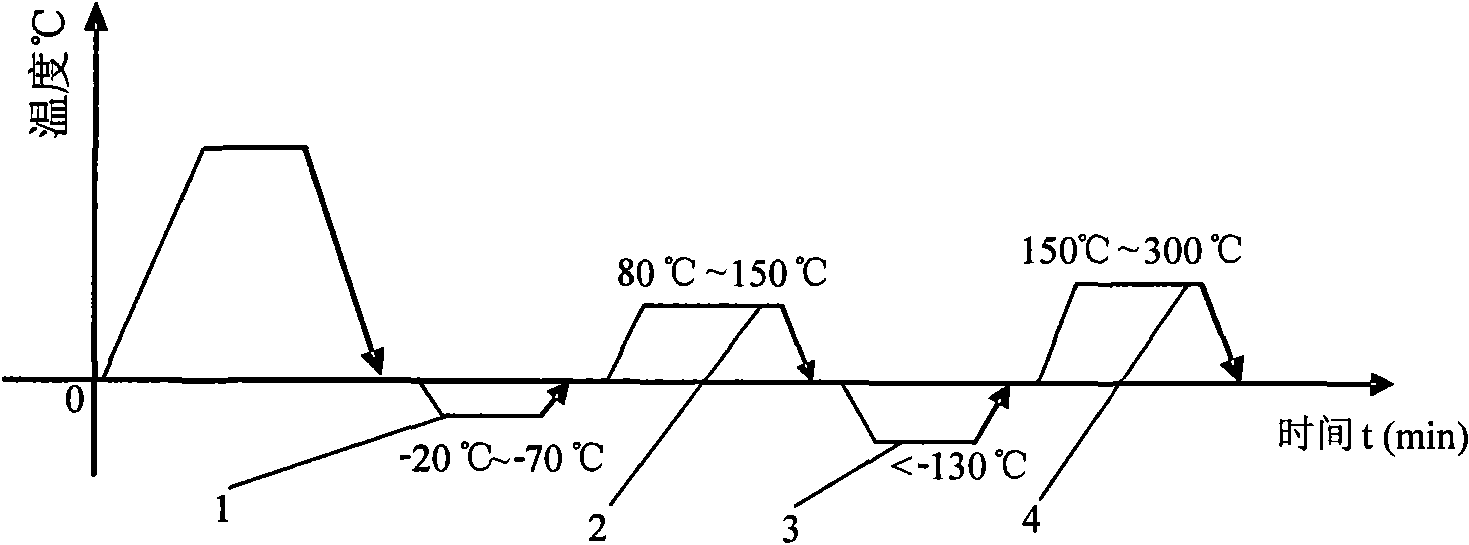
Composite temperature cold treatment process
A composite temperature and cold treatment technology, applied in the field of heat treatment of metal materials, can solve the problems such as the inability to significantly reduce the amount of retained austenite, the time of microstructure transformation, and the large temperature difference between the surface of the workpiece core, so as to avoid macro cracks and reduce Retained austenite, effect of increasing hardness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] 20mm with GCr15 material 3 The sample is example, carry out following embodiment:
[0034] GCr15 is quenched first, and immediately after quenching, cold treatment is performed. The temperature of cold treatment is -20°C to -70°C, and the time is 60 minutes. It is warmed up in the air. After reaching room temperature, the first low-temperature tempering is performed, and the temperature is 80°C ~150℃, the time is 60 minutes, cool in the air, after reaching room temperature, carry out cryogenic treatment, the temperature is -180℃~-130℃, the time is 60 minutes, then return to the temperature in the air, after reaching room temperature, carry out the second Secondary low-temperature tempering, the temperature is 150 ℃ ~ 300 ℃, the time is 120 minutes, and then cooled in the air. As a result of the treatment, the hardness is 60-64HRC.
[0035] The following table is the following table for the hardness performance of the workpiece after each embodiment specific parameter a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com