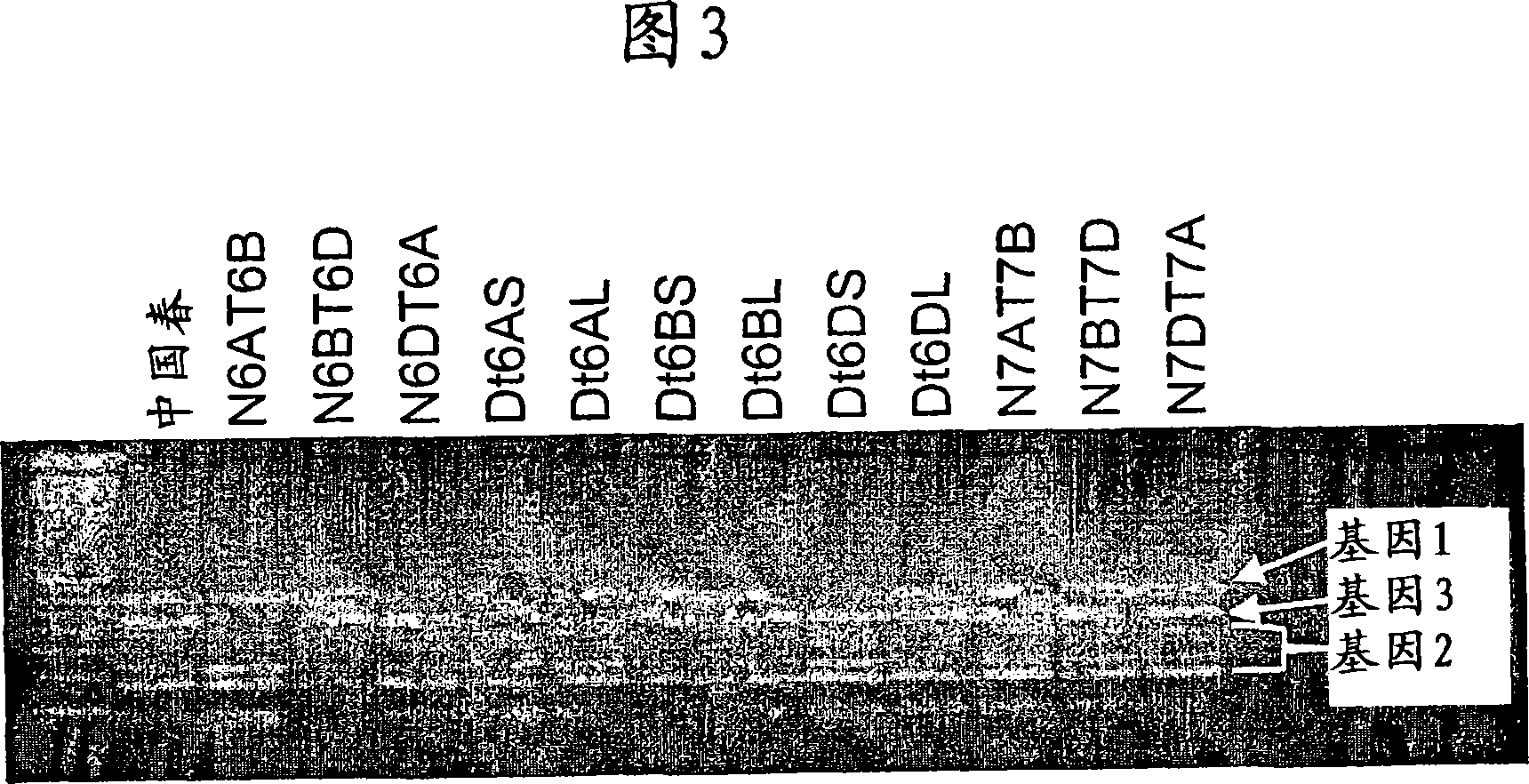
[0123] In order to determine the chromosomal positions of the three genes, a collection of "Chinese Spring" aneuploid stocks and a gene-specific, digested amplified polymorphism (CAPS) marker (provided by Pozniak et al.) )joint. It was found that N6DT6A and Dt6DS lacked gene 1, while N6BT6D and Dt6BS did not have gene 2, and N6AT6B and Dt6AS lacked gene 3 (Figure 2-3). This indicates that gene 1 is located on the long arm of chromosome 6D, gene 2 is located on 6B, and gene 3 is located on 6A. Now, rename the homologous genes (genes 1-3) to AHASL1D, AHALSL1B, and AHASL1A, respectively, and the last letter indicates the genome.
Embodiment 3
[0124] Example 3: The tolerance level is affected by the mutant AHASL gene
[0125] The most common mutations observed in wheat result in Ser to Asn substitutions at positions equivalent to Ser653 in Arabidopsis (called S653(At)N). Typically, after spraying imazamouse at a ratio sufficient to detect the difference of plants grown in the greenhouse, 24 samples from each mutagenic line were treated according to a 0-9 rating scale (0=no damage; 9=highest damage) Individual scores (Figure 4). For each line, the specific gene that is mutated is determined. A clear correlation was found between the assessment from the herbicide spray assay and the specific homologue mutated at that location. Compared with 1B (5.4) and 1A (6.4), mutations in AHASL1D lead to higher tolerance (medium damage = 4.0).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com