Nucleic acids encoding modified cytochrome P450 enzymes and methods of use thereof
A cytochrome and nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of genetically modified host cells encoding nucleic acids, can solve problems such as high cost, limited availability of natural sources of natural products, and low yield of natural products.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
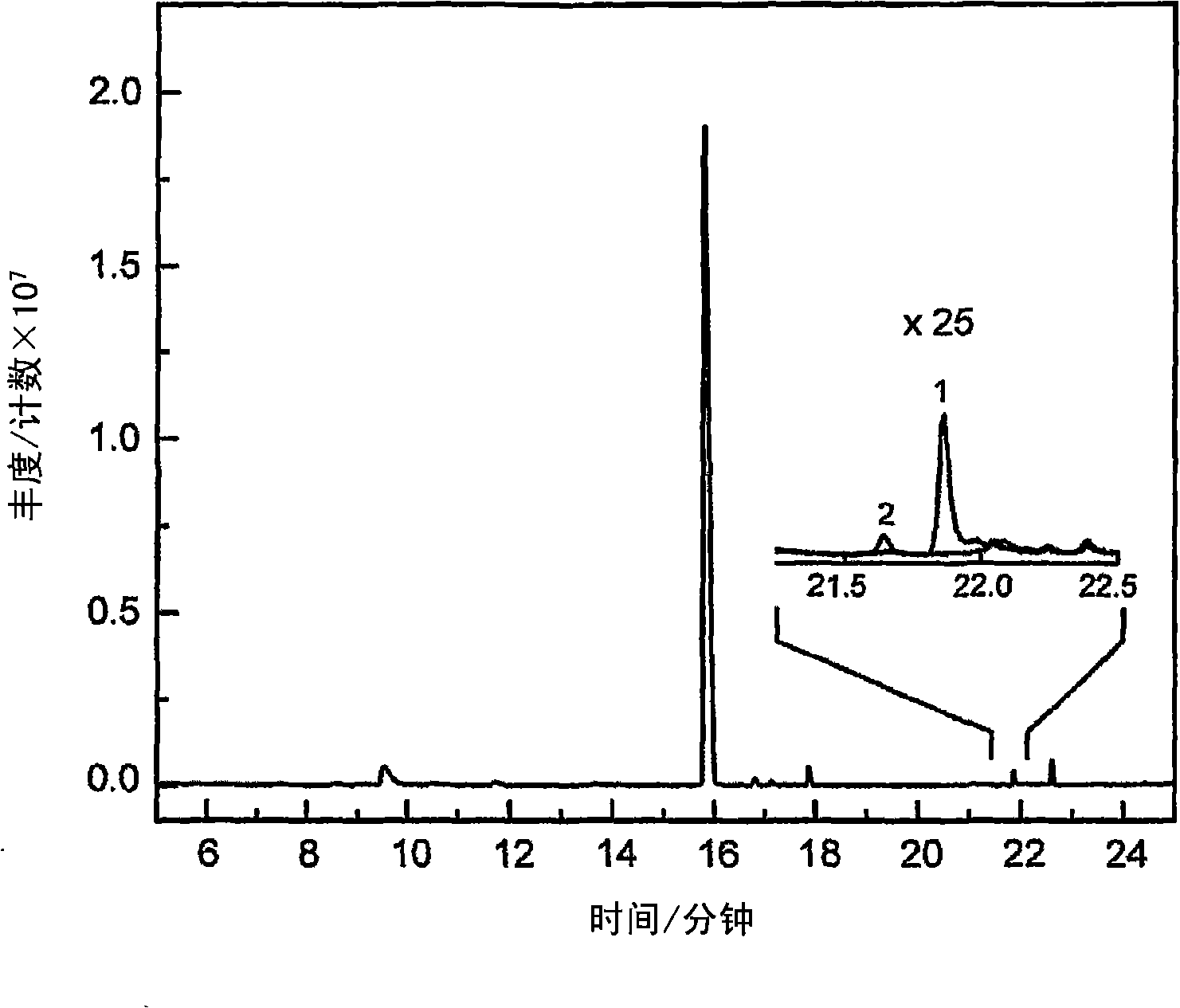
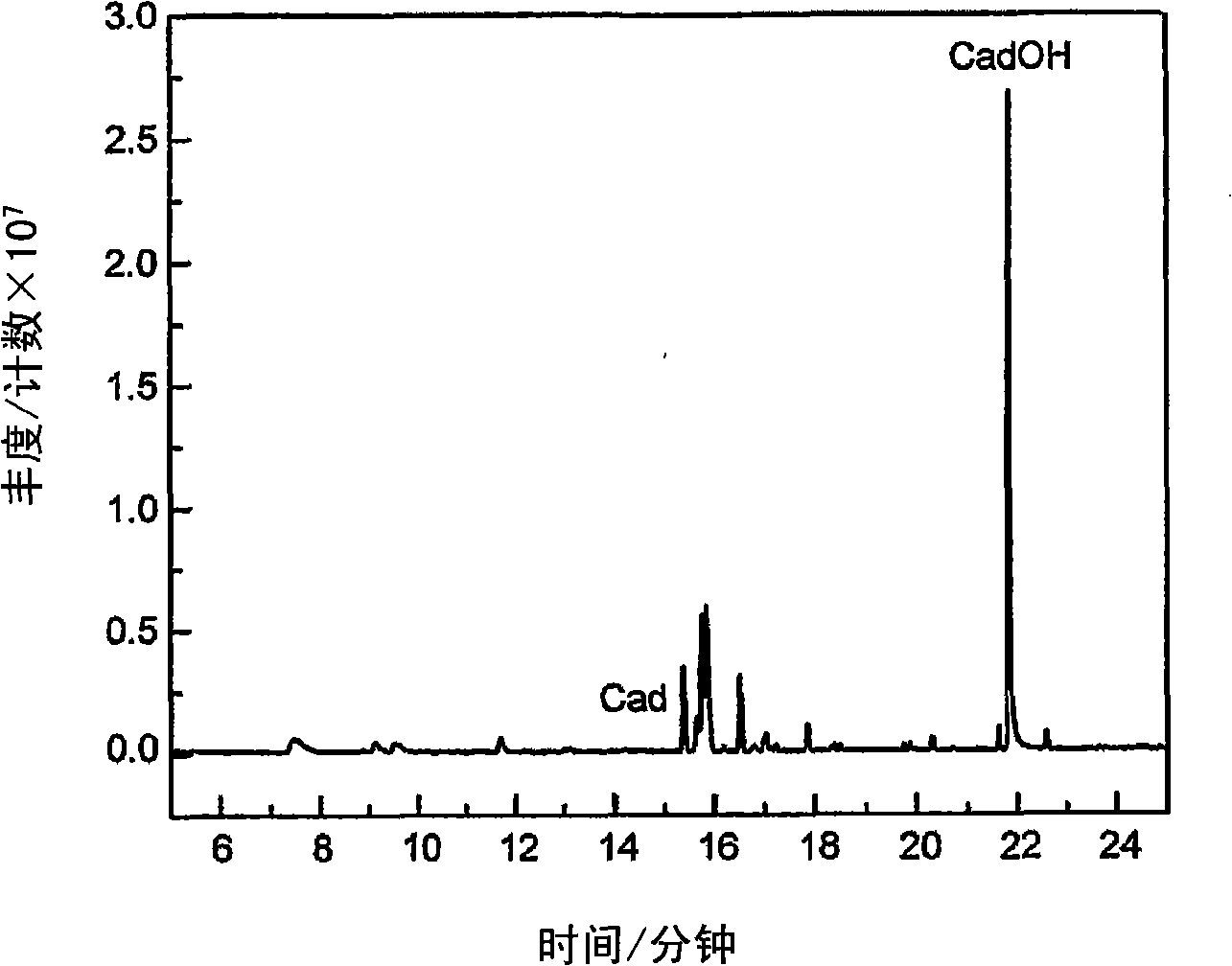
[0268] Example 1 : Production of 8-Hydroxy-delta-cadinene in Escherichia coli
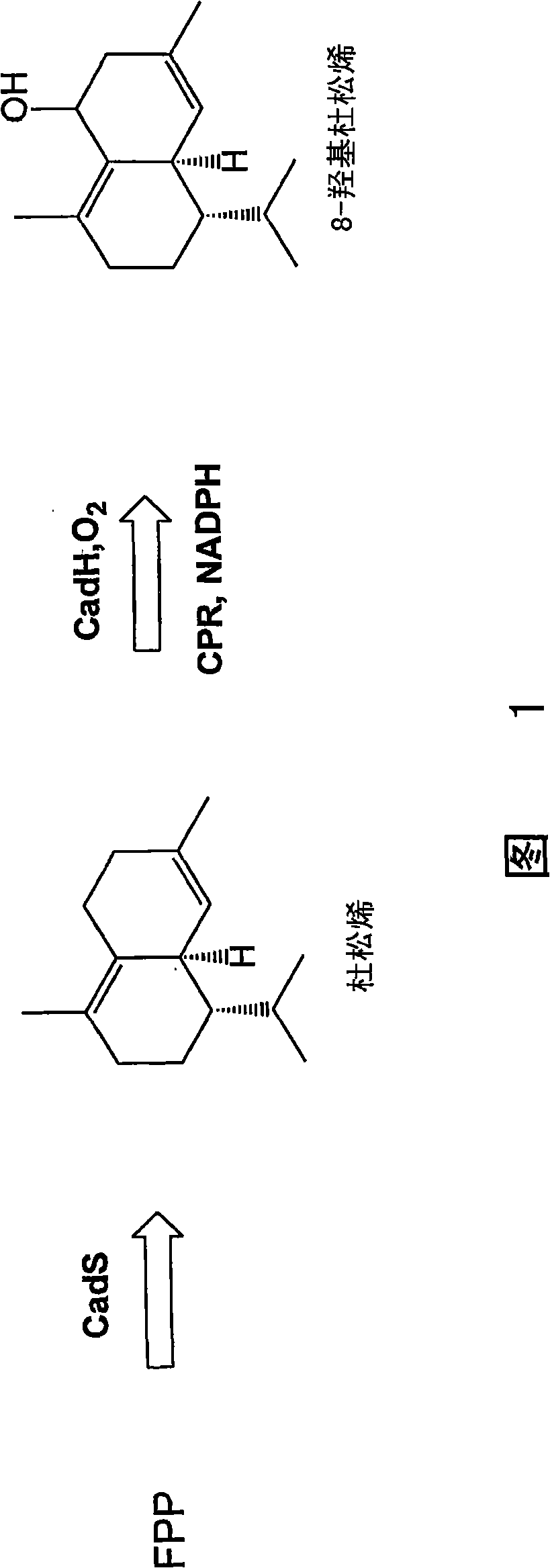
[0269] This example describes the use of natural high levels of P450 (up to 30 mg L) involved in biosynthetic pathways -1 ) to produce substrates produced in vivo. Delta-cadinene-8-hydroxylase (CadH) is a plant-derived membrane-bound P450 that hydroxylates the sesquiterpene delta-cadinene (cad) in the biosynthesis of the plant defense compound gossypol to 8-hydroxyl - delta-junpinene (CadOH). Figure 1 schematically depicts the biosynthesis of CadOH in E. coli. The terpene synthase CadS in E. coli produces a substrate (Cad) from endogenous farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP). Cad is further hydroxylated to the product (CadOH) through the action of CadH and its redox partner (CPR).
