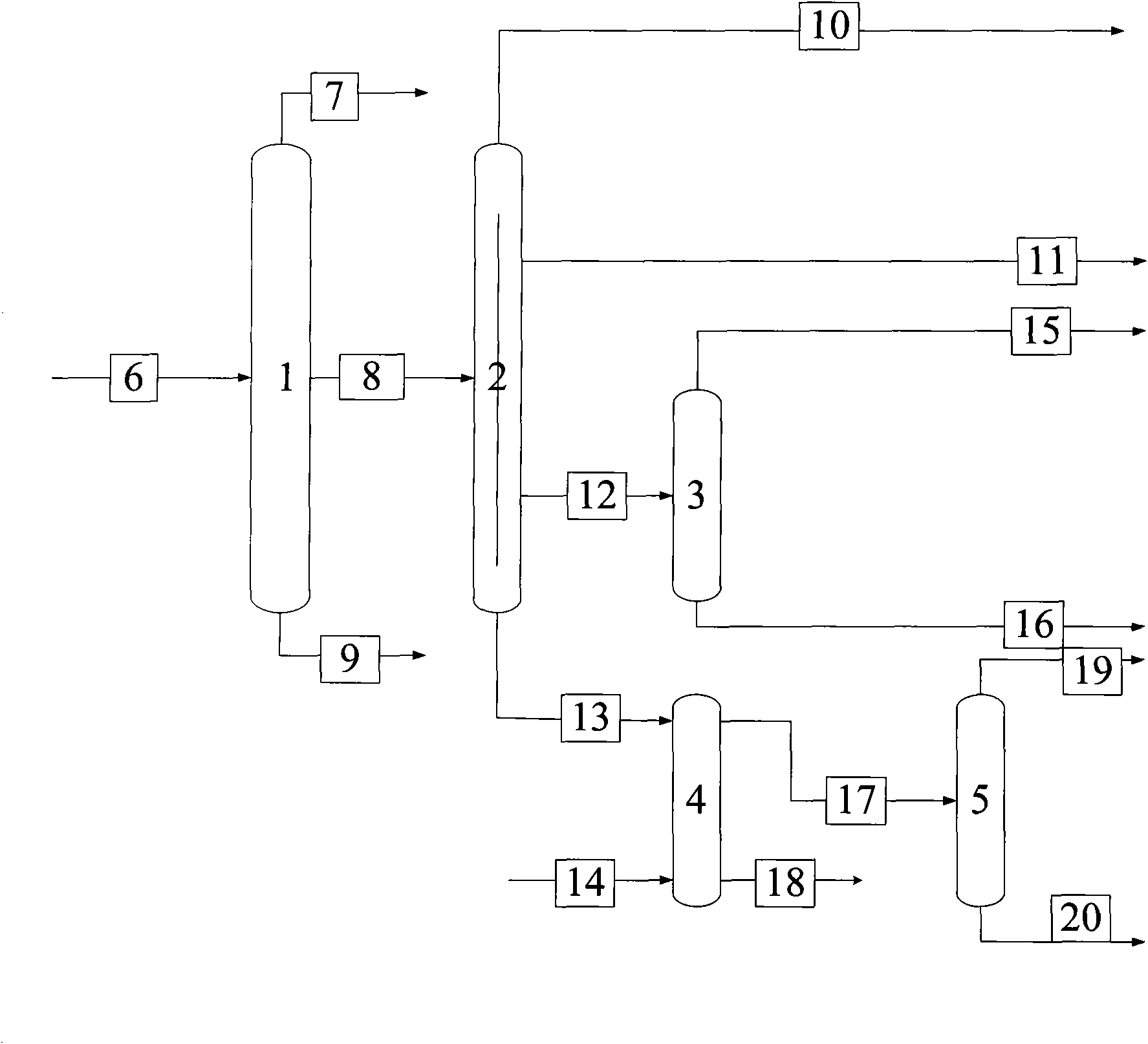Separating method of aqueous phase byproduct from Fischer-Tropsch synthesis
A technology for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis and by-products, applied in the separation/purification of carboxylic acid compounds, separation/purification of hydroxyl compounds, separation/purification of carbonyl compounds, etc., can solve the problem of direct discharge of by-products in the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis reaction economic and environmental issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
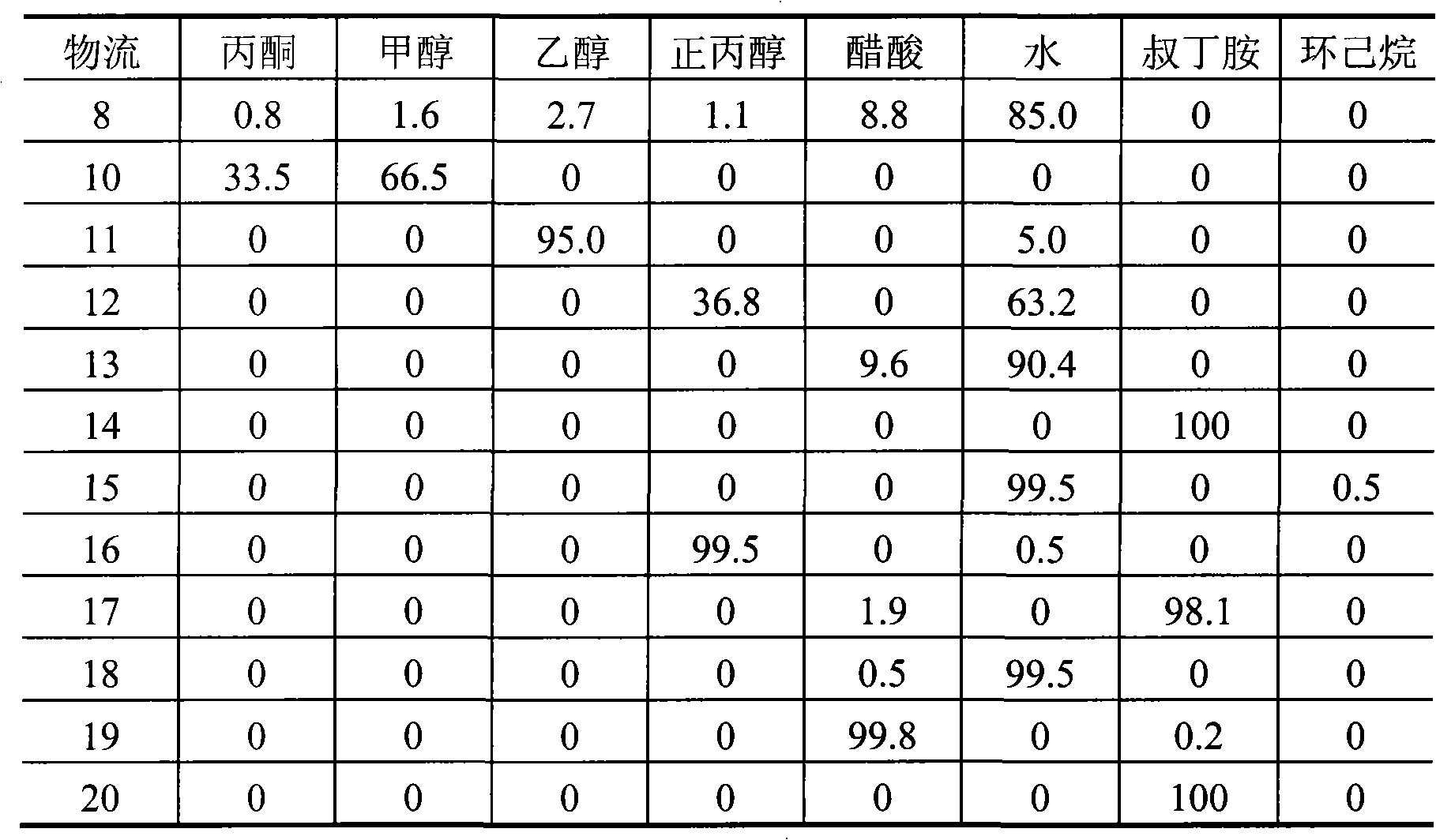
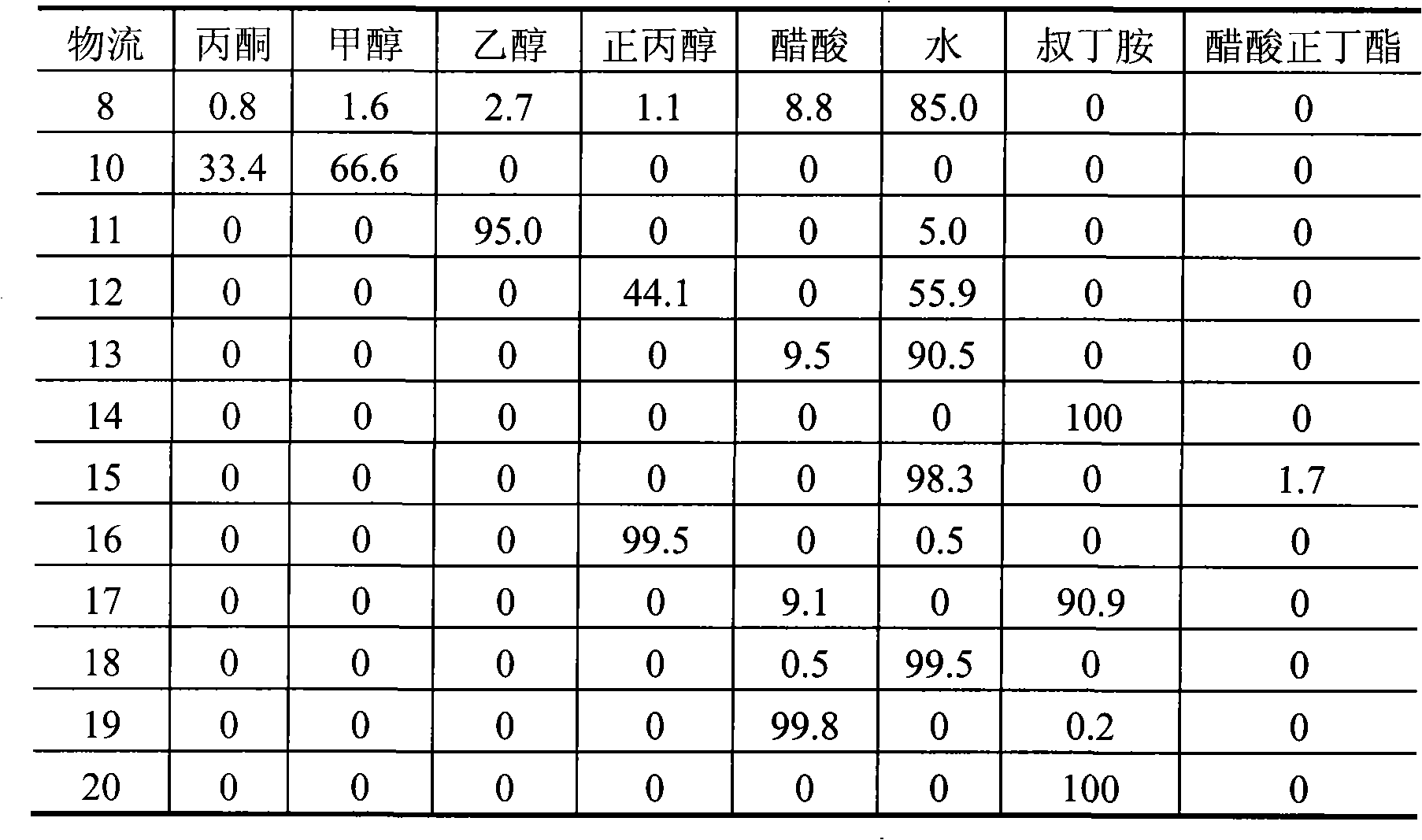
[0015] according to figure 1 As shown in the flow process, the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis aqueous phase by-product 6 (components with a boiling point less than 40°C, components with a boiling range of 50 to 120°C and components with a boiling point greater than 120°C account for 5%, 85% of the weight composition respectively and 10%) enter the common rectifying column 1 that the number of theoretical plates is 15, the feeding position is the 7th theoretical plate, the reflux ratio is 12, the control tower top temperature is 40 DEG C, and the side line is taken from the 