Patents
Literature
35results about How to "Prevent metal diffusion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
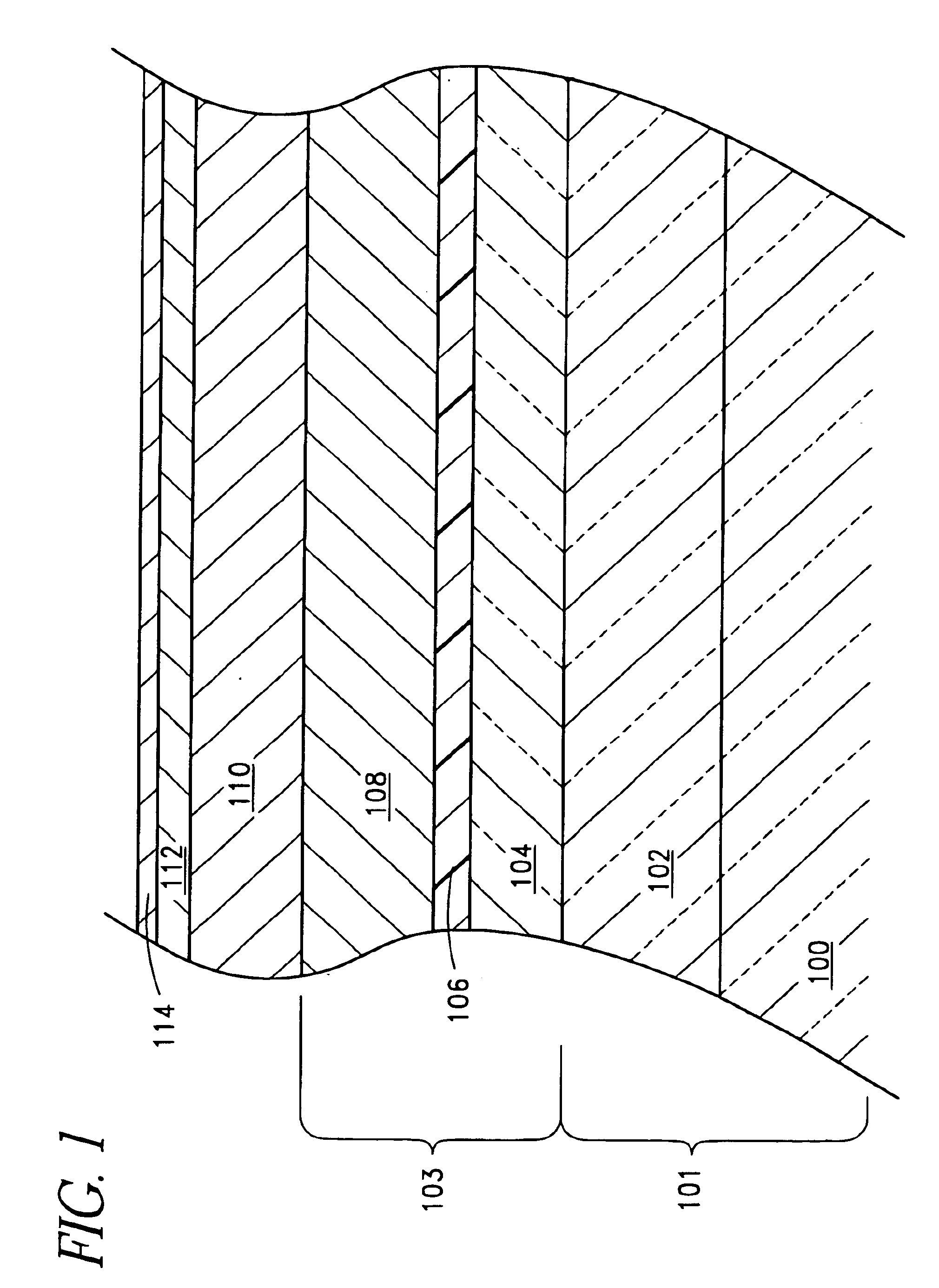
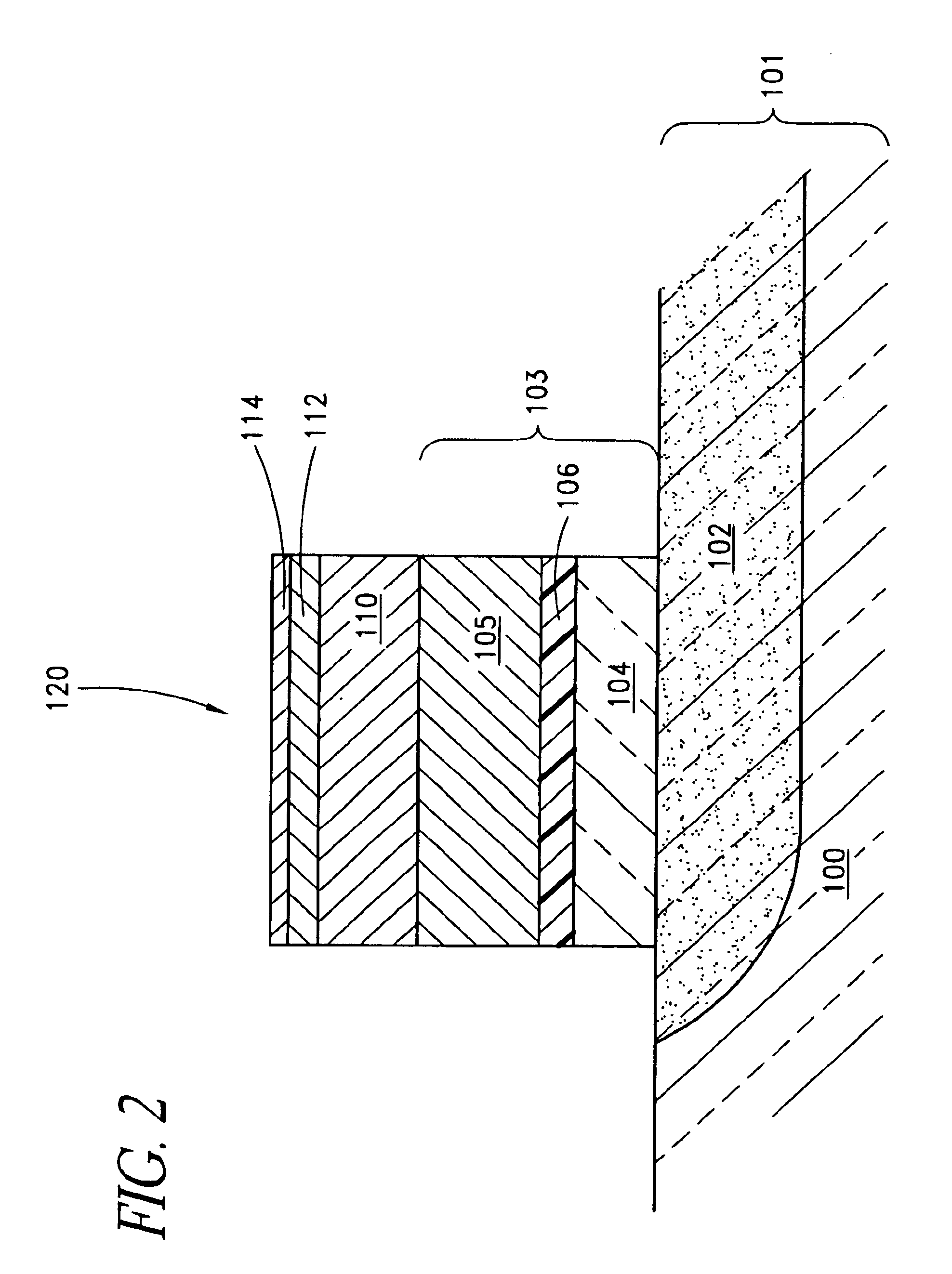
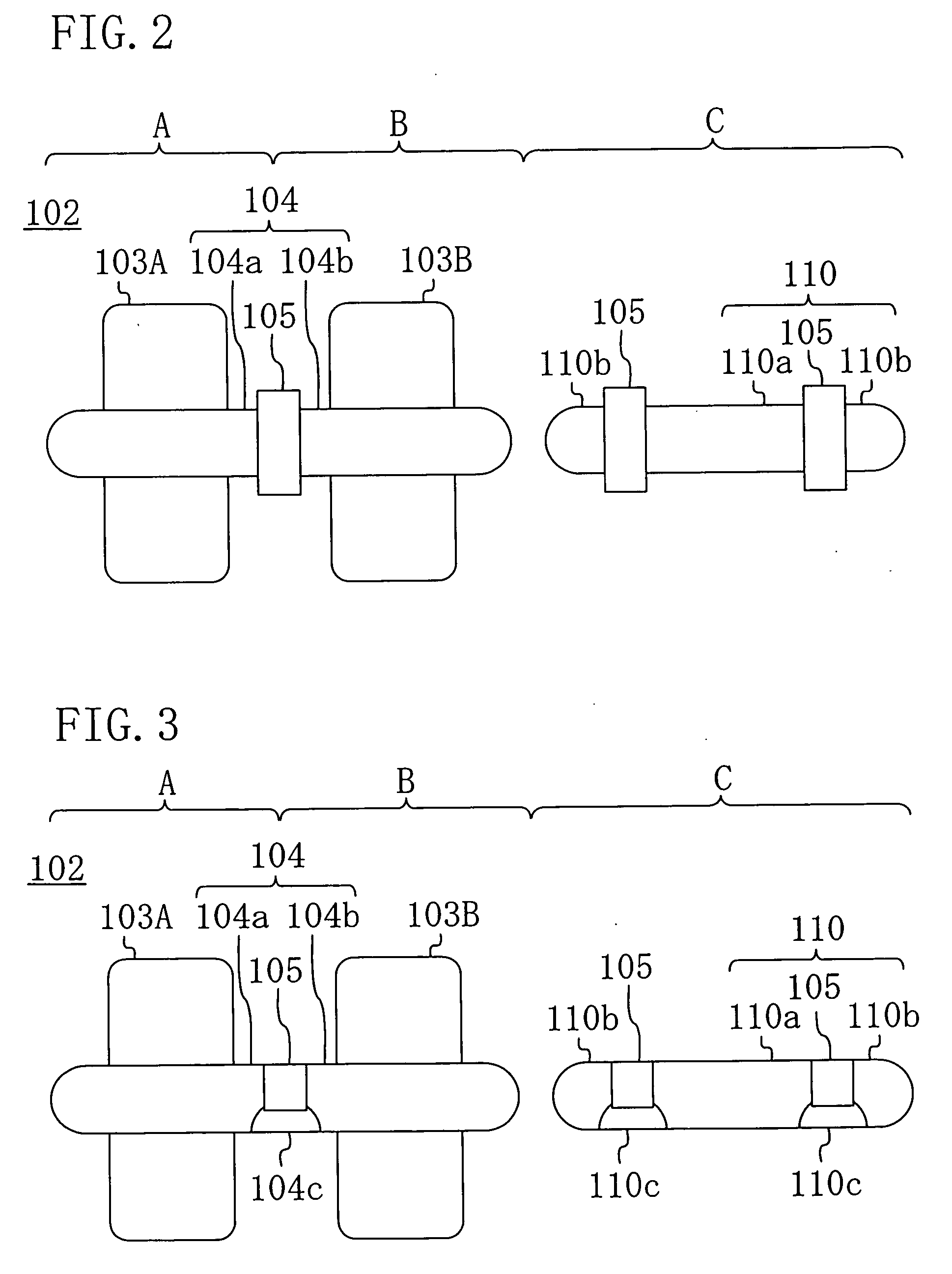
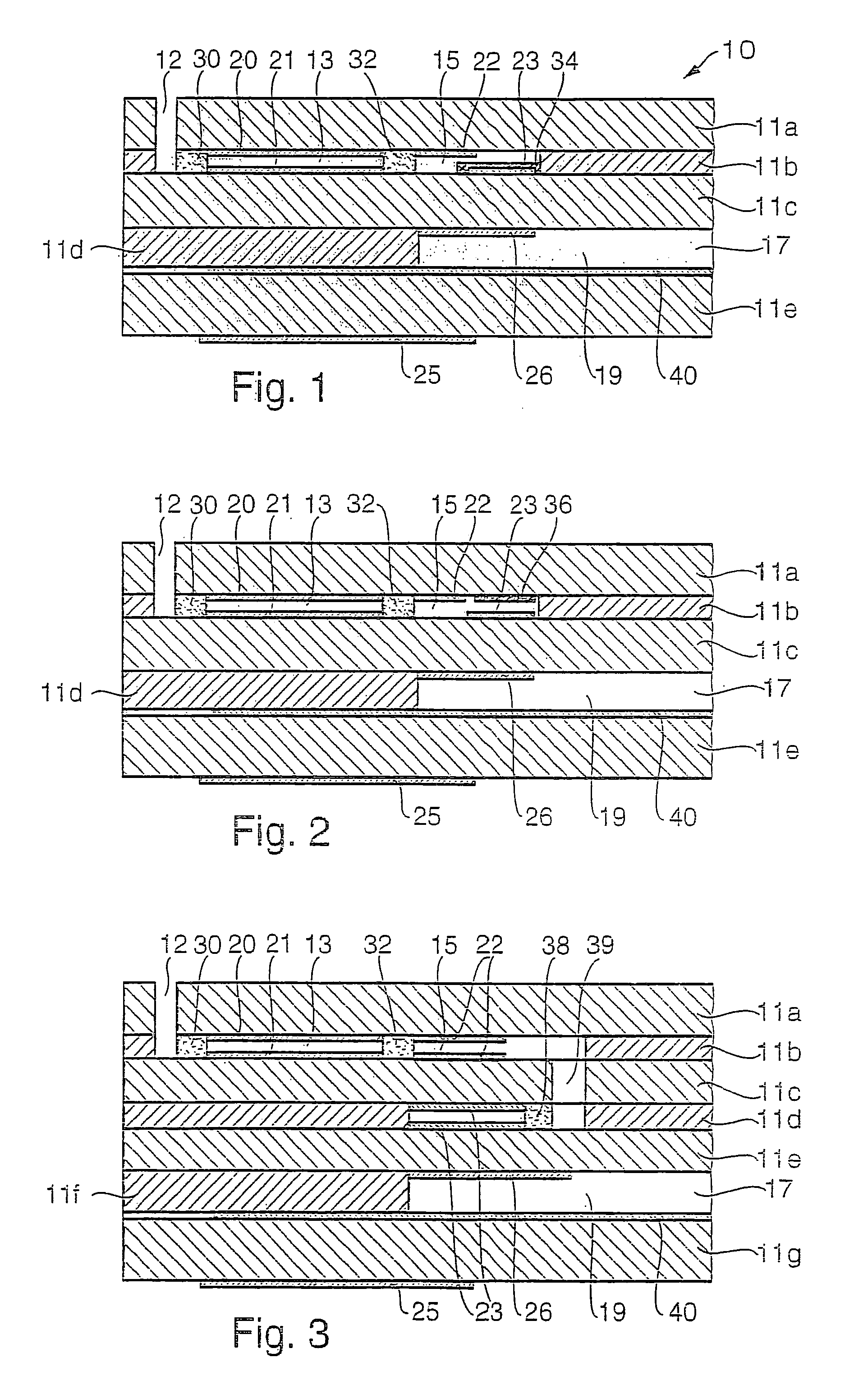
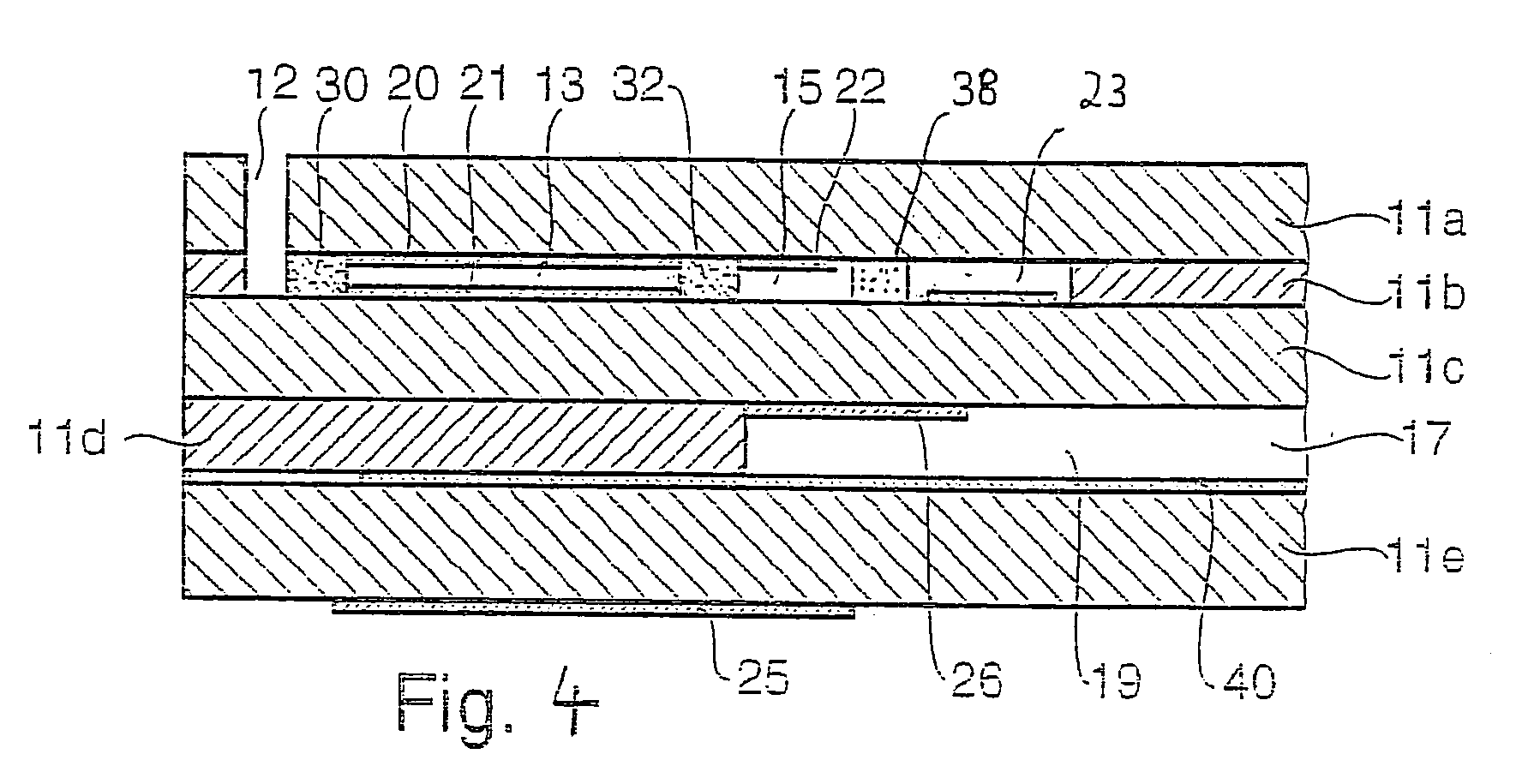
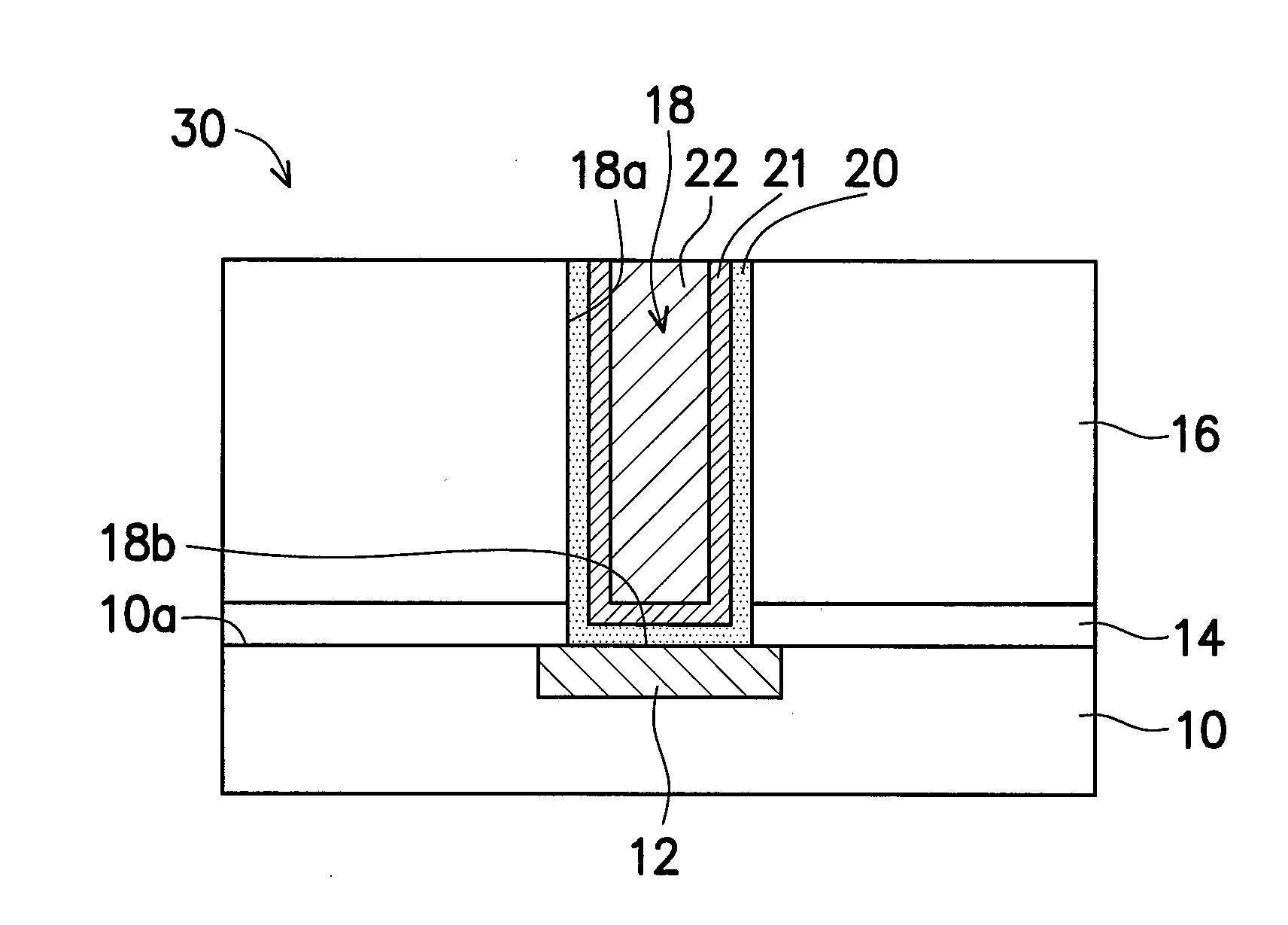
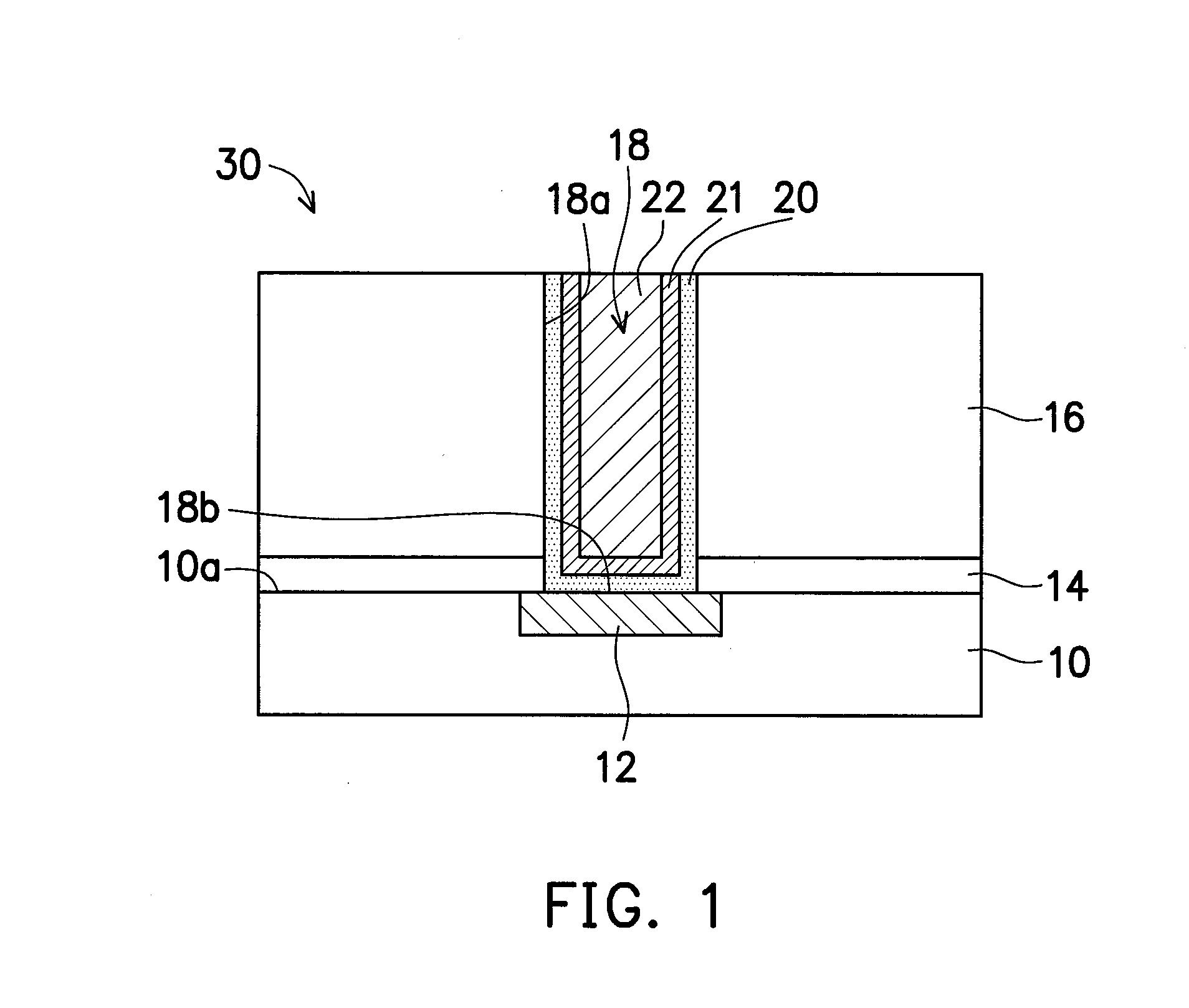
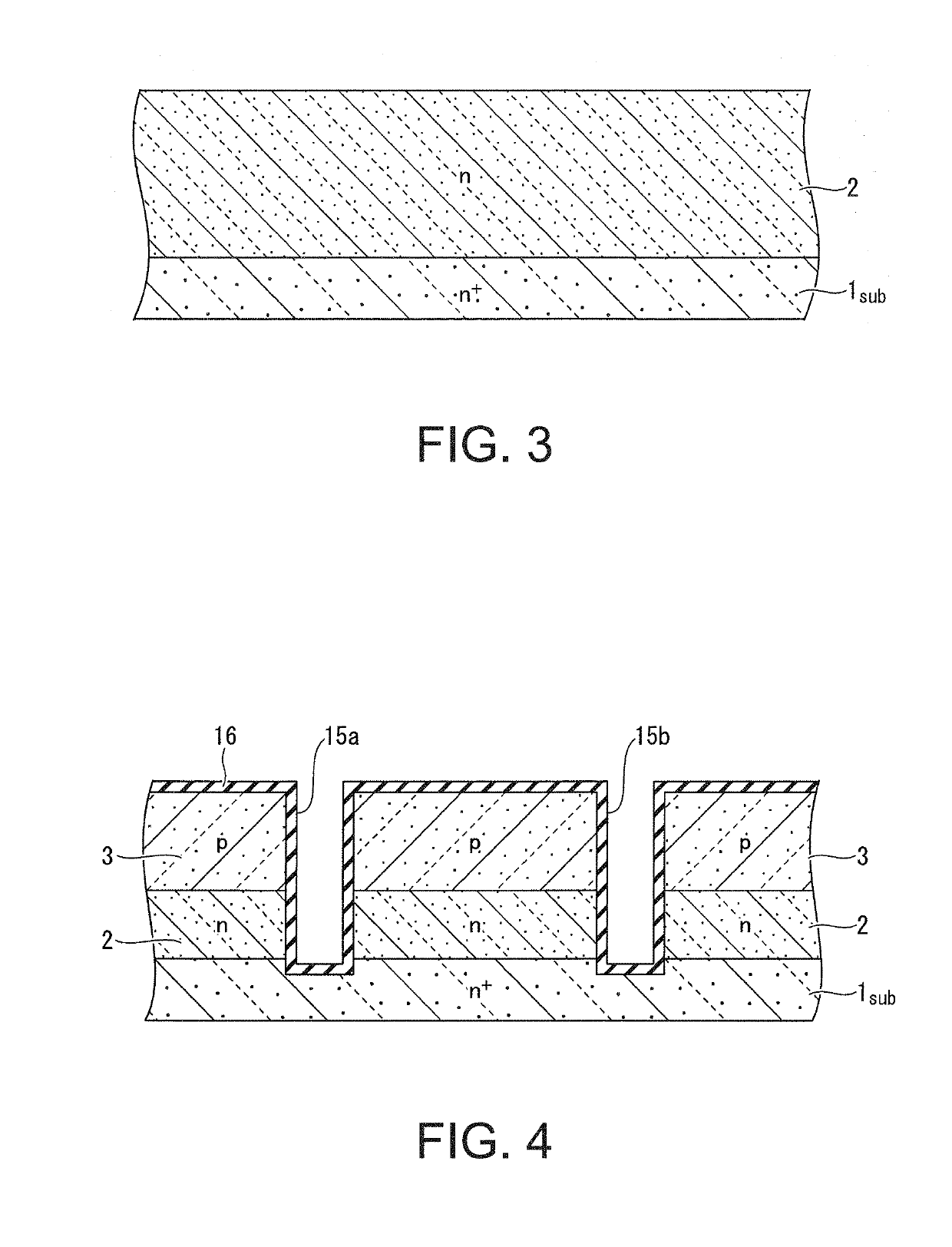
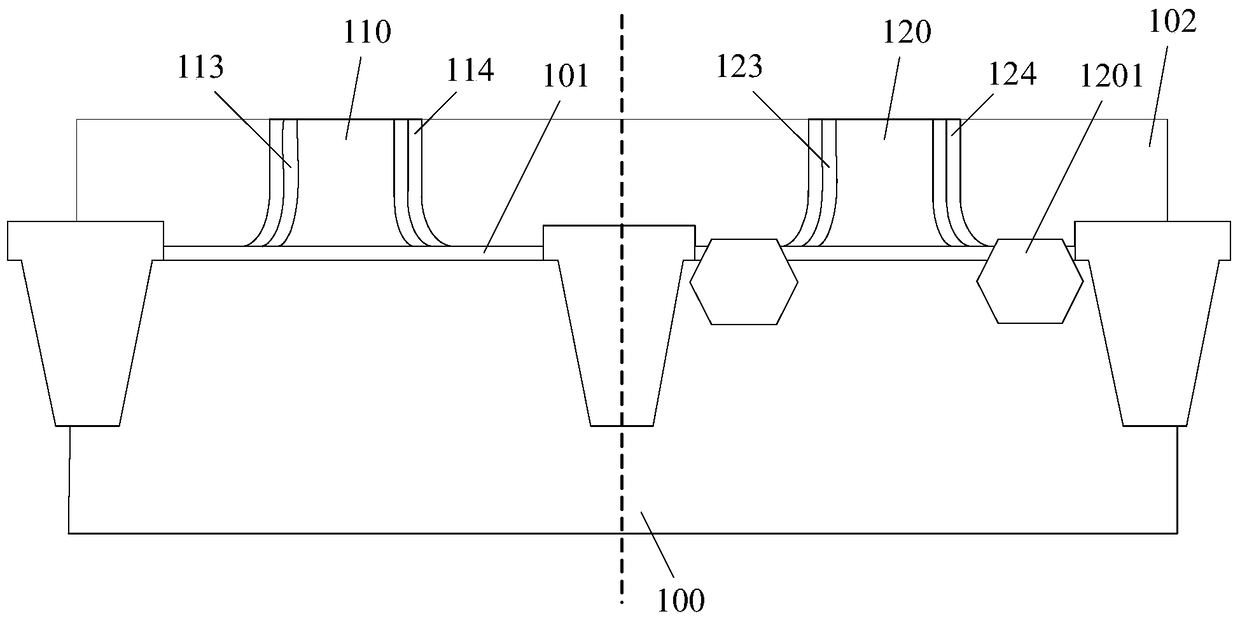
Process for realizing a connecting structure
ActiveUS9224704B2Prevent metal diffusionInhibited DiffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringDiffusion barrier
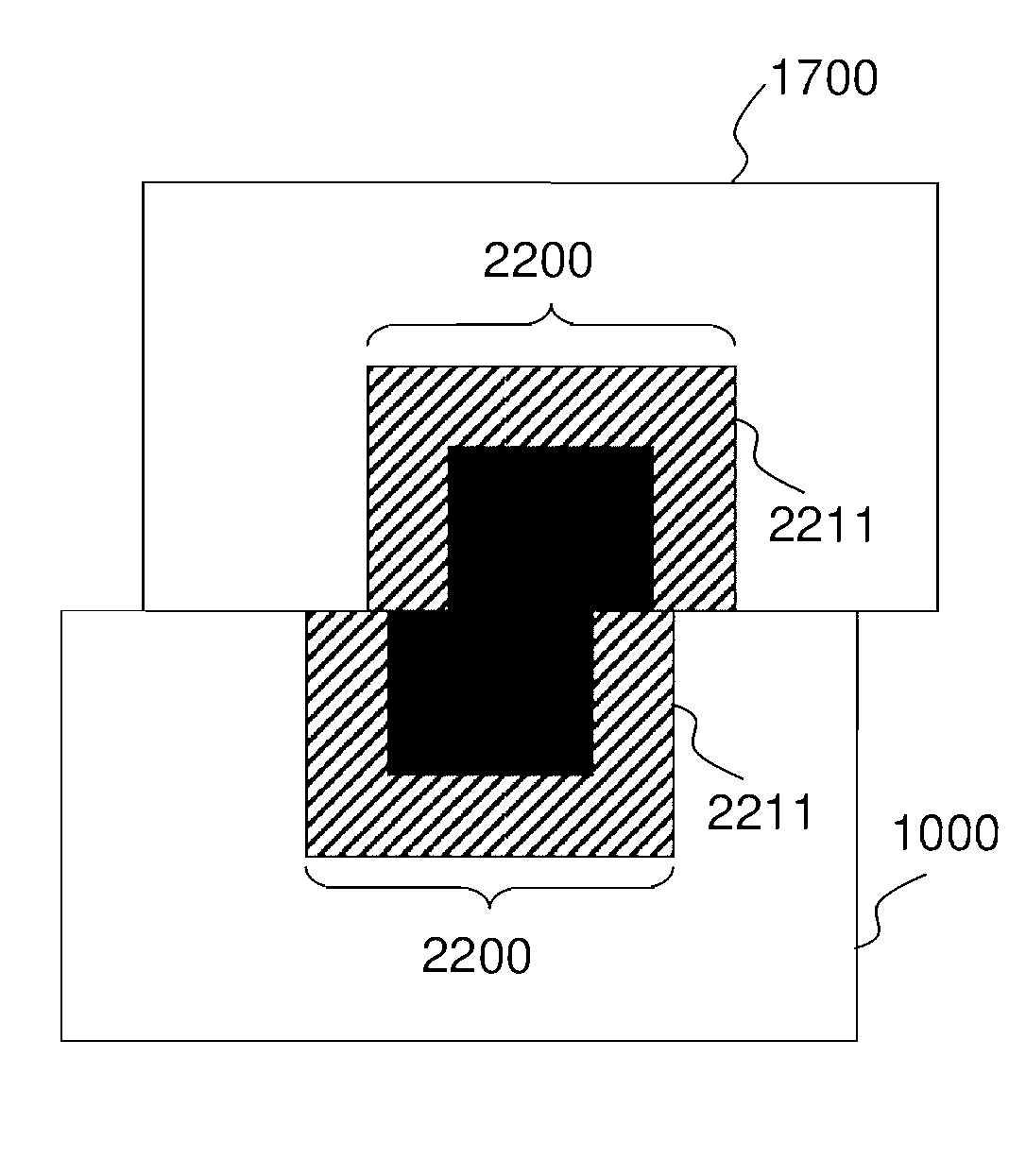
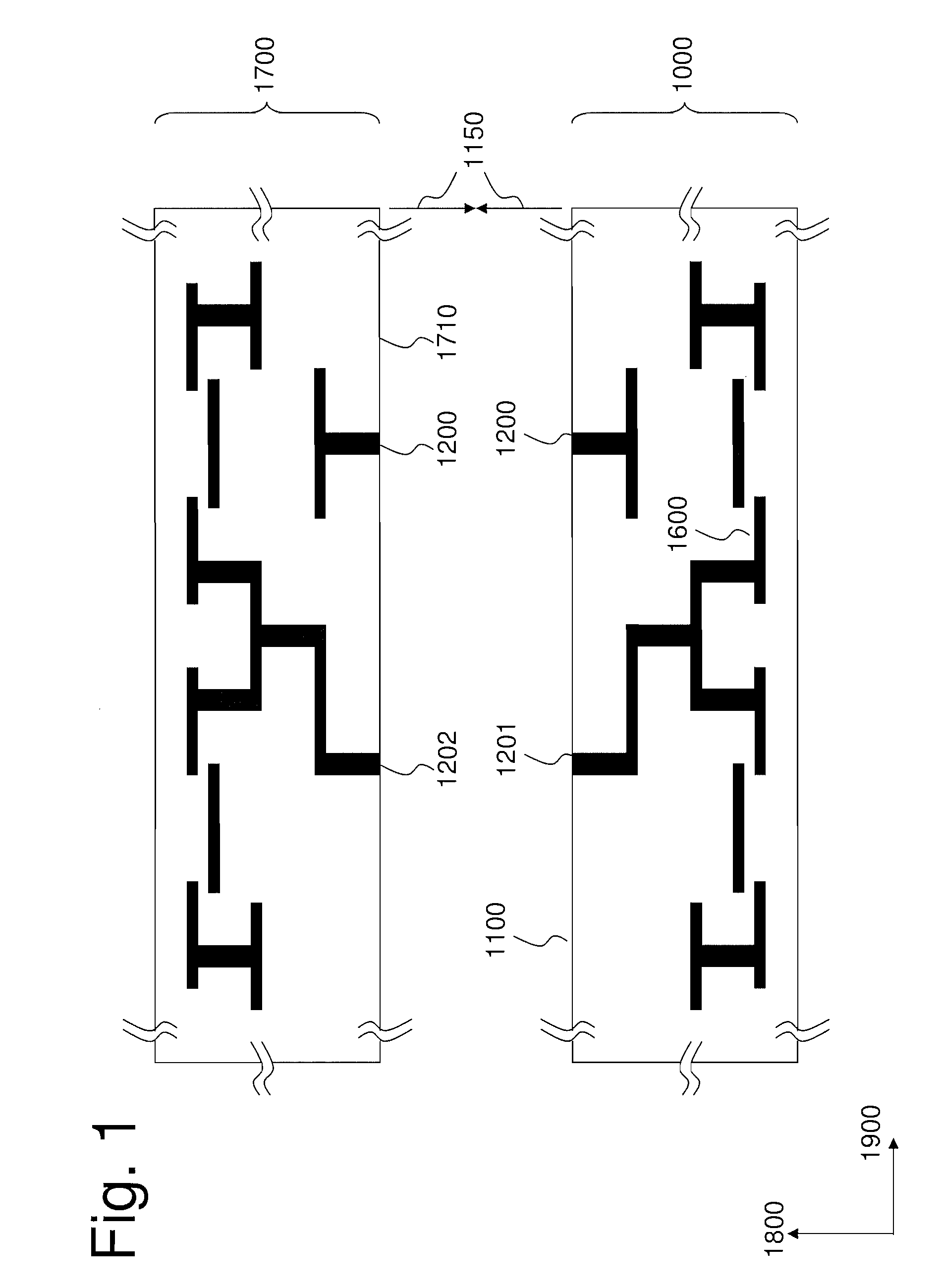
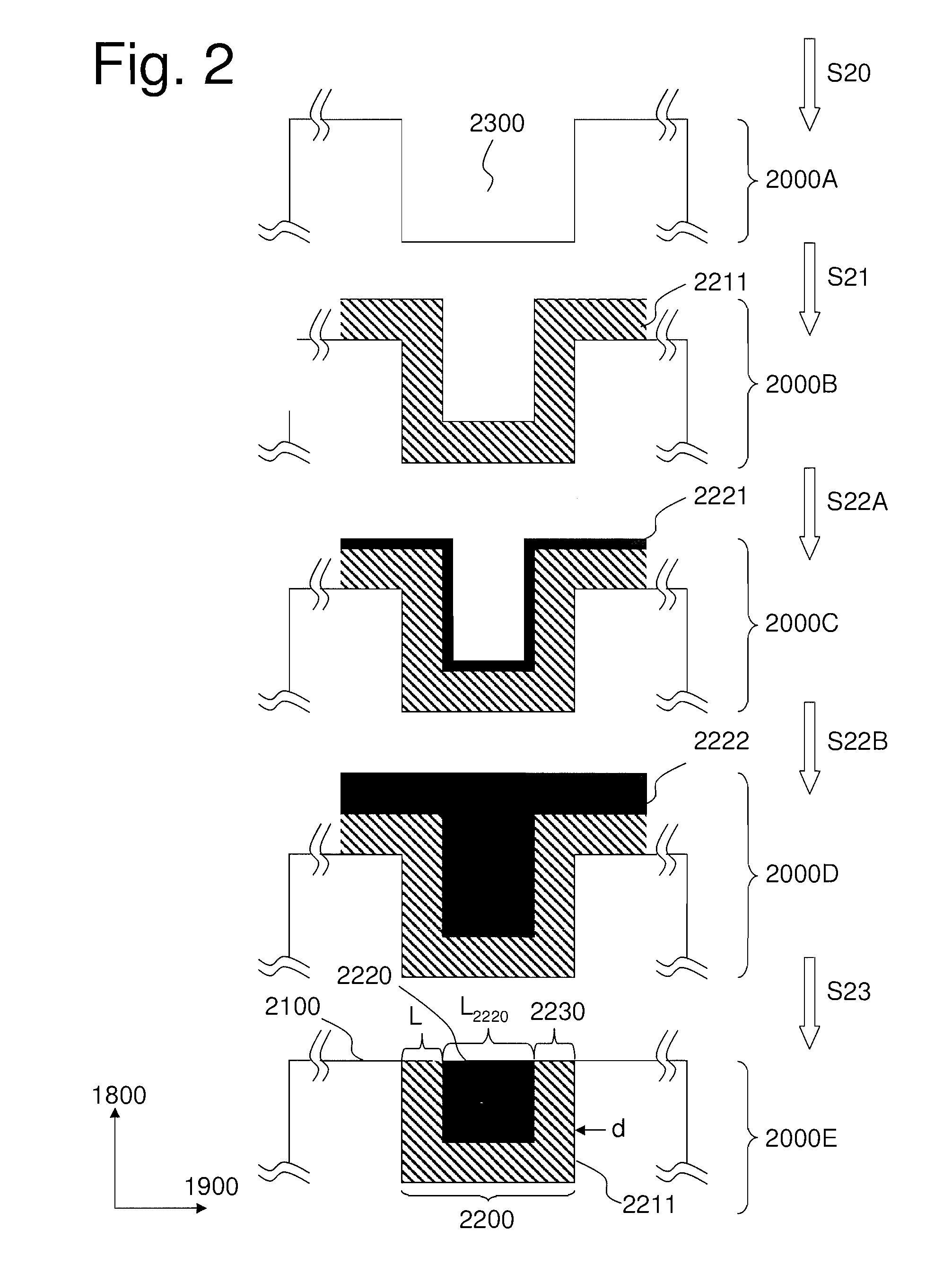
The present invention relates to a process for realizing a connecting structure in a semiconductor substrate, and the semiconductor substrate realized accordingly. The semiconductor substrate has at least a first surface, and is foreseen for a 3D integration with a second substrate along the first surface, wherein the 3D integration is subject to a lateral misalignment in at least one dimension having a misalignment value. This process includes growing a diffusion barrier structure for preventing diffusion of elements out of a conductive layer into the rest of the semiconductor substrate, wherein a first end surface, being the most outward surface of the diffusion barrier structure and being substantially parallel to the first surface, along a direction perpendicular to the first surface and going from the substrate toward the first surface, of the diffusion barrier structure can have a length, in the direction of the lateral misalignment, the length being dependent on the misalignment value, wherein the length of the diffusion barrier structure is chosen such that in a 3D integrated structure a diffusion of elements out of a conductive layer of the second substrate is prevented in the integrated state.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Method of manufacture of programmable switching circuits and memory cells employing a glass layer
InactiveUS6858482B2Prevent metal diffusionLayered productsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuitStorage cell
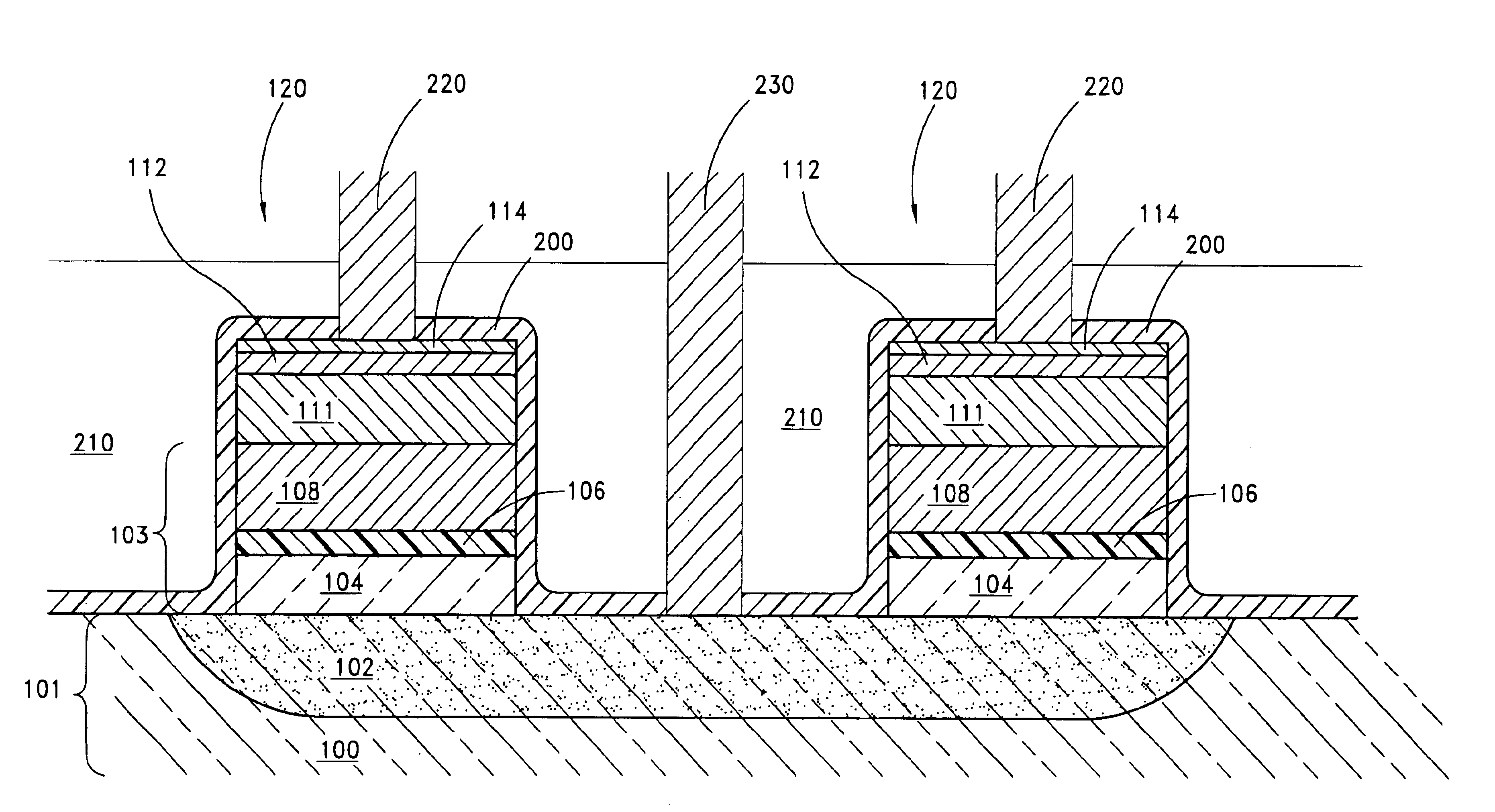
Programmable conductor memory cells in a stud configuration are fabricated in an integrated circuit by blanket deposition of layers. The layers include a bottom electrode in contact with a conductive region in a semiconductor substrate, a glass electrolyte layer that forms the body of the cell and a top electrode layer. Under the influence of an applied voltage, conductive paths grow through or along the cell body. The layers are patterned and etched to define separate pillars or cells of these stacked materials. A liner layer of an insulating material is deposited over the cells and acts as a barrier to prevent diffusion of the metal in the cell body into other parts of the integrated circuit. Remaining regions between the cells are filled with an insulating layer. At least some of the insulating layer and some of the liner layer are removed to make contact to the top electrode layer of the cell and to the substrate.