Method of detecting platelet thrombosis or organ injury
A vascular and vascular technology, applied in the field of disseminated intravascular coagulation, can solve the problems of self-tissue damage, low specificity, tissue damage, etc., and achieve the effects of rapid detection, high specificity detection, and high clinical value.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] "Example 1: Decomposition of recombinant vWF decomposing enzyme antigen by elastase"
[0056] Dissolve 1.5 μg of recombinant vWF decomposing enzyme in tris buffer / physiological saline, add elastase until the final concentration is 20nmol / L or 140nmol / L, incubate at 37°C for 15 minutes or 1 hour, and decompose 0.5μg of vWF respectively enzyme. This was separated by non-reducing SDS electrophoresis (5 to 20% gel), and then transferred to a PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) membrane by the Western blot method. After blocking with a commercially available blocking agent (Block Ace, Dainippon Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.) at room temperature for 30 minutes, they were washed with tris buffer. React in 1 μg / mL anti-vWF decomposing enzyme monoclonal antibody (WH2-22-1A: using disintegrin region of vWF decomposing enzyme as antigenic determinant) / tris buffer (pH7.4) / 10% Block Ace, react at room temperature After 1 hour, wash 3 times with tris buffer (pH7.4) / 0.05% NP-40, and then in 2...
Embodiment 2
[0065] "Example 2: Decomposition of plasmin or thrombin recombinant vWF decomposing enzyme antigen"
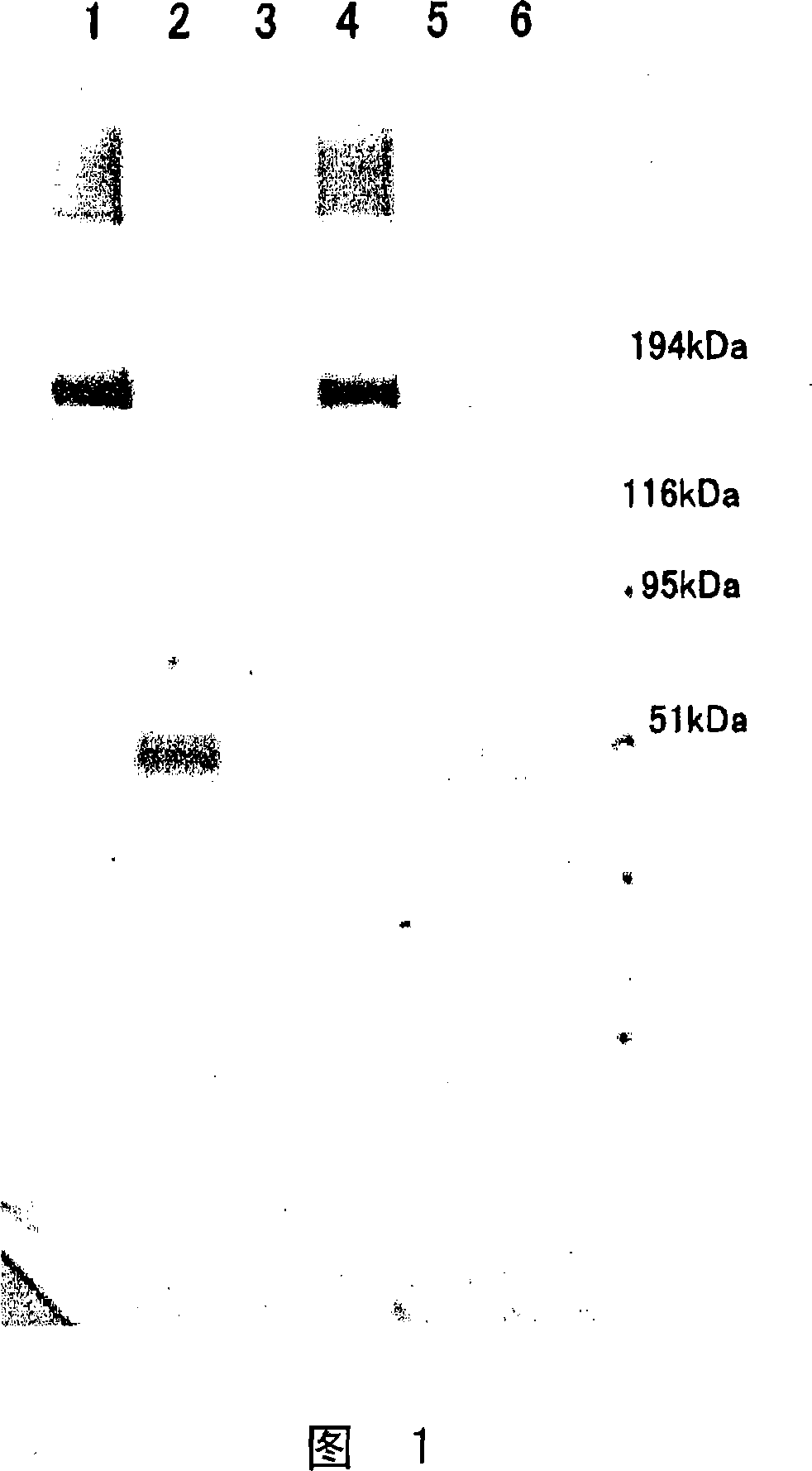
[0066] Dissolve 1.5 μg of recombinant vWF decomposing enzyme in tris buffer / normal saline, add plasminogen (final concentration 1 μmol / L) and tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) (final concentration 0.2nmol / L or 2nmol / L ), or add thrombin until the final concentration is 20mU or 200mU, and after incubating at 37°C for 15 minutes or 1 hour, take the equivalent of 0.5μg of vWF decomposing enzyme respectively. After it was separated by SDS electrophoresis, Western blot was performed in the same manner as in Example 1 to detect the band of vWF decomposing enzyme. The results are shown in Figure 2.
