Solid-state imaging device, drive method thereof and electronic apparatus
A solid-state imaging device and charge technology, which is applied in semiconductor devices, radiation control devices, televisions, etc., can solve problems such as afterimages and difficult charge transmission, and achieve the effects of increased sensitivity and increased saturation charge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0198] Example including two vertical gate electrodes
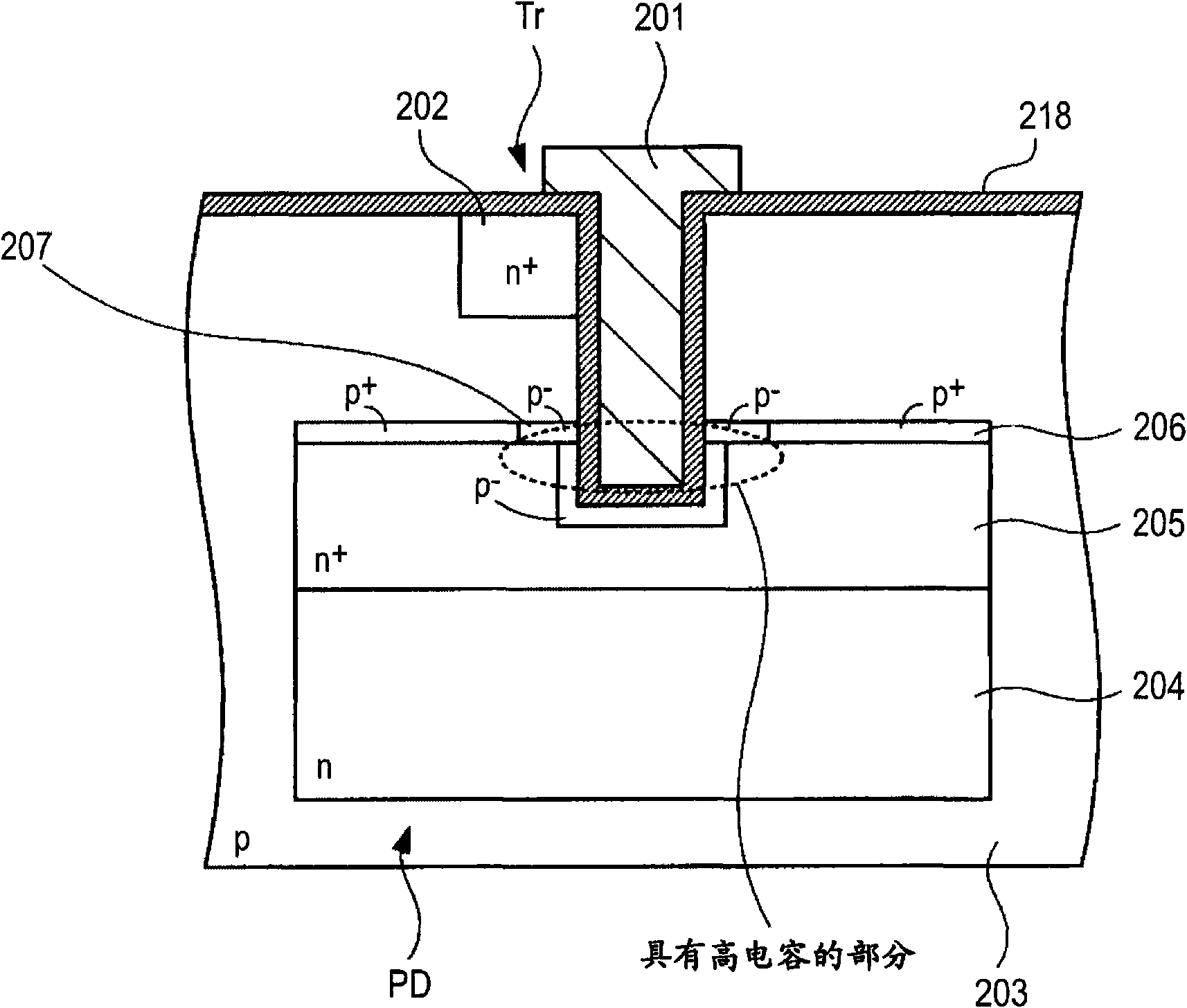
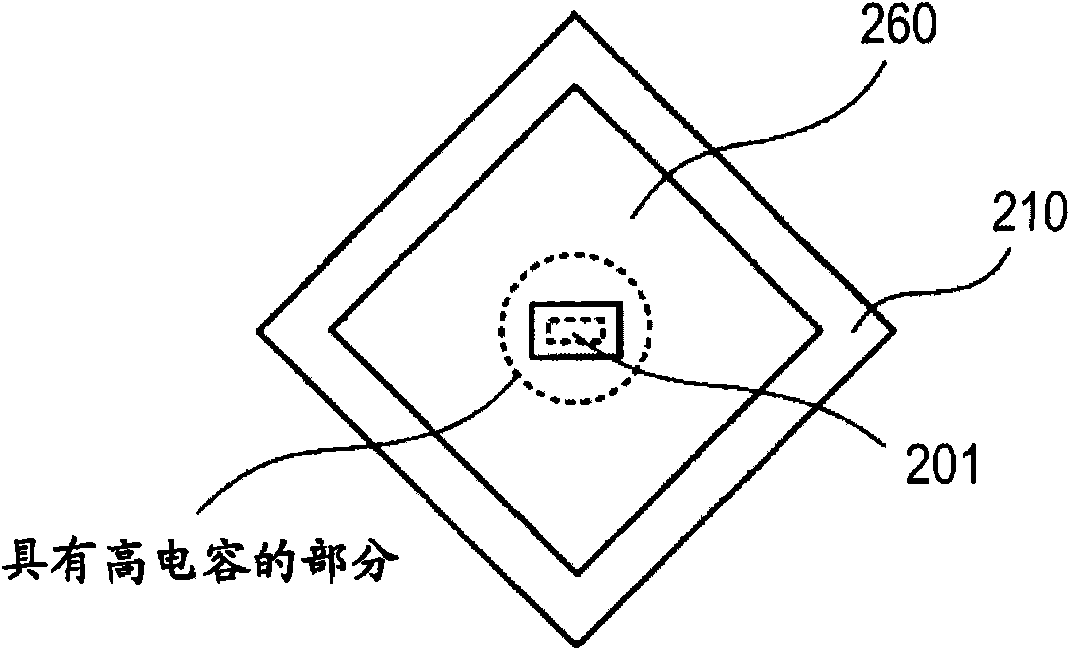
[0199] Image 6 A schematic planar structure of a solid-state imaging device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention is shown, Figure 7 shows along the Image 6 Schematic cross-sectional structure of line A-A in . Image 6 with Figure 7 are top and cross-sectional views of the relevant parts contained in a pixel. Such as Image 6 with Figure 7 As shown, the solid-state imaging device includes a photodiode PD and a charge readout transistor Tr formed in a semiconductor substrate 13 . The charge readout transistor Tr includes two vertical gate electrodes 12 a , 12 b formed at the peripheral portion of the photodiode PD and a floating diffusion region 11 formed at the corner of the photodiode region 60 near the outer region. In this embodiment, a case where the first conductivity type is the p type and the second conductivity type is the n type will be described.
[0200] The semiconductor substrate 13 ...
