Hepatitis B nucleic acid vaccine with optimized codon
A technology of codon optimization and nucleic acid vaccine, applied in the field of hepatitis B vaccine, can solve the problems of low immunogenicity, ineffective expression of foreign genes, stimulation of host immune system, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing protein expression and level
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
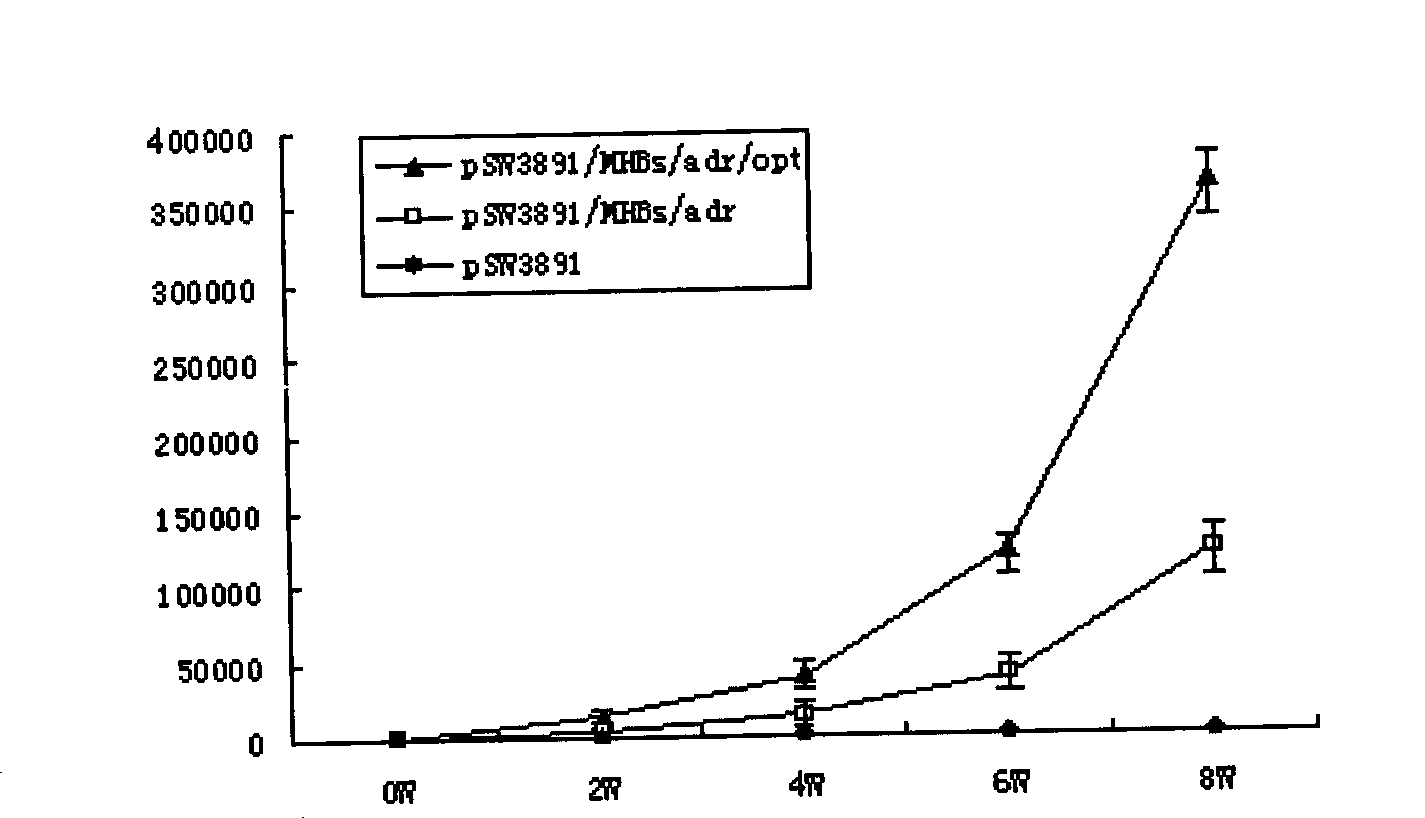
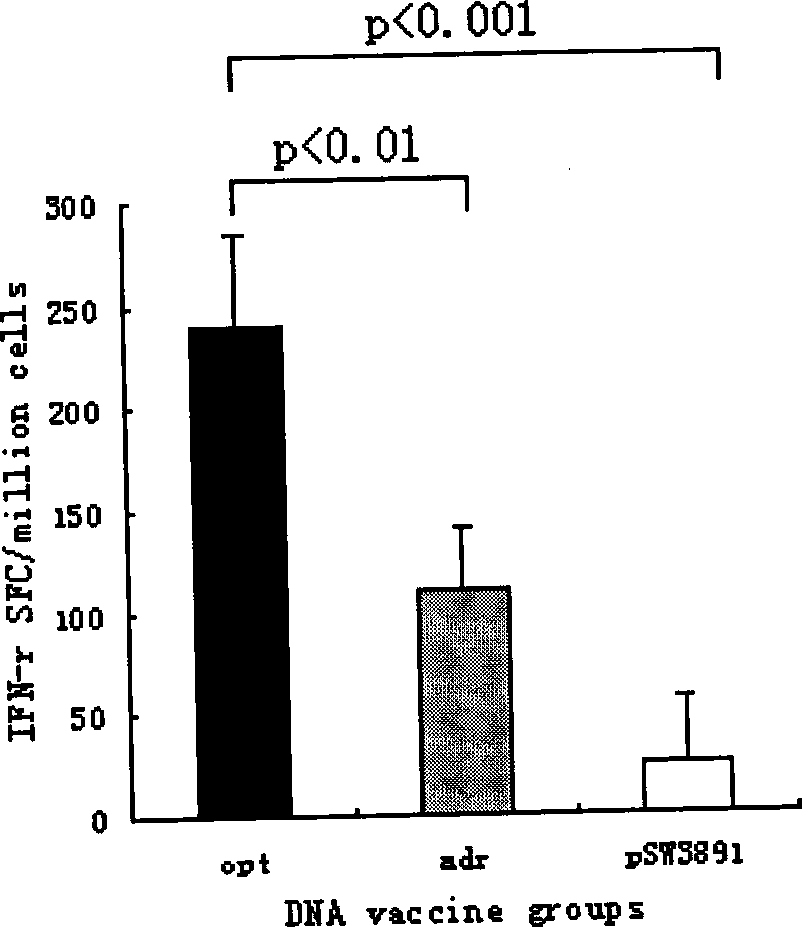
[0040] The invention is a method for introducing codon optimization into the hepatitis B virus surface antigen nucleic acid vaccine to improve the immunogenicity of the existing vaccine. After codon optimization, the hepatitis B surface antigen gene can be used to encode three proteins: large protein, medium protein and small protein, among which the codon-optimized hepatitis B surface antigen protein nucleic acid vaccine has been constructed and tested in animal experiments It is proved that codon optimization can indeed improve the immunogenicity of protein nucleic acid vaccine in hepatitis B surface antigen.
[0041] Specific method instructions:
[0042] First of all:
[0043] After optimization, the surface antigen of hepatitis B virus is named: HBs / opt, referred to as S-opt;
[0044] The surface antigen of hepatitis B virus before optimization was named: HBs / adr, referred to as S-adr;
[0045] Codon-optimized hepatitis B surface antigen protein (MHBs) nucleic acid vac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com