Method for cultivating high-female few-seed watermelon
A watermelon variety and cultivation method technology, applied in the directions of botanical equipment and methods, plant products, plant genetic improvement, etc., to achieve the effects of low price, improved transfer efficiency, and overcoming difficulties in fruit setting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
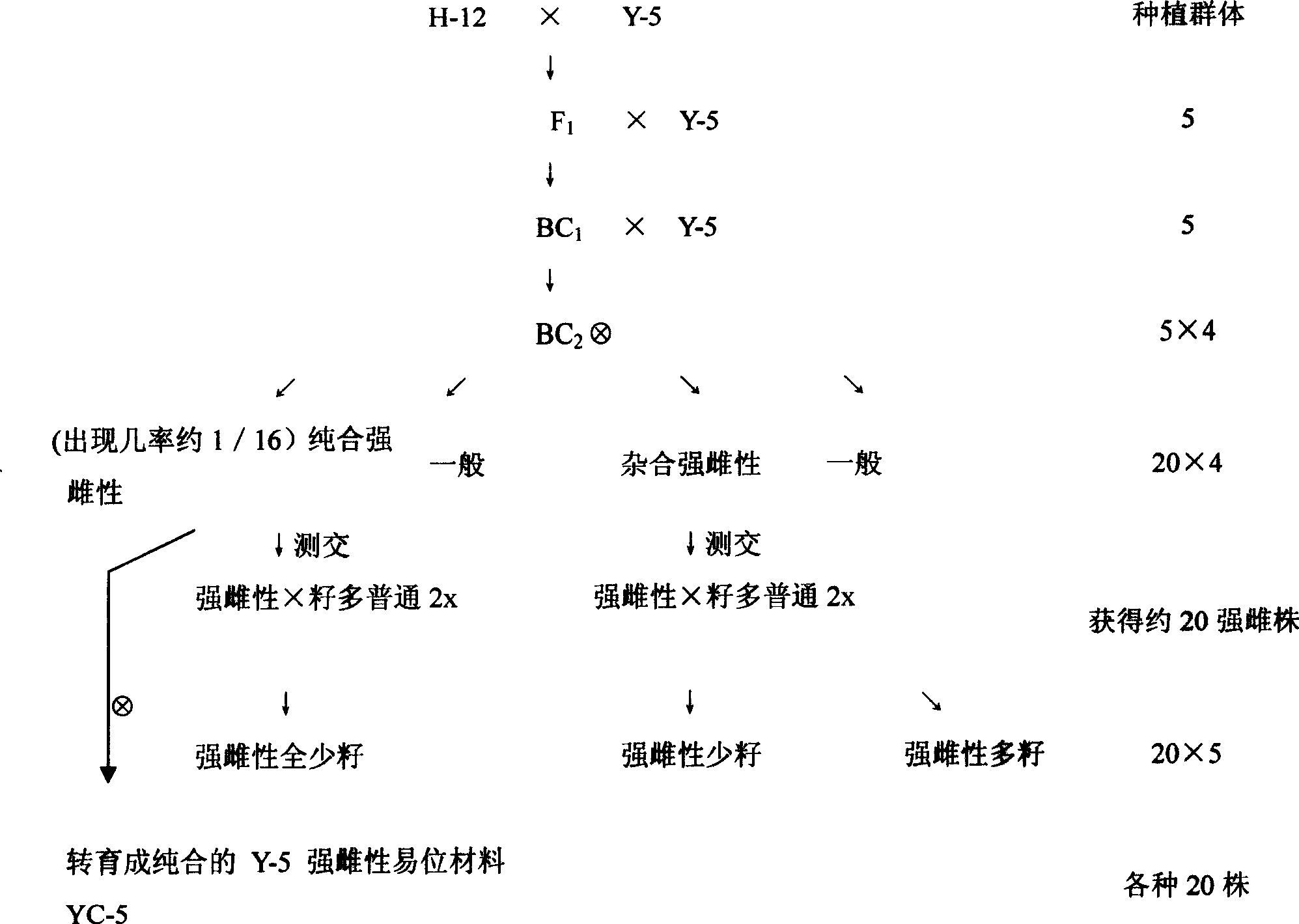
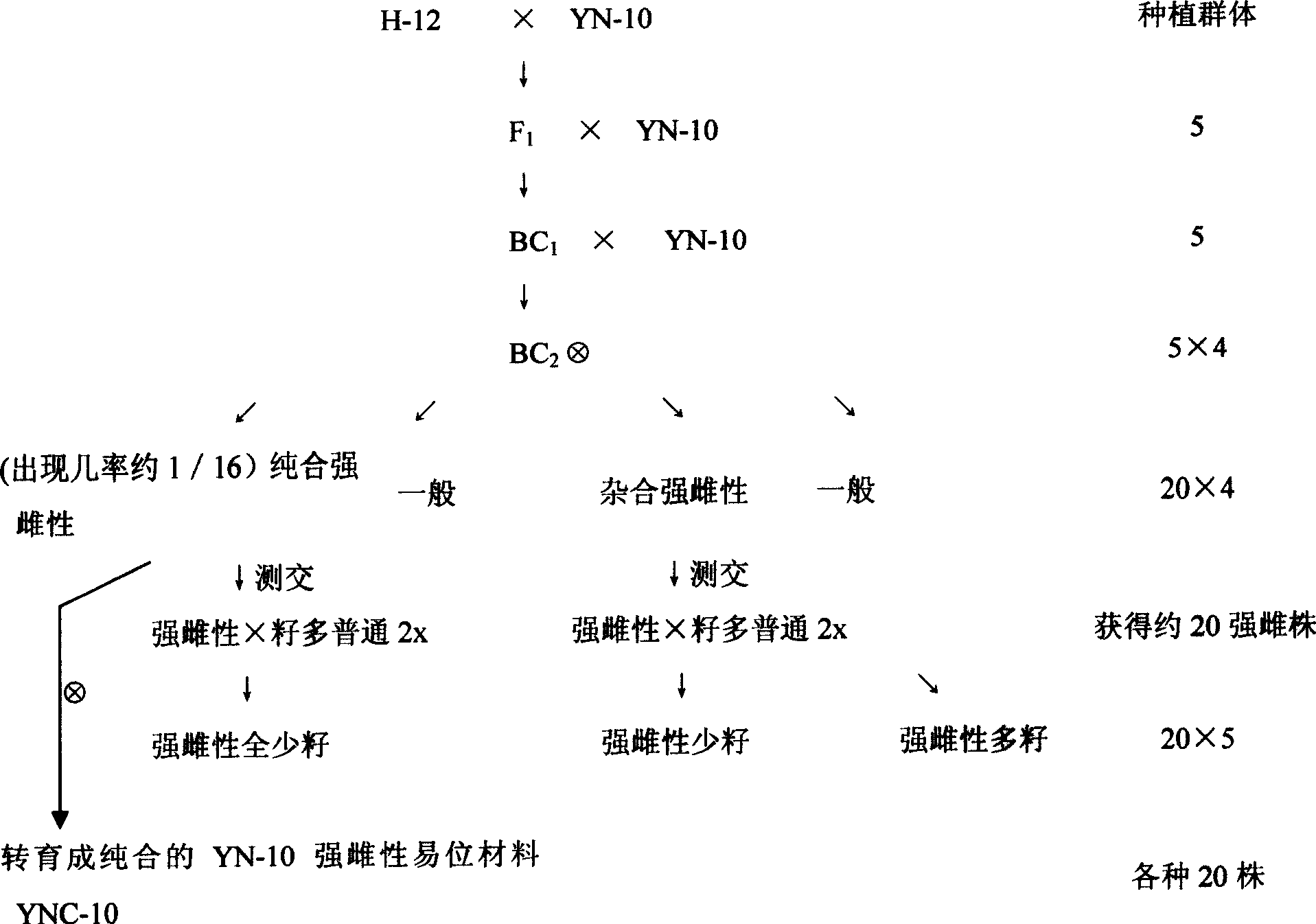
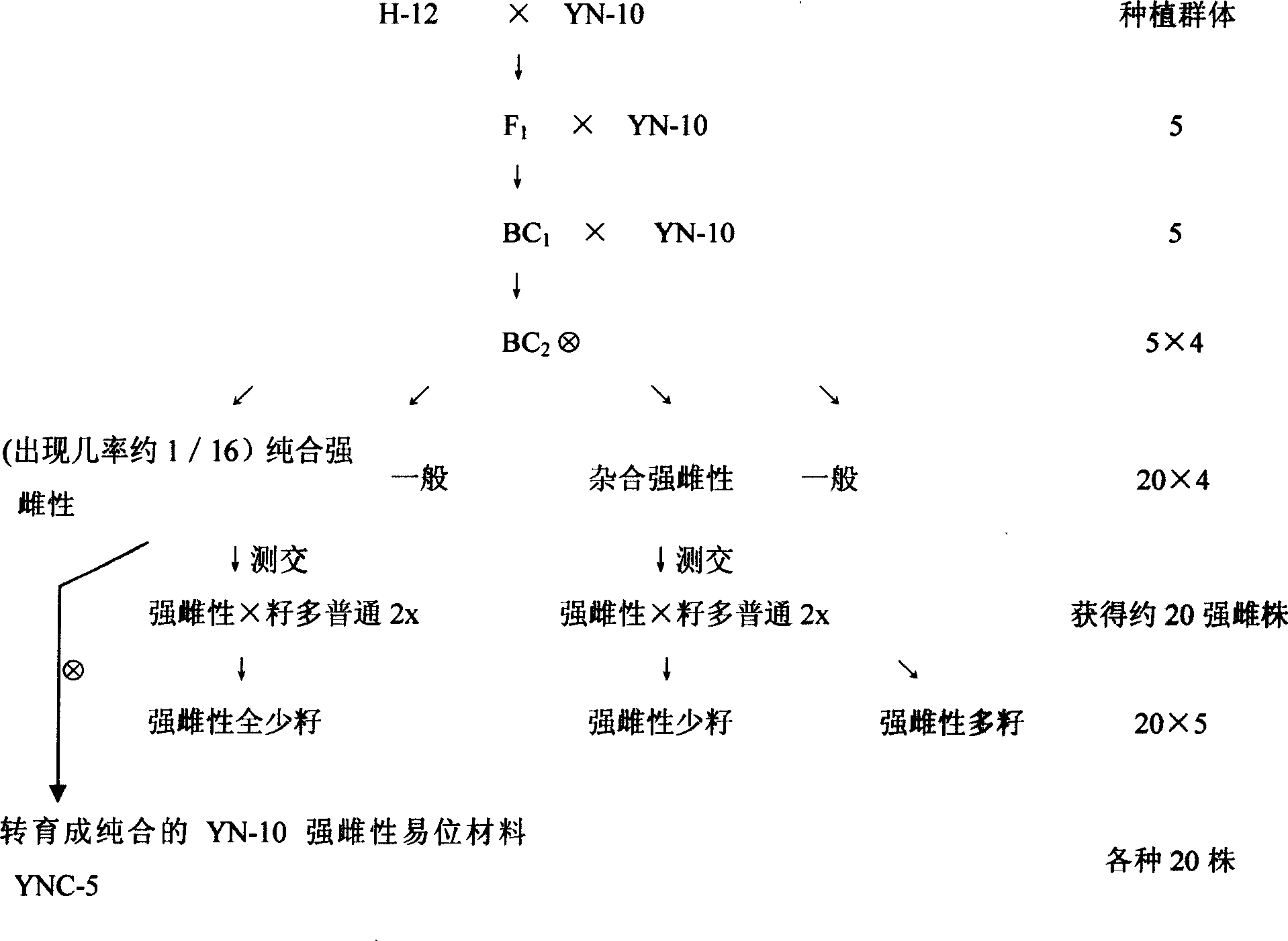
[0021] A method for cultivating strong female seedless watermelon varieties, comprising the steps of:
[0022] ①Obtaining different watermelon translocation materials: a. The few-seeded fruit that appeared in the progeny of crossing the American watermelon Jubilee breeding material with "Jinhua No. 1" can be homozygous for 6 generations and test crossed for 1 generation The basic