[0067] The corresponding relationship of each lane in Figure 2 is as follows:
[0068] 1: After adding 0.2nmol / L tPA, react at 37°C for 15 minutes
[0069] 2: After adding 2nmol / L tPA, react at 37°C for 15 minutes
[0070] 3: After adding 20mmol / L thrombin, react at 37°C for 15 minu...
Embodiment 3
[0078] "Example 3: Correlation between vWF decomposing enzyme and elastase"
[0079] In this embodiment, the plasma from normal healthy people, DIC patients and SIRS patients was used as samples to be tested, and the amount of vWF decomposing enzyme antigen and elastase were measured. The amount of vWF decomposing enzyme antigen was measured with a commercially available kit (vWF decomposing enzyme ELISA kit, Mitsubishi Chemical Yatron). In addition, the amount of elastase was expressed by measuring the amount of elastase / α1-antitrypsin using a commercially available kit (PMN Elastase / α1-PI Complex ELISA Kit, CALBIOCHEM).
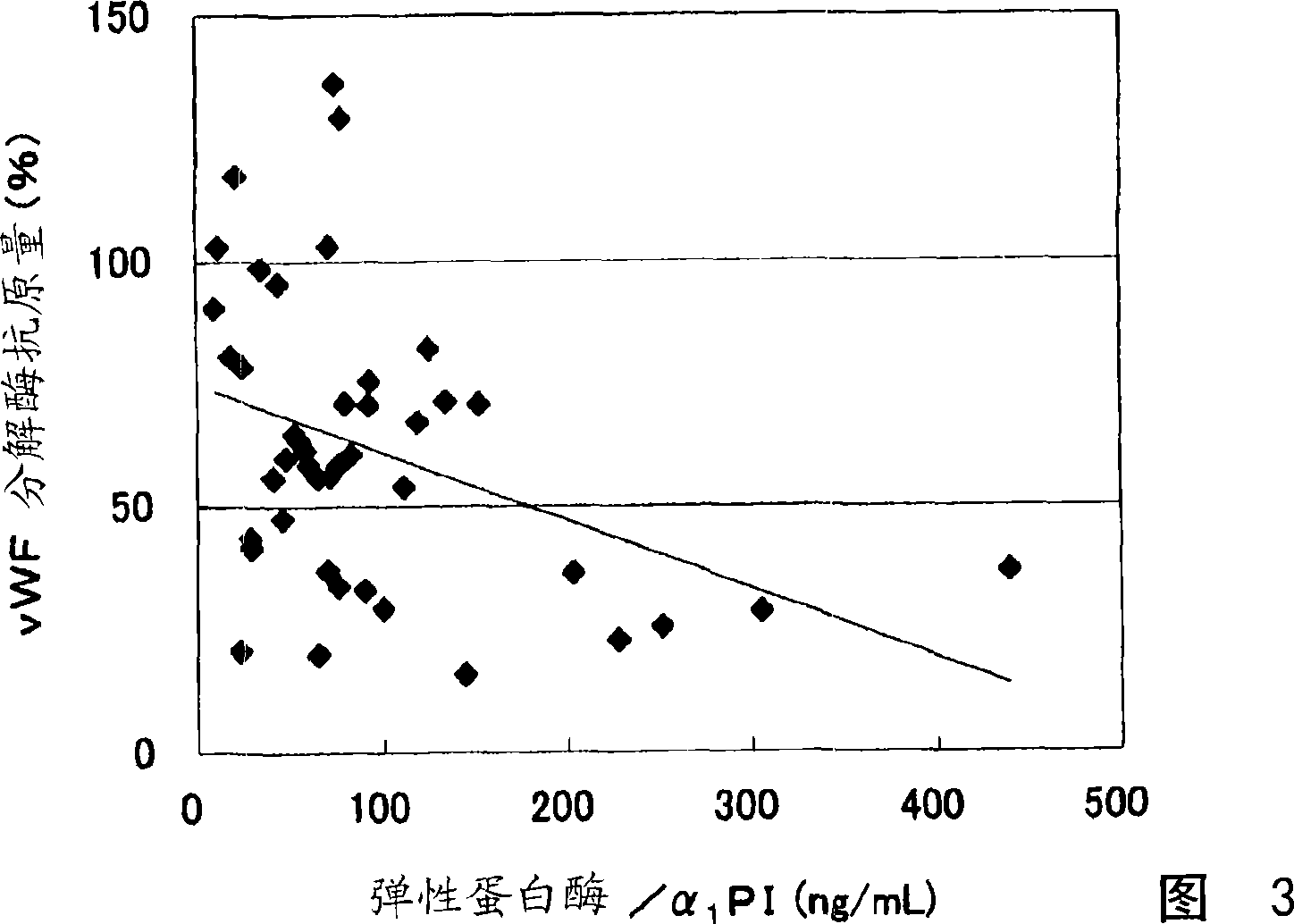
[0080] The results are shown in Figures 3 and 4. In Fig. 3, the X-axis is the amount of elastase / α1-antitrypsin (unit: ng / mL), and the Y-axis is the amount of vWF decomposing enzyme antigen (unit: %). In addition, in Fig. 4, "N.S." indicates no significant difference.
[0081] A good negative correlation was shown between elastase / α1-antitrypsin and vWF ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com