Non-refigeration method for reducing temperature sensitivity of fiber optical gyroscope scale factor
A technology of temperature sensitivity and fiber optic gyro, which is applied in the field of signal processing, can solve the problems of affecting temperature performance, reducing reliability, increasing system complexity, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing temperature sensitivity, reducing heat generation, and improving thermal environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and embodiment the present invention will be further described
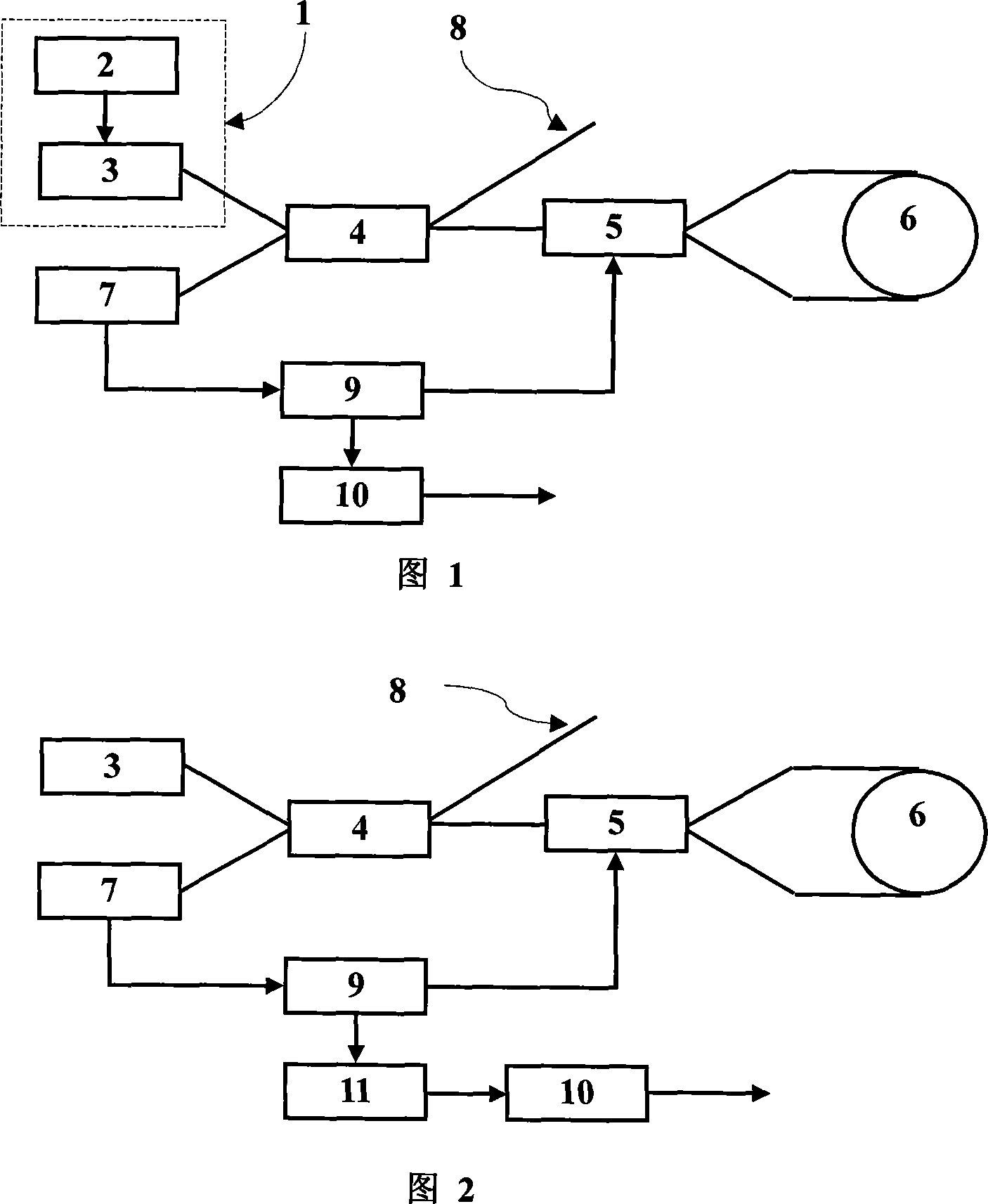
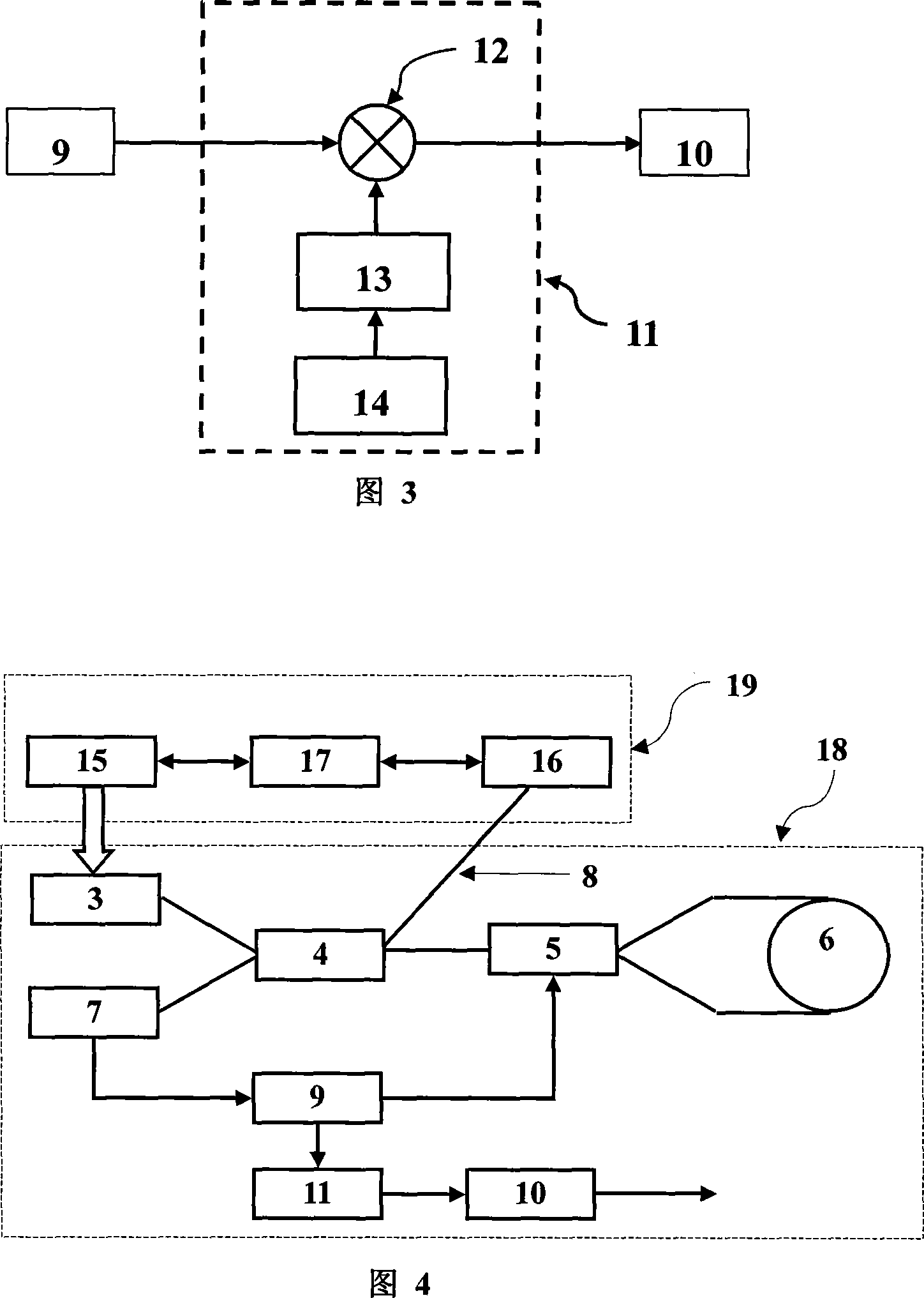
[0034] As shown in Figure 1, it is a schematic block diagram of an optical fiber gyroscope with a cooling circuit light source; wherein 1 is a light source module used by an optical fiber gyroscope, which is composed of a cooling circuit 2 and a light source 3, and the cooling circuit 2 makes the temperature of the light source constant through temperature control, thereby The stability of the average wavelength of the output light is guaranteed; after the light source outputs light, it enters the fiber coupler 4, and the fiber coupler divides the light into two parts, one part is output to the phase modulator 5, the other part is output to the dead end fiber 8, and the other part is output to the dead end fiber 8. The light of the head optical fiber 8 is an unused part of the fiber optic gyro; the phase modulator 5 receives the light of the fiber coupler 5, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com