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070093015A1Reduce circuit areaSuppress mutationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialField-effect transistor
A semiconductor device includes a first field-effect transistor including a first gate electrode and a second field-effect transistor including a second gate electrode. The first gate electrode and the second gate electrode are integrated using a connecting portion and are fully silicided with a metal in such a manner that the fist and second gate electrodes have different metal contents. A diffusion preventing film for preventing the metal from diffusing between the first and second gate electrodes is formed in at least a portion of the connecting portion.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electrically programmable metal fuse
ActiveUS8421186B2Reduce the required powerPrevent thermal crackingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityMetal strips
A metal electrically programmable fuse (“eFuse”) includes a metal strip, having a strip width, of a metal line adjoined to wide metal line portions, having widths greater than the metal strip width, at both ends of the metal strip. The strip width can be a lithographic minimum dimension, and the ratio of the length of the metal strip to the strip width is greater than 5 to localize heating around the center of the metal strip during programming. Localization of heating reduces required power for programming the metal eFuse. Further, a gradual temperature gradient is formed during the programming within a portion of the metal strip that is longer than the Blech length so that electromigration of metal gradually occurs reliably at the center portion of the metal strip. Metal line portions are provides at the same level as the metal eFuse to physically block debris generated during programming.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Electrically programmable metal fuse
ActiveUS20120306048A1Reduce the required powerPrevent thermal crackingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectromigrationMetal
A metal electrically programmable fuse (“eFuse”) includes a metal strip, having a strip width, of a metal line adjoined to wide metal line portions, having widths greater than the metal strip width, at both ends of the metal strip. The strip width can be a lithographic minimum dimension, and the ratio of the length of the metal strip to the strip width is greater than 5 to localize heating around the center of the metal strip during programming. Localization of heating reduces required power for programming the metal eFuse. Further, a gradual temperature gradient is formed during the programming within a portion of the metal strip that is longer than the Blech length so that electromigration of metal gradually occurs reliably at the center portion of the metal strip. Metal line portions are provides at the same level as the metal eFuse to physically block debris generated during programming.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method for forming a three-component nitride film containing metal and silicon
InactiveUS6426117B1Avoid condensationPrevent metal diffusionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInorganic chemistryReactive gas
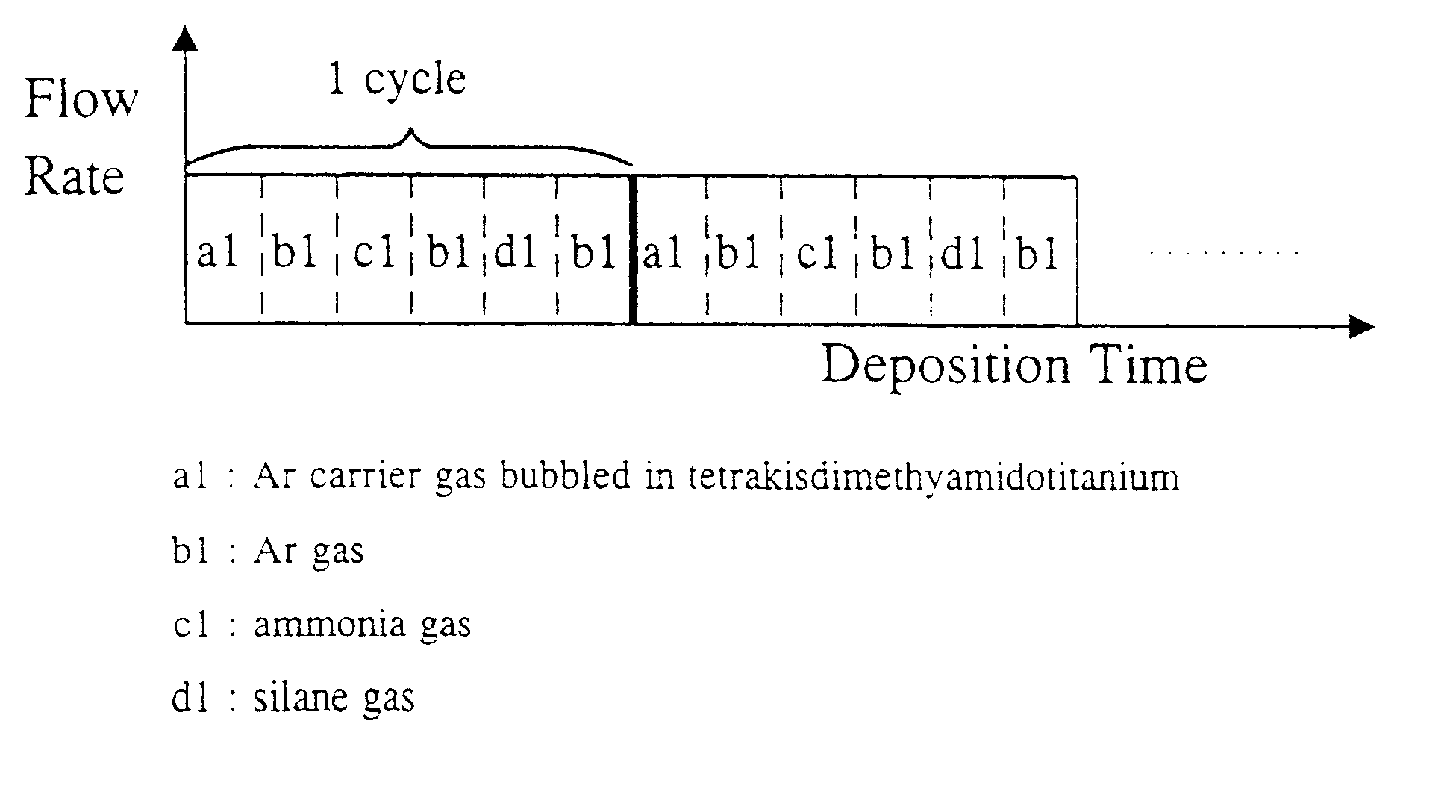
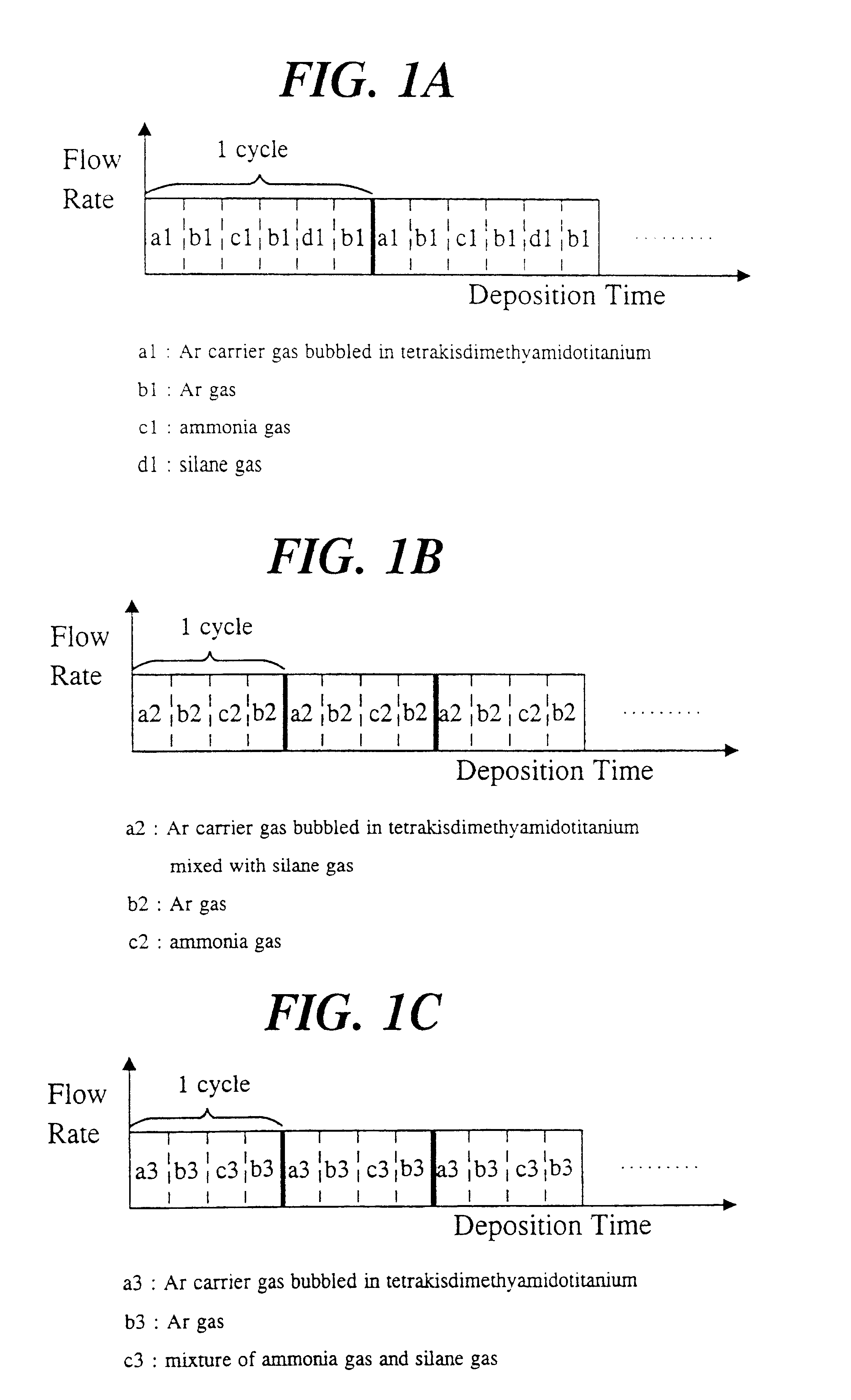
A method for forming a three-component film containing metal, silicon and nitrogen for use in semiconductor devices on a substrate. The method of the present invention comprises the steps of: preparing separate reactive gases each including at least one selected from the group consisting of a gaseous metal compound, a gaseous silicon compound and an ammonia gas under conditions such that the gaseous meta compound and the ammonia gas does not form a mixture; determining a sequential gas supply cycle of the reactive gases so that supplies of the gaseous metal compound, the gaseous silicon compound and the ammonia gas are each included at least once within one gas supply cycle; and applying the reactive gases to the substrate by repeating the gas supply cycle at least once. According to the present invention, a three-component nitride film can be formed with a uniform thickness despite unevenness of a semiconductor substrate surface.
Owner:ASM KOREA LTD
Method for manufacturing crystalline silicon-based solar cell and method for manufacturing crystalline silicon-based solar cell module
ActiveUS20160133779A1Improve conversion efficiencyReduce material costsFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess regionLaser light
A method for manufacturing a crystalline silicon-based solar cell having a photoelectric conversion section includes a silicon-based layer of an opposite conductivity-type on a first principal surface side of a crystalline silicon substrate of a first conductivity-type, and a collecting electrode formed by an electroplating method on a first principal surface of the photoelectric conversion section. By applying laser light from a first or second principal surface side of the photoelectric conversion section, an insulation-processed region his formed where a short-circuit between the first principal surface and a second principal surface of the photoelectric conversion section is eliminated. On the collecting electrode and / or the insulation-processed region, a protecting layer s formed for preventing diffusion of a metal, which is contained in the collecting electrode into the substrate. After the protecting layer is formed, the insulation-processed region is heated to eliminate leakage between the substrate and the silicon-based layer.