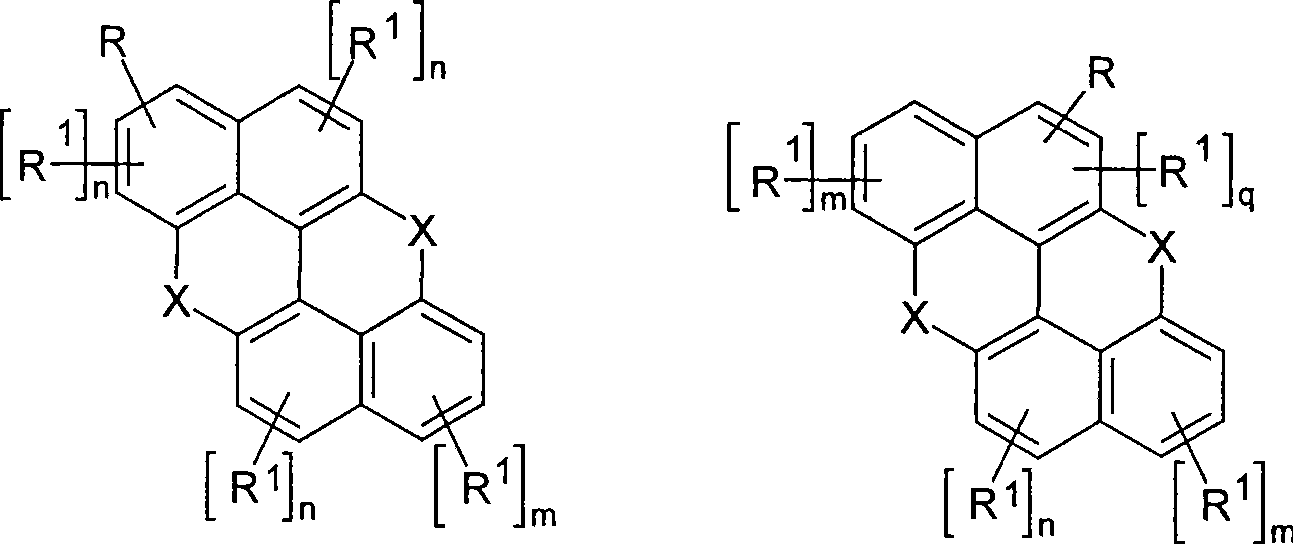
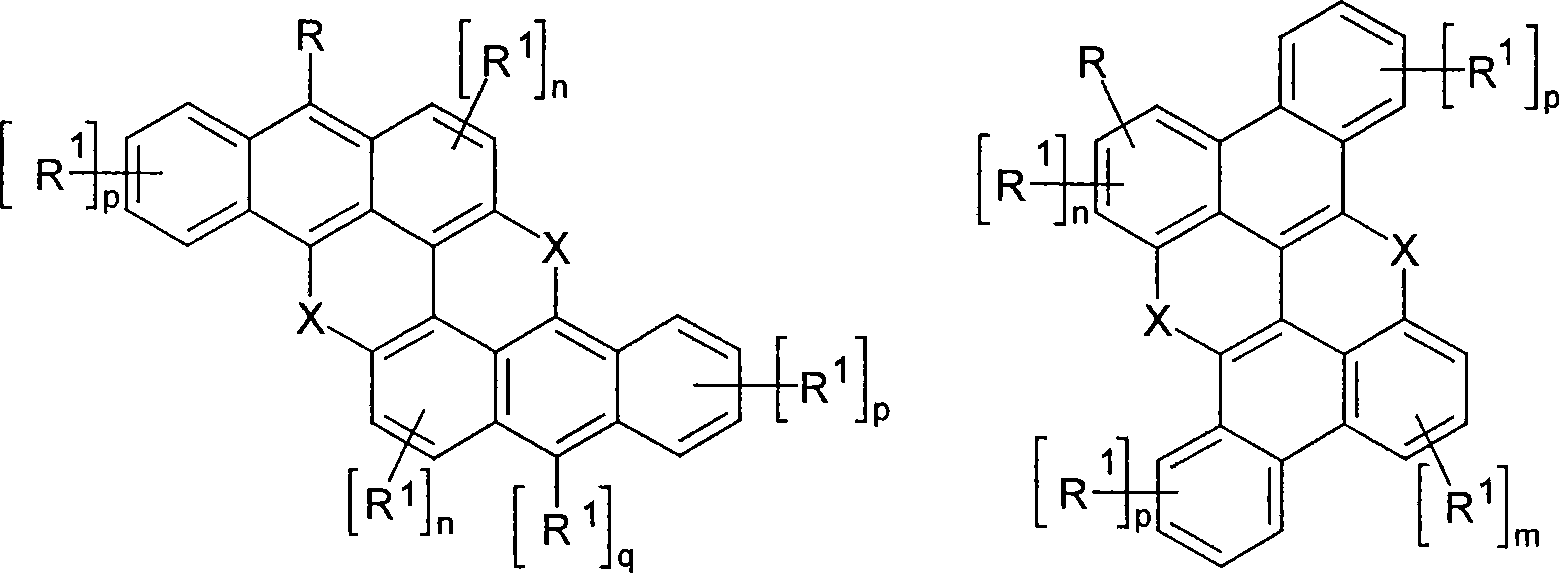
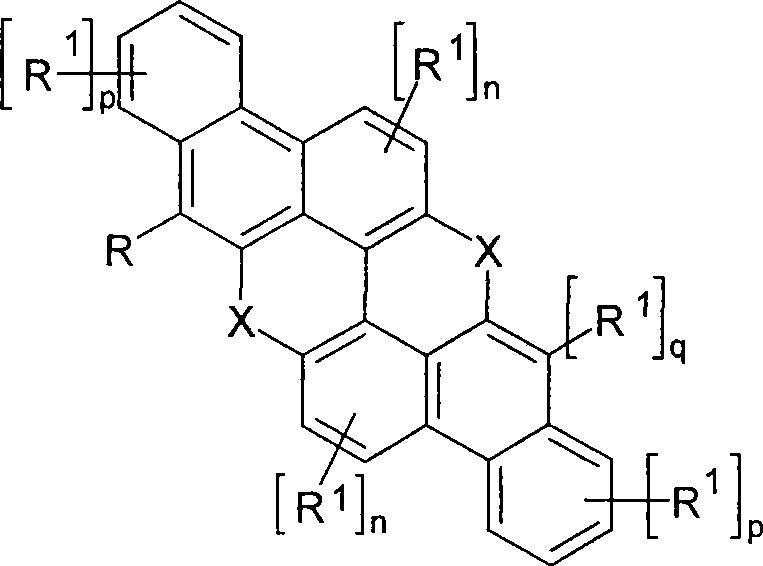
Novel materials for organic electroluminescent devices
A general formula and compound technology, applied in the field of new materials for organic electroluminescent devices, can solve problems such as insufficient thermal stability, difficult processing, synthesis and processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0200] Example 1: 5,5'-Dibromo-peridoxanthene and xanthene
[0201]
[0202] A suspension of 28.2 g (100 mmol) of per-xanthenoxanthene and 36.5 g (205 mmol) of N-bromosuccinimide in 200 ml of o-dichlorobenzene was stirred at 180° C. for 6 hours. After cooling, the solid was filtered off with suction, washed five times with 200 ml of ethanol each time and dried in vacuo. The crude product was recrystallized twice from ortho-dichlorobenzene, yielding 41.4 g (94 mmol) of 5,5'-dibromo-peri-xanthene-xanthene, corresponding to 94.0% of theory, with a purity of 99.0% according to HPLC.
Embodiment 2
[0203] Example 2: 5,5',7,7'-tetrabromo-peridoxanthene and xanthene
[0204]