material for homozygous non-homologous chromosome translocation breeding was bred, code-named Y-5; b. Non-homologous chromosome translocation was found in the material isolated from the male degenerate offspring of watermelon. This backcross was used to breed a homozygous male sterile non-homologous chromosomal translocation material, code-named YN-10; c. Non-homologous chromosomal translocation test: Y-5 and YN-10 were crossed and observed Its F 1 The abortion rate of generation seeds and pollen showed that the abortion rate of seeds was about 75%, and the abortion rate of pollen was also about 75%....
Embodiment 2
[0028] The determination method of non-homologous chromosome translocation is as follows: ① Genetic analysis is carried out on the test cross of different seedless materials with normal seeded materials as the female parent, and the F 1 50% of the fruit set normal seeds; 50% of the fruit set half of the seeds, and the pollen abortion rate was 50%, the cytological identification was carried out, and when the chromosomes formed a "cross" junction or formed a "bridge", it was determined to be non-homologous Chromosomal translocation material; ② use known homozygous translocation material as female parent, and the non-homologous chromosomal translocation material as male parent cross, F 1 It shows that the pollen abortion rate is about 75%, and the number of seeds of a single melon is about 25% of the normal fruit, so it is determined that the tested material and the female parent are different translocations.
Embodiment 3
[0030] A method for cultivating strong female watermelon varieties with few seeds, using "Jingxin No. 1" instead of "Jinhua No. 1" in Example 1, and other materials and steps are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com