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
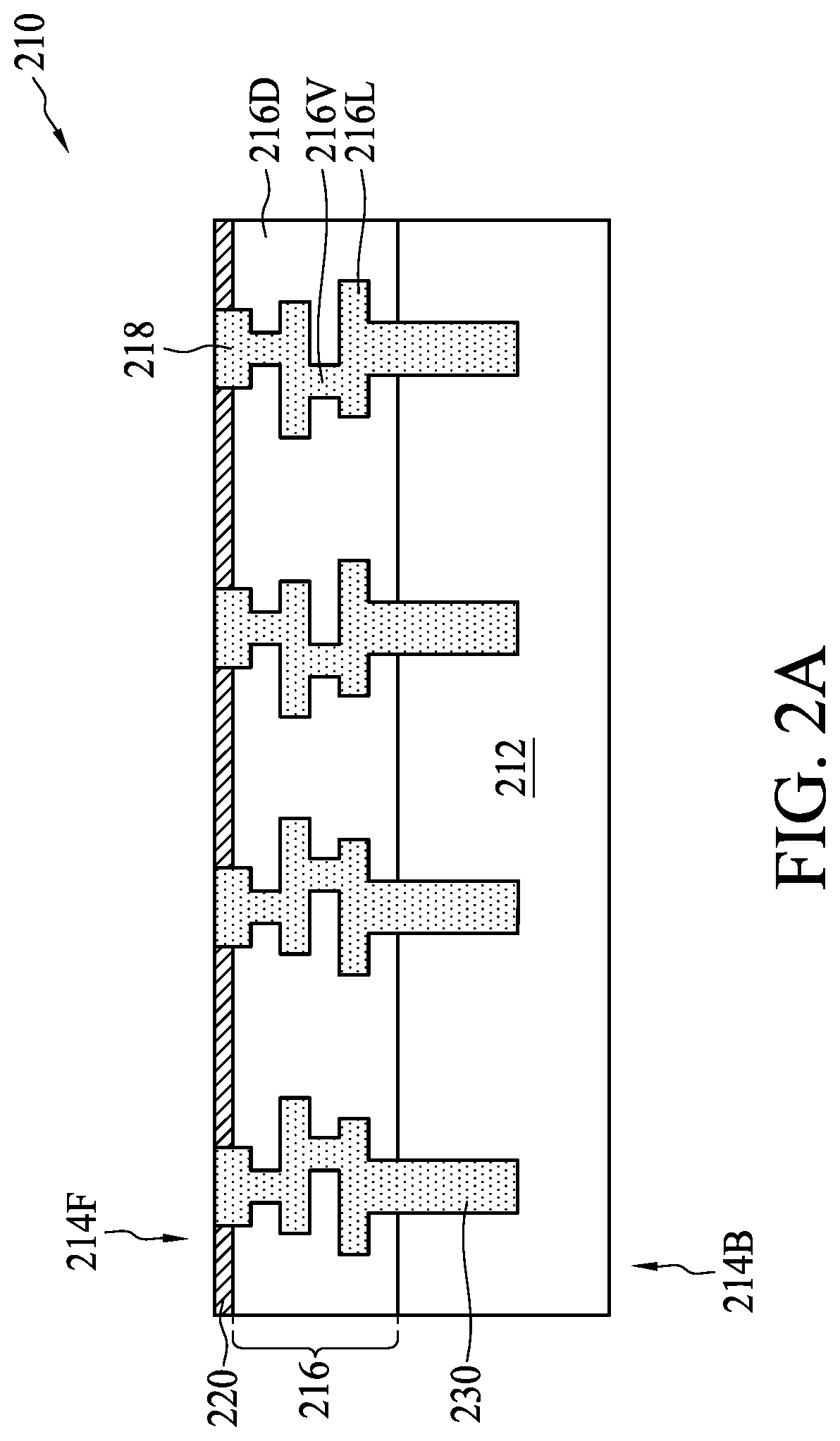
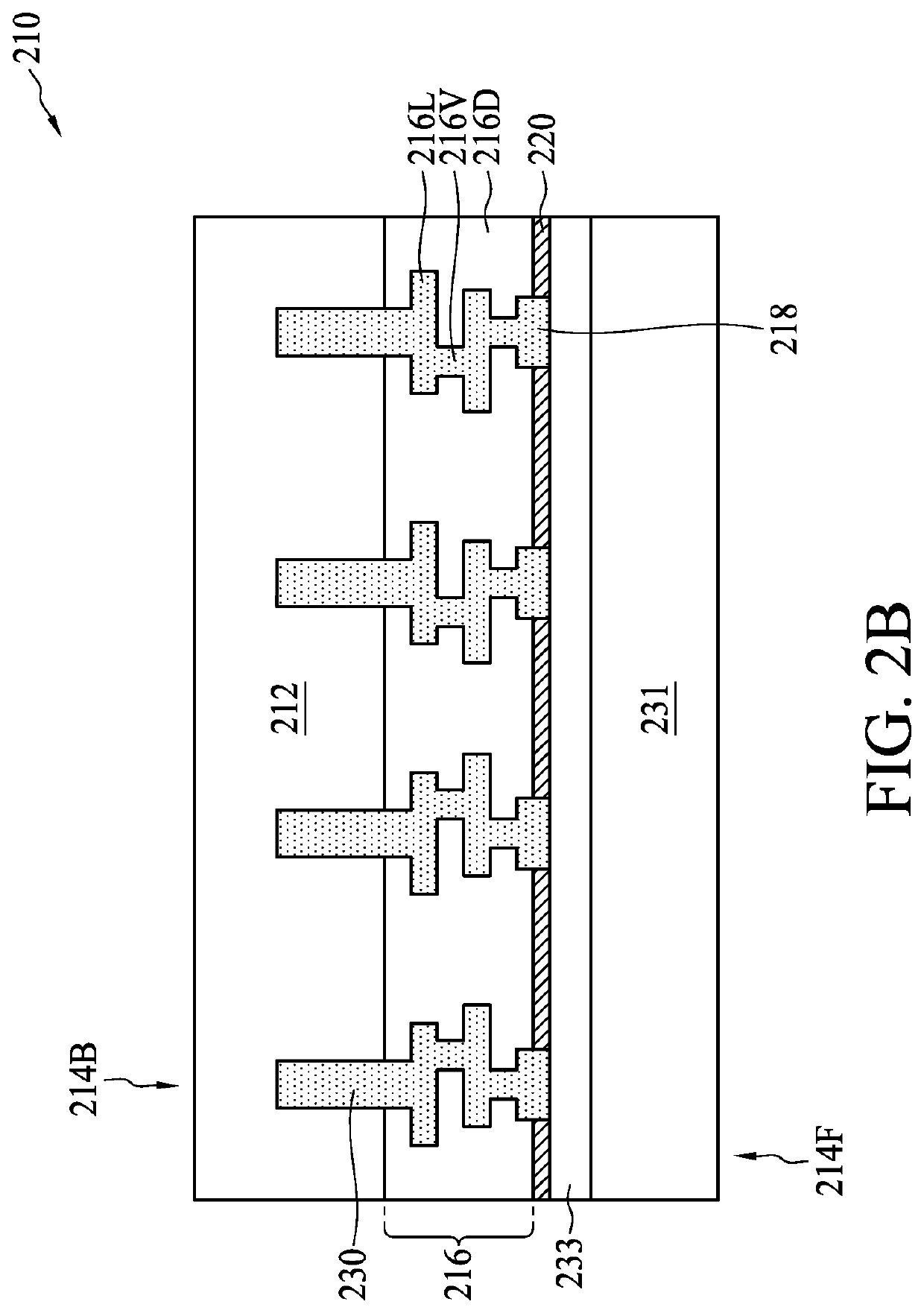
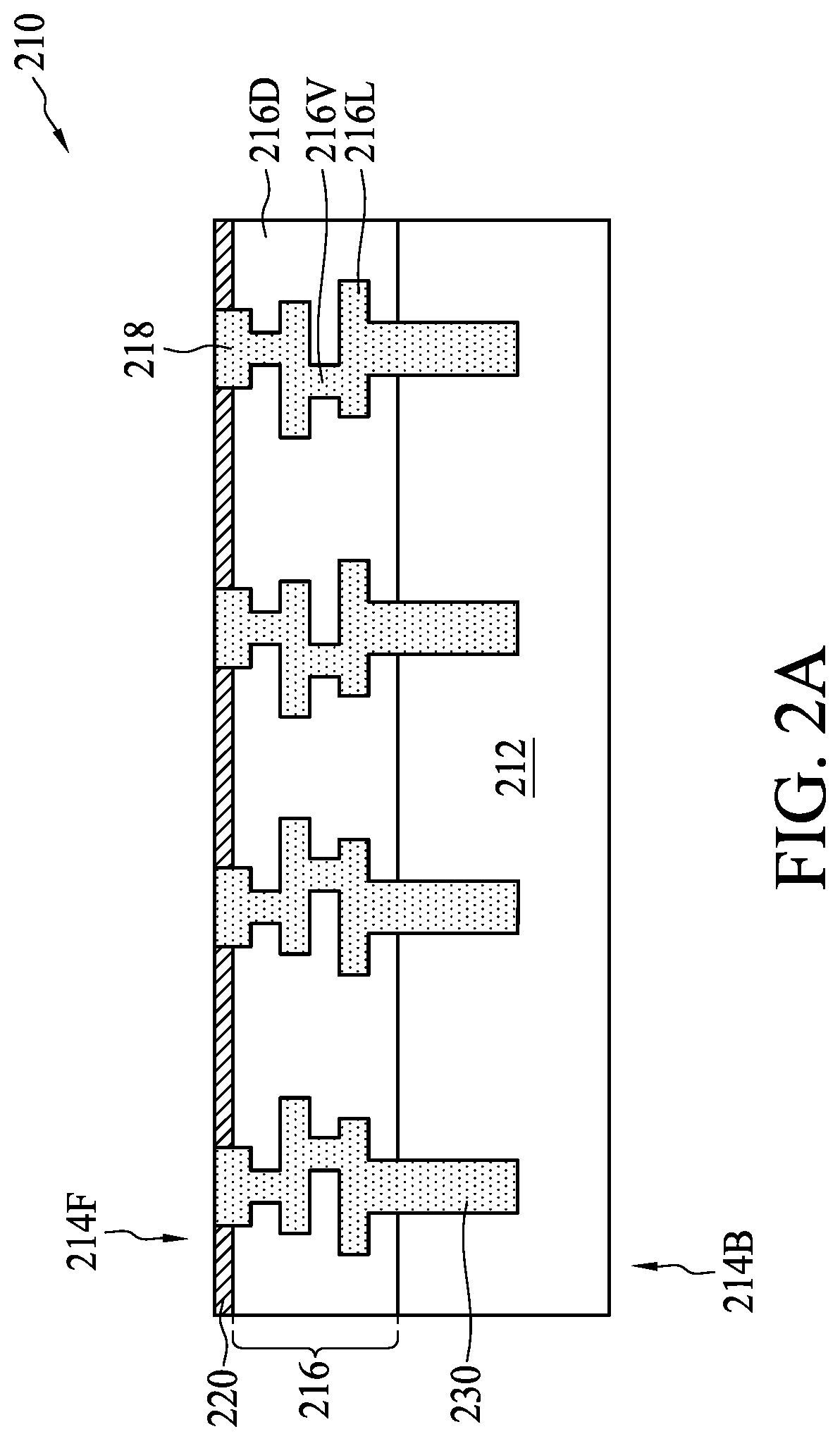
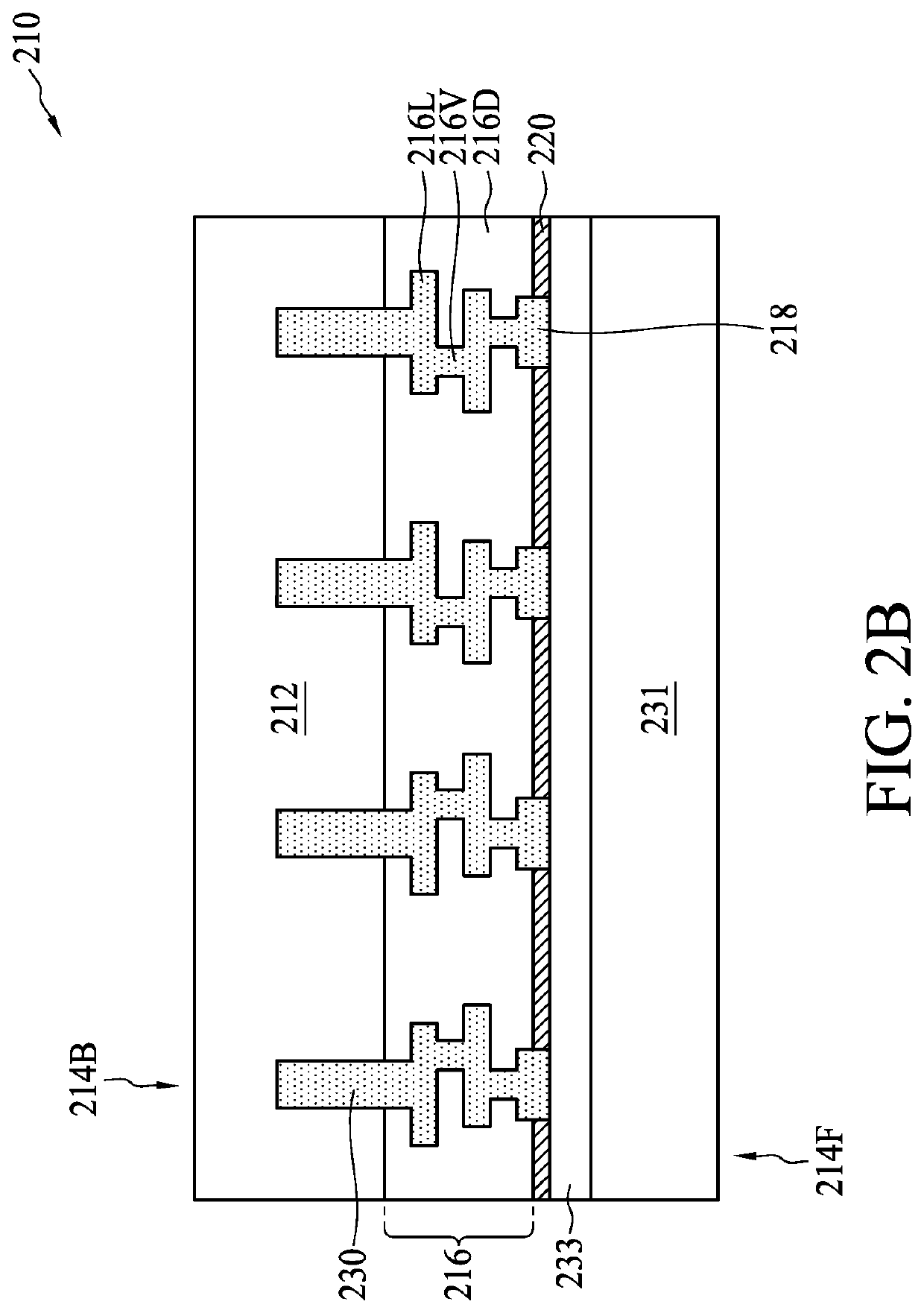
Stacked semiconductor structure
InactiveUS20160268230A1Improve barrier propertiesImprove electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureEngineering
A stacked semiconductor structure includes a first wafer, a second wafer, a first insulting layer, and a second insulating layer. The first wafer includes a first front surface, a first back surface, and a first interconnection structure. The first interconnection structure includes at least a first top metal layer exposed on the first front surface of the first wafer. The second wafer includes a second front surface, a second back surface, and a second interconnection structure. The second interconnection structure includes at least a second top metal layer exposed on the second front surface of the second wafer. The first insulating layer is formed on the first front surface of the first wafer, and the second insulating layer is formed on the second front surface of the second wafer. The first insulating layer and the second insulating layer contact each other.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor package structure and method for preparing the same
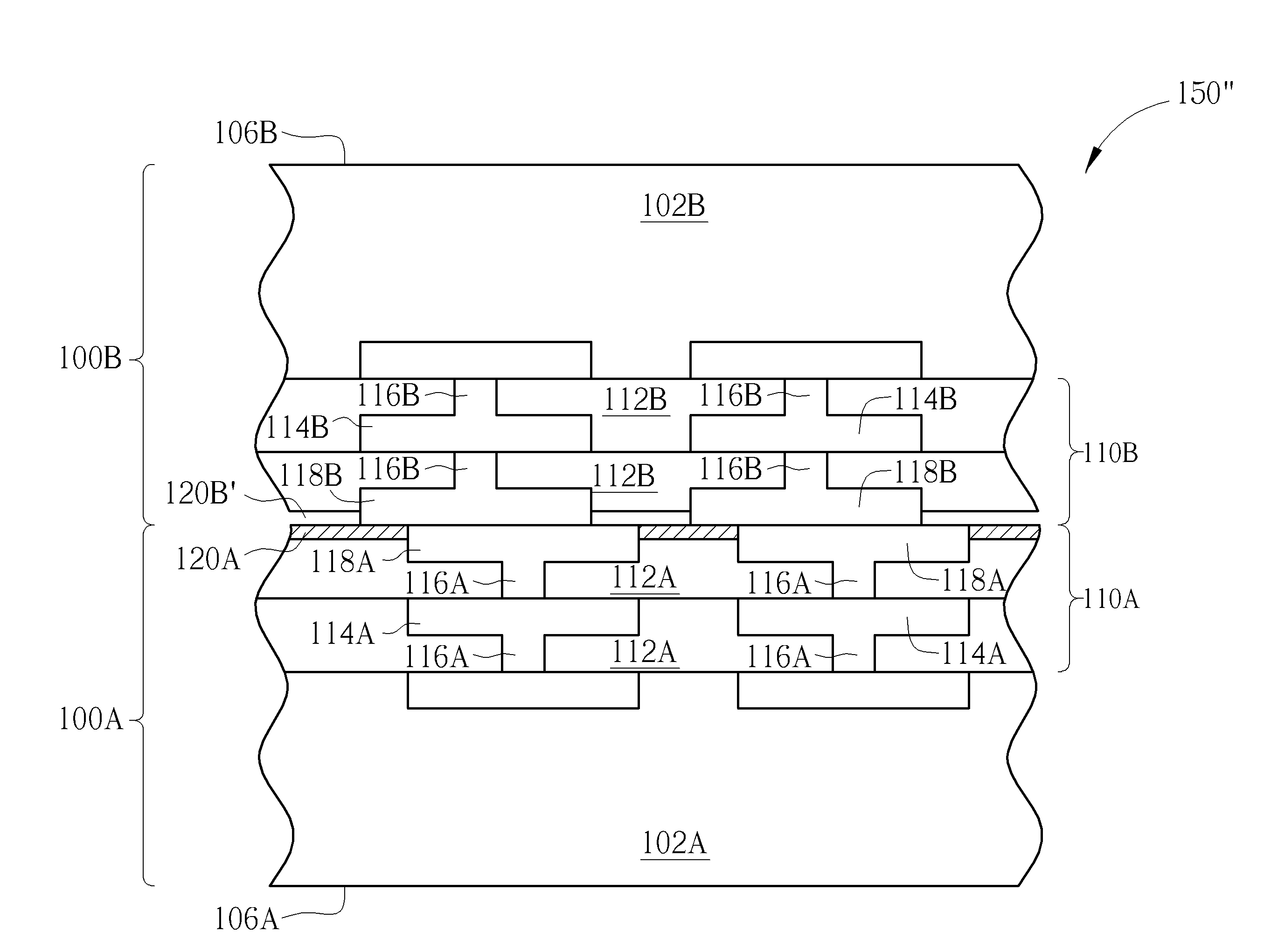
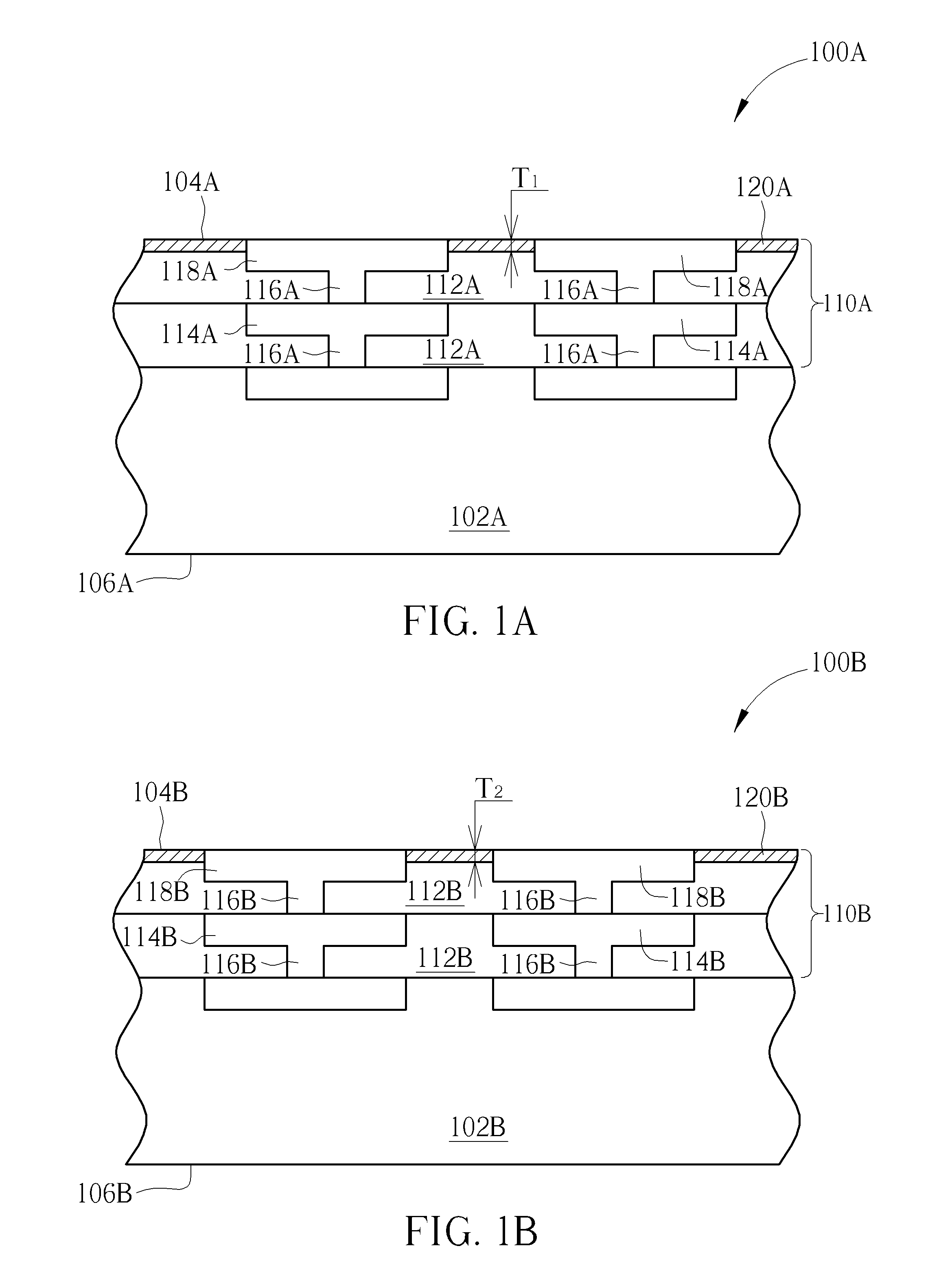
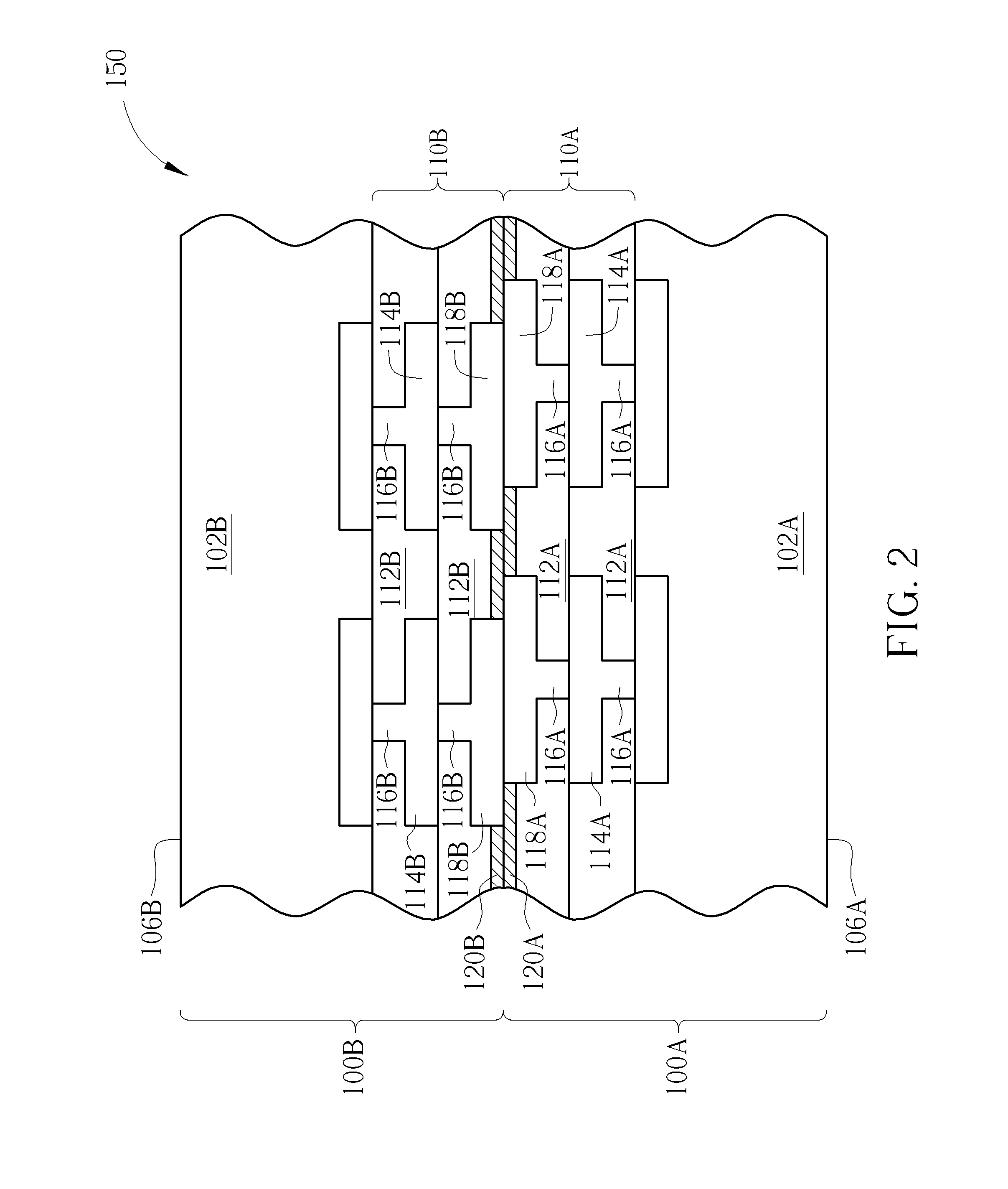
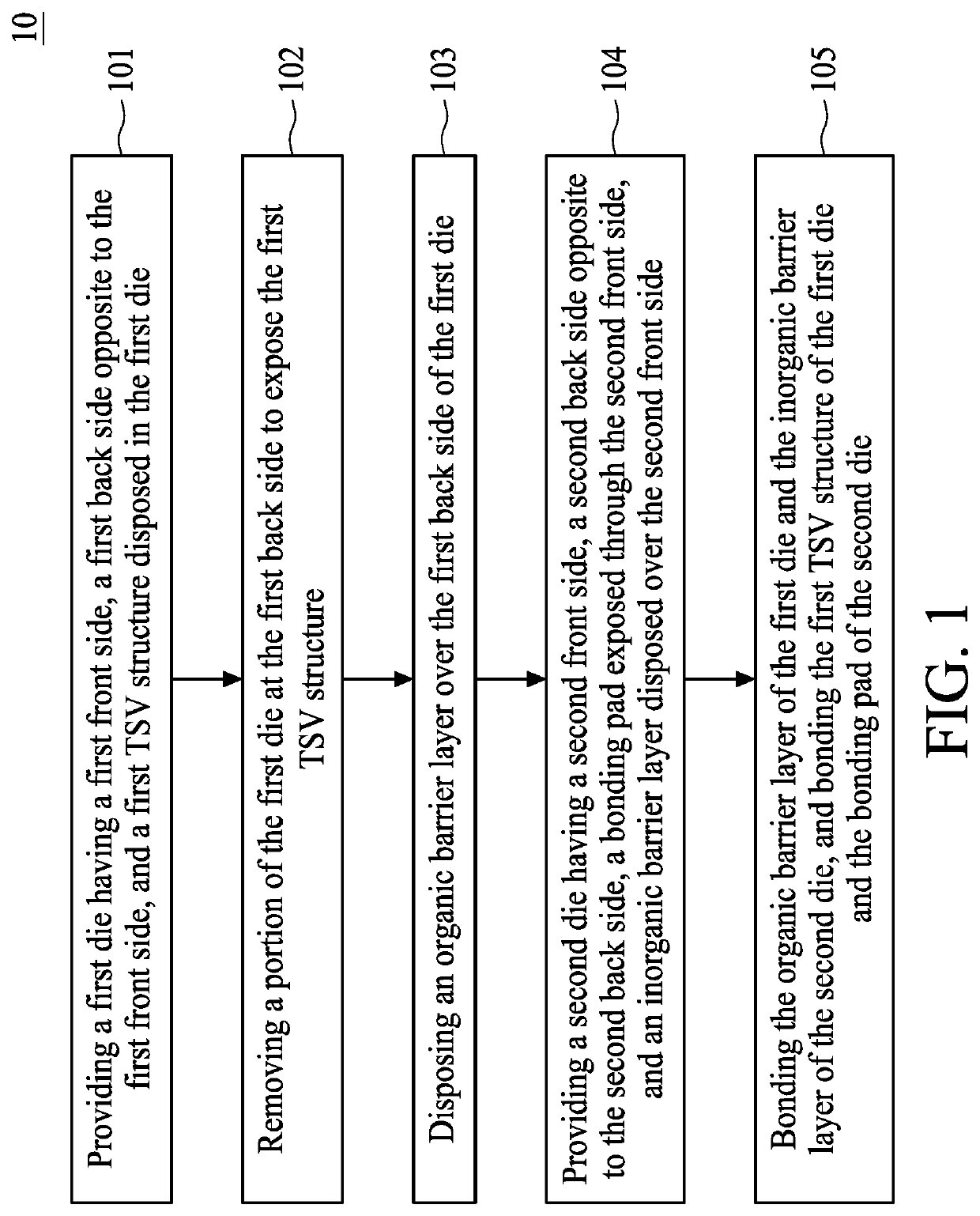
ActiveUS20200303361A1Prevent metal diffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageEngineering physics
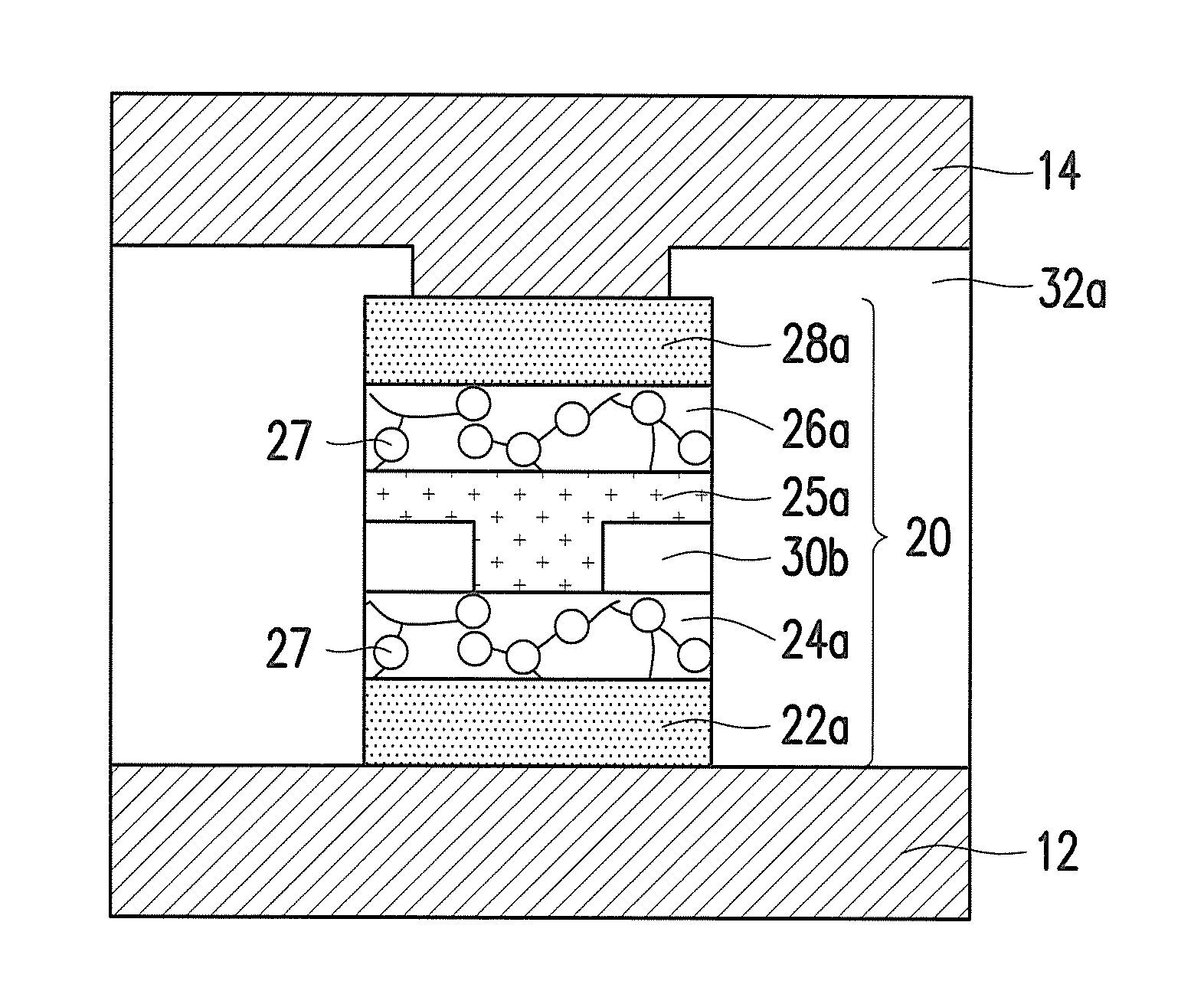
The present disclosure provides a semiconductor package structure. The semiconductor package structure includes a first die, a second die and a hybrid bonding structure disposed between the first die and the second die. The first die includes a first front side and a first back side opposite to the first front side. The second die includes a second front side and a second back side opposite to the second front side. The hybrid bonding structure is disposed between the first back side of the first die and the second front side of the second die. The first die and the second die are bonded to each other by the hybrid bonding structure. The hybrid bonding structure includes an organic barrier layer and an inorganic barrier layer bonded to each other.
