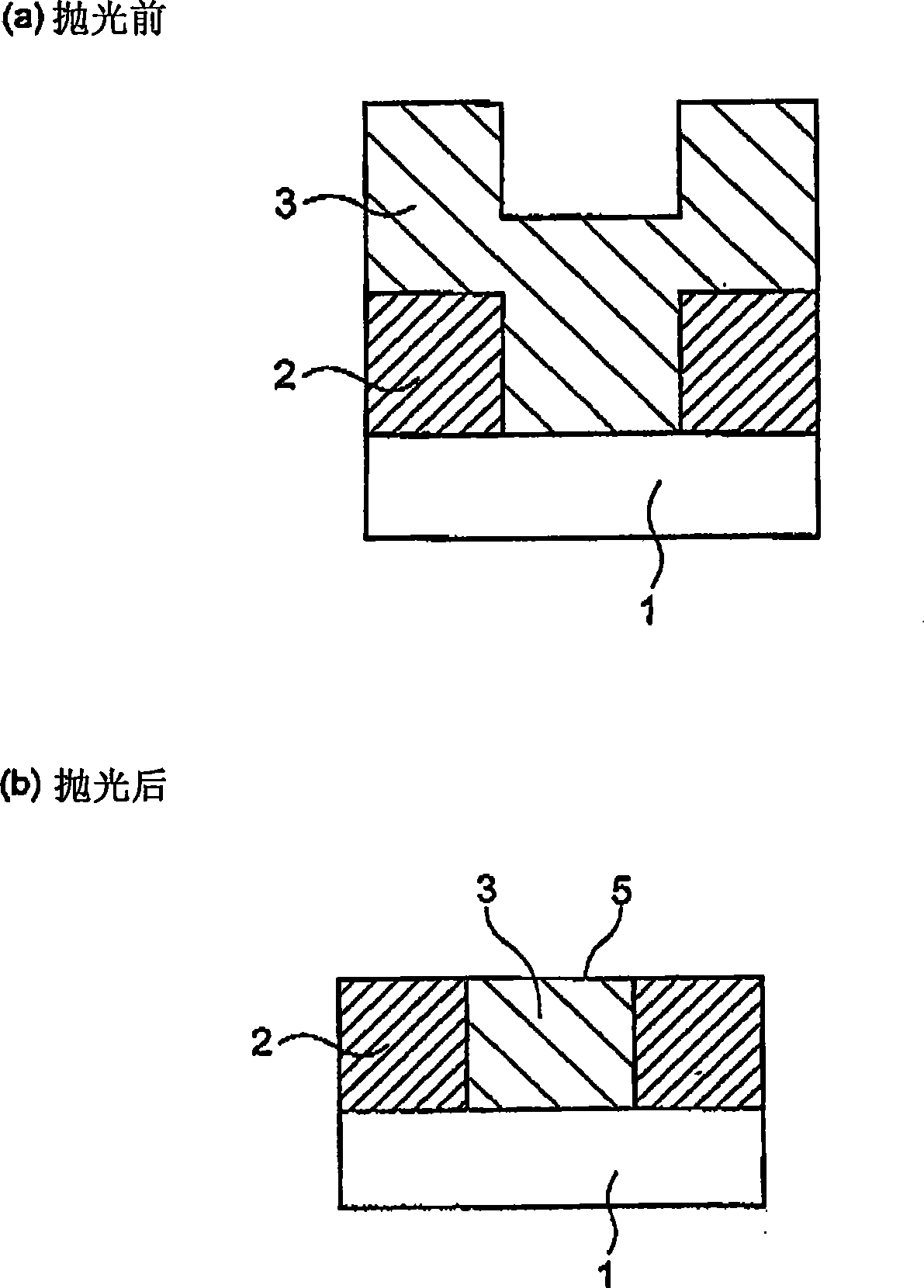
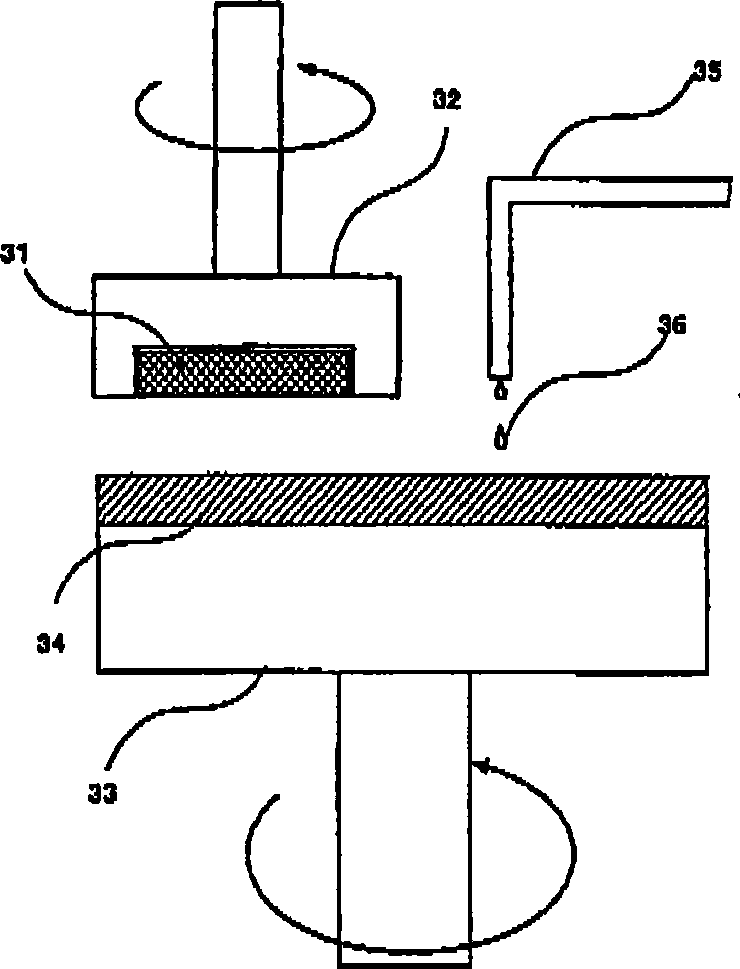
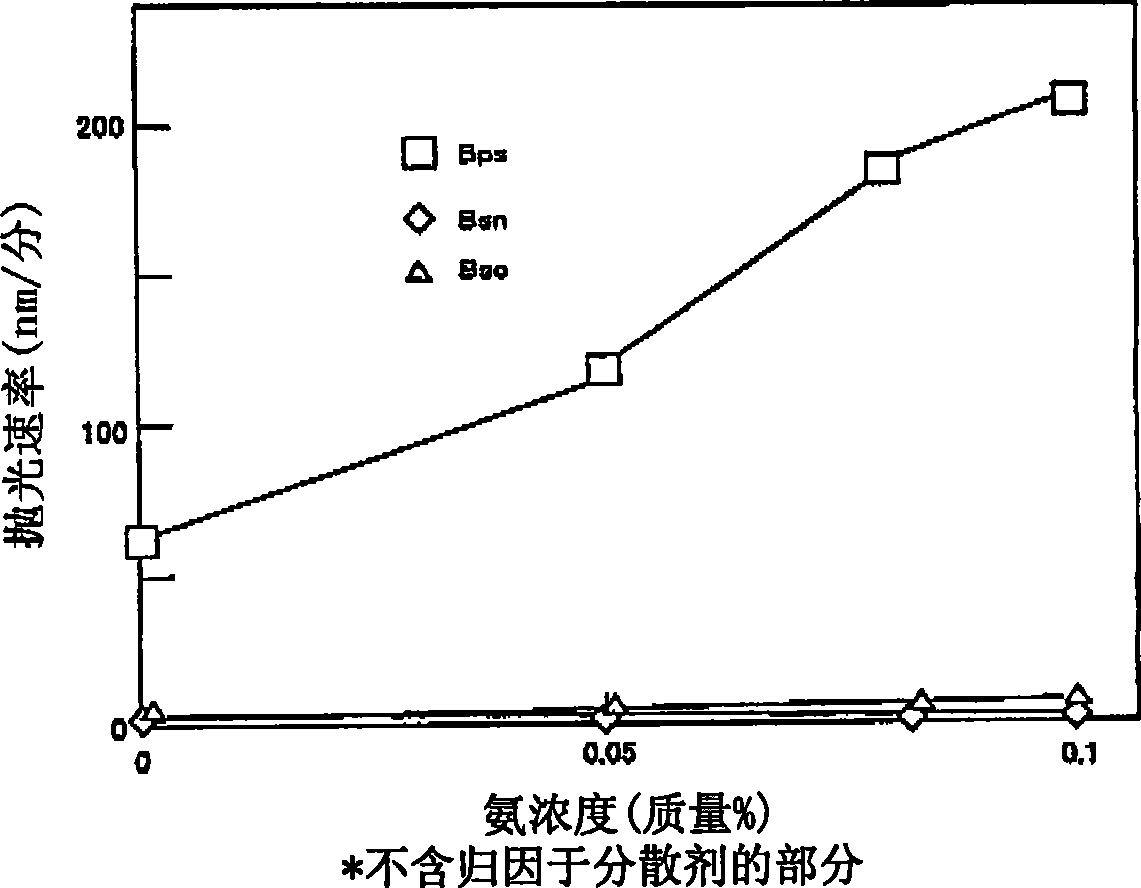
Polishing agent for semiconductor integrated circuit device, polishing method, and method for manufacturing semiconductor integrated circuit device
A technology of integrated circuits and polishing agents, which is applied in the field of polishing, can solve problems such as changes in the polishing rate of silicon nitride films or silicon dioxide films, and achieve a high degree of planarization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0084] Examples of the present invention will be illustrated below. Examples 1 to 4 are examples of the present invention, and examples 5 to 8 are comparative examples. In these examples, "%" means "mass%" unless otherwise specified, and the characteristic values were evaluated in the following ways.
[0085] (pH value)
[0086] The pH was measured with pH81-11 manufactured by Yokogawa Electric Corporation.
[0087] (Average particle size of abrasive grains)
[0088] The average particle diameter was measured by a laser light scattering-diffraction apparatus (trade name LA-920, manufactured by Horiba, Ltd.).