[0205] A suspension of 28.2 g (100 mmol) of per-xanthenoxanthene and 73.0 g (410 mmol) of N-bromosuccinimide in 300 ml of o-dichlorobenzene was stirred at 180° C. for 16 hours. After cooling, the solid was filtered off with suction, washed five times with 200 ml of ethanol each time and dried in vacuo. The crude product was recrystallized twice from o-dichlorobenzene to give 55.0 g (92 mmol) of 5,5',7,7'-tetrabromo-peridoxanthene and xanthene, corresponding to 92.0% of theory, according to HPLC The purity is 99.0%.
Embodiment 3
[0206] Example 3: 3,3', 5,5', 7,7'-hexabromo-peri-xanthene and xanthene
[0207]
[0208] A suspension of 28.2 g (100 mmol) of per-xanthenoxanthene and 142.4 g (800 mmol) of N-bromosuccinimide in 500 ml of o-dichlorobenzene was stirred at 180° C. for 28 hours. After cooling, the solid was filtered off with suction, washed five times with 200 ml of ethanol each time and dried in vacuo. The crude product was purified three times with boiling o-dichlorobenzene to obtain 72.5 g (96 mmol) of 3,3',5,5',7,7'-hexabromo-peridoxanthene and xanthene, corresponding to 96.0 of theoretical value %, 99.0% purity according to HPLC.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com