Owner:NAN YA TECH
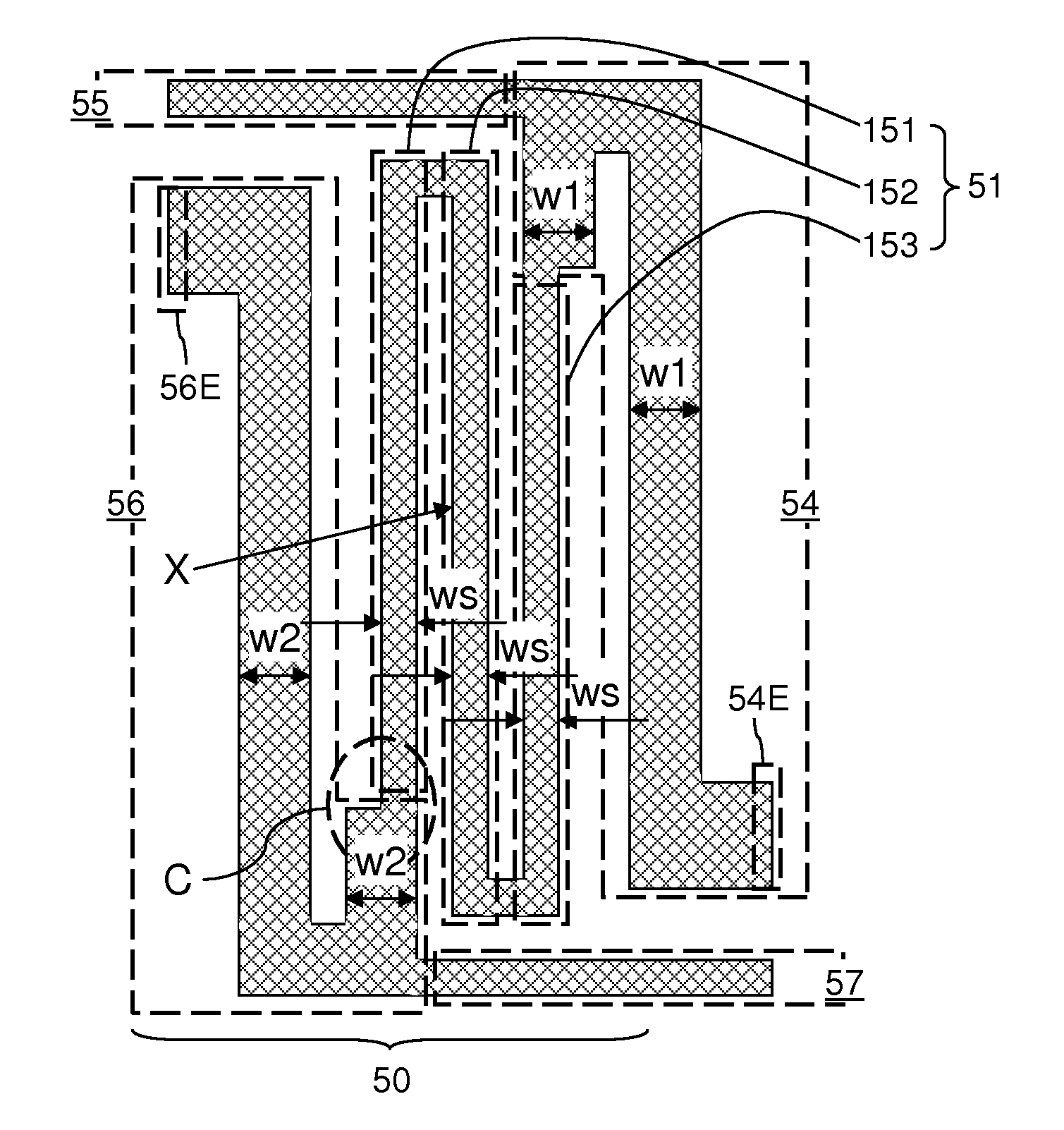
Structure of TFT electrode for preventing metal layer diffusion and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS20050274947A1Prevent metal diffusionReduce riskTransistorSubstation/switching arrangement detailsGas phaseActive layer
The invention provides a TFT electrode structure and its manufacturing method that can prevent metal diffusion occurring in the fabrication of a TFT, and thereby reduce the risk of contamination of the chemical vapor deposition process due to metallic ion diffusion. The transparent pixel electrode is formed after the gate electrode metal so that the pixel transparent electrode can be used as a barrier layer to prevent metal diffusion under high temperature from the gate electrode metal to adjacent insulating layers or the active layer. Further, the method used to form the transparent pixel electrode is a low-temperature physical vapor deposition process, which affected less by the processing environment, and the transparent pixel electrode is a conductive layer that is not affected by metal diffusion.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP +7
Solid-state imaging device and method for making the same
InactiveUS20060145346A1Capacitance be generateReduce light reflectionTelevision system detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-stateEngineering
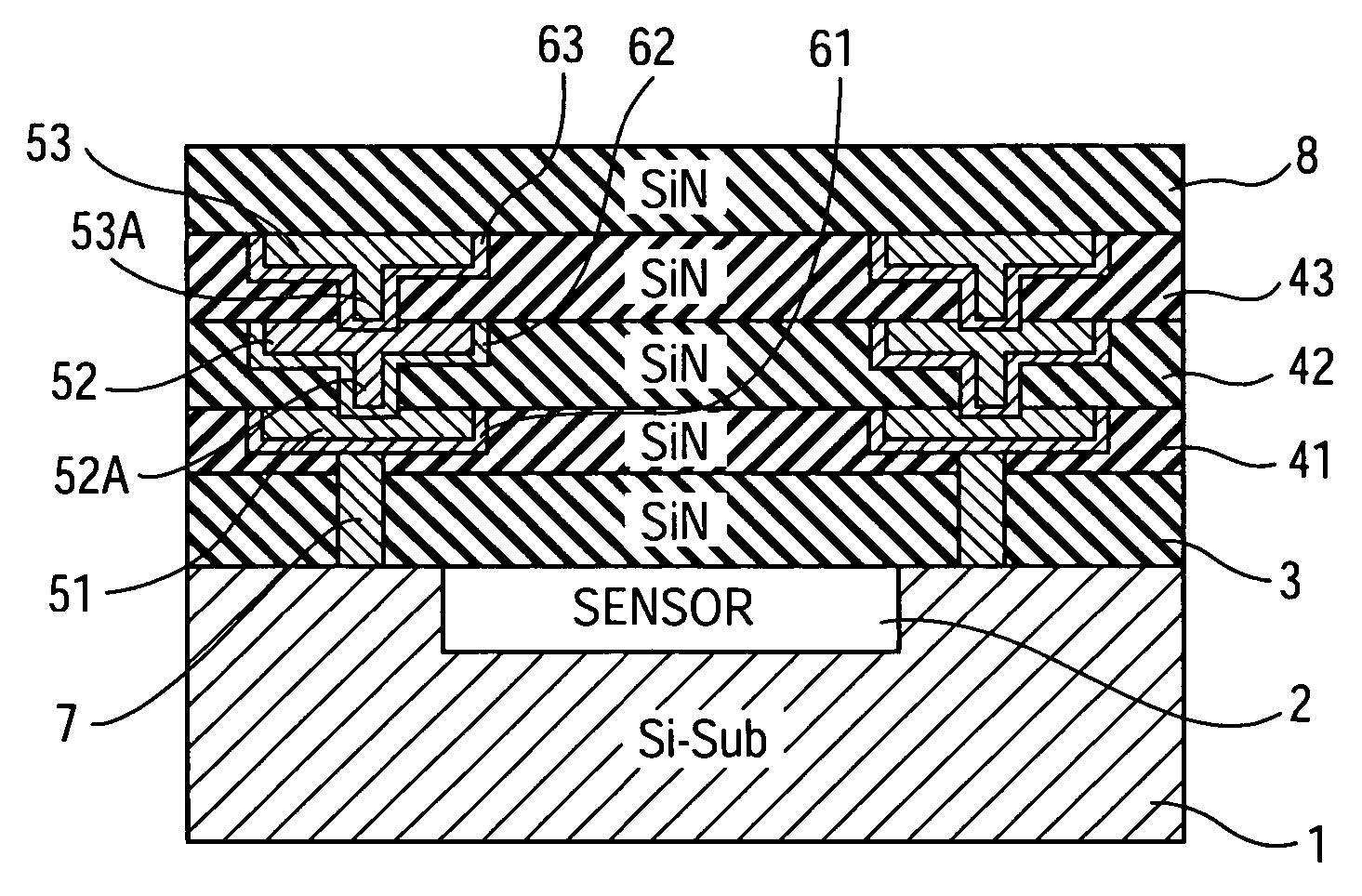
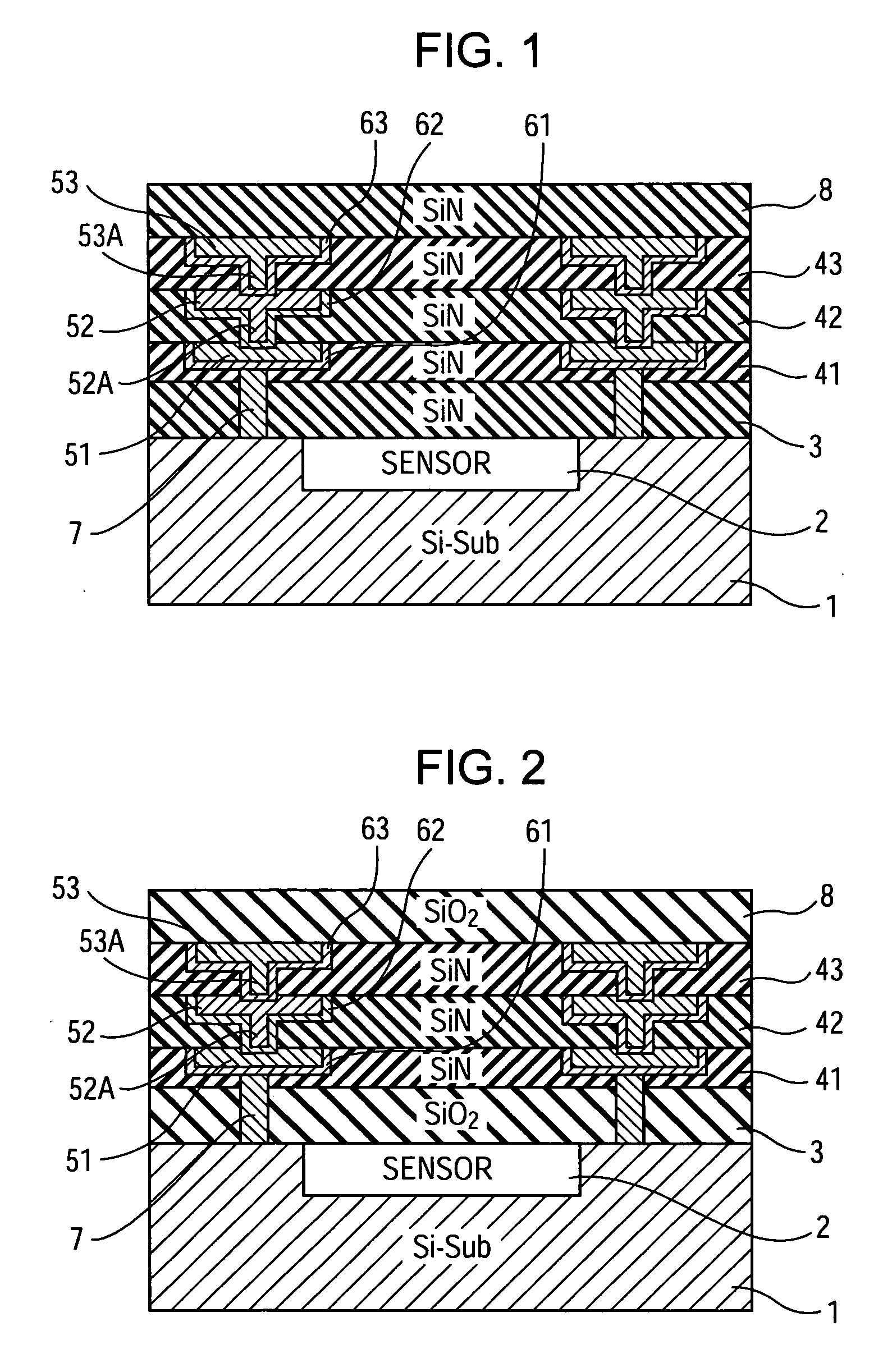
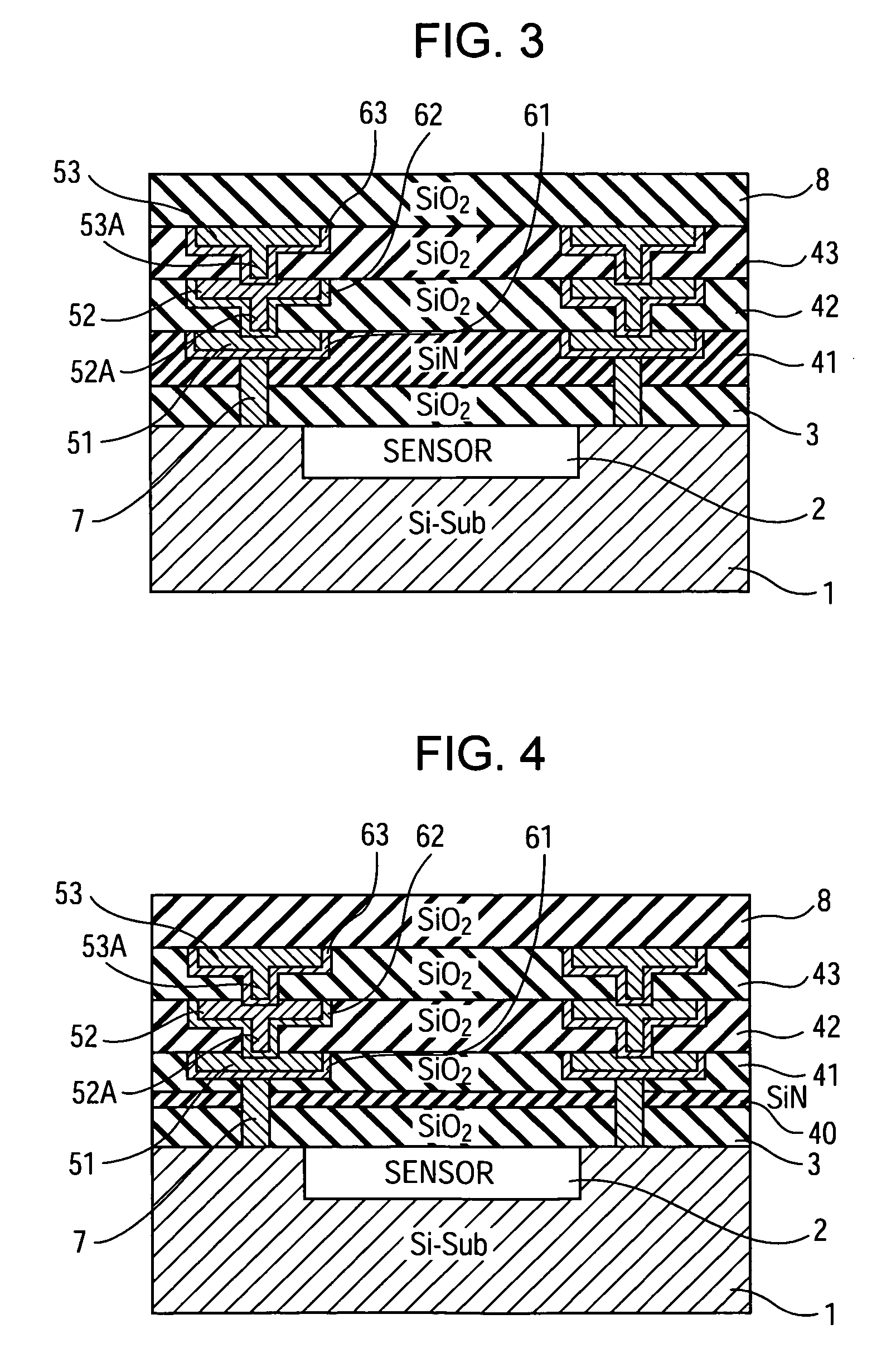
A solid-state imaging device includes a semiconductor substrate, one or more wiring interlayer films disposed on or above the semiconductor substrate, and one or more metal wires embedded in the wiring interlayer films. The one or more wiring interlayer films are composed of a diffusion preventing material that prevents the diffusion of the metal wire.
