Node self-locating method based on sampling of wireless sensor network in three-dimensional space
A wireless sensor, three-dimensional space technology, applied in radio/induction link selection arrangement, positioning, radio wave measurement system, etc. Eliminate accumulated errors, avoid the shortest path accumulation mechanism, avoid cumbersome and error effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
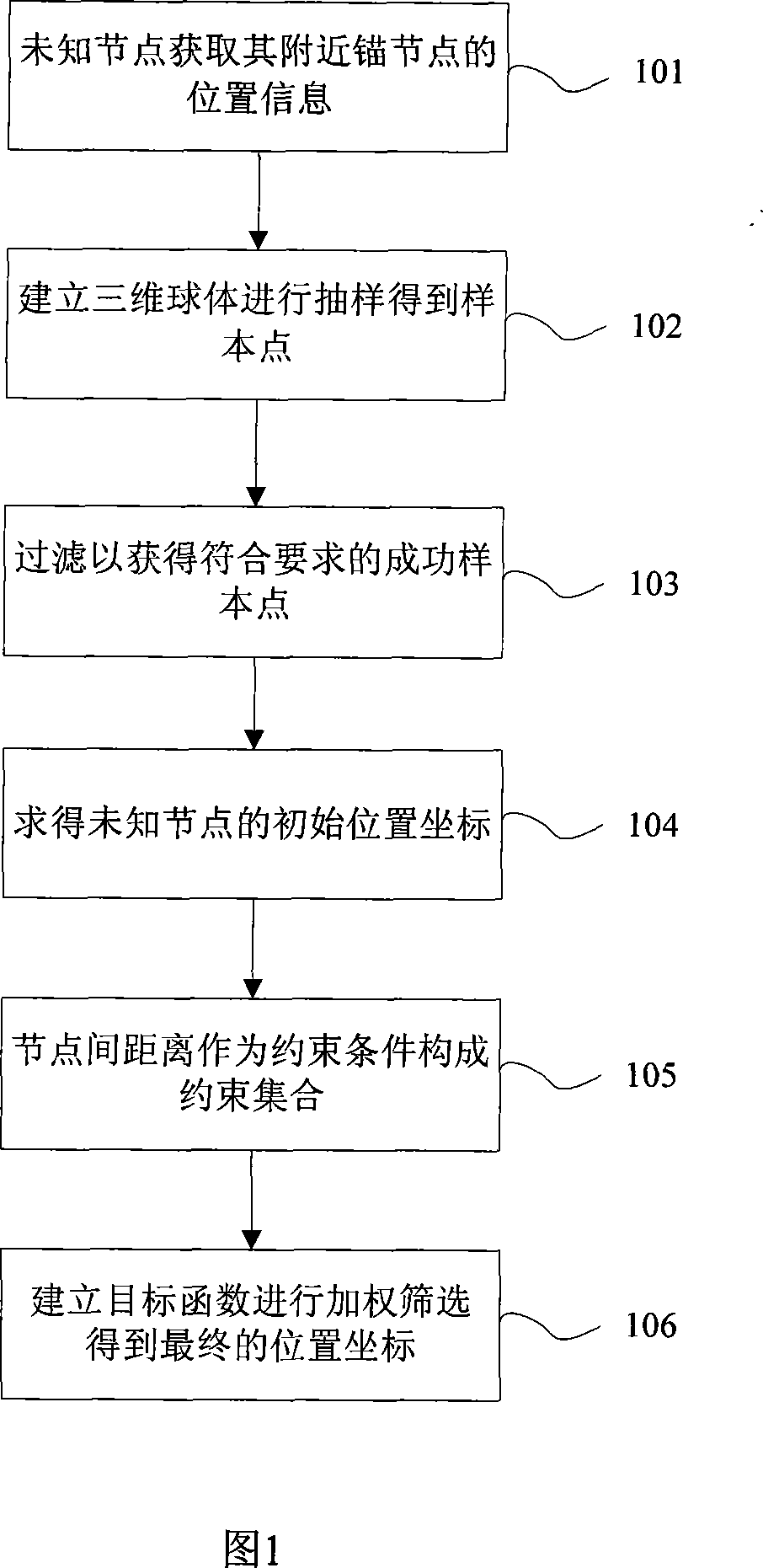
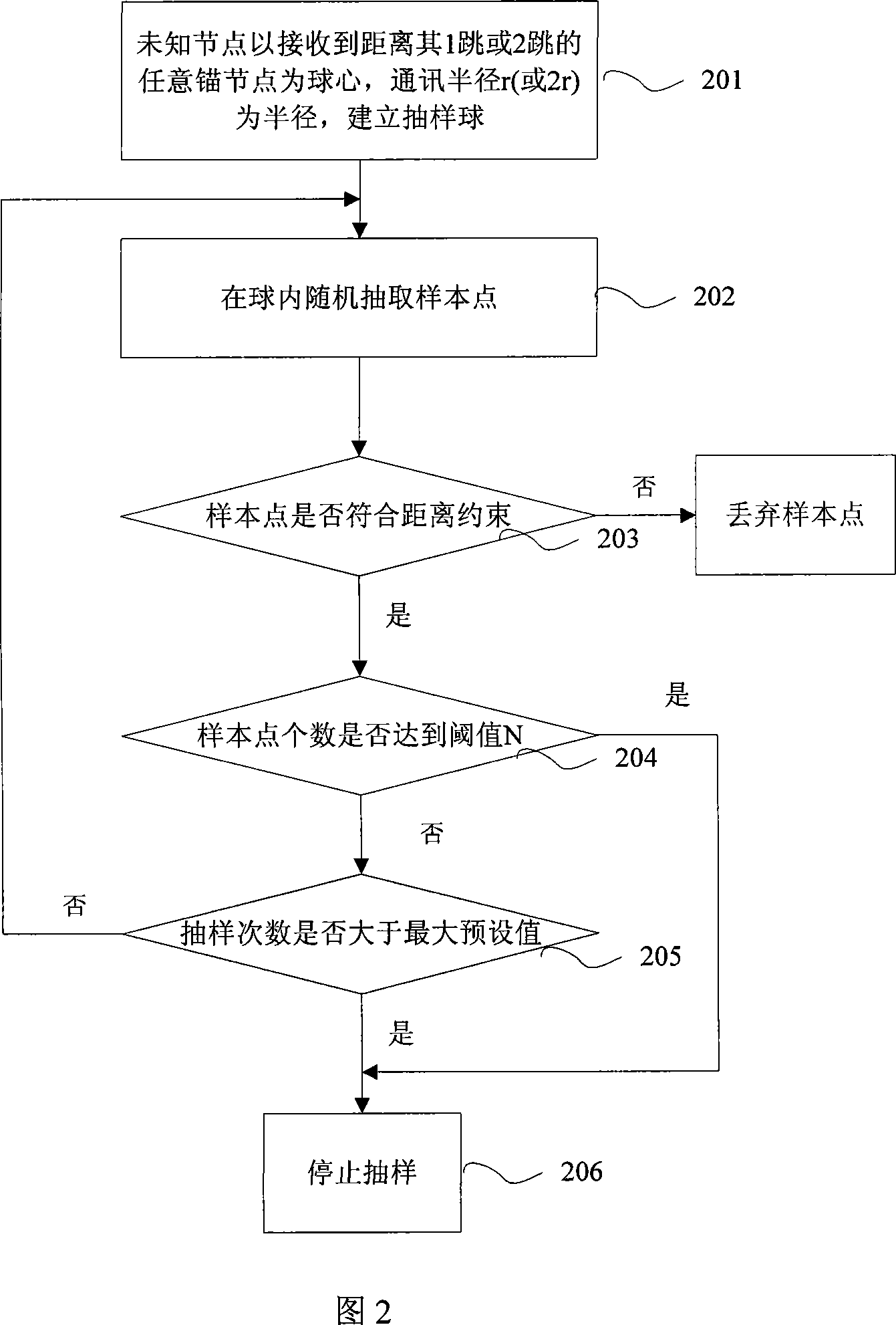
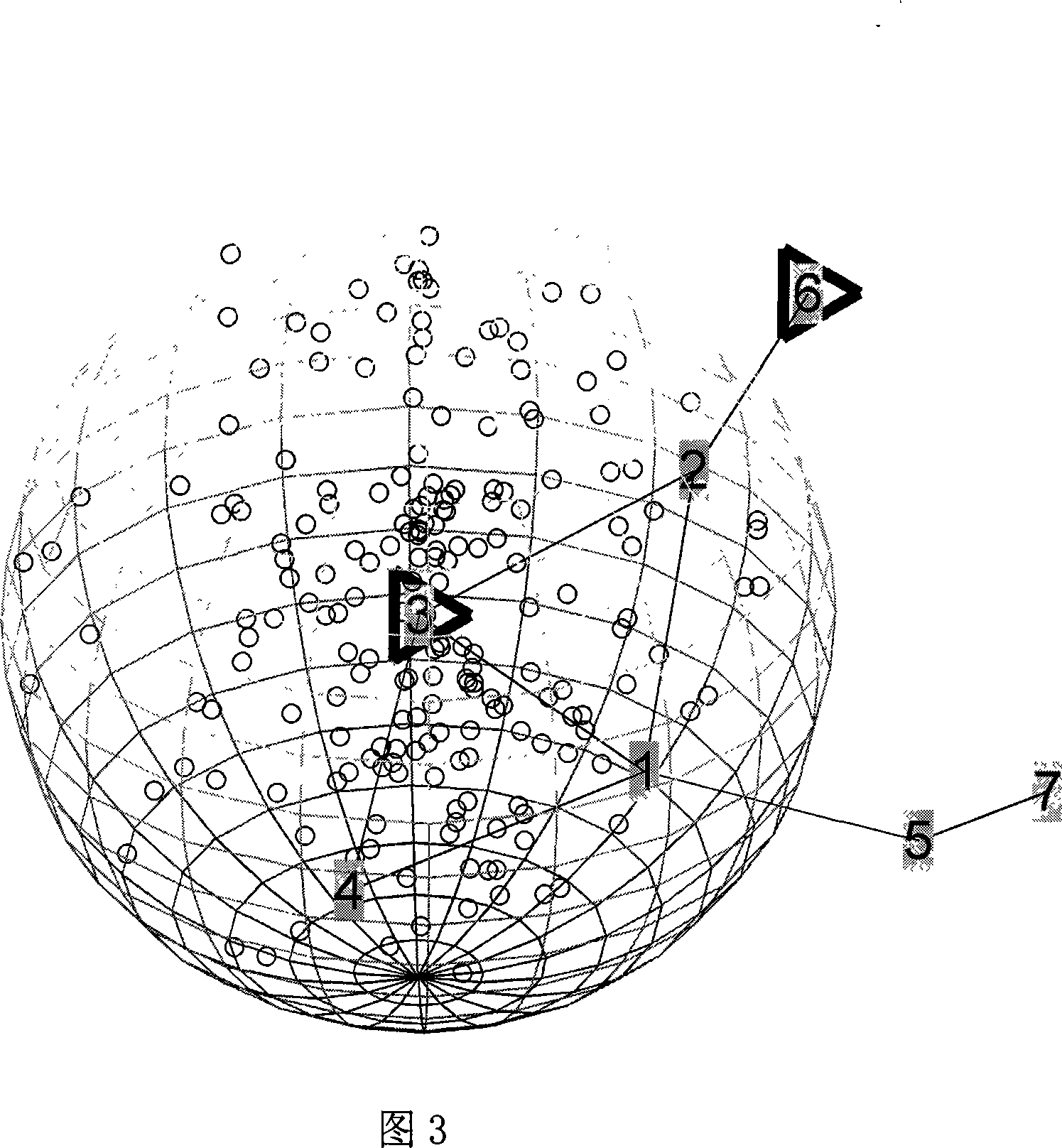
[0043] A wireless sensor network self-positioning method based on sampling in a three-dimensional space of the present invention, please refer to Figures 1, 2, and 3, and its specific steps are as follows:
[0044] 101: The unknown node obtains the location information of its nearby anchor nodes, specifically: each anchor node broadcasts its own location information and a data packet with an initial counter information of 0, and when the unknown node receives a data packet of an anchor node, it judges whether to receive it If the data packet passing the anchor node is true, the data packet is discarded; otherwise, the location information of the anchor node is saved, and the counter in the data packet is increased by 1 to determine whether the value of the counter is greater than 1, and if it is, the data packet is not forwarded. Save the number of hops away from this anchor node; otherwise, forward the data packet and save the number of hops away from this anchor node.
[004...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com