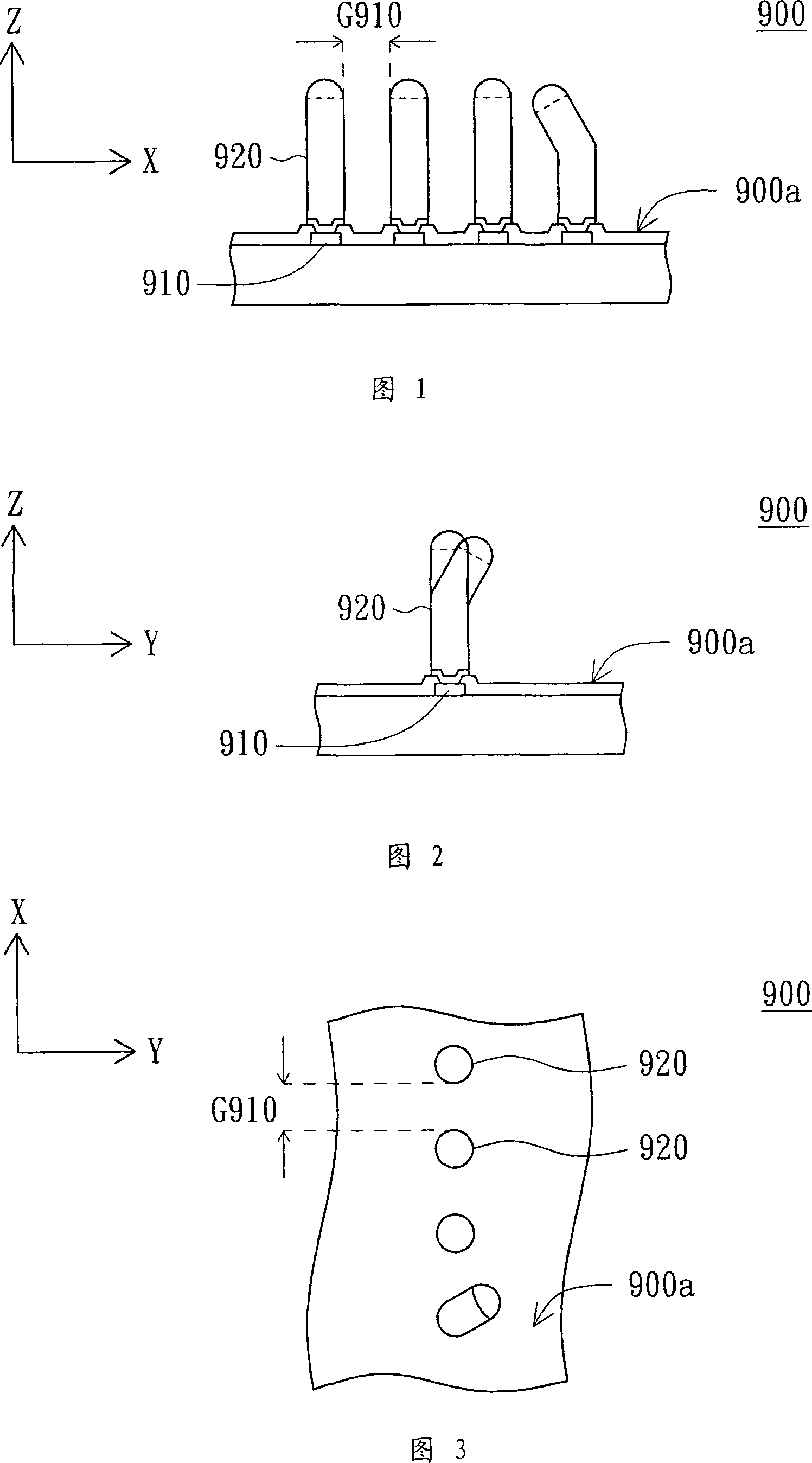
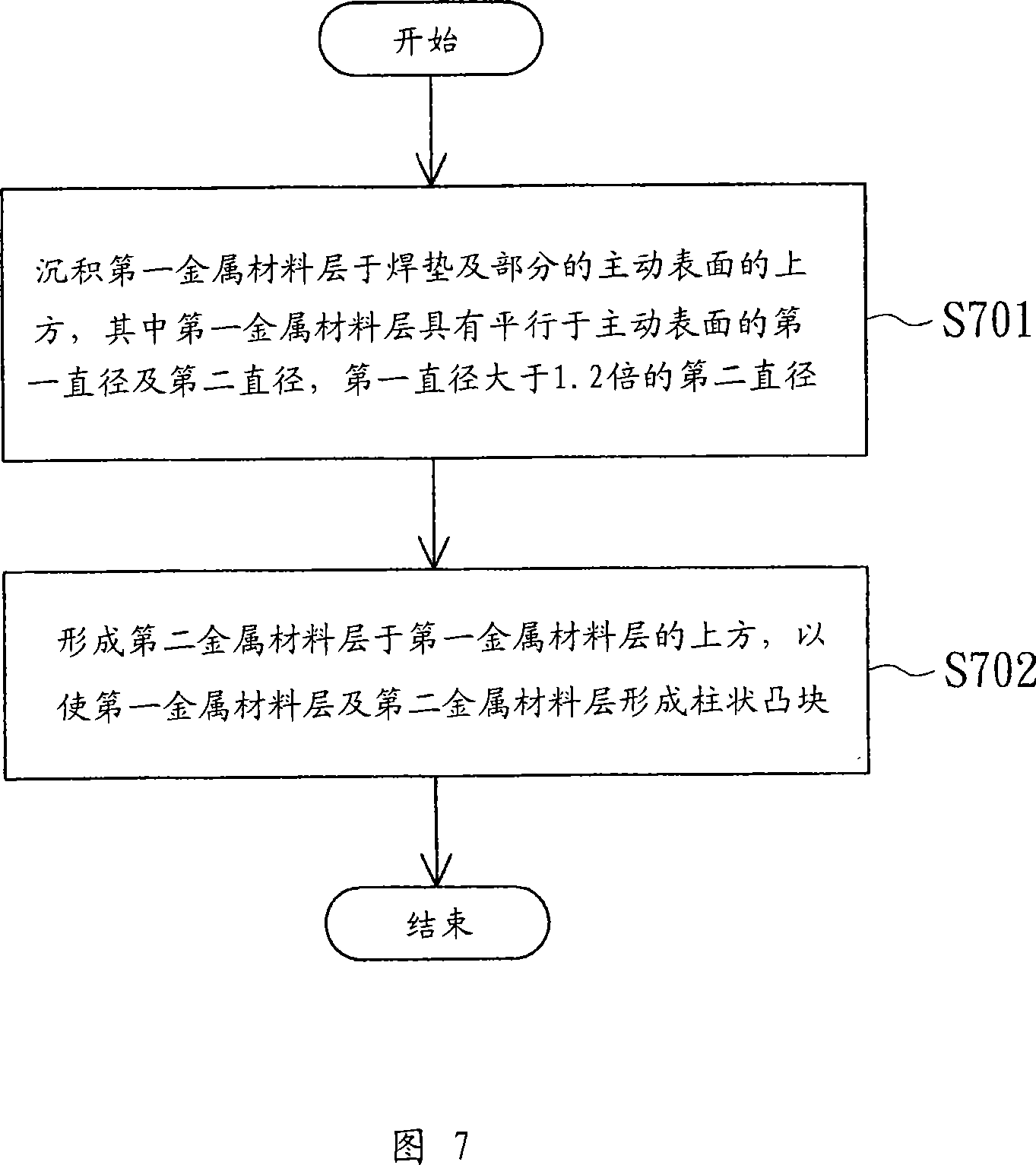
Chip and its making method
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, electrical solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problems of heavy labor costs, bump 920 bending, waste, etc., to improve product yield and increase structure The effect of strength, good structural strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
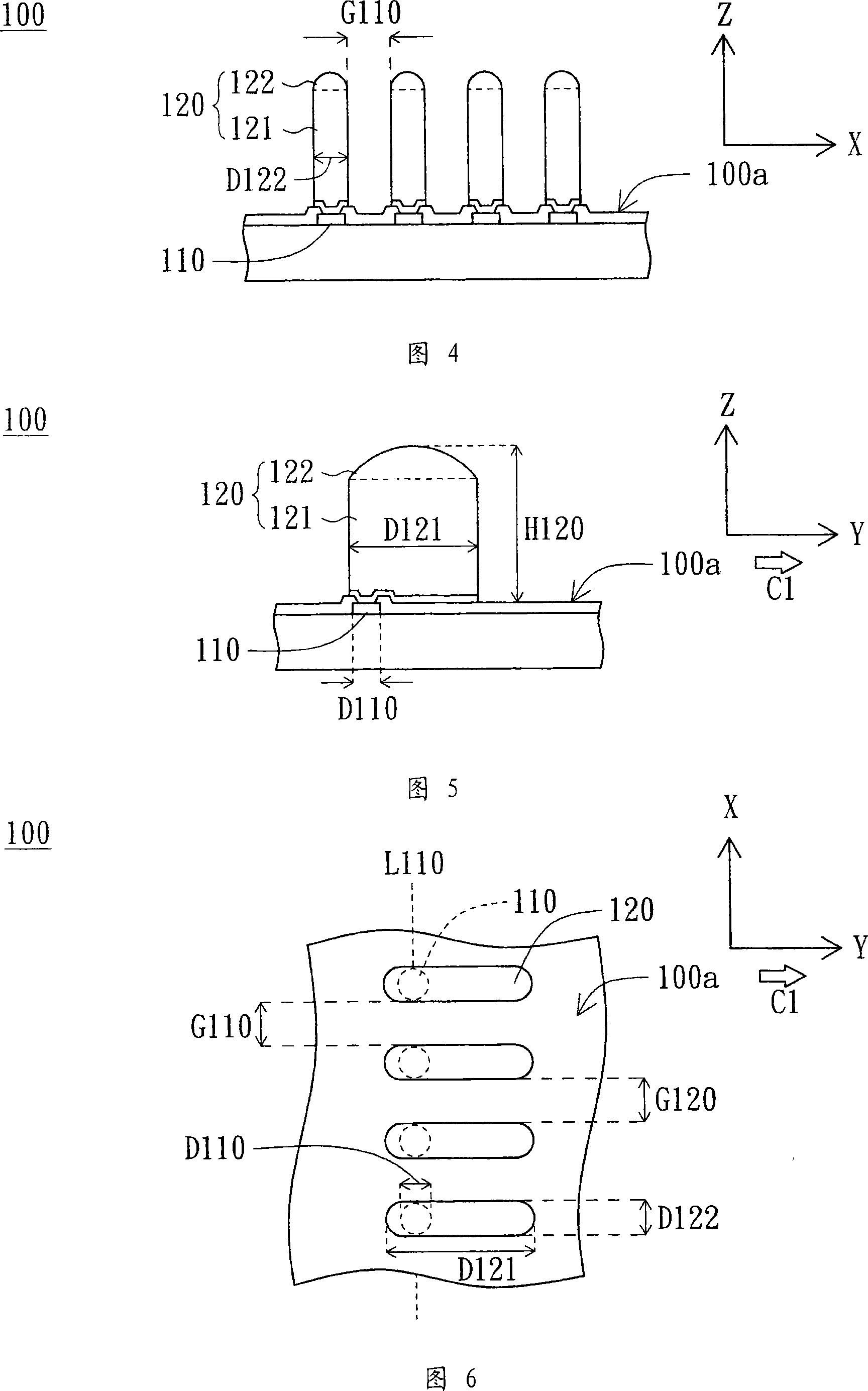
[0039] Please refer to Figures 4 to 6 at the same time. 4-5 are schematic side views of the semiconductor device 100 according to the first embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 6 is a top view of the semiconductor device 100 in FIGS. 4-5. As shown in FIG. 4, the semiconductor element 100 has an active surface 100a. The semiconductor device 100 includes at least one pad 110 and at least one bump 120 . The welding pad 110 is disposed on the active surface 100 a and is a connecting structure for electrically connecting the active surface 100 a and the bump 120 . The bump 120 is vertically disposed on the pad 110 . As shown in Figure 6, the bump has a first diameter (Dimension) D121 