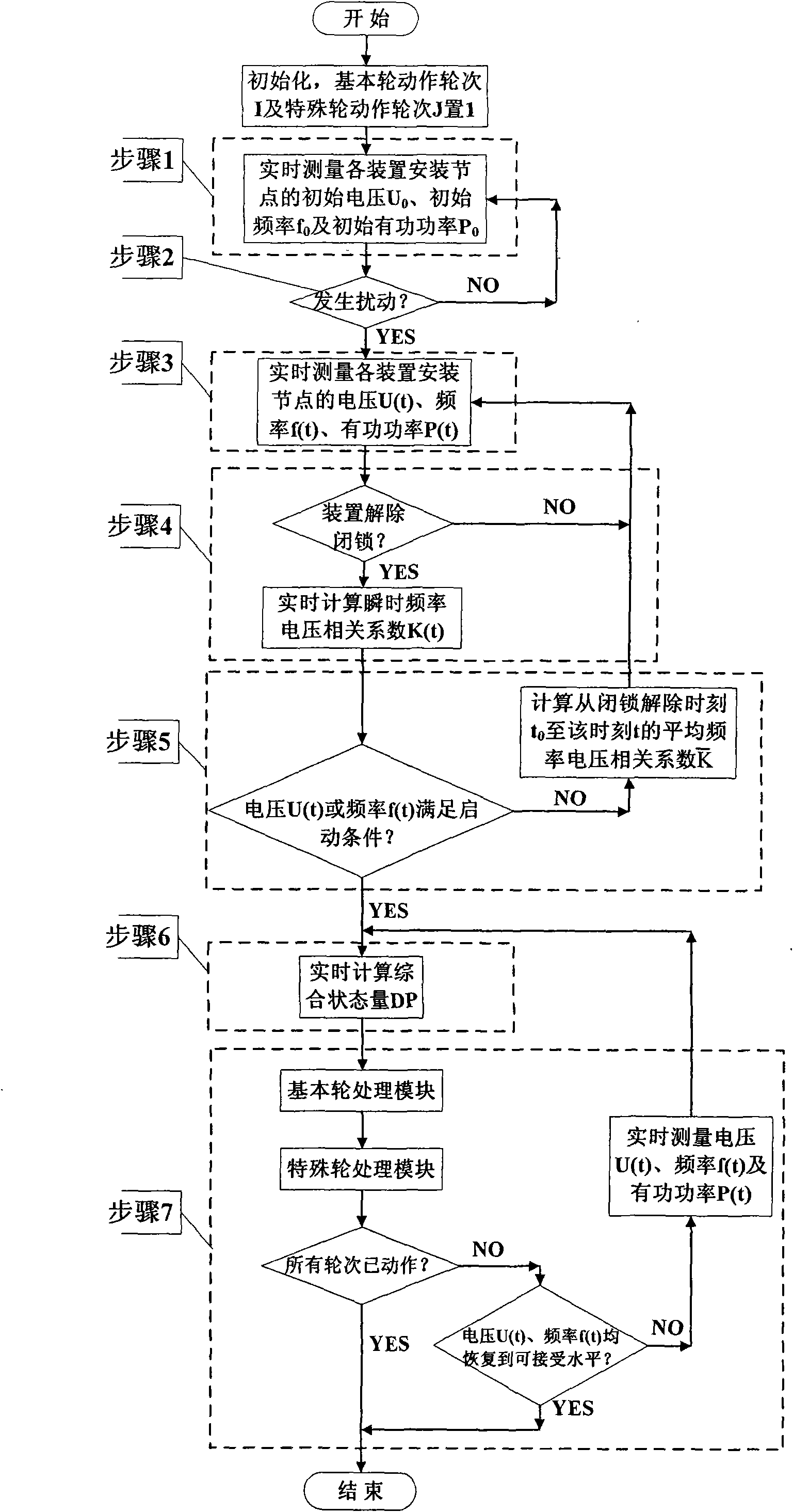
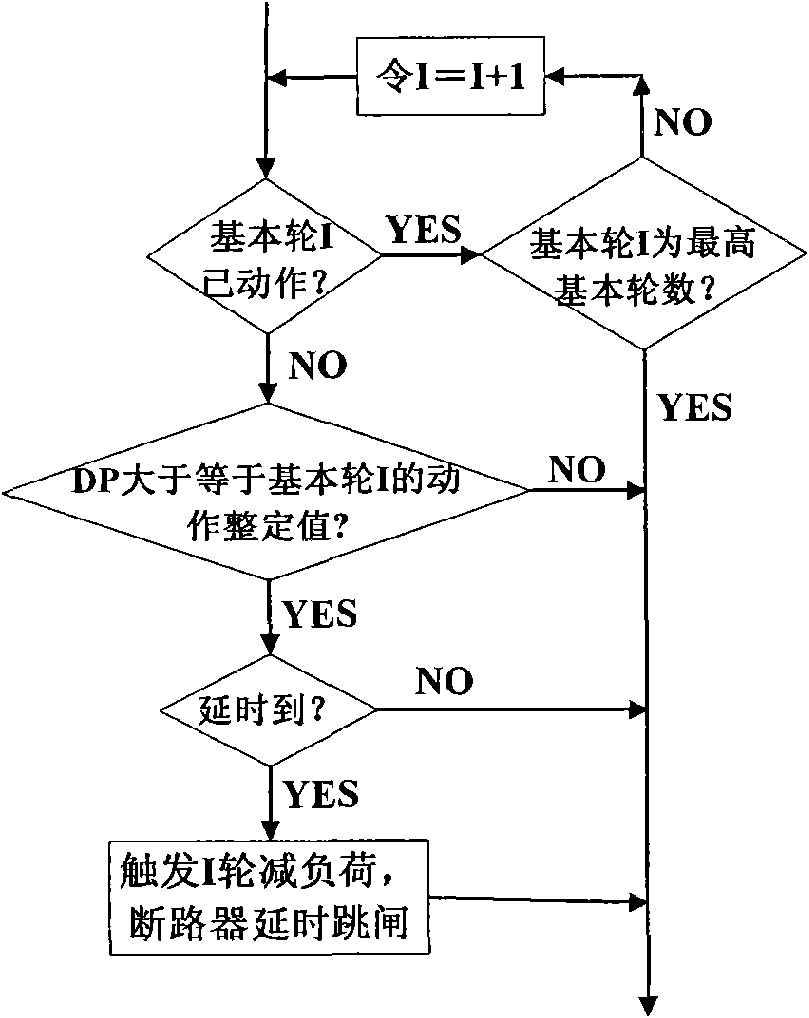
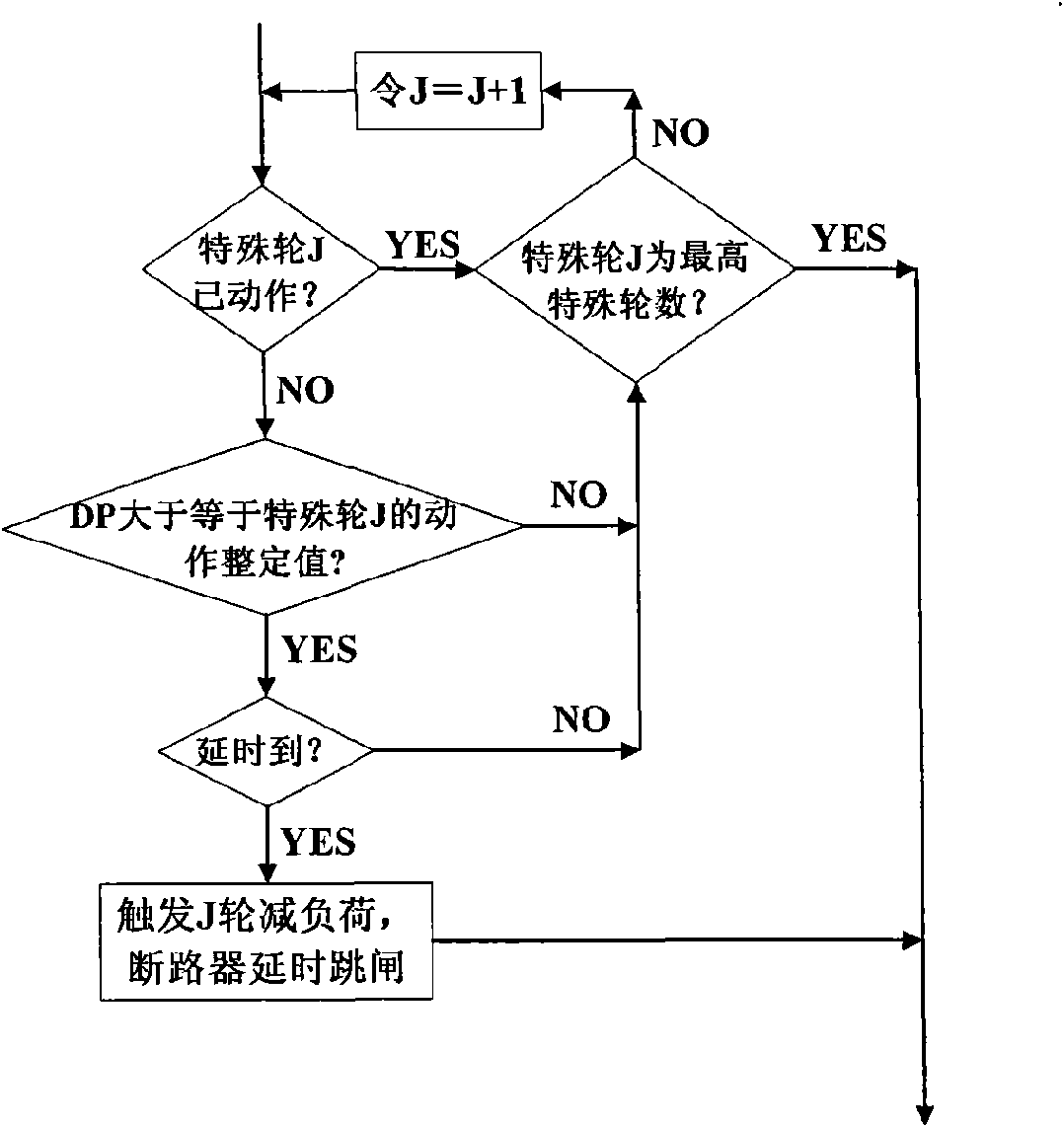
Automatic load-reducing control method for integrating the voltage frequency dynamic mutual influence
A technology of dynamic interaction and voltage frequency, applied in the direction of AC network voltage adjustment, electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve problems such as difficult dynamic interaction, redundant load shedding, and control device refusal to avoid large-scale power outages, Avoiding safe and stable damage and reducing the effect of load shedding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0045]Example 1: An embodiment of an automatic load shedding control method for different operating conditions
[0046] The geographic wiring of an actual receiving power grid (region A) is as follows: Figure 5 shown. The power grid in this area is connected to the main grid through two 500kV double-circuit lines of Bus1-Bus3 and Bus2-Bus3. When a main transformer of Bus3 fails, the transformer protection action cuts it off, and at the same time the other main transformer protection malfunctions, the isolated network in this area operates and there is a large power shortage. If part of the load cannot be removed quickly, it will cause a rapid collapse of frequency or voltage.
