Semiconductor device and method for fabricating same
A semiconductor and device technology, applied in the field of semiconductor devices and their manufacturing, can solve the problems of reducing the yield and increasing the defect density of the first gate insulating film, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
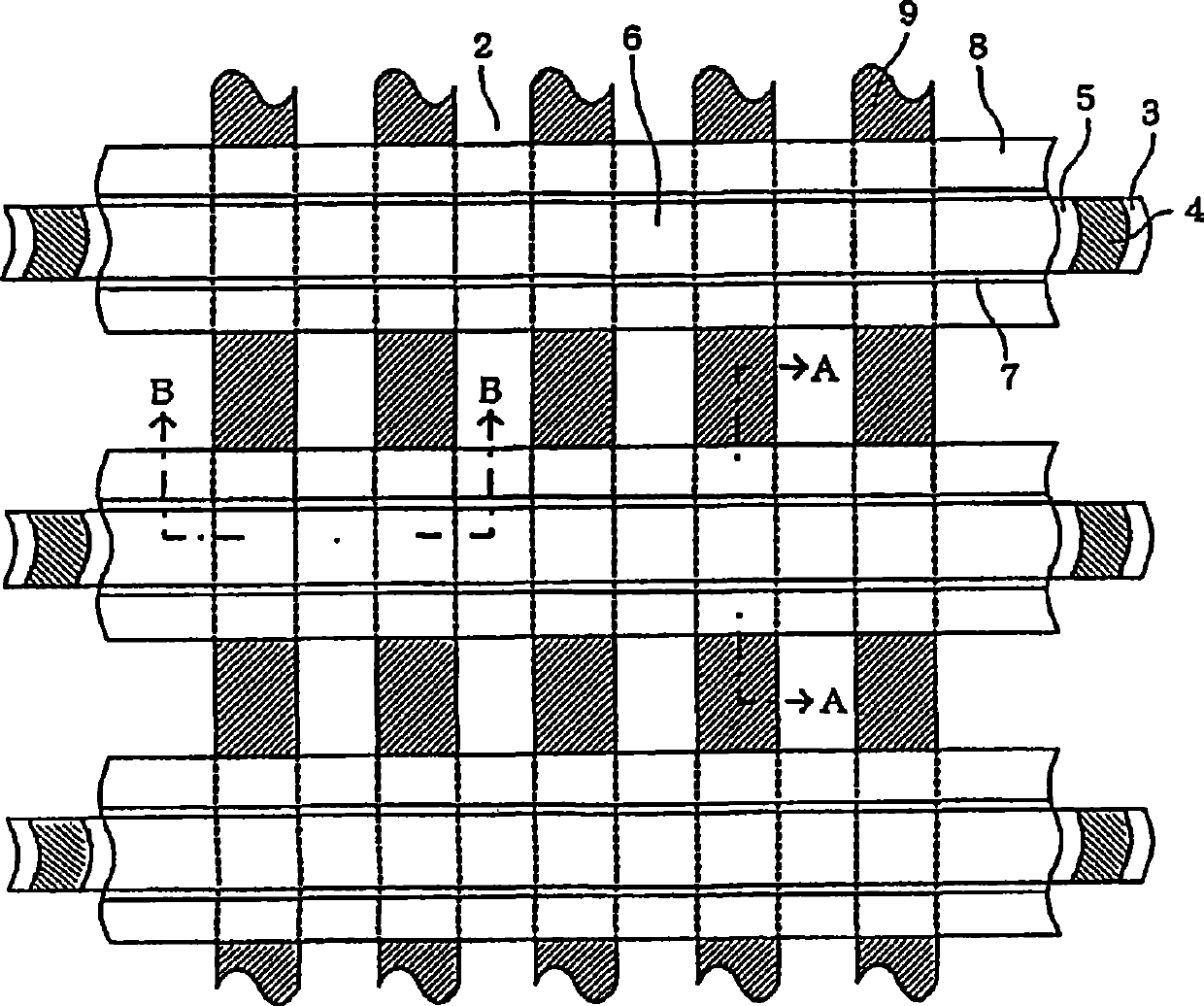
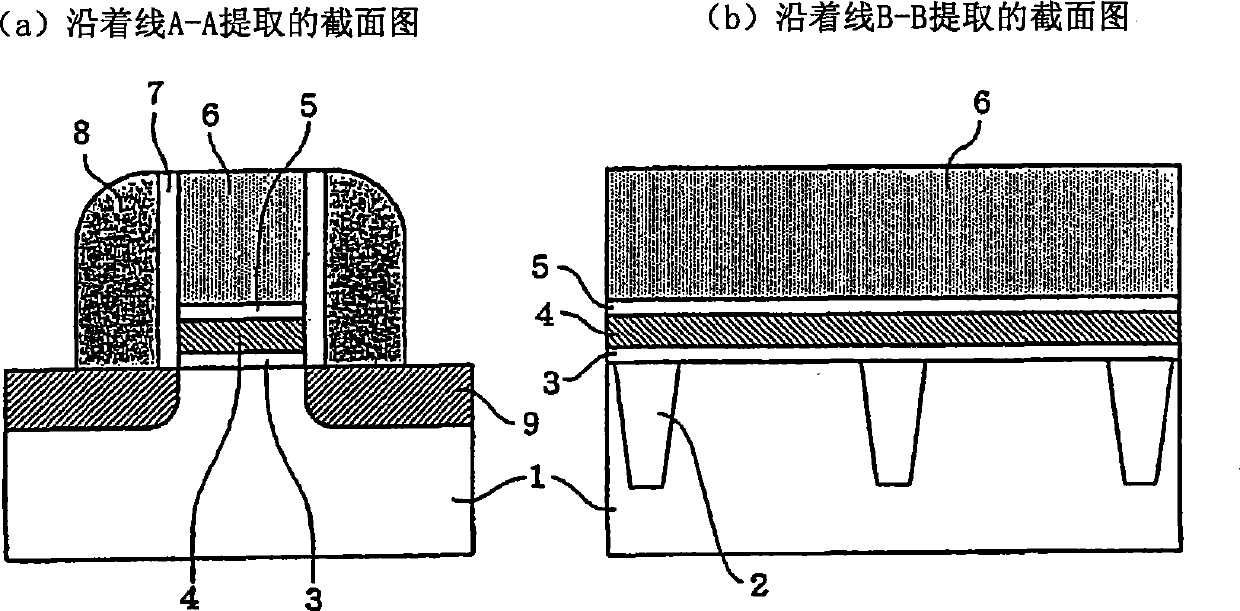
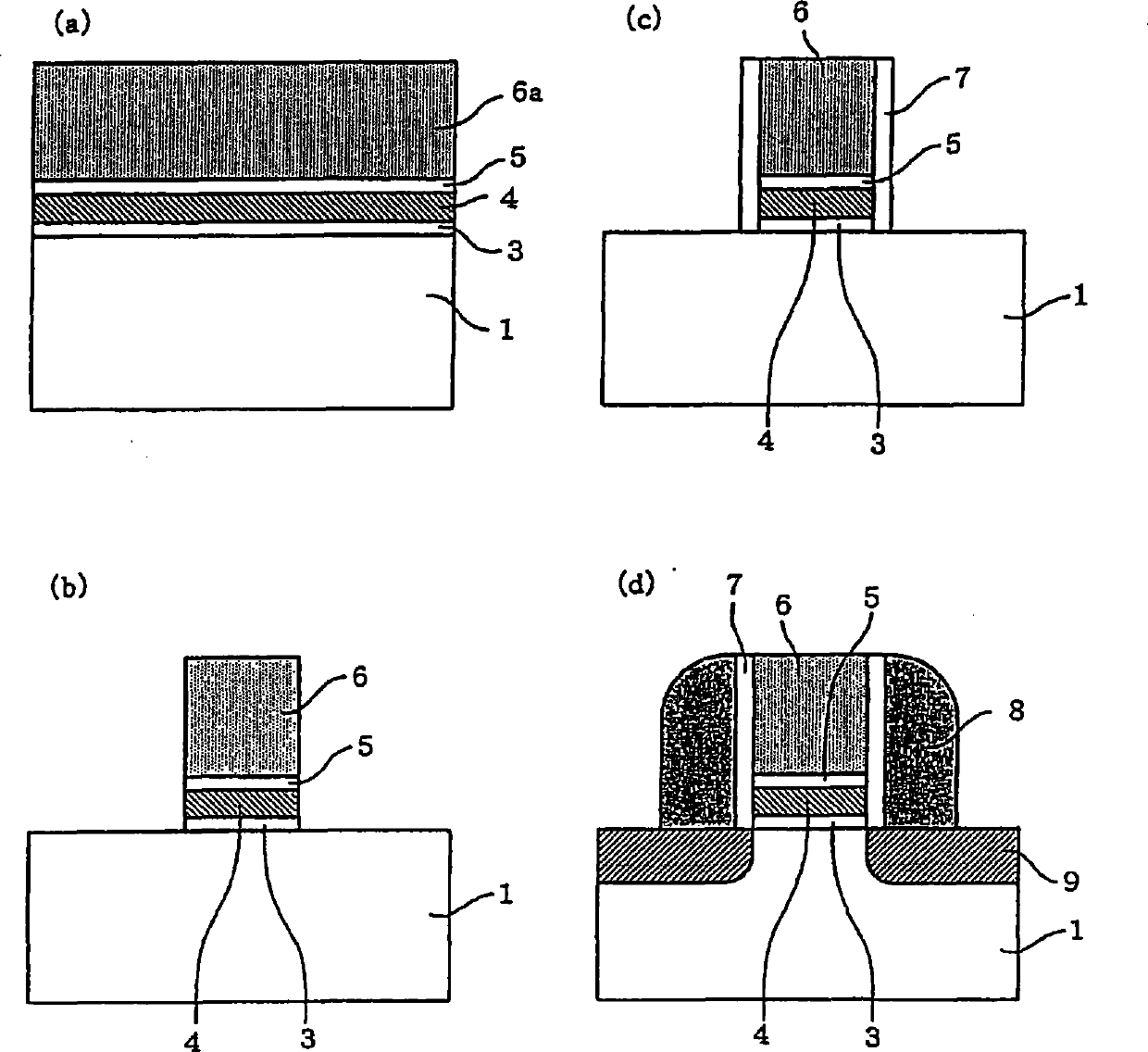
[0038] Figure 14is a top view of Example 1 of the present invention. Figure 15 (a) and 15(b) are along Figure 14 The cross-sectional view extracted by lines A-A and B-B. exist Figure 14 and 15 in, with Figure 9 and 10 The same parts as those in the first exemplary embodiment shown in the Figure 9 and 10 The same reference numerals are denoted in and repeated explanations thereof are omitted. In this example, the portion of the charge accumulating layer 4 immediately below the gate conductor 6 becomes the high trap surface density region 4a, and a part of the outer portion of the gate conductor becomes the trap surface density lower than that of the high trap surface density region 4a. The low