[0089] (dispersion stability of polishing agent)
[0090] The "agglutination and sedimentation time" in the examples was determined based on the time from when 20 mL of the polishing agent was put into a glass test tube with a diameter of 18 mm and allowed to stand for 2 days until separation into two layers occurred to produce a supernatant.
[0091] (Polishing p...
example 1
[0106] Stir and mix cerium oxide abrasive grains and ammonium polyacrylate with a molecular weight of 5,000 as a dispersant in deionized water, the mass ratio is 100:0.7, and the mixture is ultrasonically dispersed and filtered to obtain a powder with a concentration of 10% abrasive grains and 0.07% dispersant concentrated mixture. The mixture was diluted 5-fold with deionized water to obtain abrasive mixture A having a concentration of 2.0% abrasive particles and a concentration of 0.014% dispersant. Abrasive mixture A had a pH of 7.6 and an average particle diameter of 0.19 μm.
[0107] Subsequently, polyoxypropylene diamine (amine-based water-soluble polymer, trade name Polyether-Amine, manufactured by BASF) with a molecular weight of 230 as an additive and basic compound ammonia were dissolved in deionized water, thus obtaining Additive solution B1 with polyoxypropylene diamine concentration and 0.1% ammonia concentration.
[0108] Stir and mix additive solution B1 and a...
example 2
[0111]Abrasive mixture A was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1; additive solution B2 was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the ammonia concentration was adjusted to 0.16% in the preparation of additive solution B1. Additive solution B2 and abrasive grain mixture A are mixed in a mass ratio of 1:1 to obtain a concentration of 1.0% abrasive grains, 0.007% ammonium polyacrylate dispersant concentration, 1.0% polyoxypropylene diamine additive concentration, 0.08% ammonia concentration and Polishing compound with a pH of 10.9.
[0112] The prepared polishing agent was evaluated in the same manner as in Example 1. Table 1 shows the composition of the polishing agent and the evaluation results of polishing performance.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com