Owner:SONY CORP
Sensor element of a gas sensor
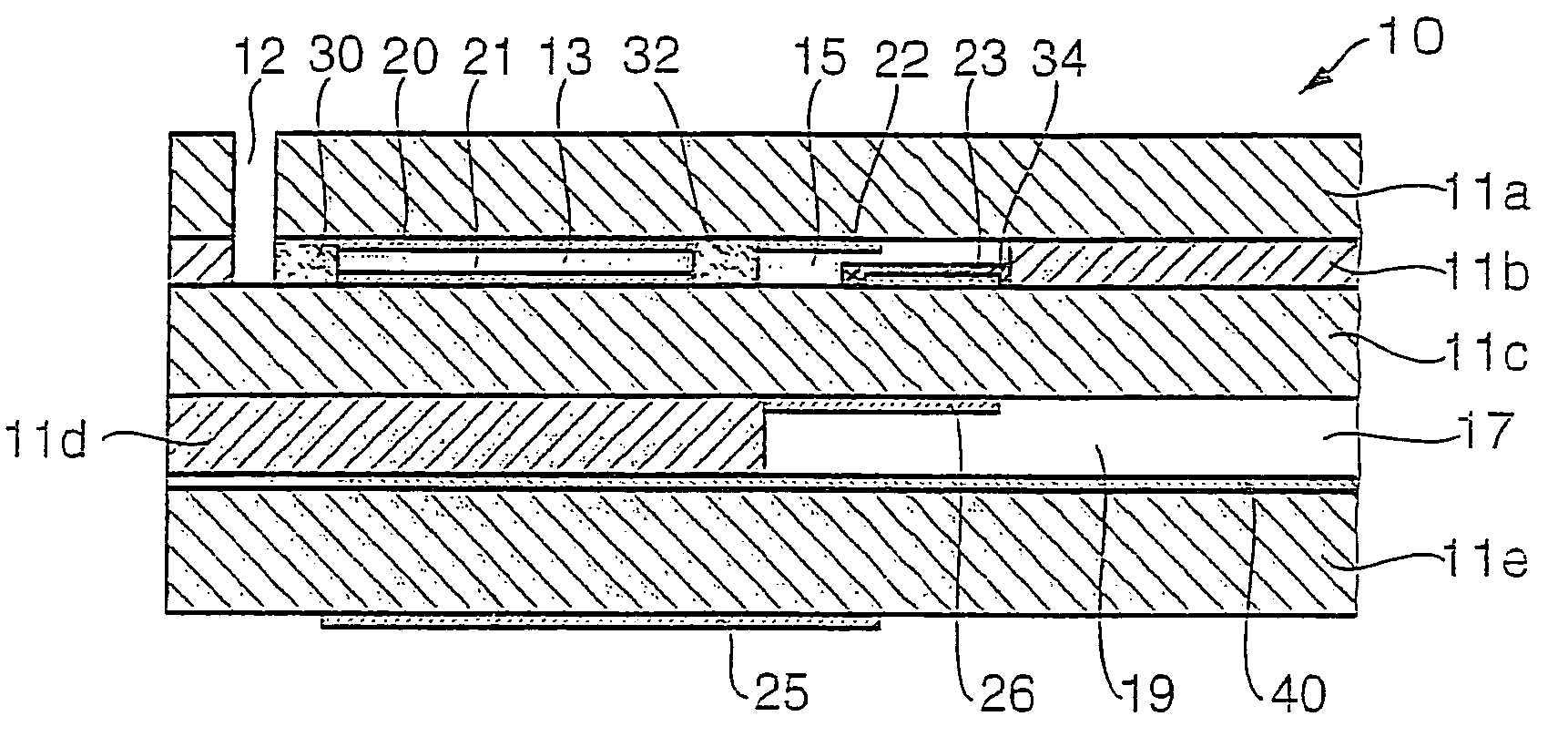
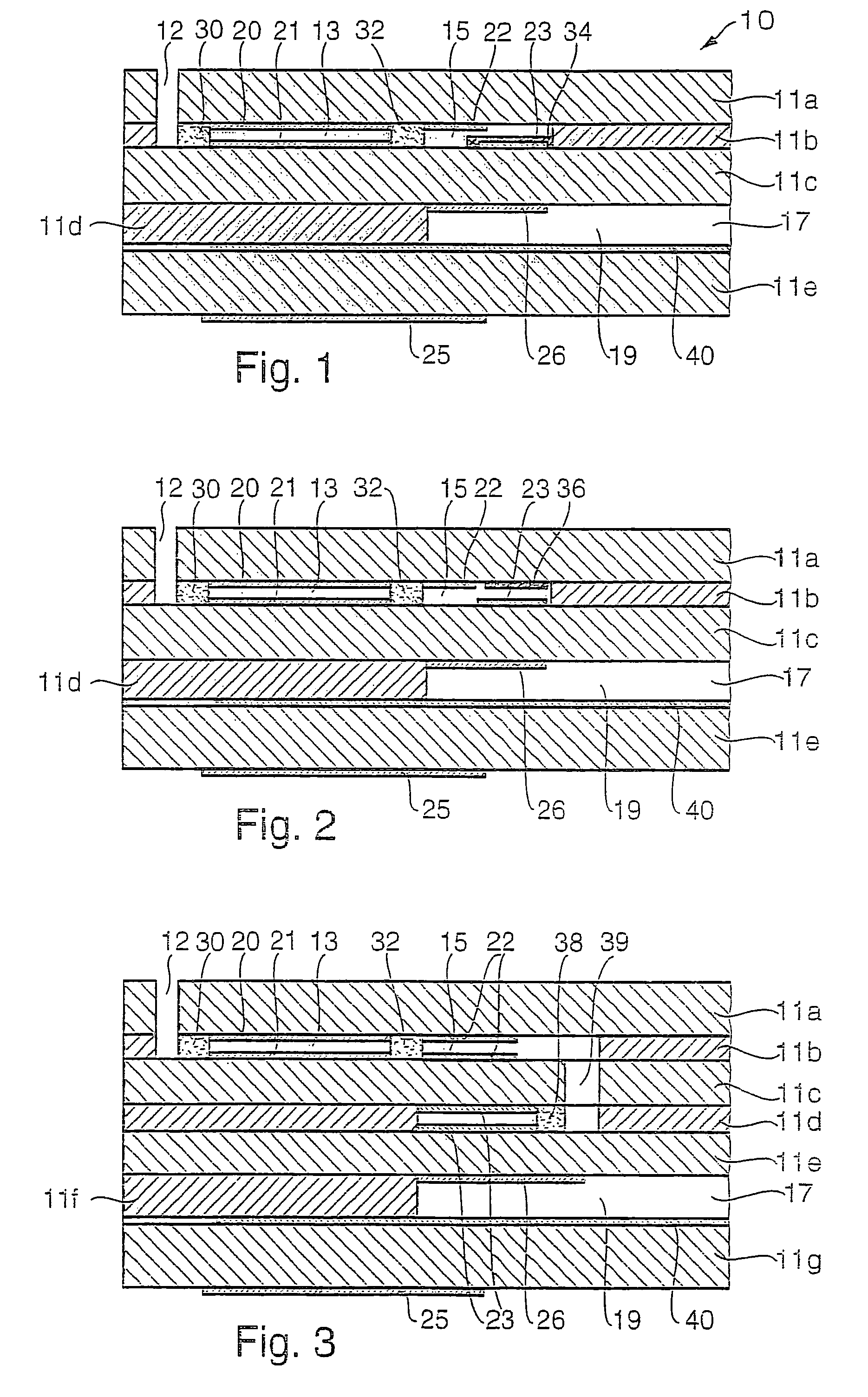
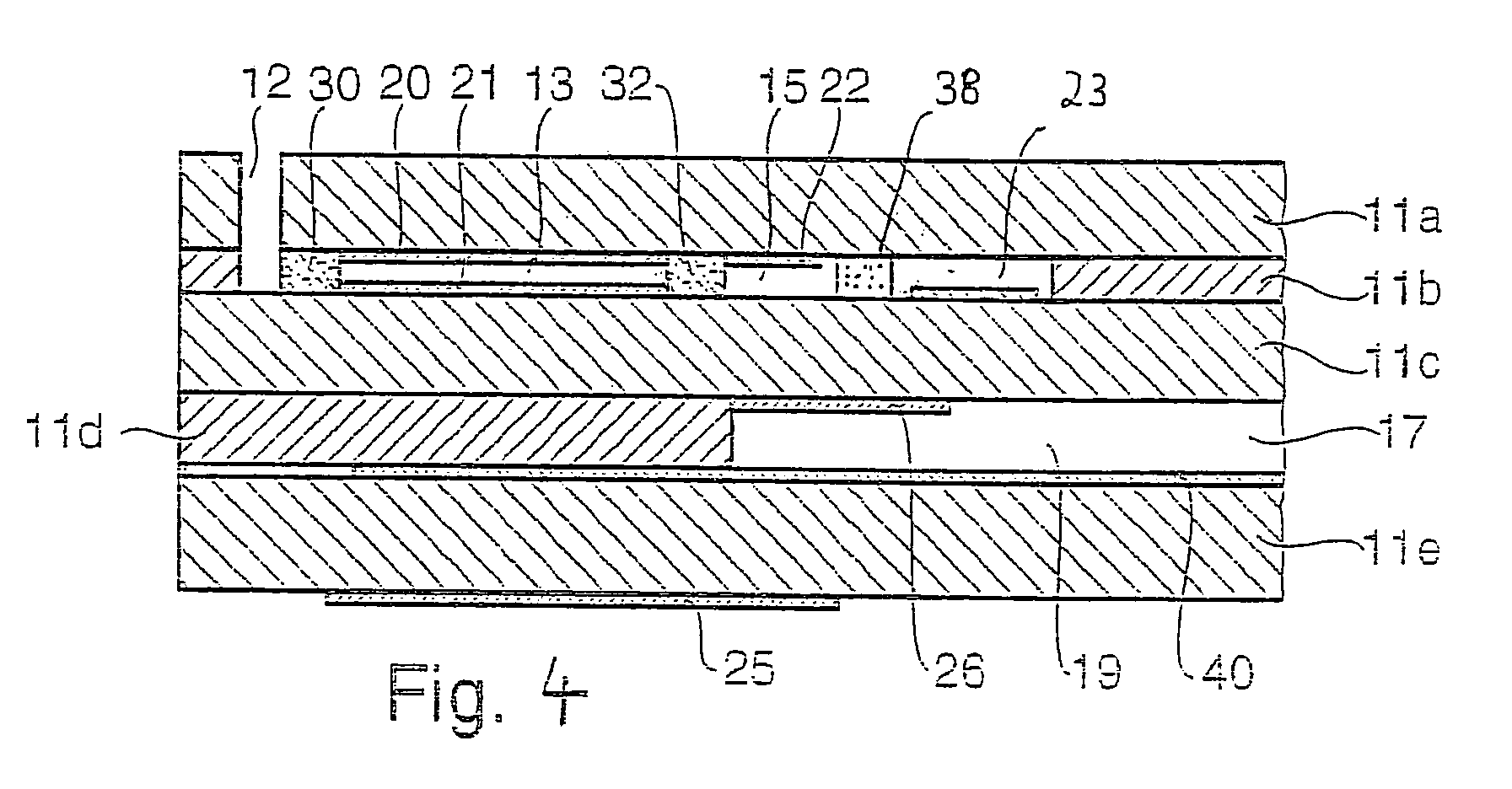
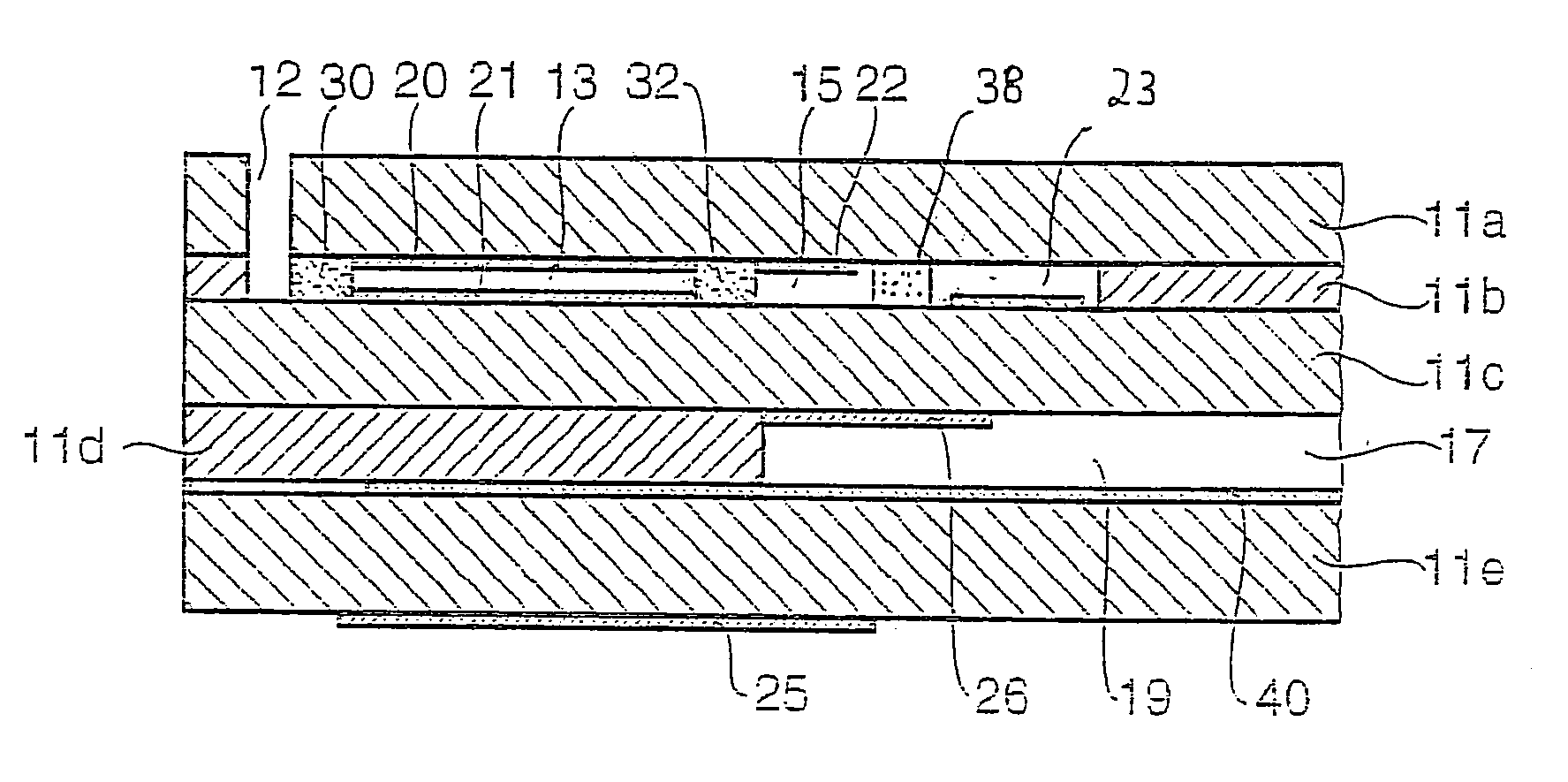
InactiveUS7037415B2Prevent metal diffusionHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesDiffusionCombustion
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Sensor element of a gas sensor
InactiveUS20040089054A1Prevent metal diffusionHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTesting metalsExhaust gasDiffusion
A sensor element of a gas sensor is described, this sensor being used to determine the concentration of at least one component of a gas mixture, in particular in exhaust gases of internal combustion engines. It includes at least two electrodes (22, 23) which are situated in an internal gas space (15) which is in direct contact with the gas mixture, the one electrode (22) containing a first material and the second electrode (23) containing a second material. The internal gas space (15) contains a means (34, 26, 38, 39) which acts physically and / or chemically to prevent diffusion of metal between the electrodes (22, 23).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Single metal damascene structure and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20130299990A1Reduce contact resistanceImprove equipment reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAlloyCopper
A single metal damascene structure including an insulating layer, a metal filling layer and a barrier layer is provided. The insulating layer has an opening therein, and the metal filling layer is positioned in the opening. The barrier layer is located between the filling metal layer and the insulating layer. The material of the barrier layer includes an alloy, and the ally includes a copper element and at least one another metal.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Systems and methods for preparing films comprising metal using sequential ion implantation, and films formed using same
ActiveUS20120235281A1Inhibits diffusion of metalControl of reactionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingChemistryElectrically conductive
Systems and methods for preparing films comprising metal using sequential ion implantation, and films formed using same, are provided herein. A structure prepared using ion implantation may include a substrate; an embedded structure having pre-selected characteristics; and a film within or adjacent to the embedded structure. The film comprises a metal having a perturbed arrangement arising from the presence of the embedded structure. The perturbed arrangement may include metal ions that coalesce into a substantially continuous, electrically conductive metal layer, or that undergo covalent bonding, whereas in the absence of the embedded structure the metal ions instead may be free to diffuse through the substrate. The embedded structure may control the diffusion of the metal through the substrate and / or the reaction of the metal within the substrate.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Method of drying coating film formed on pet film surface and coating film drying furnace
ActiveUS20130219738A1Avoid temperature riseIncrease temperatureDrying solid materials with heatPretreated surfacesOrganic solventMetallurgy
A method of drying a coating film formed on a surface of a PET film includes radiating an infrared ray having a dominant wavelength of 3.5 μm or less from an infrared heater onto a PET film on whose surface the coating film containing water or an organic solvent having an absorption spectrum of 3.5 μm or less has been formed, where the infrared heater has a structure such that an outer circumference of a filament is covered with a protection tube, and a partition wall for forming a flow passageway of a cooling fluid that restrains rise in temperature of a heater surface is provided in a space surrounding this protection tube, and bringing cooling air into contact with the surface of the PET film / coating film has been formed, so as to dry the PET film at a temperature lower than a glass transition point of the PET film.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Structure of TFT electrode for preventing metal layer diffusion and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS7045817B2Reduce riskLess affectedTransistorSubstation/switching arrangement detailsDiffusionEnvironment effect
The invention provides a TFT electrode structure and its manufacturing method that can prevent metal diffusion occurring in the fabrication of a TFT, and thereby reduce the risk of contamination of the chemical vapor deposition process due to metallic ion diffusion. The transparent pixel electrode is formed after the gate electrode metal so that the pixel transparent electrode can be used as a barrier layer to prevent metal diffusion under high temperature from the gate electrode metal to adjacent insulating layers or the active layer. Further, the method used to form the transparent pixel electrode is a low-temperature physical vapor deposition process, which affected less by the processing environment, and the transparent pixel electrode is a conductive layer that is not affected by metal diffusion.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP +7
Metal/ceramic bonding substrate and method for producing same
ActiveUS20140057131A1Improve thermal conductivityPrevent metal diffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsMetalCeramic substrate
A metal / ceramic bonding substrate includes: a ceramic substrate; a metal plate bonded directly to one side of the ceramic substrate; a metal base plate bonded directly to the other side of the ceramic substrate; and a reinforcing member having a higher strength than that of the metal base plate, the reinforcing member being arranged so as to extend from one of both end faces of the metal base plate to the other end face thereof without interrupting that the metal base plate extends between a bonded surface of the metal base plate to the ceramic substrate and the opposite surface thereof.
Owner:DOWA METALTECH CO LTD
Apparatus for preparation of silicon crystals with reduced metal content
InactiveUS20070074653A1Reduce metal pollutionAvoid Metal ContaminationAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthIngotMetal contamination
A crystal pulling apparatus for producing a silicon crystal ingot having a reduced amount of metal contamination. The apparatus includes a growth chamber and a component disposed within the growth chamber having a protective layer of silicon nitride for preventing metal contamination of the crystal.
