Epitaxial wafer and method of producing same
A technology of epitaxial wafers and manufacturing methods, which is applied in manufacturing tools, chemical instruments and methods, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, etc. It can solve the problems of inability to measure LPD, large surface roughness, and reduce the amount of epitaxial layer polishing, etc., to achieve reduced detection The effect of critical size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
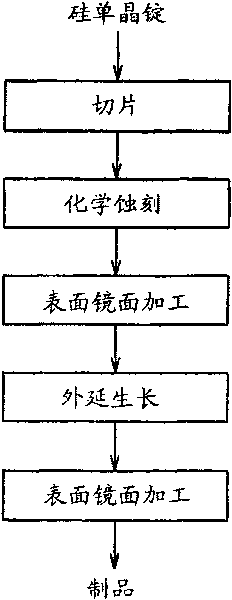
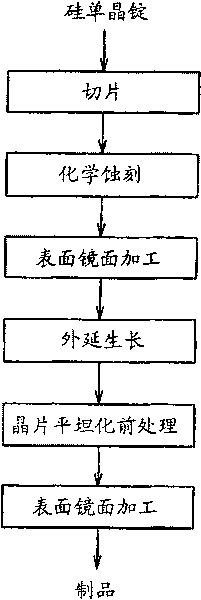
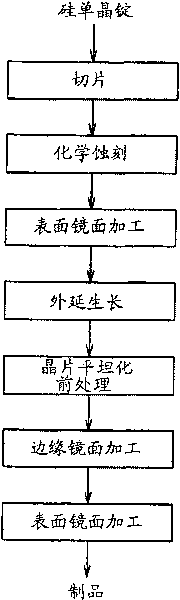
[0050] An embodiment is to slice a silicon single crystal ingot with a diameter of 305 nm to form a (110) wafer with a thickness of 900 μm. After the main surface of the sliced wafer was chemically etched using an alkali solution, the surface and the back surface were subjected to mirror finishing by chemical polishing using colloidal silica. Next, 5% by volume of trichlorosilane (SiHCl 3 ), through decomposed silicon atoms, epitaxial growth of a single crystal silicon layer on a silicon wafer to form a 3 μm thick single crystal silicon layer. Next, a wafer planarization pretreatment process of immersing the wafer in a 5 ppm aqueous ozone solution at a temperature of 10 to 20°C for 1 to 10 minutes was performed to form a film with a thickness of 10 The oxide film was then subjected to surface mirror-finishing of the main surface of the wafer by chemical polishing using colloidal silica in a polishing amount of 0.2 μm, thereby manufacturing an epitaxial wafer.
[0051] For...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| critical dimension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com