Nitrogen austenite steel microstructure predicting method
A technology of microstructure and prediction method, which is applied in the direction of testing metals, measuring devices, surface/boundary effects, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, and achieve the effects of clear output, friendly interface, and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
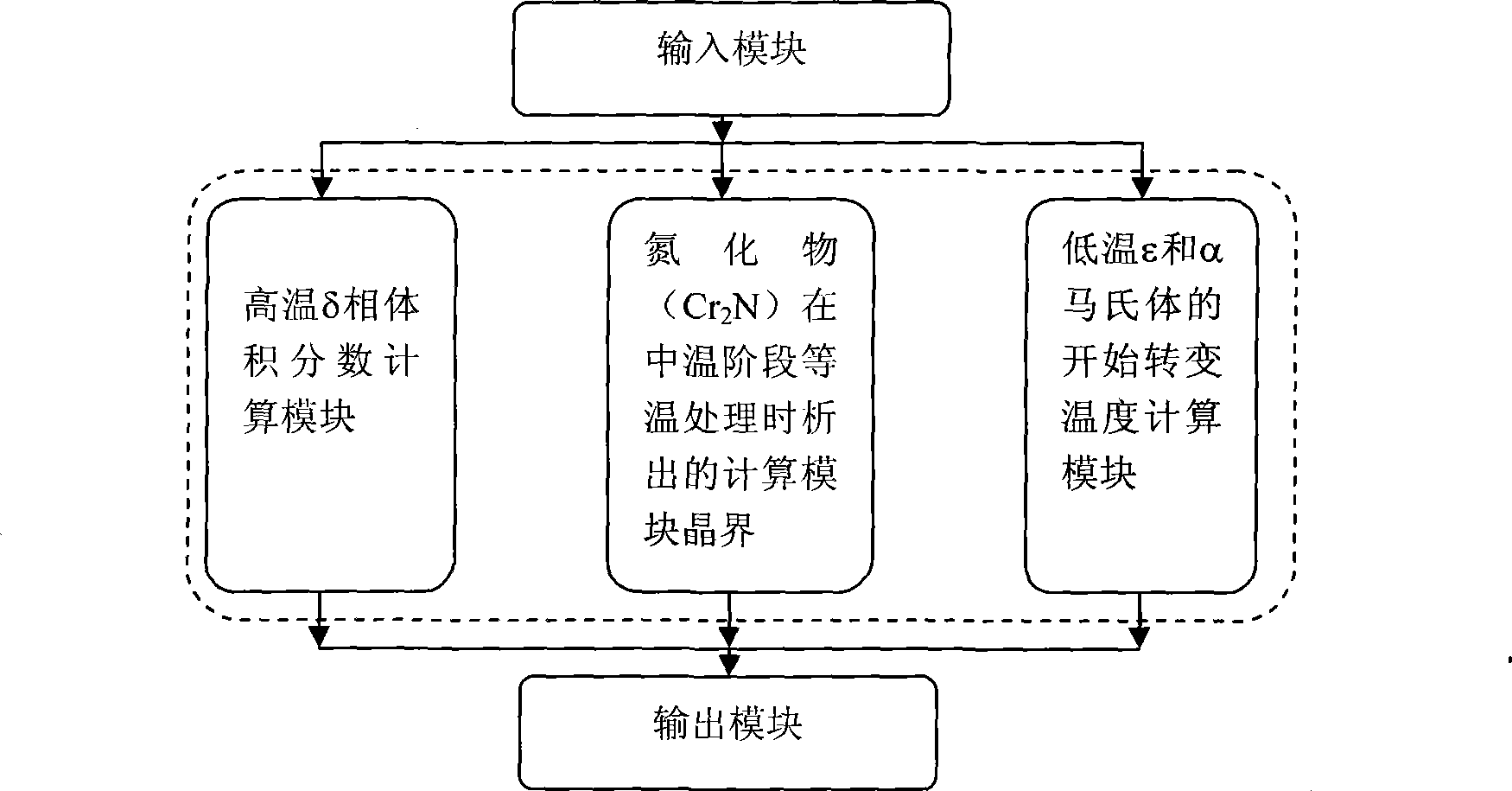
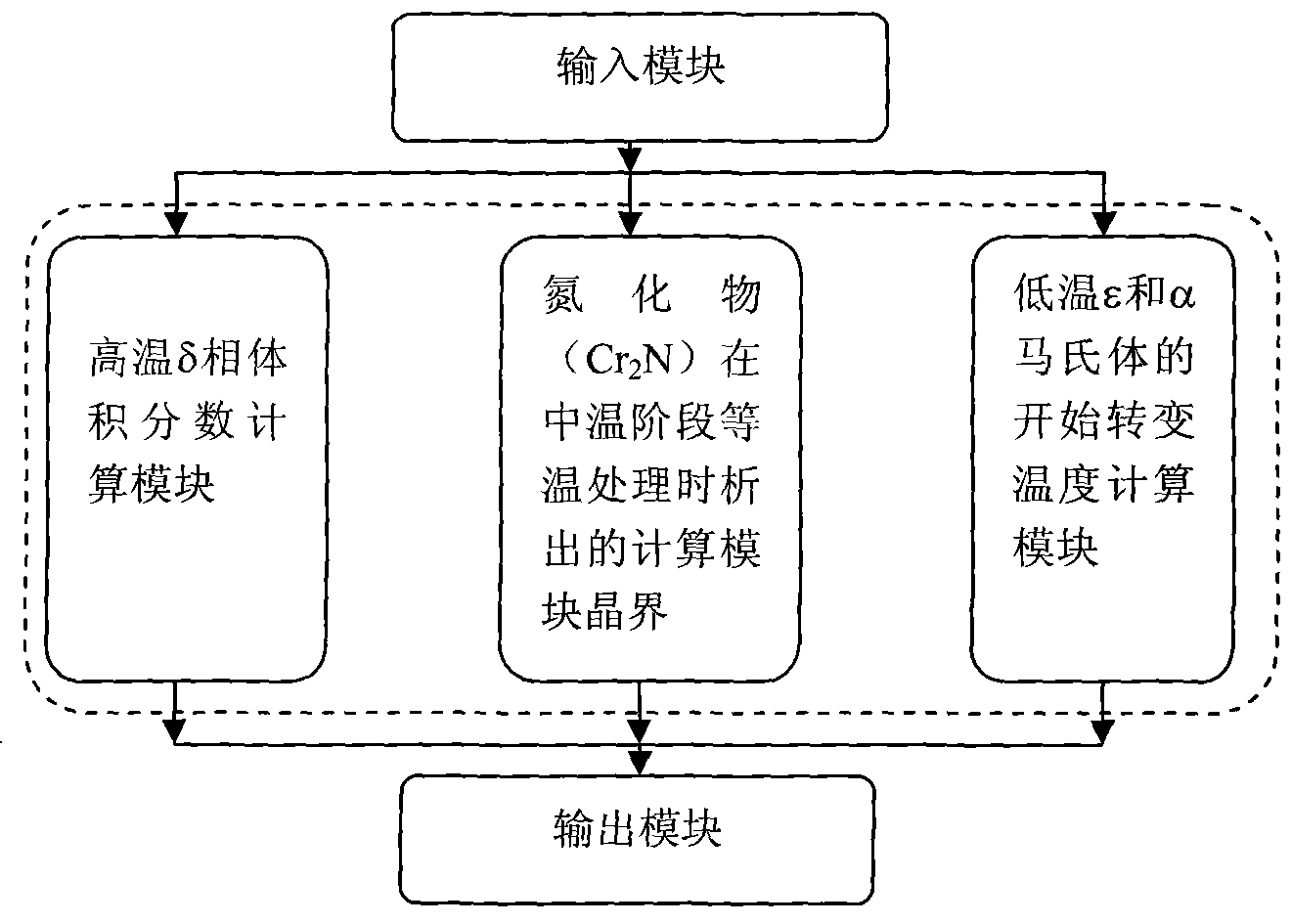
[0025] Process such as figure 1
[0026] After the alloying elements are input in the input module, the high temperature δ phase volume fraction calculation module in the calculation module will use the formula
[0027] T δ (℃)=T 4 -21.2[Cr]+15.8[Ni]-223
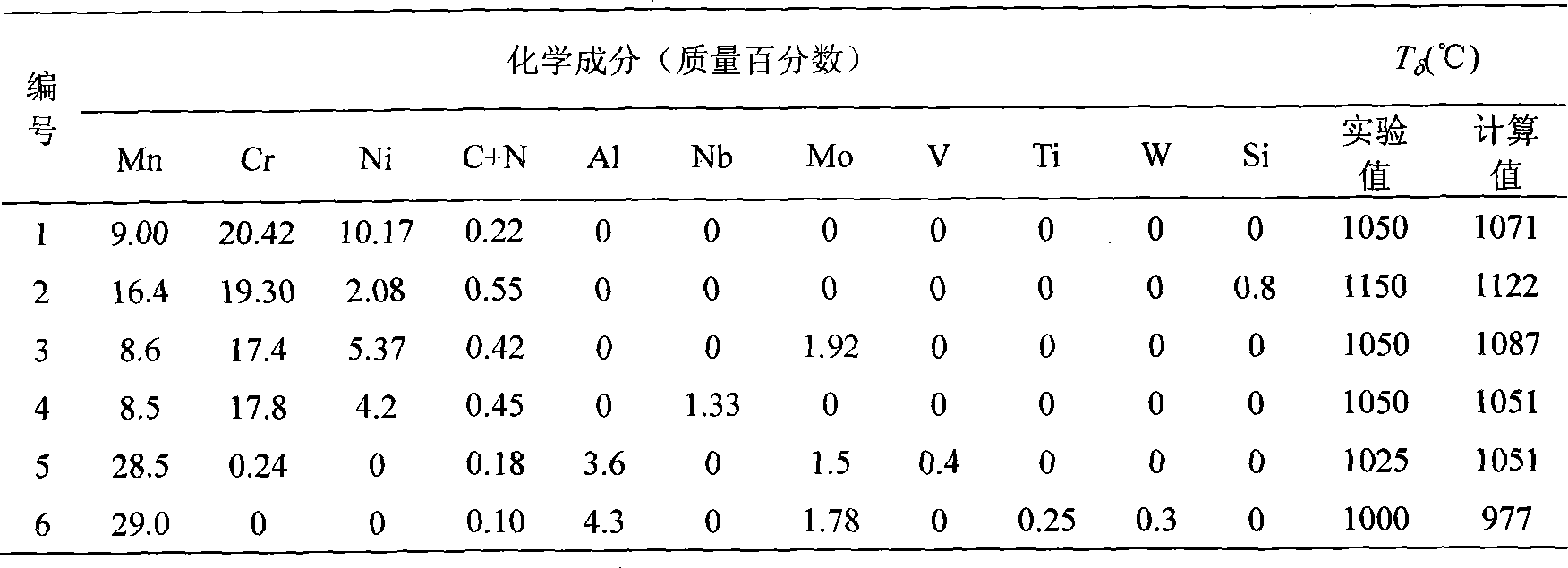
[0028] Calculation of T for Nitrogen-Containing Austenitic Steels δ temperature, part of the calculation results are shown in Table 1, and according to the formula