Owner:MEMC ELECTONIC MATERIALS INC
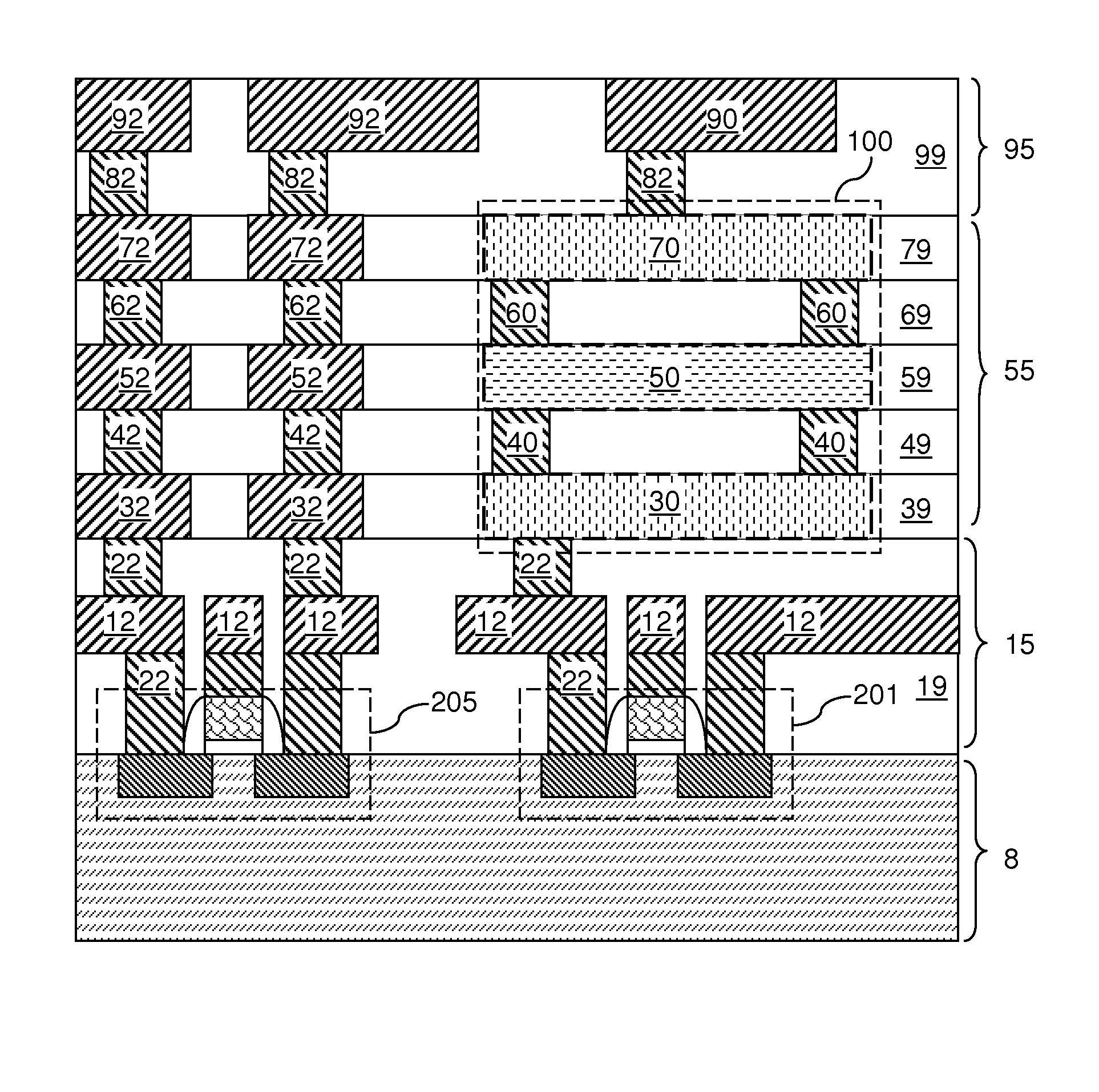
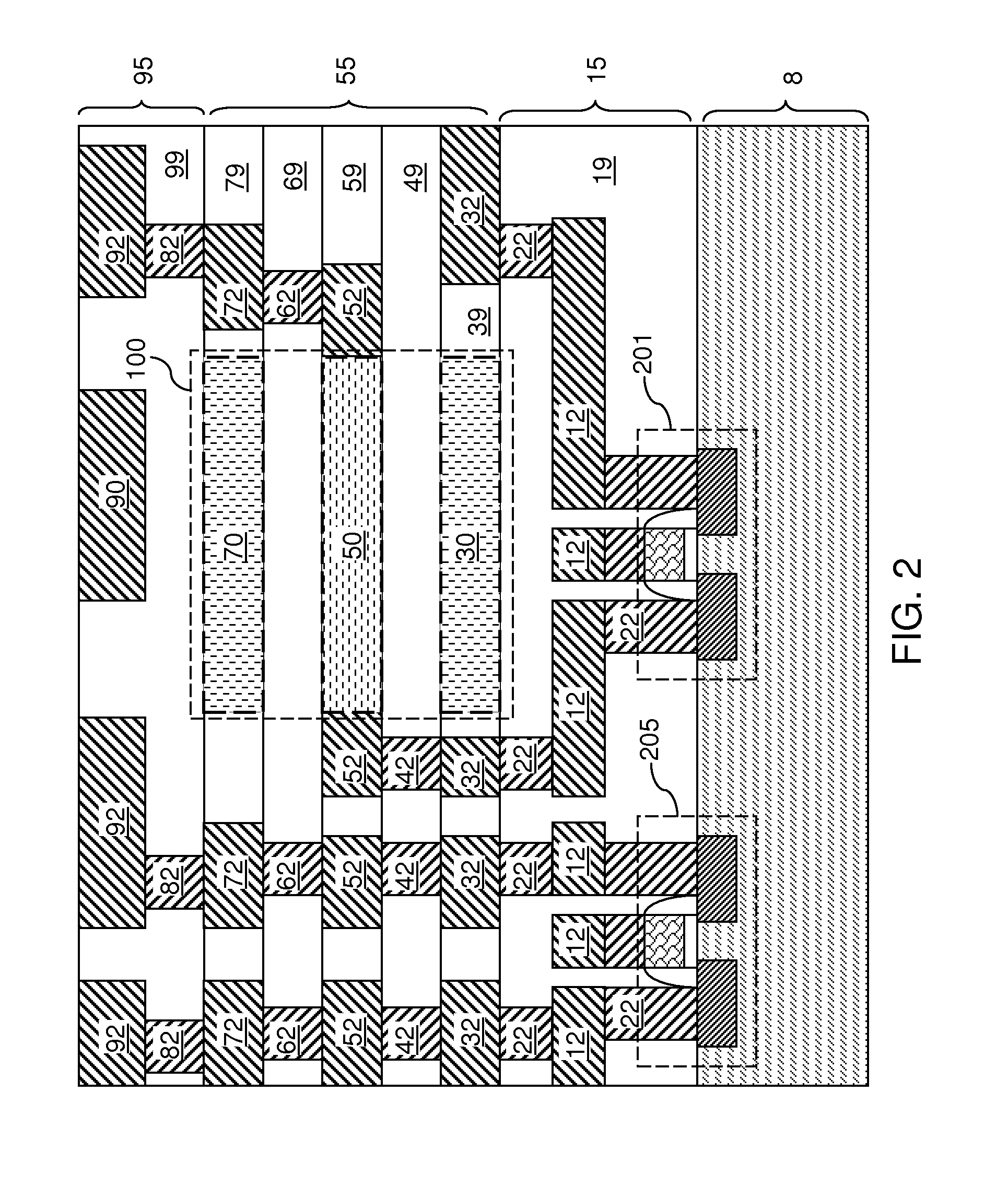
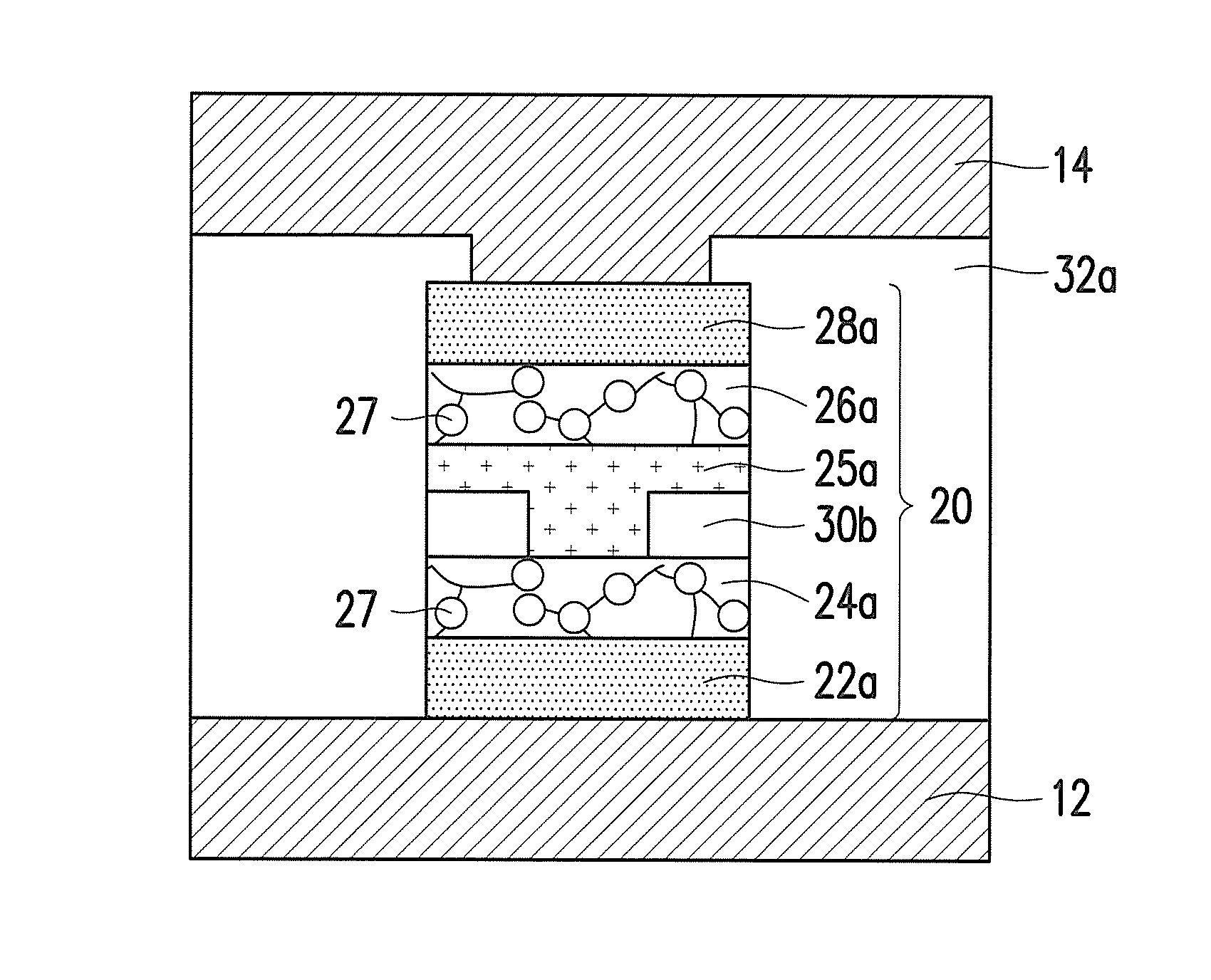
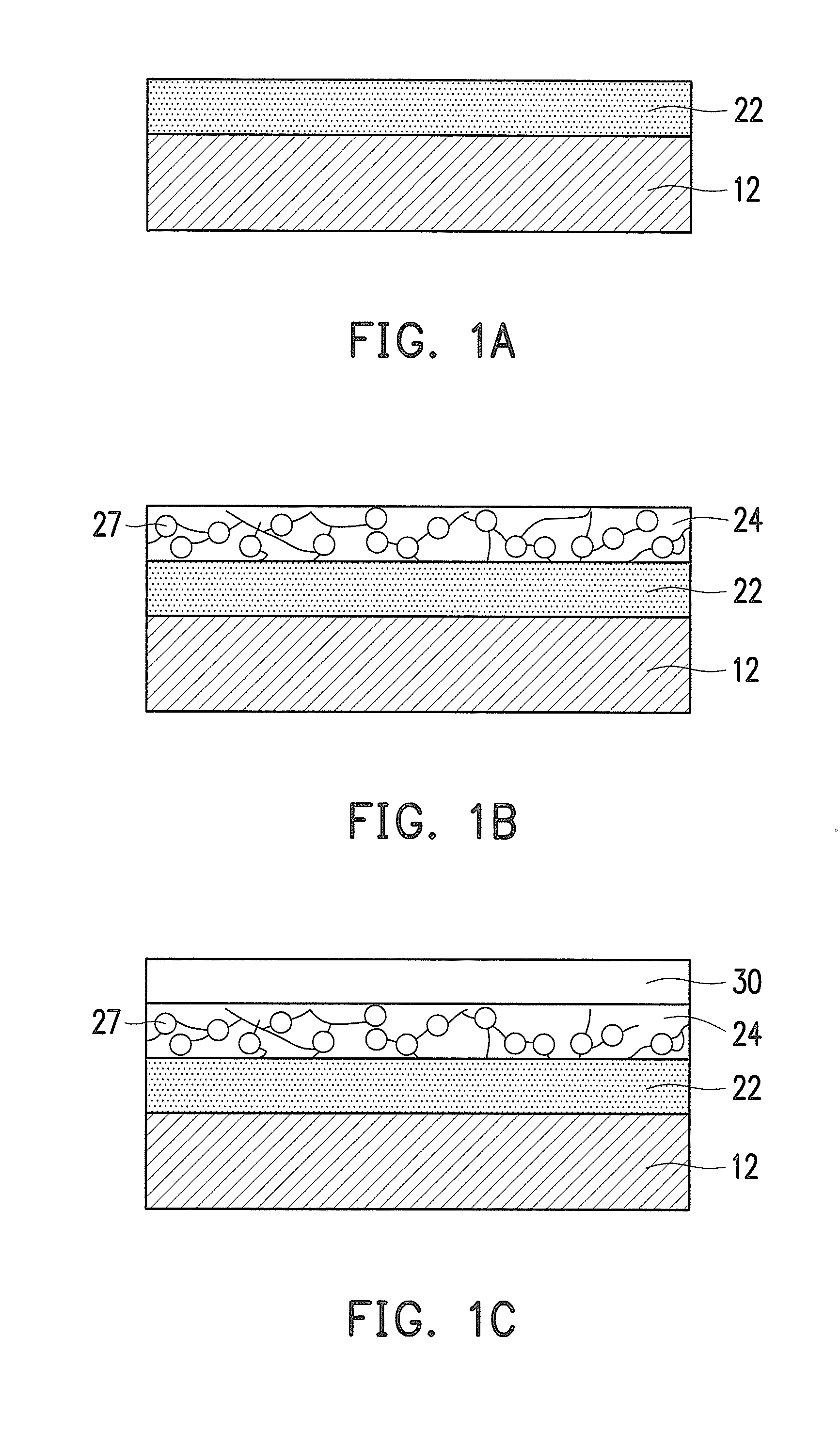
Memory device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20160197272A1Prevent metal diffusionImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBulk negative resistance effect devicesDiffusion barrierPhase change
A memory device is provided. A first conductive layer, a first diffusion barrier layer, a phase change layer, a second diffusion barrier layer and a second conductive layer are disposed on a first electrode layer in sequence to form a stacking structure. A dielectric layer is disposed on the first electrode layer and covers a sidewall of the stacking structure and part of a top surface of the second conductive layer. A second electrode layer is disposed on the dielectric layer and the second conductive layer. Barrier enhancing components are provided between a bottom surface of the first diffusion barrier layer and a top surface of the second diffusion barrier layer. Further, a method of manufacturing a memory device is provided.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Hydrogen permeable membrane, fuel cell and hydrogen extracting apparatus equipped with the hydrogen permeable membrane, and method of manufacturing the hydrogen permeable membrane
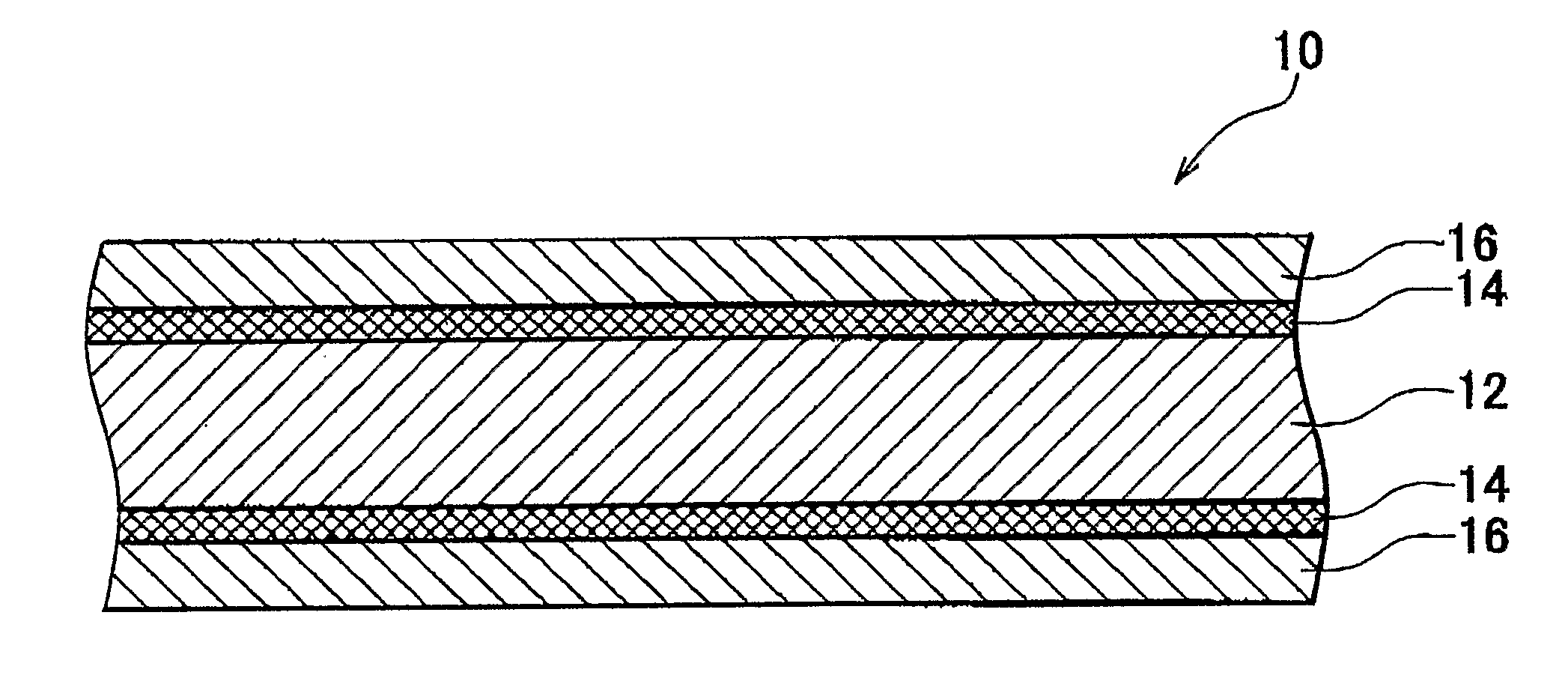
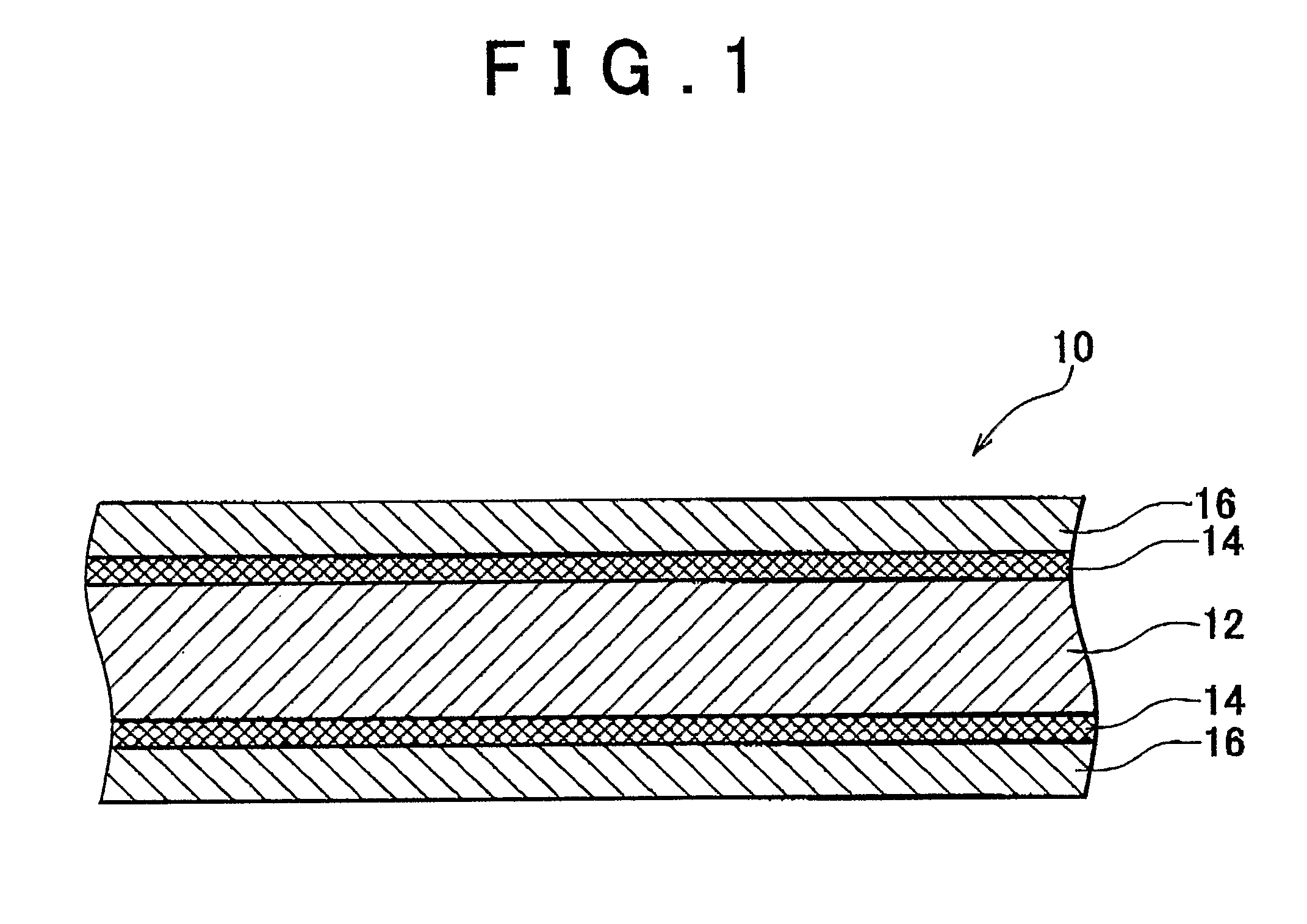
A hydrogen permeable membrane (10) for selectively allowing hydrogen to permeate therethrough includes a metal base layer (12) containing vanadium (V), a metal coating layer (16) containing palladium (Pd), and an intermediate layer (14) that is formed between the metal base layer (12) and the metal coating layer (16) and made of a metal having a higher melting point than the metal base layer (12) and the metal coating layer (16) and possessing hydrogen permeability.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing same
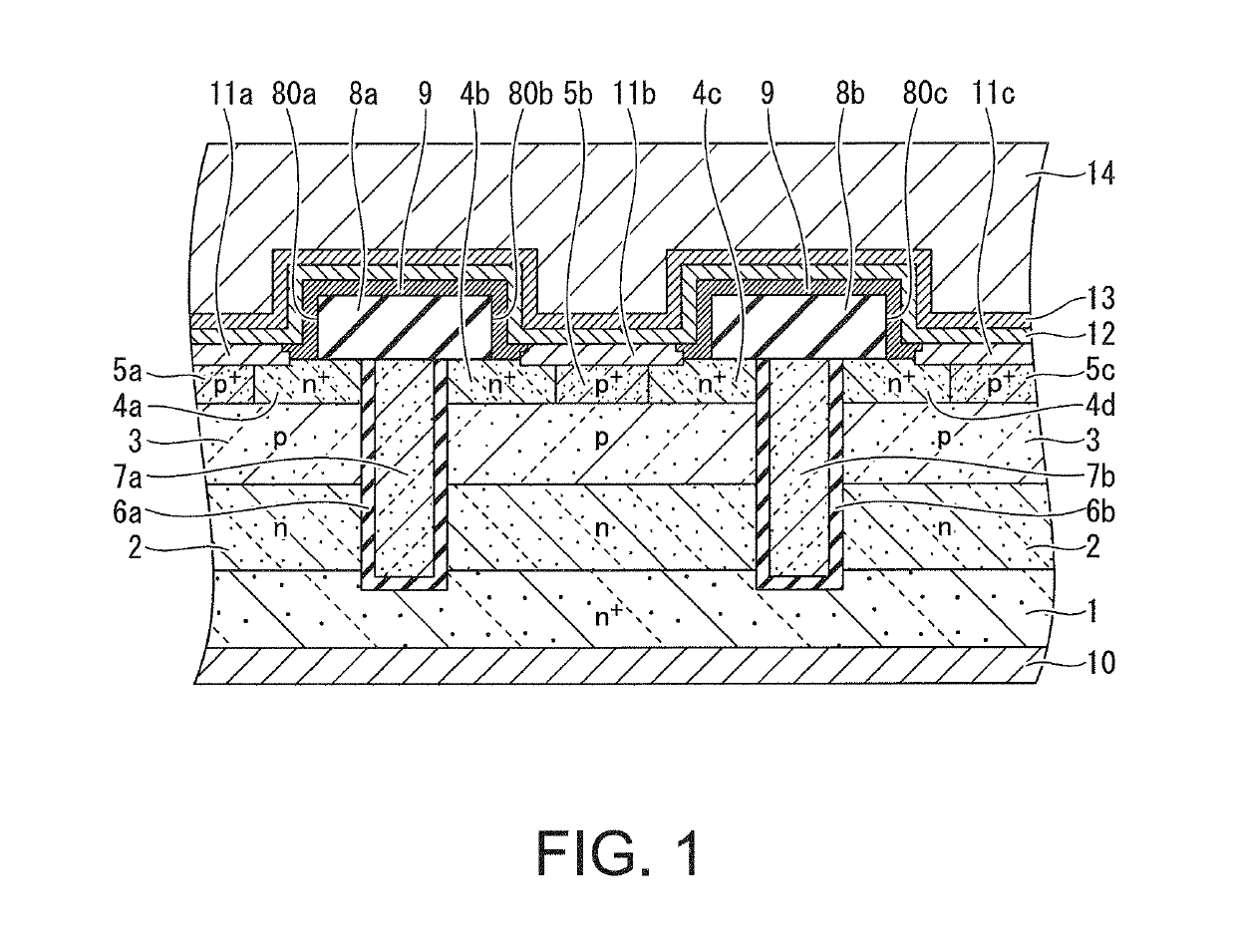
ActiveUS20190115439A1Stable electrical characteristicsImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceOhmic contact
A semiconductor device includes a first barrier film covering the main surface of the active region and the insulating film layer, the first barrier film having an ohmic contact hole that exposes a contact portion of the ohmic contact formation region within the window of the insulating film layer; a base contact layer filled into the ohmic contact hole and making ohmic contact with the contact portion of the ohmic contact formation region; a second barrier film made of titanium, covering the base contact layer and the first barrier film; and a third barrier film made of titanium oxide and titanium nitride, covering a surface of the second barrier film.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Self-assembled monolayers as sacrificial capping layers
PendingUS20210175118A1Prevent metal diffusionAvoid contaminationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryEngineering
A substrate processing method includes providing a substrate containing a metal surface and a dielectric material surface, selectively forming a sacrificial capping layer containing a self-assembled monolayer on the metal surface, removing the sacrificial capping layer to restore the metal surface, and processing the restored metal surface and the dielectric material surface. The sacrificial capping layer may be used to prevent metal diffusion into the dielectric material and to prevent oxidation and contamination of the metal surface while waiting for further processing of the substrate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method for producing piezoelectric actuator
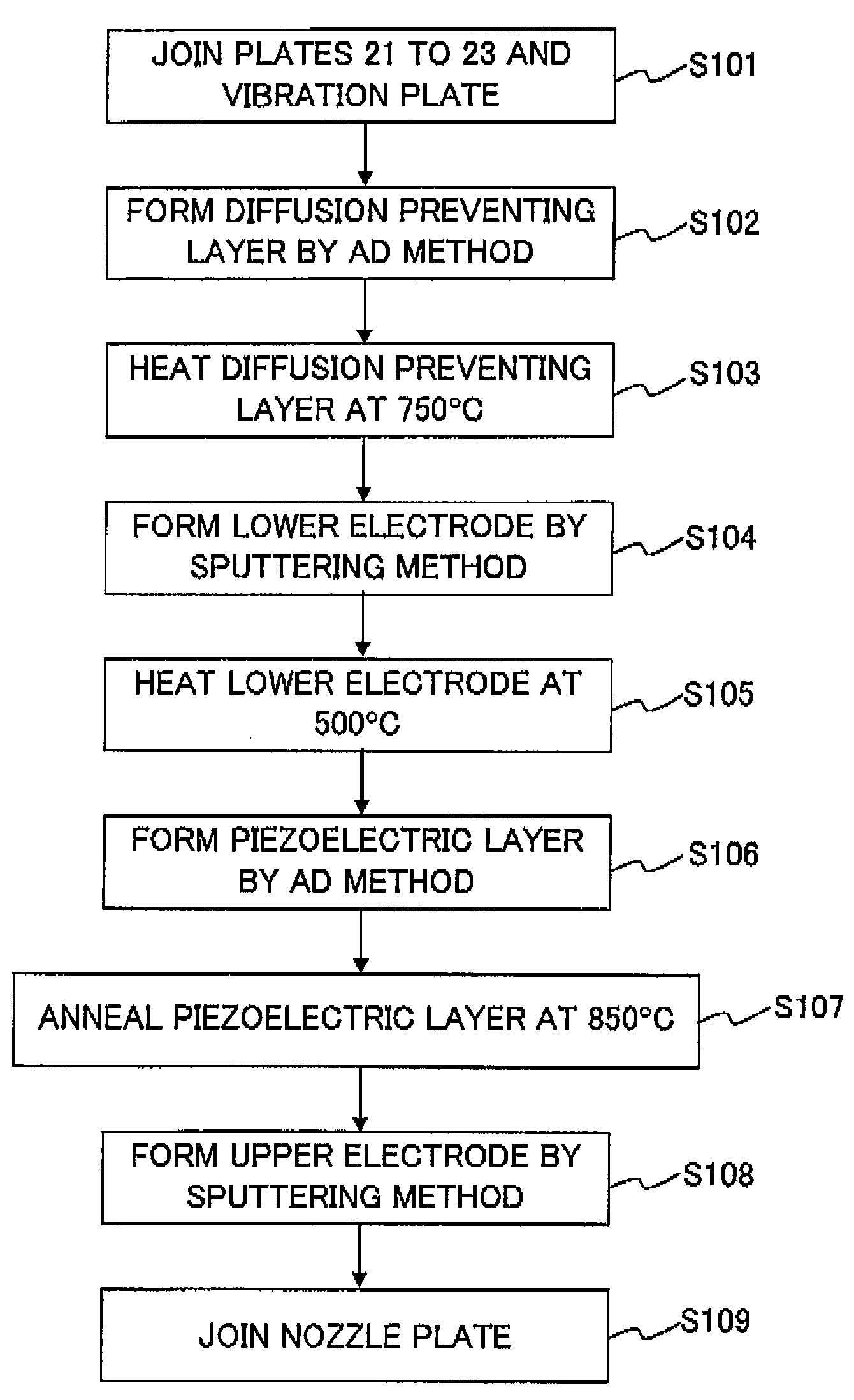
ActiveUS20080235927A1Avoid crackingPrevent peelingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksPiezoelectric actuatorsMetallic materials
A method for producing a piezoelectric actuator includes forming a diffusion preventing layer on one surface of a substrate formed of a metallic material for preventing a diffusion of a metal from the substrate, heating a diffusion preventing layer at a first temperature in order to relieve a residual stress in the diffusion preventing layer, forming an electrode on a surface of the diffusion preventing layer, the surface not facing the substrate, forming a piezoelectric layer of a piezoelectric material on a surface of the electrode, the surface not facing the diffusion preventing layer, and annealing the piezoelectric layer at a second temperature. Accordingly, it is possible to prevent the electrode from being exfoliated from the diffusion preventing layer. Moreover, it is possible to prevent a crack being developed in the piezoelectric layer.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
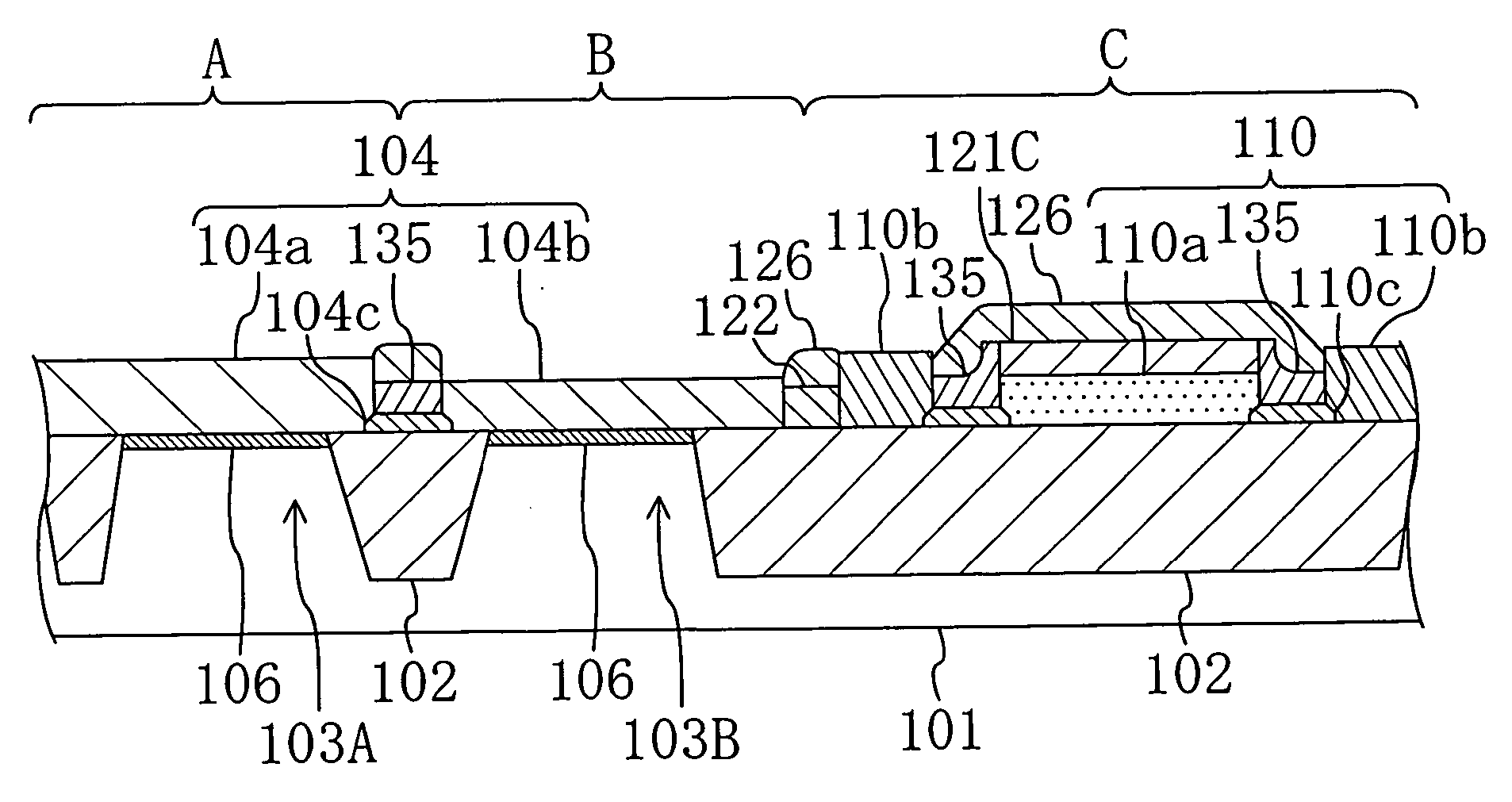
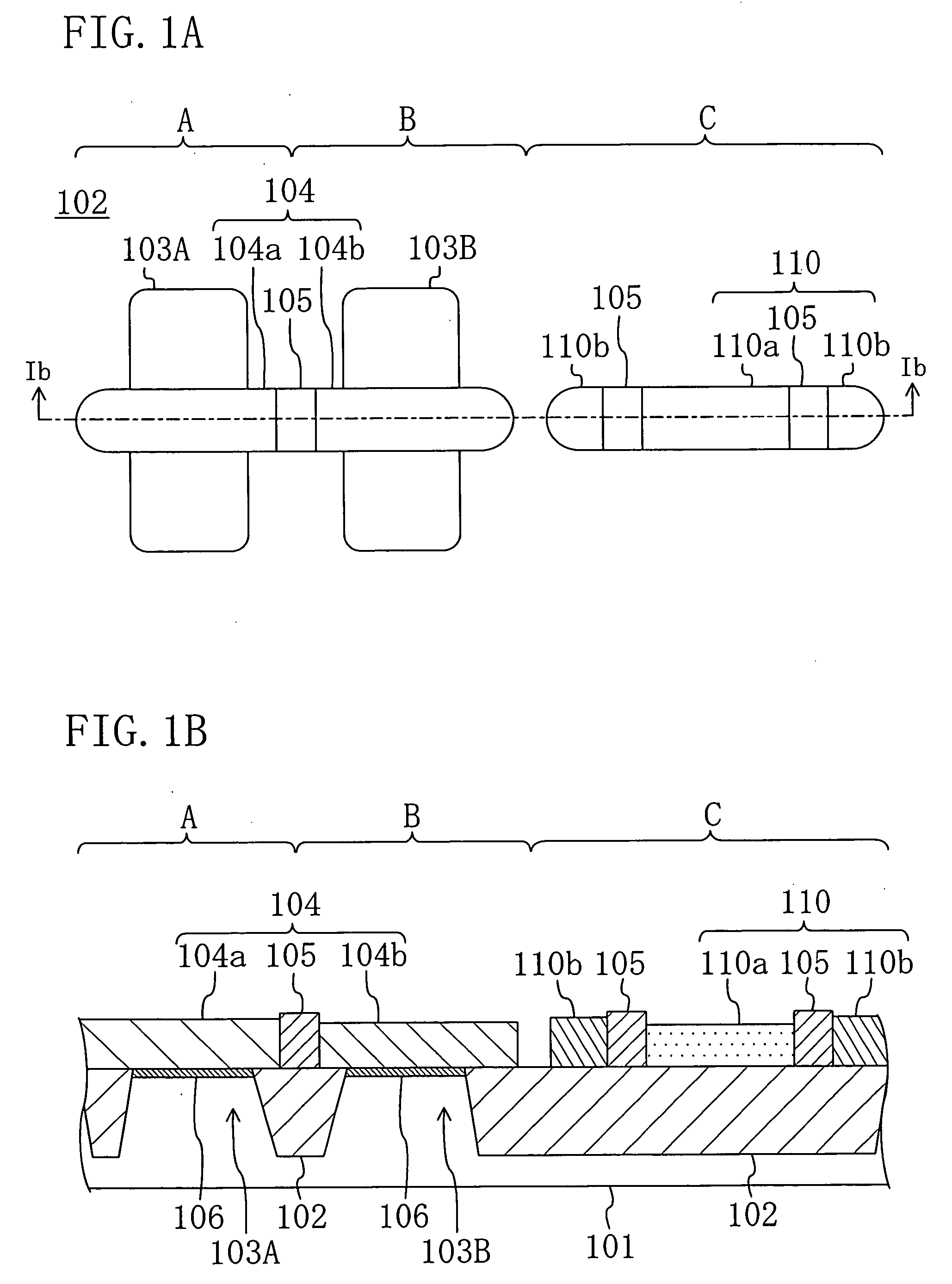
Semiconductor package including hybrid bonding structure and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS10910357B2Prevent metal diffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageEngineering physics
The present disclosure provides a semiconductor package structure. The semiconductor package structure includes a first die, a second die and a hybrid bonding structure disposed between the first die and the second die. The first die includes a first front side and a first back side opposite to the first front side. The second die includes a second front side and a second back side opposite to the second front side. The hybrid bonding structure is disposed between the first back side of the first die and the second front side of the second die. The first die and the second die are bonded to each other by the hybrid bonding structure. The hybrid bonding structure includes an organic barrier layer and an inorganic barrier layer bonded to each other.