and a second diameter D122 parallel to the active surface 100a (the first diameter D121 is shown in Figures 5 and 6, and the second diameter D122 shown in Figures 4 and 6). The first diameter D121 is greater than 1.2 times the second diameter D122. Because in this embodiment, the structur...
no. 2 example
[0064] The difference between the semiconductor device 200 and its manufacturing method in this embodiment and the semiconductor device 100 and its manufacturing method in the first embodiment lies in the disposition of bumps 220 , and the rest of the same parts will not be repeated here. Please refer to FIG. 11 , which shows a configuration diagram of the bumps 220 of the semiconductor device 200 according to the second embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, the semiconductor device 200 includes several bonding pads 110 and several bumps 220 . Each bump 220 corresponds to each pad 110 , and the directions C1 , C2 extending from the pads 110 of the bumps 220 are substantially parallel to each other. The pads 110 are arranged along the straight line L110 , and the bumps 220 alternately extend from the pads 110 toward opposite directions C1 , C2 to form a fan-shaped arrangement.
[0065] Therefore, there is a larger distance G220 between the protrusions 220 ex...
no. 3 example
[0069] The difference between the semiconductor device 300 and its manufacturing method in this embodiment and the semiconductor device 200 and its manufacturing method in the second embodiment lies in the structural design of the bump 320 , and the rest of the same parts will not be repeated here. Please refer to FIG. 12 , which shows a configuration diagram of the bumps 320 of the semiconductor device 300 according to the third embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, the bump 320 of the semiconductor device 300 has a cross section parallel to the active surface 300a, and the cross section is substantially a T-shaped structure.
[0070] As shown in FIG. 12 , the substantially T-shaped bump 320 extends a first distance D31 from the pad 110 toward a first direction C31 , and then extends a second distance D32 toward a second direction C32 and a third direction C33 respectively. The first distance D31 is greater than 1.2 times the width D110 of the pad 110 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com