Embodiment 2
[0218] Example including two vertical gate electrodes
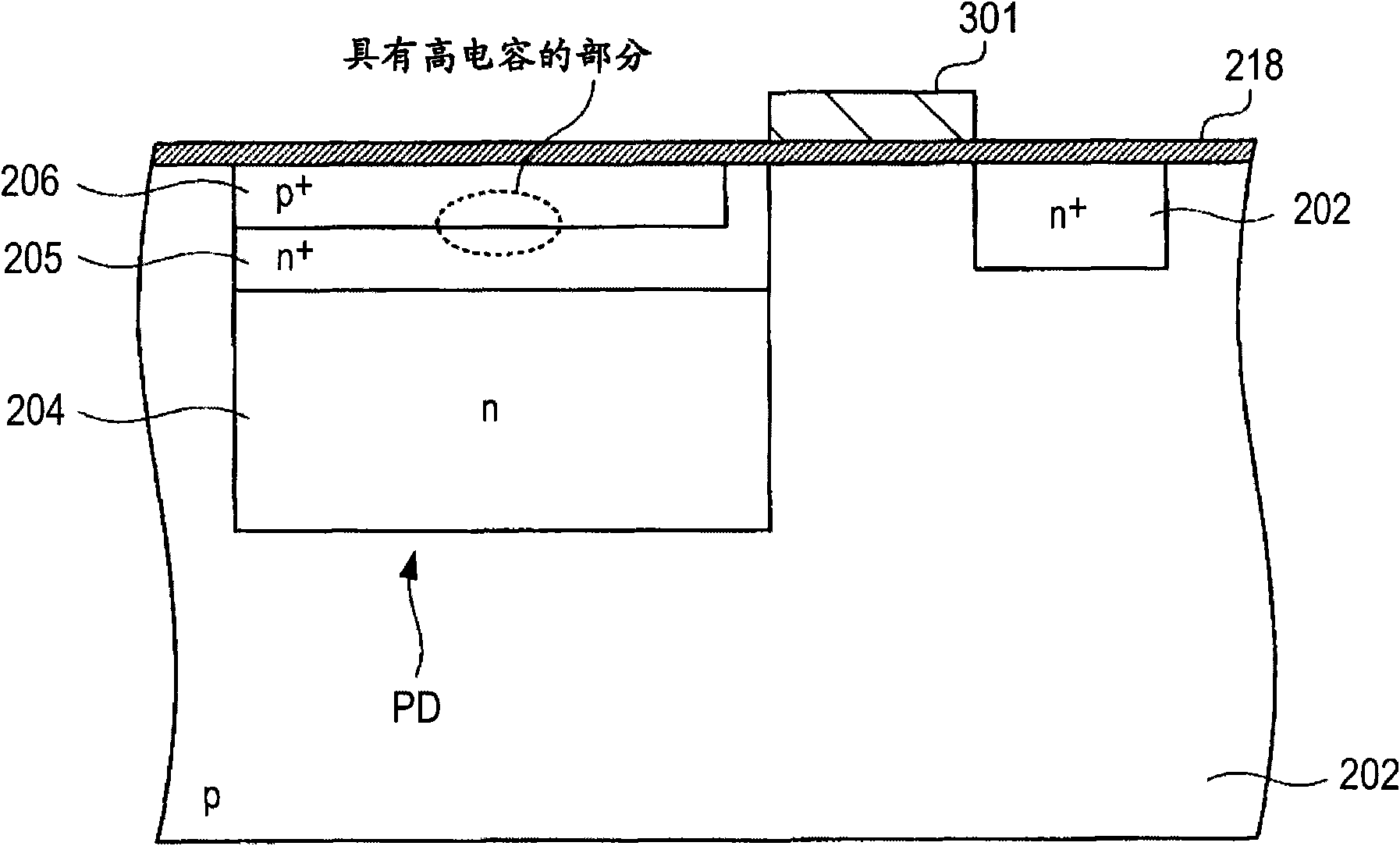
[0219] Figure 9 A schematic planar structure of a solid-state imaging device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention is shown, Figure 10 A cross-sectional structure along line B-B is shown. This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in the formation position of the floating diffusion region 11 . exist Figure 9 with Figure 10 in, with Image 6 with Figure 7 Corresponding parts are denoted by the same reference numerals, and repeated explanations are omitted.
[0220] In the solid-state imaging device of this embodiment, the floating diffusion region 11 is formed on the surface side of the semiconductor substrate 13 from the corner of the photodiode region 60 sandwiched by the vertical gate electrodes 12a, 12b to the inside of the photodiode region 60 . The floating diffusion region 11 is shared between the two vertical gate electrodes 12a, 12b. In the present embodiment, the floating diffusion region...
Embodiment 3
[0224] Example including two vertical gate electrodes and horizontal gate electrodes
[0225] Figure 11 A schematic planar structure of a solid-state imaging device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention is shown, Figure 12 shows along the Figure 11 The cross-sectional structure of the C-C line in . exist Figure 11 with Figure 12 in, with Image 6 with Figure 7 Corresponding parts are denoted by the same reference numerals, and repeated explanations are omitted.
[0226] In the solid-state imaging device of the present embodiment, the charge readout transistor Tr included in one pixel includes a horizontal gate electrode 19 , vertical gate electrodes 12 a and 12 b , and a floating diffusion region 11 .
[0227] Two vertical gate electrodes 12 a , 12 b are formed at the outer peripheral portion of the photodiode region 60 , respectively, along both edges constituting the corners of the photodiode region 60 . On the upper surface of the semiconductor su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com