[0029] V δ (%)=0.715exp[0.015(T-T δ )]
[0030] The volume fraction of delta phase was calculated. The calculation results are output in the output module.
[0031] Table 1 T of partial austenitic steel δ
[0032]
Embodiment 2
[0034] In the input module, after inputting the alloy composition and temperature, the nitride (Cr 2 N) The grain boundary precipitation time calculation module adopts the formula during isothermal treatment in the middle temperature stage
[0035] lnt s =-9.9+324.8 / (1348-T)+10723.7 / T+89.0Mn / T+130.6Cr / T-171.5Ni / T
[0036] -3241.7(1.2N+C) / T+44.5Mo / T-3701.3V / T
[0037] Calculate the Cr 2 The time when N starts intergranular precipitation. Part of the calculation results are shown in Table 2. It can be seen that there is little difference between the calculation results and the experimental values. Calculation results enter the output module and output.
[0038] Table 2 Cr of some austenitic steels at different temperatures 2 The time for N to start intergranular precipitation
[0039]
[0040]
Embodiment 3
[0042] After entering the alloy composition in the input module, the low temperature ε and α martensite start transformation temperature module in the calculation module, using the formula
[0043] m s (K)=731-227(C+N)-17.6Ni-22.5Mn-17.3Cr-16.2Mo
[0044] m εs (K)=630-261.4(C+N)-13.7Mn-13.1Cr-17.9Ni-38.5Al
[0045] M can be calculated for austenitic steels s and M εs , and some calculation results are shown in Table 3 and Table 4. The calculation result is output to the user through the output module.
[0046] Table 3 M of some materials s The experimental and calculated values of
[0047]
[0048] Table 4 M of some materials εs The experimental and calculated values of
[0049]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com