trap surface density region 4b, and the part outside of this part becomes the non-trap region 4c that does not contain charge traps. The non-trap region 4c contains no nitrogen and is almost completely converted into a silicon oxide film. In the memory cell of Example 1, e...
example 2
[0040] Figure 16 is a top view of Example 2 of the present invention. Figure 17 (a) and 17(b) are along Figure 16 The cross-sectional view extracted by lines A-A and B-B. exist Figure 16 and 17 in, with Figure 9 and 10 The same parts as those in the first exemplary embodiment shown in the Figure 9 and 10 The same reference numerals are denoted in and repeated explanations thereof are omitted. In this example, the portion of charge accumulating layer 4 immediately below gate conductor 6 becomes high trap surface density region 4a, and the portion outside the end of the gate conductor becomes non-trap region 4c free of charge traps. The non-trap region 4c outside the end of the gate conductor does not contain nitrogen and is almost completely converted into a silicon oxide film. In the memory cell of Example 2, there were no charge traps at the portion outside the gate conductor. The charge accumulation layer 4 inside the gate conductor 6 or inside the gate condu...
example 3
[0042] Figure 18 is a top view of Example 3 of the present invention. Figure 19 (a) and 19(b) are along Figure 18 The cross-sectional view extracted by lines A-A and B-B. exist Figure 18 and 19 in, with Figure 9 and 10 The same parts as those in the first exemplary embodiment shown in the Figure 9 and 10 The same reference numerals are denoted in and repeated explanations thereof are omitted. In this example, the portion of the charge accumulation layer 4 immediately below the gate conductor 6 becomes the initial film thickness region 4d whose thickness remains unchanged, but the region of the charge accumulation layer 4 outside the gate conductor becomes the thickness region 4d. Thin film region 4e smaller than initial thickness. A portion of the charge accumulating layer 4 becomes a non-trap region 4c. In this example, the charge accumulating layer (4e) including the charge traps outside the end of the gate electrode is made thinner than the charge accumulati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com