Method for quantizing characterization of thin film surface topography based on multi-dimension system theory
A technology of surface topography and system theory, applied in the field of quantitative representation, can solve problems such as difficult separation and extraction, distortion of measurement information, and insufficient identification, and achieve the effect of detailed decomposition scale
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
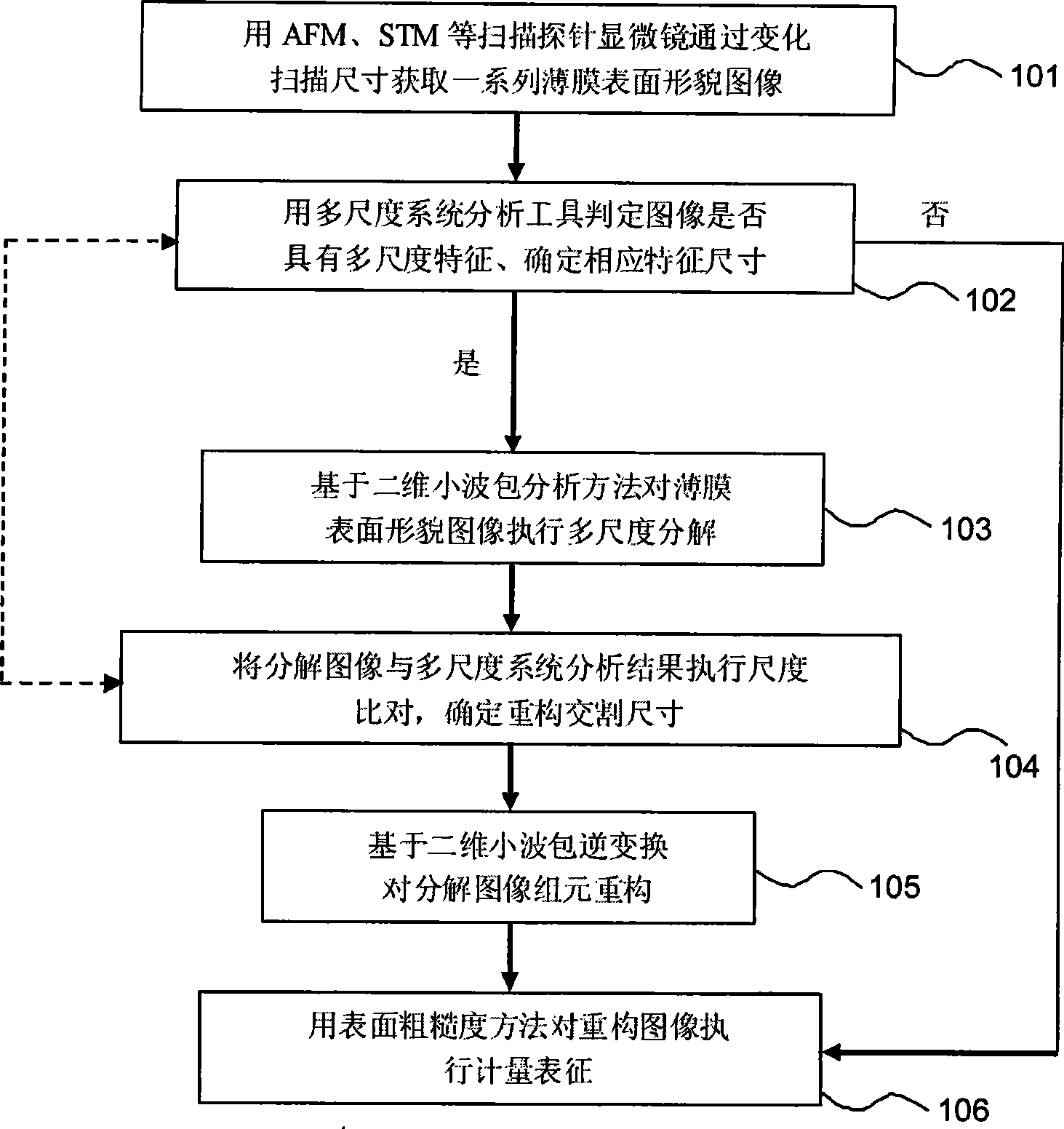
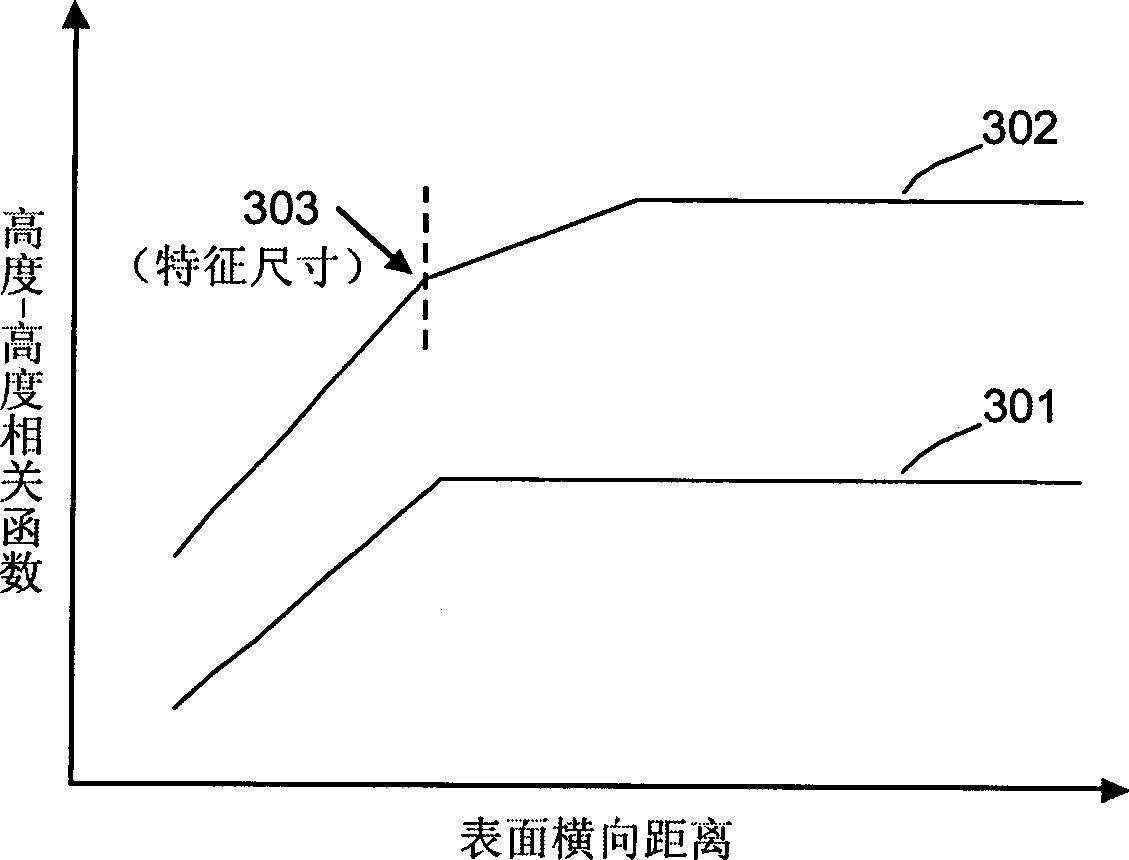
