Process of extracting cotton bast fiber and vegetable dyeing agent from cotton stalk
A plant dyeing agent and cotton lint technology, which can be used in dyeing, textiles, and papermaking, and can solve the problems of cotton stalks for textile fibers, environmental pollution, and damage to wearers and producers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
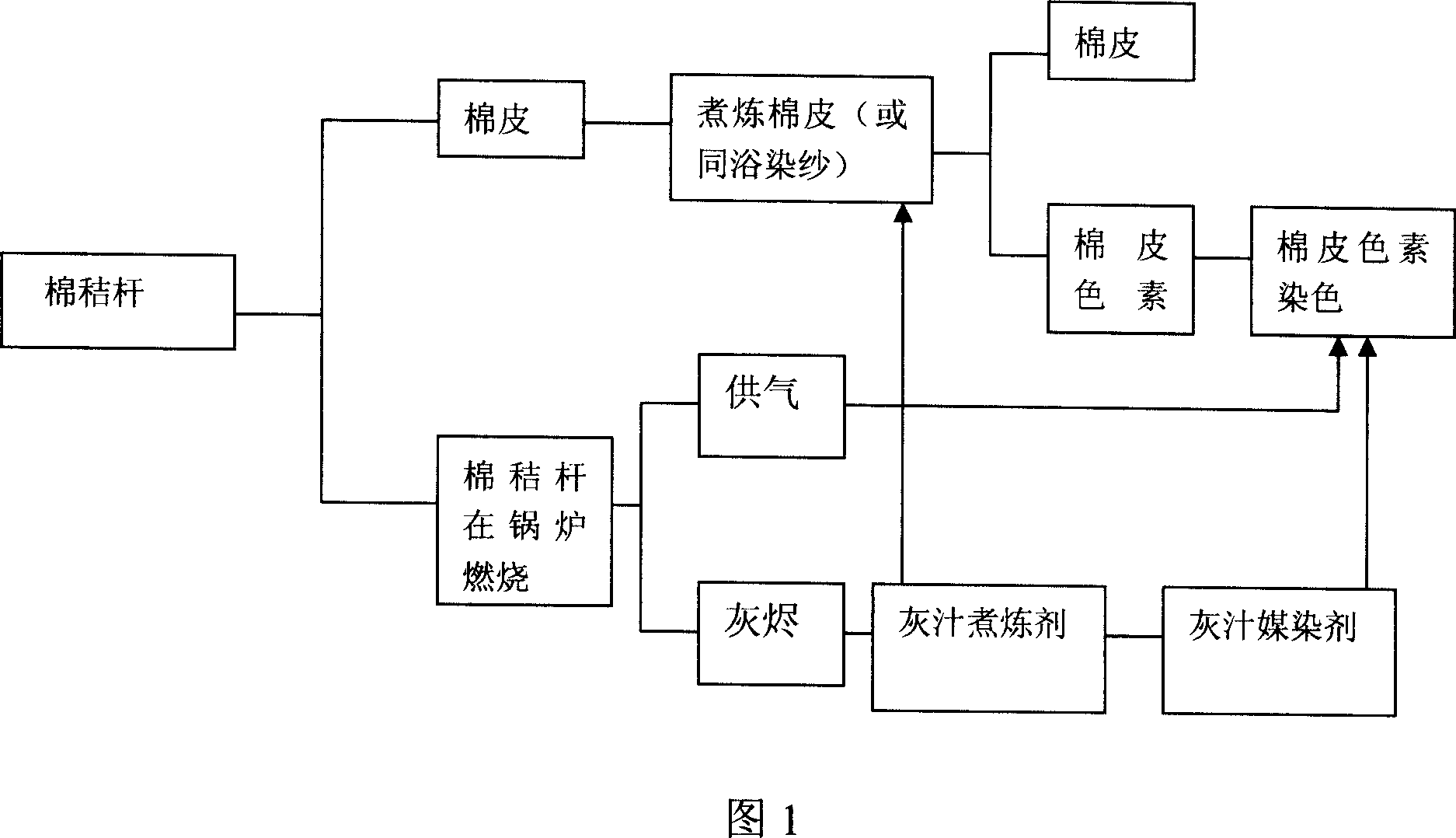
[0019] As shown in Figure 1: 1, the cotton stalk gets the leather tie and puts into the pot (also can dye the cotton yarn wrapped in the same bath) and compact it. 2. Peeled cotton straw replaces coal (saving national resources) for boiler use, heating and gas supply. 3. The ashes after the cotton stalks are burnt are collected in a dissolver, and water is added to make ash juice with a concentration of 15%. 4. Pour the prepared ash juice into the cooking pot. The weight ratio of ash juice and cotton lint is 1:20. The heating and scouring temperature is 95°C-100°C for 1 hour. The cooking liquid is discharged into the dyeing vat, and the cloth, Dyed yarn ready to use. 5. Take out the boiled cotton skin and put it into a warm water pool to wash, decontaminate and dehydrate. 6. Repeat 1, 4, and 5 two to three times on the dehydrated cotton lint, and the original brown cotton lint fiber can be obtained (if bleaching is required, add ash juice and hydrogen peroxide to the pot and...
Embodiment 2
[0021] As shown in Figure 1: 1, the cotton stalk gets the leather tie and puts into the pot (also can dye the cotton yarn wrapped in the same bath) and compact it. 2. Peeled cotton straw replaces coal (saving national resources) for boiler use, heating and gas supply. 3. The ashes after the cotton stalks are burnt are collected in a dissolver, and water is added to make ash juice with a concentration of 15%. 4. Pour the prepared ash juice into the cooking pot, the weight ratio of ash juice and cotton lint is 1:23, heat and cook at a temperature of 95°C-100°C for 2 hours, drain the cooking liquid into the dyeing vat, dye the cloth, Dyed yarn ready to use. 5. Take out the boiled cotton skin and put it into a warm water pool to wash, decontaminate and dehydrate. 6. Repeat 1, 4, and 5 two to three times on the dehydrated cotton lint, and the original brown cotton lint fiber can be obtained (if bleaching is required, add ash juice and hydrogen peroxide to the pot and boil for 2 h...
Embodiment 3
[0023] As shown in Figure 1: 1, the cotton stalk gets the leather tie and puts into the pot (also can dye the cotton yarn wrapped in the same bath) and compact it. 2. Peeled cotton straw replaces coal (saving national resources) for boiler use, heating and gas supply. 3. The ashes after the cotton stalks are burnt are collected in a dissolver, and water is added to make ash juice with a concentration of 15%. 4. Pour the prepared ash juice into the cooking pot. The weight ratio of the ash juice and the cotton skin is 1:25. The heating and scouring temperature is 95°C-100°C for 3 hours. The cooking liquid is discharged into the dyeing vat, and the cloth, Dyed yarn ready to use. 5. Take out the boiled cotton skin and put it into a warm water pool to wash, decontaminate and dehydrate. 6. Repeat 1, 4, and 5 two to three times on the dehydrated cotton lint, and the original brown cotton lint fiber can be obtained (if bleaching is required, add ash juice and hydrogen peroxide to th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com