Owner:NAN YA TECH
Memory device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9455404B2Prevent metal diffusionImprove reliabilityElectrical apparatusDiffusion barrierPhase change
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Method for producing piezoelectric actuator
ActiveUS9186898B2Avoid crackingPrevent peelingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksPiezoelectric actuatorsMetallic materials
A method for producing a piezoelectric actuator includes forming a diffusion preventing layer on one surface of a substrate formed of a metallic material for preventing a diffusion of a metal from the substrate, heating a diffusion preventing layer at a first temperature in order to relieve a residual stress in the diffusion preventing layer, forming an electrode on a surface of the diffusion preventing layer, the surface not facing the substrate, forming a piezoelectric layer of a piezoelectric material on a surface of the electrode, the surface not facing the diffusion preventing layer, and annealing the piezoelectric layer at a second temperature. Accordingly, it is possible to prevent the electrode from being exfoliated from the diffusion preventing layer. Moreover, it is possible to prevent a crack being developed in the piezoelectric layer.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Manufacturing method for semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090061637A1Simple manufacturing methodIncrease the number ofSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorMetal
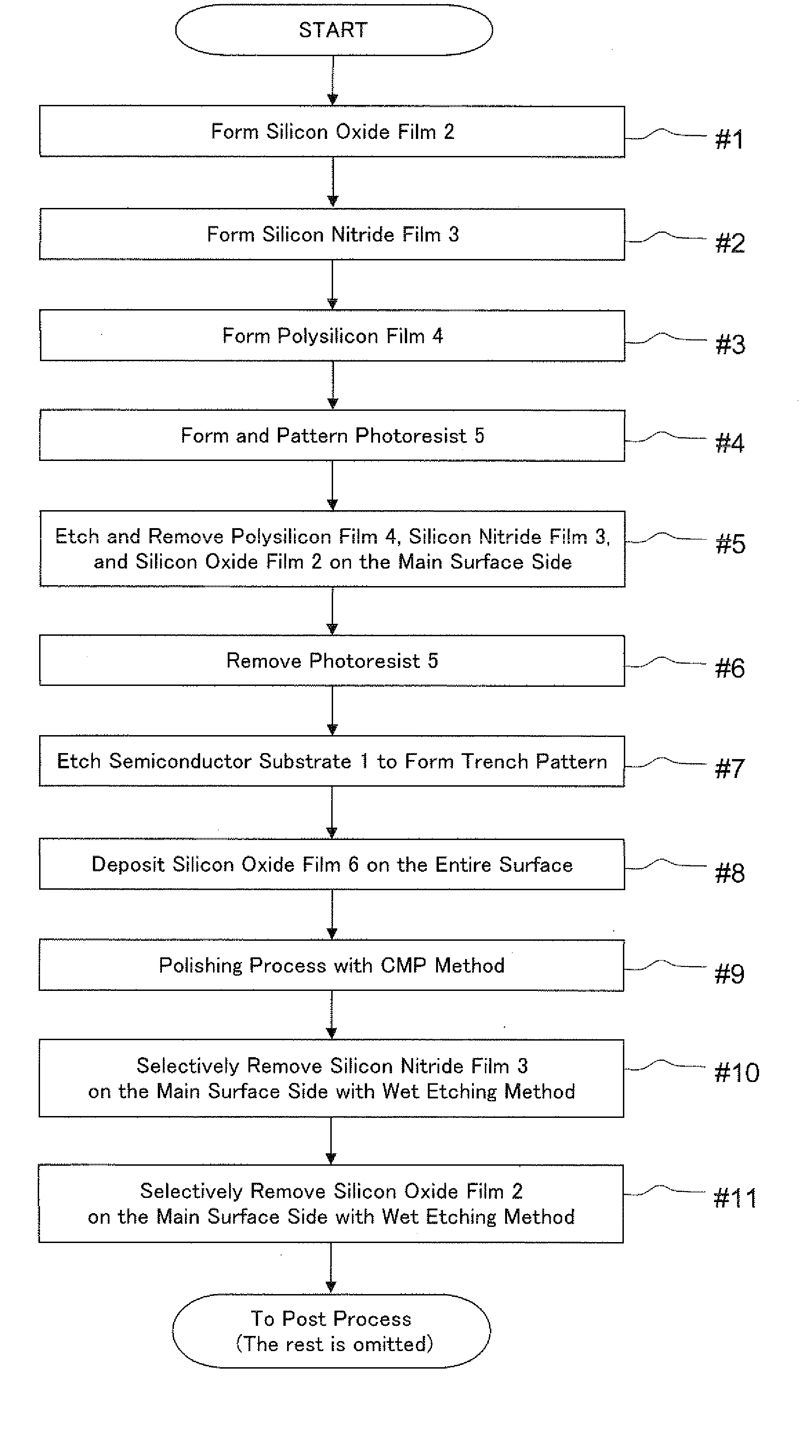
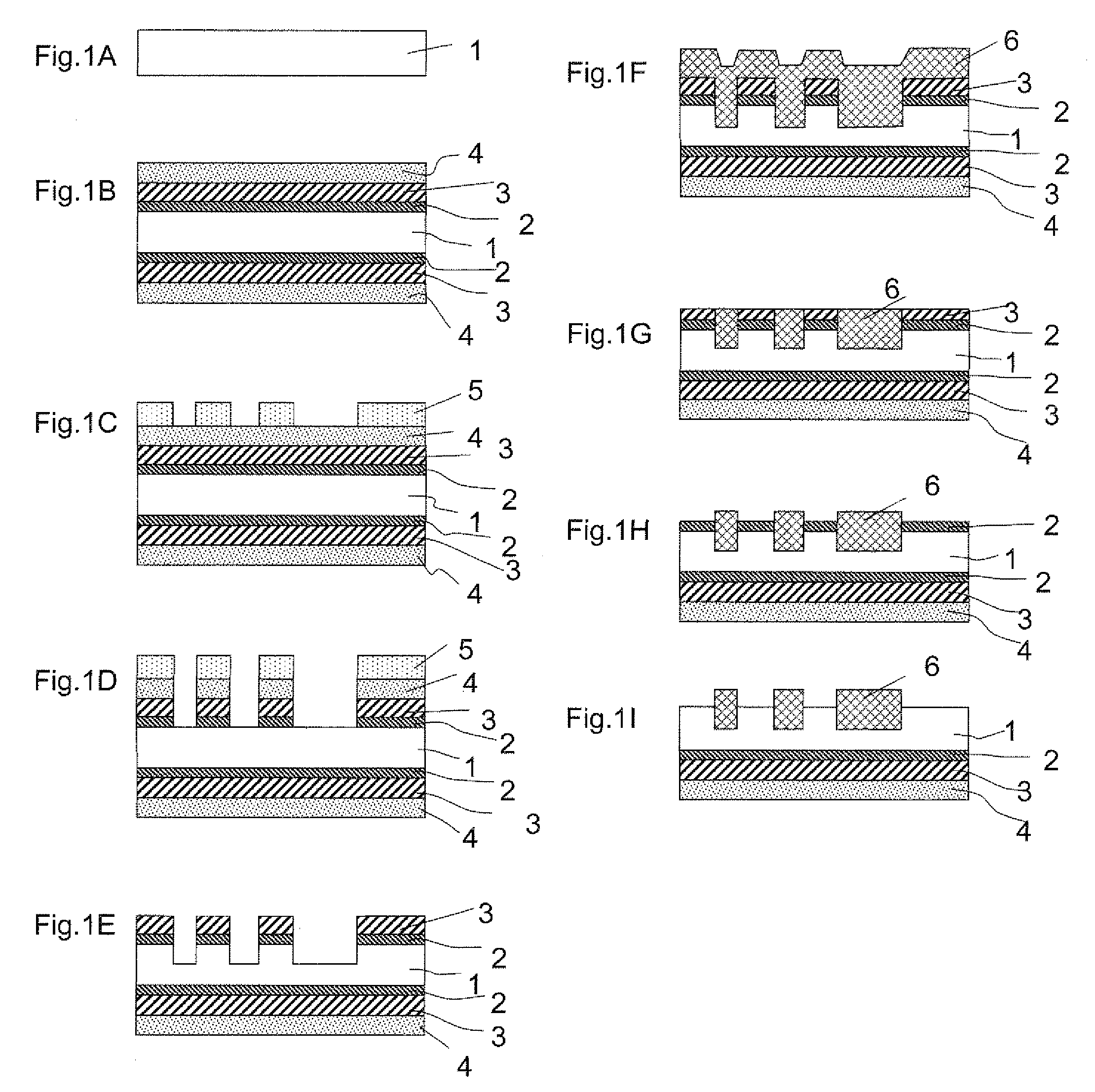
A manufacturing method for a semiconductor device includes: forming a first material film, a second material film, each having a function of preventing metal diffusion, and a third material film of which the etching rate for a first etchant is sufficiently lower than that of the first material film and the etching rate for a second etchant is sufficiently lower than that of the second material film, in this order on the outer peripheral surface of the semiconductor substrate; forming a trench structure; forming a buried insulating film and flattening it; removing the second material film through a wet etching process using the second etchant until the first material film formed on the main surface side is exposed; and removing the first material film on the main surface side through a wet etching process using the first etchant until the semiconductor substrate is exposed on the main surface side.
Owner:SHARP KK
How to form a mos transistor
ActiveCN106298484BPrevent metal diffusionImprove performanceSemiconductor devicesIon bombardmentInterface layer
The invention provides an MOS transistor forming method, which comprises the steps of providing a semiconductor substrate; forming a pseudo grid structure on the semiconductor substrate, wherein the two sides of the pseudo grid structure are provided with foot-shaped bottoms; forming an interlayer dielectric layer on the semiconductor substrate at the periphery of the pseudo grid structure, wherein the upper surface of the interlayer dielectric layer is flush with the upper surface of the pseudo grid structure; removing the pseudo grid structure to form a groove, wherein the two sides of the groove are provided with foot-shaped bottom corners; forming an interface layer at the bottom of the groove; forming a high-k dielectric layer at the bottom and the side wall of the groove, wherein the high-k dielectric layer covers the interface layer; forming a first diffusion barrier layer on the high-k dielectric layer; subjecting the part of the first diffusion barrier layer that is right facing the notch part of the groove to ion bombardment treatment through the sputtering process; after the ion bombardment treatment, forming a second diffusion barrier layer on the first diffusion barrier layer. The method improves the performance of an MOS transistor.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Systems and methods for preparing films comprising metal using sequential ion implantation, and films formed using same
ActiveUS8946864B2Prevent metal diffusionAvoid reactionDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsIon implantationMetal
Systems and methods for preparing films comprising metal using sequential ion implantation, and films formed using same, are provided herein. A structure prepared using ion implantation may include a substrate; an embedded structure having pre-selected characteristics; and a film within or adjacent to the embedded structure. The film comprises a metal having a perturbed arrangement arising from the presence of the embedded structure. The perturbed arrangement may include metal ions that coalesce into a substantially continuous, electrically conductive metal layer, or that undergo covalent bonding, whereas in the absence of the embedded structure the metal ions instead may be free to diffuse through the substrate. The embedded structure may control the diffusion of the metal through the substrate and / or the reaction of the metal within the substrate.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com