8th theoretical plate The fraction 8 with a boiling range of 50-120°C exits, and the side stream fraction 8 enters the separation column 2 with a theoretical plate number of 50. The theoretical plate number on the upper part of the dividing plate is 10, and the number of theoretical plates on the lower part is also 10. The liquid phase distribution fraction on the side is 0.7, the gas phase distribution fraction ...
Embodiment 2
[0019] according to figure 1 As shown in the flow process, the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis aqueous phase by-product 6 (components with a boiling point less than 40°C, components with a boiling range of 50 to 120°C and components with a boiling point greater than 120°C account for 5%, 85% of the weight composition respectively and 10%) enter the common rectifying column 1 that the number of theoretical plates is 60, the feed position is the 35th theoretical plate, the reflux ratio is 1, the control tower top temperature is 40 ℃, and the side line is taken from the 40th theoretical plate The distillate 8 with a boiling range of 50-120°C exits, and the side draw 8 enters the separation column 2 with a theoretical plate number of 200. The theoretical plate number on the upper part of the dividing plate is 40, and the number of theoretical plates on the lower part is also 60. The upper part of the dividing plate is left The liquid phase distribution fraction on the side is 0.31, the ...
Embodiment 3
[0023] according to figure 1As shown in the flow process, the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis aqueous phase by-product 6 (components with a boiling point less than 40°C, components with a boiling range of 50 to 120°C and components with a boiling point greater than 120°C account for 5%, 85% of the weight composition respectively and 10%) enter the common rectifying column 1 that the number of theoretical plates is 30, the feeding position is the 17th theoretical plate, the reflux ratio is 3, the control tower top temperature is 40 ℃, and the side line is taken from the 20th theoretical plate The fraction 8 with a boiling range of 50-120°C is discharged, and the side stream fraction 8 enters the separation column 2 with a theoretical plate number of 120. The theoretical plate number on the upper part of the dividing plate is 20, and the number of theoretical plates on the lower part is also 30. The liquid phase distribution fraction on the side is 0.52, the gas phase distribution fra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com