Hose clamping device
A hose and clamping mechanism technology, applied in the field of hose clamps, can solve the problems of poor sealing safety performance, insufficient clamping force of high-pressure pipes, inconvenient loading and unloading, etc., achieving considerable economic benefits, saving manpower, material and financial resources, Easy installation and disassembly
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
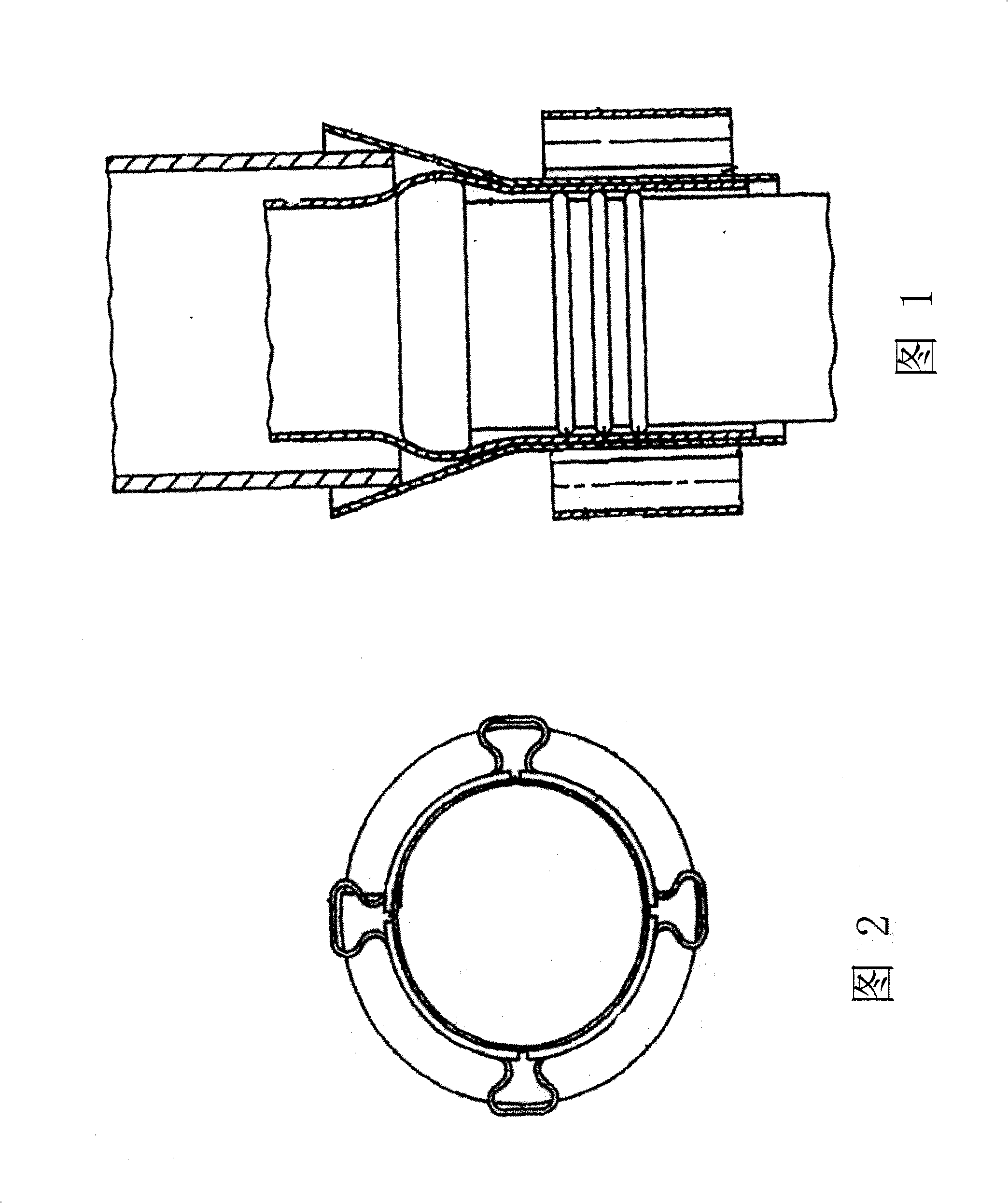
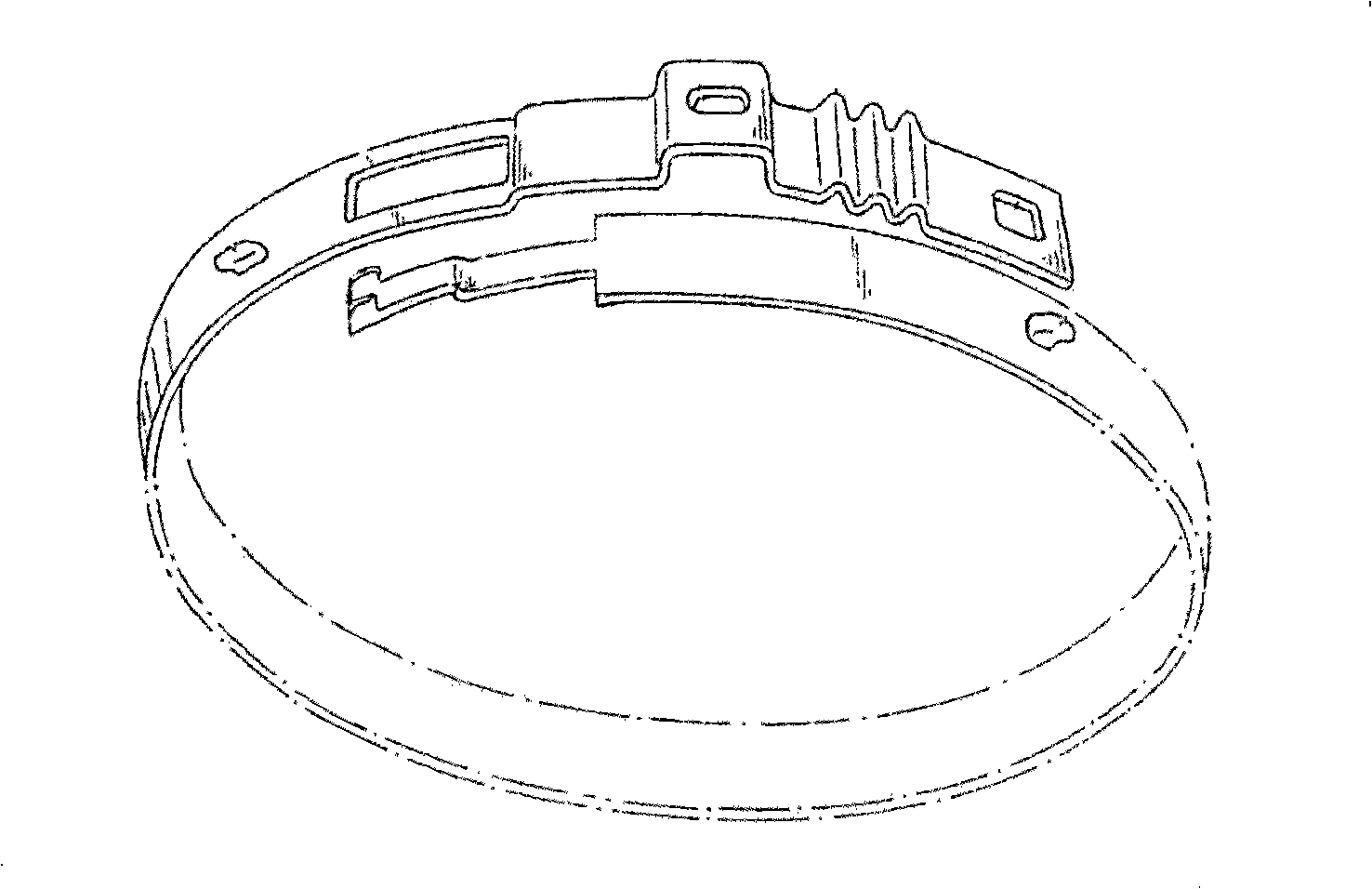
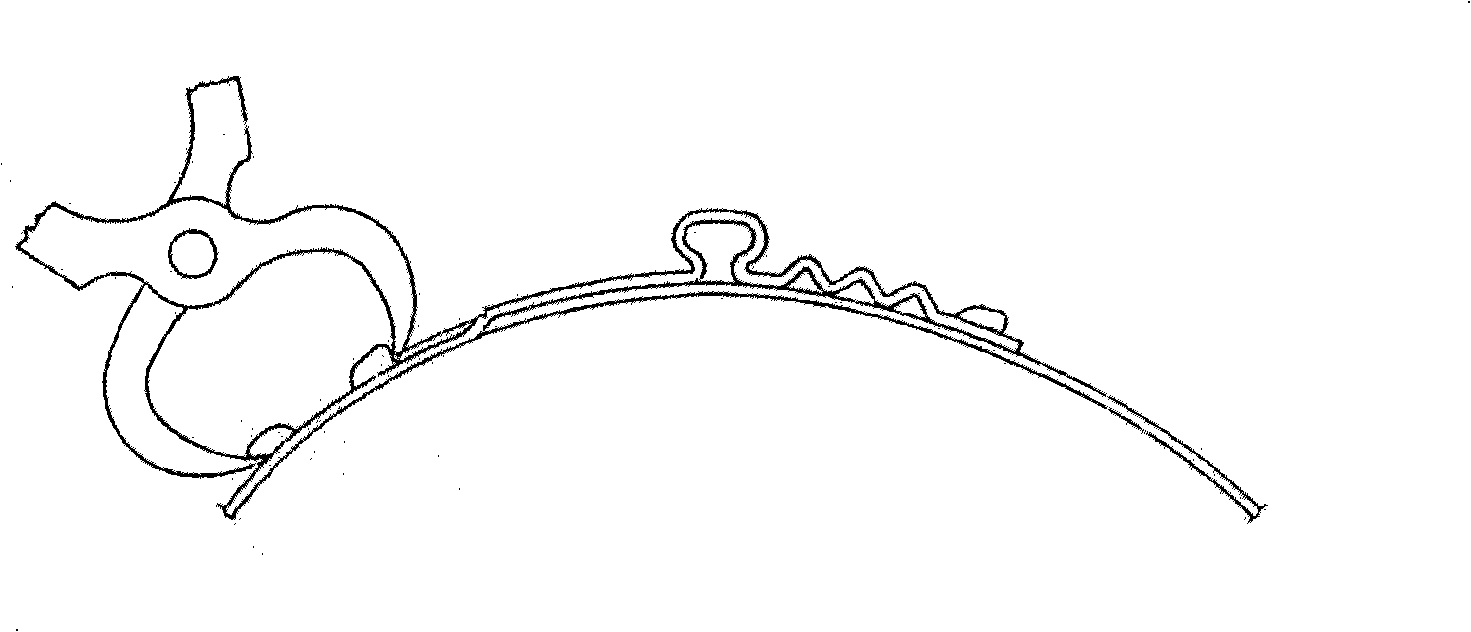
[0048] A hose clamping mechanism, as shown in Figure 5, includes a hose joint 4 coaxial with the hose 3, an inner cone nut 1 and a pipe bolt 2, the outer diameter of the hose joint 4 is the same as that of the hose 3 The apertures of the inner holes match, and the inner cone nut 1, as shown in Figure 6, has a large aperture end as a screw-in end, and the corresponding small aperture end is the end of the inner cone nut 1; the inner cone nut 1 The thread is a tapered thread, and the small diameter A of the thread at the end of the inner cone nut 1 is slightly larger than the outer diameter of the hose; the pipe bolts 2, as shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8, have threaded ends evenly distributed 2 along the circumferential direction of the pipe wall More than one strip mouth parallel to the central axis, the inner diameter C of the central hole is slightly larger than the outer diameter of the hose. When using this hose clamping device to clamp the hose, first insert the hose joint...
Embodiment 2
[0056] As shown in Figure 9, it is another embodiment of the hose clamping device. The difference from Example 1 is that in order to improve the reliability of the connection or to be used in occasions with high working pressure, the end of the hose joint 4 has a set of anti-falling protruding edges 8, and the outer diameter of the anti-falling protruding edges 8 Close to or slightly larger than the inner diameter of the hose 3; along the direction from the end of the hose joint 4 to the end of the joint, the outer diameter of the anti-falling protrusion 8 increases sequentially; there is no anti-falling protrusion on the hose joint 4 The pipe section along the edge has a round boss 7 formed by a smooth increase in outer diameter near the inside of the head. The outer diameter end of the round boss 7 is closely fitted with the hose, and the round boss 7 is the hose. The connection between the pipe section of the joint and the pipe head. The pipe section without anti-falling o...
Embodiment 3
[0058] As shown in Figure 10, it is also an embodiment of the present invention. The difference from Embodiment 2 is that there are flanges 9 and 9' on the inner sides of the two ends of the pipe bolt 2 respectively, and the flanges 9 and 9' The inner diameter of the pipe is slightly larger than the outer diameter of the flexible pipe; the joint between the flange 9 and the flexible pipe away from the head of the pipe bolt 2, that is, the clamping position, is arc-shaped. This design is also to increase the clamping force, make the connection reliable, or be used in occasions with high working pressure.
[0059] The hose joint 4 of the present invention can be a joint of symmetrical shape that connects two or more directions, so as to realize the connection between two or more hoses. As shown in FIG. 11 , double hose connectors 6 connected symmetrically to one another are adopted, and the rest of the structure is the same as that in Embodiment 2, which is used for clamping and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com