[0047] Considering three different operation modes, under each mode, the power received by the power grid from the external network accounted for 9%, 19%, and 27% of the total load in the area. It is assumed that each main load node in the grid has been equipped with an automatic load shedding contr...
example 2
[0057] Example 2: An embodiment of an automatic load shedding control method for different load characteristics
[0058] Variations in load characteristics can be characterized by different descriptions of the load model. Different load characteristics have a great influence on the transient voltage and transient frequency response after a fault, but the traditional low-frequency and low-voltage load shedding control method does not consider the influence of load characteristics on the dynamic process of the system in the real-time control algorithm, so it is difficult to compare Adapt to changes in load characteristics well, and in some cases may cause the device to refuse to move and cause the grid to collapse.
[0059] still with Figure 5 The mode 3 of the power grid in region A is shown as an example, and the fault scenario is the same as that of example 1. Two types of load models are considered: model 1 is static load, and model 2 is comprehensive load considering a c...
example 3
[0062] Example 3: An embodiment of an automatic load shedding control method for different fault types
[0063] by Image 6 The power grid in region B is shown as an example. The five small power plants in the whole network are responsible for 60.5% of the load power supply in the network, and a certain amount of hot backup is left (the hot backup capacity accounts for 10.9% of the total load of the whole network). In normal operation mode, about 40% of the load demand needs to be received from the main network through the 500kV double circuit line between Bus1-Bus2.
[0064] When the bus1-bus2 double circuit of the connection line is suddenly disconnected due to a fault, the area will operate in isolation, and there will be a large power shortage. It is necessary to quickly remove the excess load through the load shedding control device.
[0065] After the time-domain simulation of the power grid, it is found that when the tie line is disconnected in different fault forms, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com