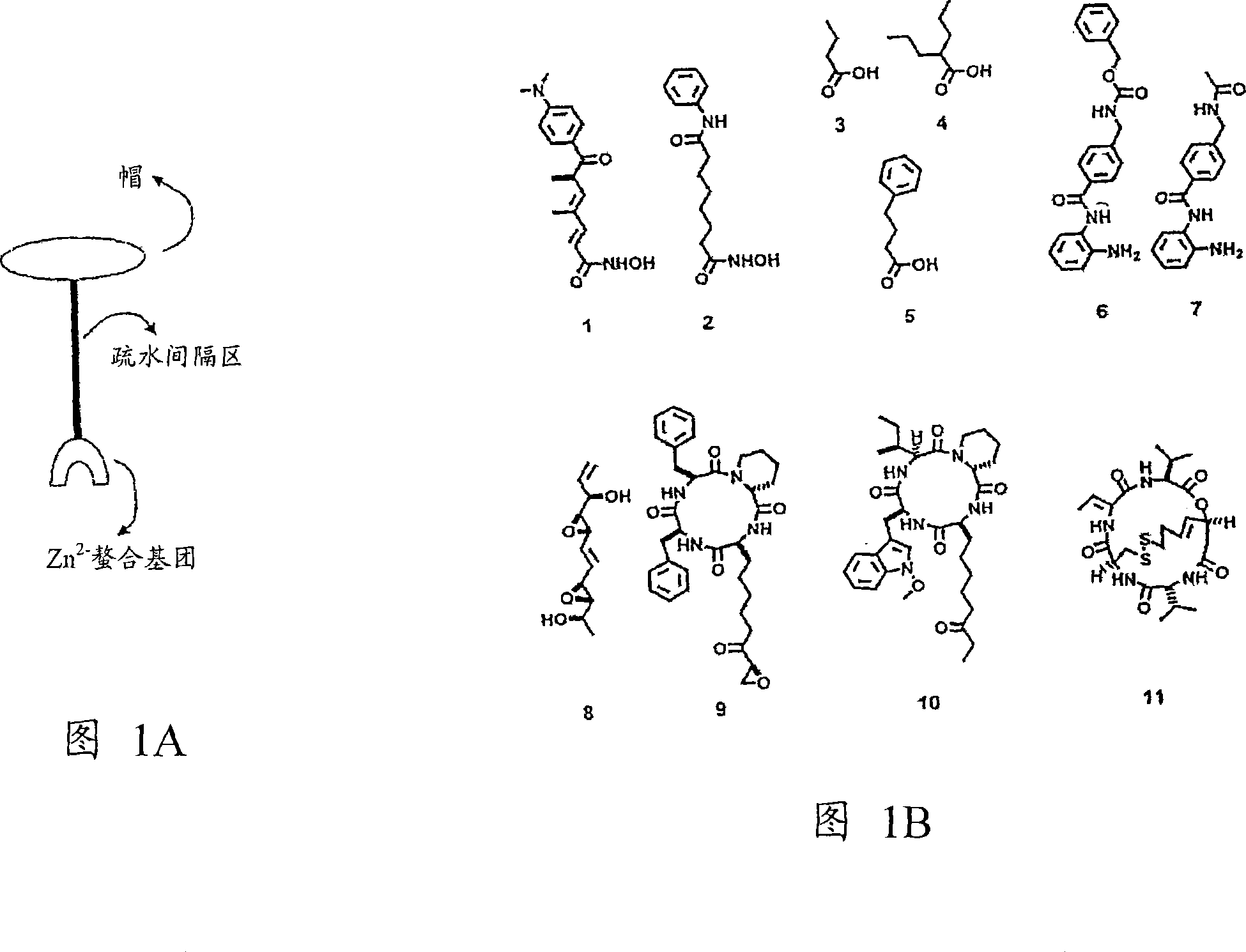
Histone deacetylase inhibitors sensitize cancer cells to epidermal growth factor inhibitors
A technology of epidermal growth factor and deacetylase, which is applied in the fields of histone deacetylase inhibitors and epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors, and can solve problems such as loss of membrane localization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] The following examples describe the expression of E-cad in gefitinib-sensitive and gefitinib-resistant NSCLC cell lines.
[0088] Growth inhibition of 21 NSCLC strains and one uterine cell line by gefitinib was analyzed by MTT assay. Among these 21 NSCLC strains, the IC of six cell lines H3255, H358, H322, Calu3, H1648, HCC78 50 50 ≥10μM. This diverse growth response to gefitinib was used to identify genes that were differentially expressed in this panel of cell lines.
[0089] Using real-time RT-PCR, a positive correlation was detected between E-cad expression and sensitivity to gefitinib (r=0.76, p50 = 0.015 μM) the highest E-cad expression was detected. A positive correlation of E-cad expression was detected in microarrays developed from 20 cell lines (r=0.74, p=0.0002). At the protein level, E-cad expression was evaluated in western blot analysis of 11 NSCLC cell lines. As previously shown, there was no correlation between EGFR expression and sensitivity to gefi...
Embodiment 2
[0092] The following examples describe the expression of E-cad regulatory molecules in NSCLC cell lines.
[0093] The Wnt pathway is known to be involved in the regulation of E-cad expression. in IC 50 50 Molecules in the Wnt / E-cad pathway (Wntl, Wnt5A, Wnt5B, Wnt6, Wnt7A, frizzled, Axin Expression of (axin)1, disheveled, GSK3, α-catenin, β-catenin, γ-catenin and E-cad). E-cad was upregulated the most (200-fold) in sensitive cell lines compared to resistant cell lines. None of the other molecules in the wnt pathway were similarly differentially expressed in sensitive and resistant cell lines.