[0035] (1) First, a scanning probe microscope is used to scan the surface of the film sample in multiple stages to obtain a series of surface topography images of the film sample with different scan sizes:
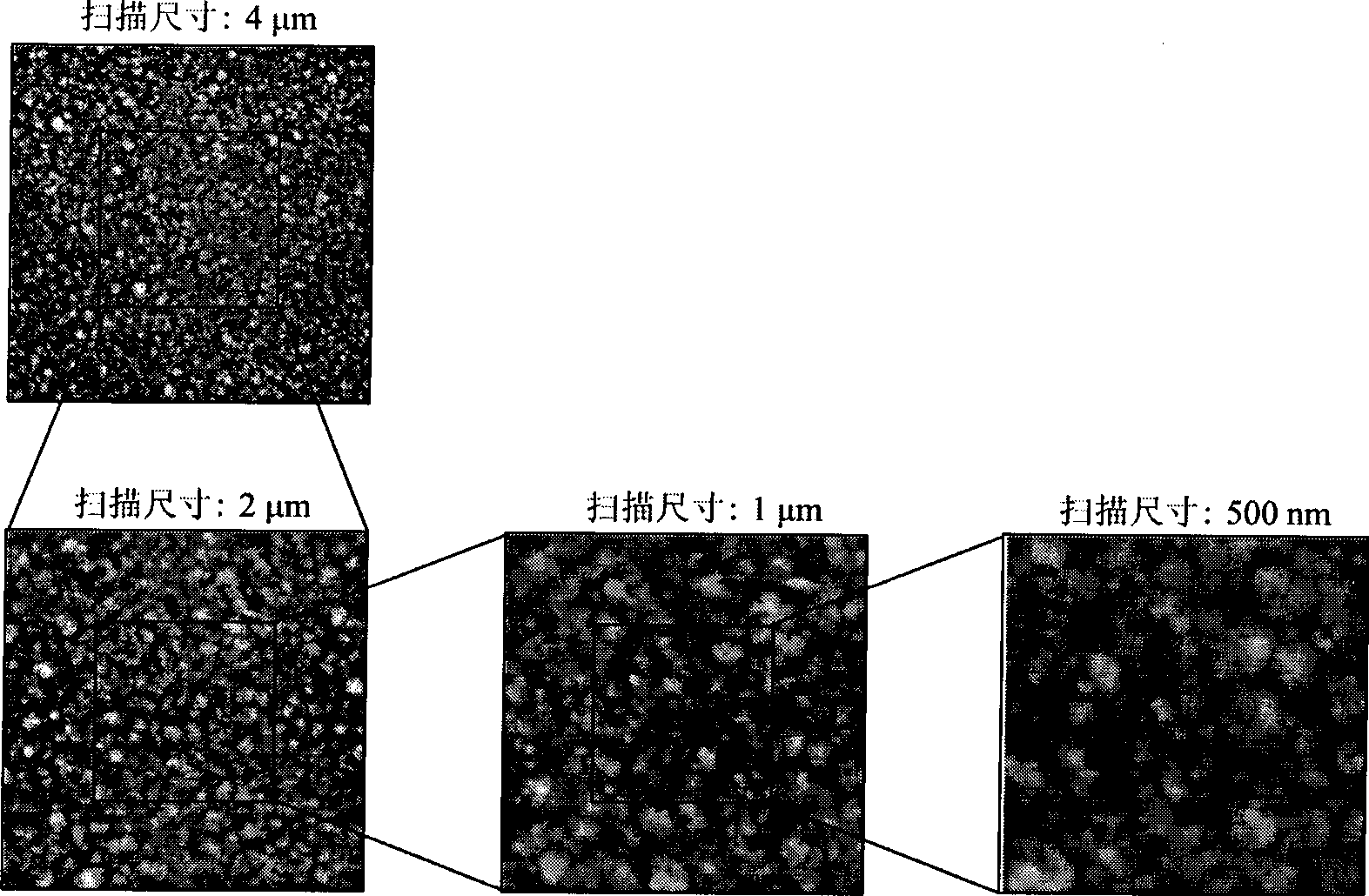
[0036] Firstly, a Cu film was deposited on a Si single crystal substrate by radio frequency magnetron sputtering process, and the deposition process parameters were: background vacuum degree 5×10 -5 Pa; sputtering power 100W; substrate temperature 300K; sputtering Ar pressure 0.5Pa; Cu film thickness about 200nm.
[0037] according to figure 1In step 101 of the flowchart, a WET-SPM-9500J3 atomic force microscope (AFM) is used to scan the Cu thin film sample. The lateral limit resolution of the AFM device is 0.2nm, and the pixel value is 512 pixels × 512 pixels. However, considering that the diameter of the probe used is about 10nm, too small image scanning size will cause serious convolution effect and distort the image. Therefore, in this example, the minimum scan size ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com