[0270] The CadH expression vector includes the CadH gene and the gene encoding the cytochrome P450 reductase (CPR) redox partner of C. tropicalis. This construct was co-transformed into E. coli with a compatible expressi...
Embodiment 2
[0289] Example 2 : Oxidation of amorphadiene by amorphadiene oxidase (AMO)
[0290] This example describes the in vivo (eg, in living cells in in vitro culture) oxidation of amorphadiene by amorphadiene oxidase (AMO), also known as CYP71AV1, isolated from Artemisia annua. Various constructs containing the nucleotide sequence encoding the AMO were generated and tested to optimize the yield of the oxidation product. Figure 22 Various AMO constructs are schematically depicted. (1) nAMO, isolated from the natural AMO sequence of Artemisia annua. (2) sAMO, based on a codon-optimized synthetic AMO gene expressed in Escherichia coli. (3) A13-AMO, a synthetic AMO gene in which the wild-type transmembrane domain is replaced by the A13 N-terminal sequence of Candida tropicalis. (4) A17-AMO, a synthetic AMO gene in which the wild-type transmembrane domain is replaced by the A17 N-terminal sequence of Candida tropicalis. (5) Bov-AMO, a synthetic AMO gene in which the wild-type tran...
Embodiment 3
[0293] Example 3 : Substrate Oxidation in Cells Expressing the Complete Mevalonate Pathway
[0294] Substrate oxidation was also performed in cells expressing the complete mevalonate pathway starting with acetyl-CoA. The following example of CadOH generation utilizes 3 plasmids: (1) pMevT containing AtoB, HMGR and HMGS, (2) pMBIS (contains DNA encoding MK, PMK, PMD, IDI (IPP isomerase) and IspA (FPP synthase) nucleotide sequence) and (3) expression vectors containing CadH, CPR and CadS. Cells were cultured at 20°C in TB glycerol supplemented with heme supplement, delta-aminolevulinic acid. The CadOH titer produced by the cells was as high as 60mg / L. data see Figure 32 .
[0295] In the second example, the following 2 plasmids were used to produce artemisinic acid: (1) containing the encoding MevT (AtoB, HMGR and HMGS) (see Figure 35A and B), expression vectors of the nucleotide sequences of the MBIS (MK, PMK, PMD, IDI, and IspA) and ADS operons, and (2) nucleosides en...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com