[0094] E-cad regulation involves four zinc finger transcription factors TF-8, slug, snail and SIP1. Evaluation of cell line microarray data revealed that TF-8 was most differentially expressed (10.4-fold) in sensitive and resistant cell lines compared to the other three molecules slug, snail and SIP1.
[0095] Expression of TF-8 was confirmed by RT-PCR. A negative correlation was ...
Embodiment 3
[0097] The following example describes the effect of E-cadherin on gefitinib-induced apoptosis in NSCLC cell lines.
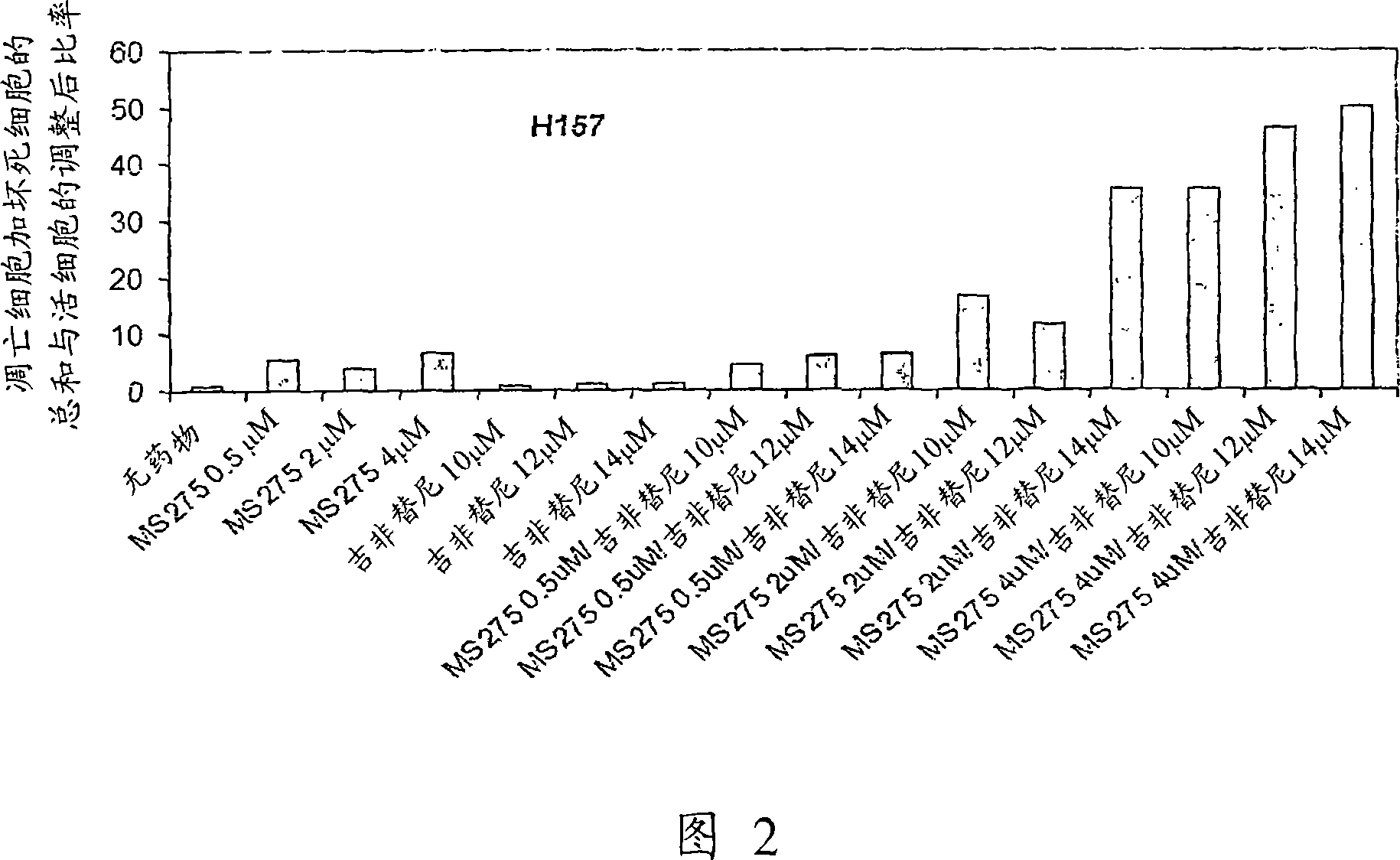
[0098] To evaluate the effect of gefitinib in inducing apoptosis and cell death in gefitinib-sensitive and resistant NSCLC cell lines. When the cell lines were treated with 10 μM gefitinib, a 35-fold increase in apoptosis and cell death was detected in the most sensitive cell line, H325 5. At the same concentration, apoptosis and cell death were increased 2.3-3.4-fold in the less sensitive cell lines (H322, H358 and Calu3), but not in the more tolerant cell lines (H460, H520, H157 and A549) Apoptosis or necrosis was detected.
[0099]The role of E-cad in the apoptotic response of NSCLC cell lines to gefitinib was assessed by transfecting the gefitinib-resistant cell line H157 with adenovirus encoding E-cad. This cell line was chosen due to its lack of E-cad expression, presence of EGFR and resistance to gefitinib. The H157 cell line was transfected with E-ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com