Method for the rapid pyrolysis of lignocellulose
A lignocellulose and pyrolysis technology, applied in the field of rapid pyrolysis of lignocellulose, can solve the problems of limited thermal conductivity, high technical cost, incomplete CO combustion, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
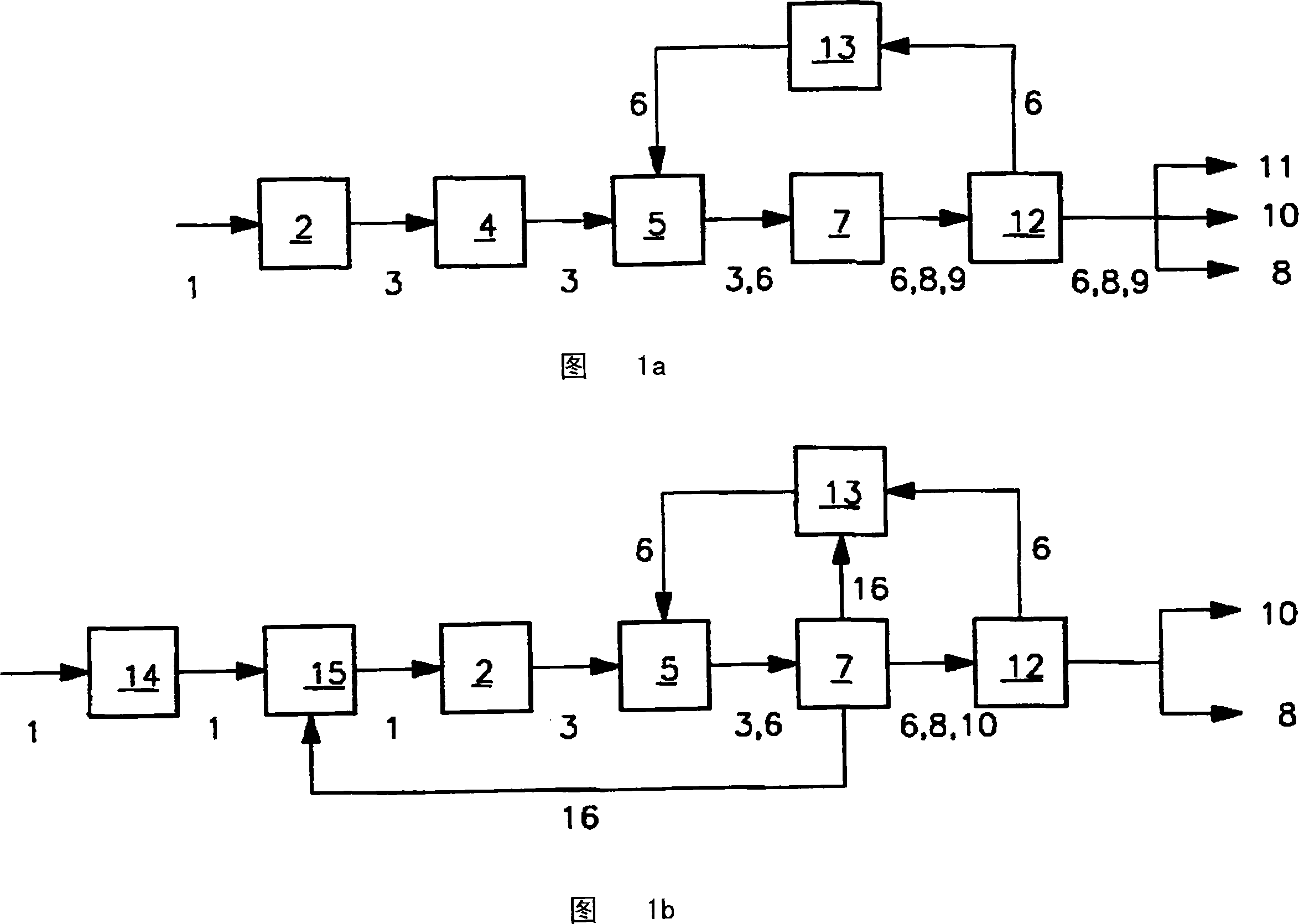
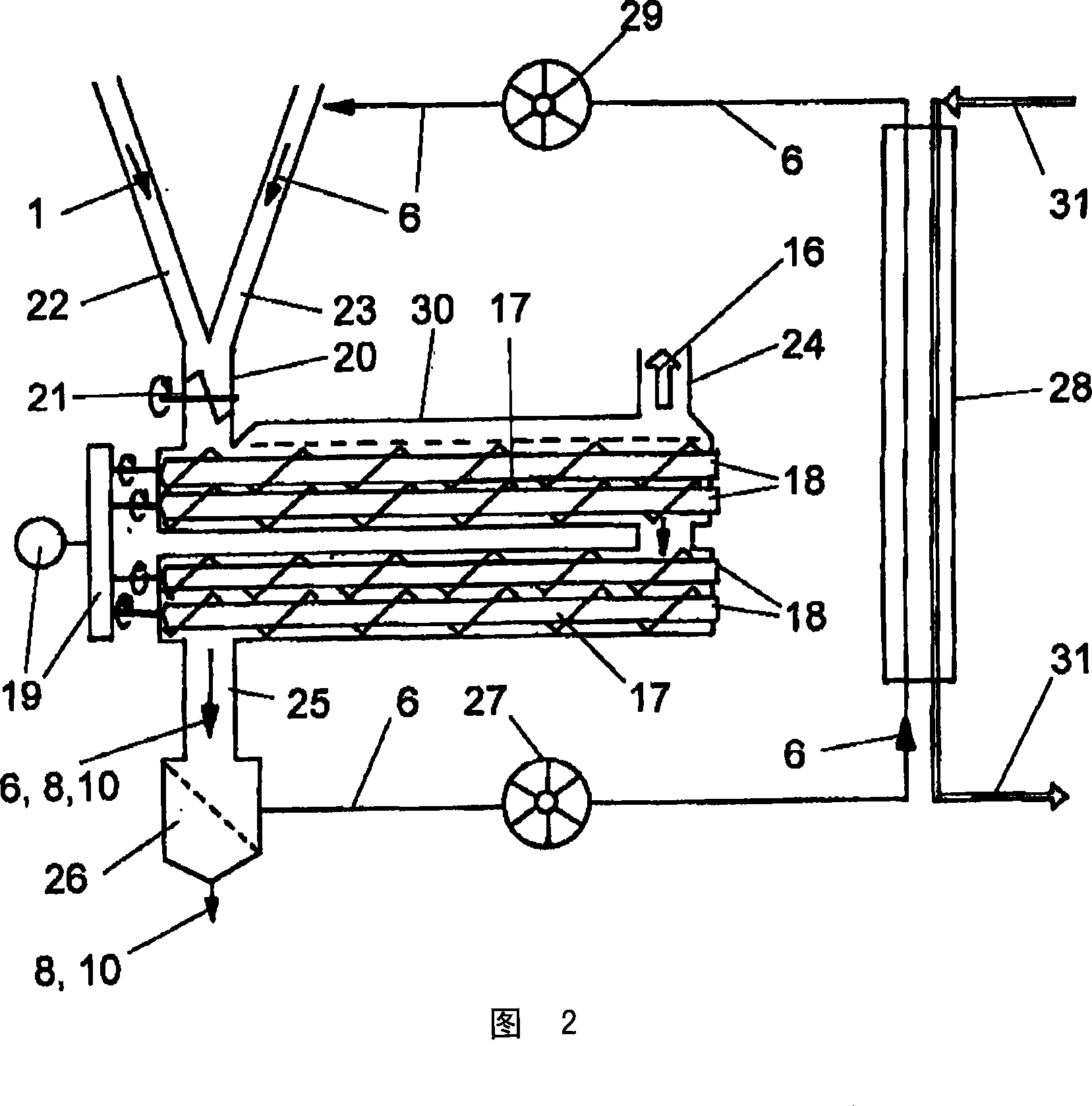
[0039] As shown in FIG. 1 a , in a first step lignocellulose 1 is introduced as a stream into a mechanical comminution process 2 and subsequently into a drying process 4 in the form of lignocellulose particles 3 . It is preferable to preheat to 170 to 200° C. for drying, and then introduce the lignocellulose particles into the mixing process 5 mixed with the heat-conducting particles 6 , so as to perform the rapid pyrolysis process 7 together. In the fast pyrolysis range, the material is preferably conveyed by means of one or more conveying screws.
[0040] In the range of mixing and fast pyrolysis, the preferably preheated lignocellulosic particles are heated very quickly as described above. This process is achieved by transferring heat to the lignocellulosic particles from heat-conducting particles 6 heated to more than 350° C., preferably to about 500 to 650° C., preferably from a preheating temperature between 170 and 200° C. The lower onset temperature of the thermal pyr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com