Establishing method of non-antibiotic resistance selecting and marking system based on QAPRTase gene and application
A technology for antibiotic resistance and gene selection, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as the research and development of non-antibiotic resistance selection systems that have not been seen, and achieve the effect of stable transgenic plasmid strains and high plasmid copy number
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1. Construction of Escherichia coli strain BW25113ΔQAPRTase with QAPRTase gene knockout
[0039] The QAPRTase gene on the genome of the strain BW25113 was knocked out using the Red recombination system. The BW25113 strain, pKD46 plasmid, pKD13 plasmid and pCP20 plasmid in the experiment were all purchased from the Yale CGSC E. coli Collection Center. The experimental procedure is as follows:
[0040] (1) Prepare competent cells for electrotransformation of BW25113 strain by conventional methods, and electrotransform competent cells with pKD46 plasmid, and the electroporation parameters are 2500V, 6ms; apply the bacterial solution after recovery culture to LB plates (containing 50 μg / mL of Amp ), cultured at 30°C until a single colony was formed.
[0041] (2) Select Amp from the tablet R Single colonies were cultured in LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / mL Amp and 1 mM L-arabinose until OD 600 Prepare electroporation competent cells at about 0.3.
[0042] (3) ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Embodiment 2, the construction of non-antibiotic resistance plasmid vector
[0054] Based on the three plasmids pUC19, pBAD-hisA and pCDNA3.1+, which respectively represent T vector, prokaryotic expression plasmid and eukaryotic expression plasmid, the QAPRTase gene of Escherichia coli BW25113 and the QAPRTase gene of mouse were used to replace these three plasmids. Antibiotic resistance genes in a base plasmid.
[0055] 1. Construction of a plasmid that replaces the antibiotic resistance gene on the pUC19 plasmid with the Escherichia coli QAPRTase gene
[0056] (1) PCR amplification of basic plasmid sequences except antibiotic resistance genes. Using the pUC19 plasmid as a template, a pair of primers were designed, and MluI and XhoI restriction sites were respectively introduced at the 5' ends of the primers. The sequences of the designed primers were as follows:
[0057] F: CCGACGCGTACTCTTTCCTTTTCAATA
[0058] R: CCGCTCGAGCTGTCAGACCAAGTTTAC
[0059] The PCR system...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Embodiment 3, the comparison of antibiotic selection system and QAPRTase selection system of the present invention
[0105] 1. Comparison of transformation efficiency between antibiotic selection system and QAPRTase selection system
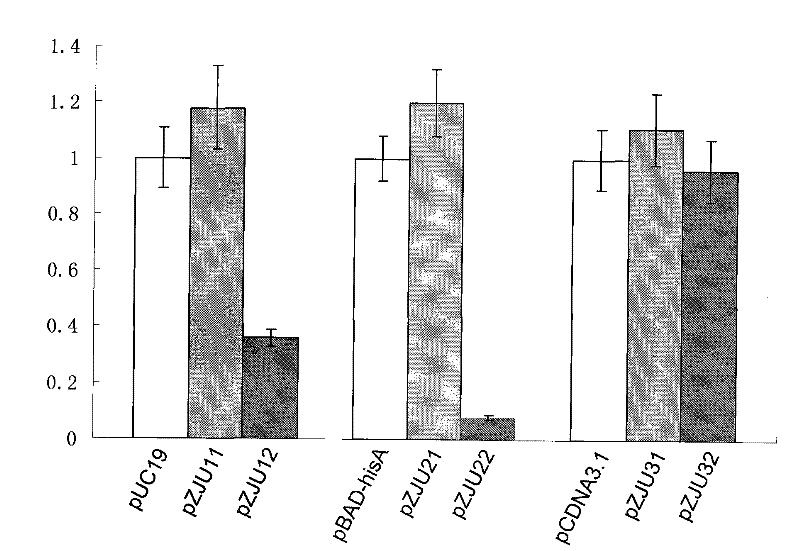
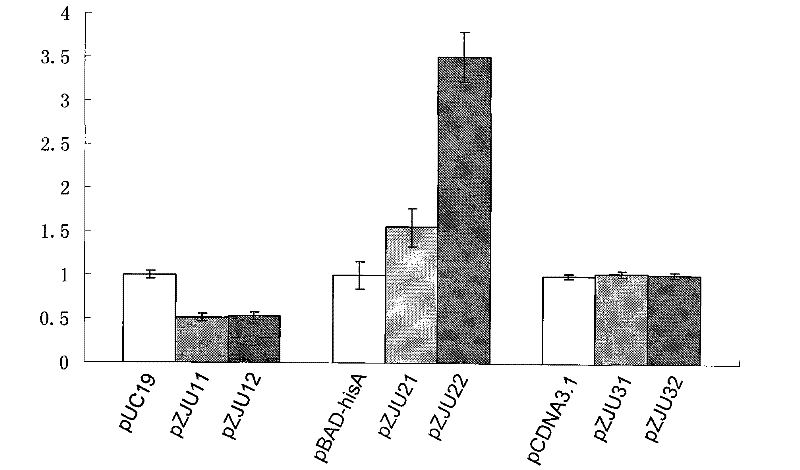
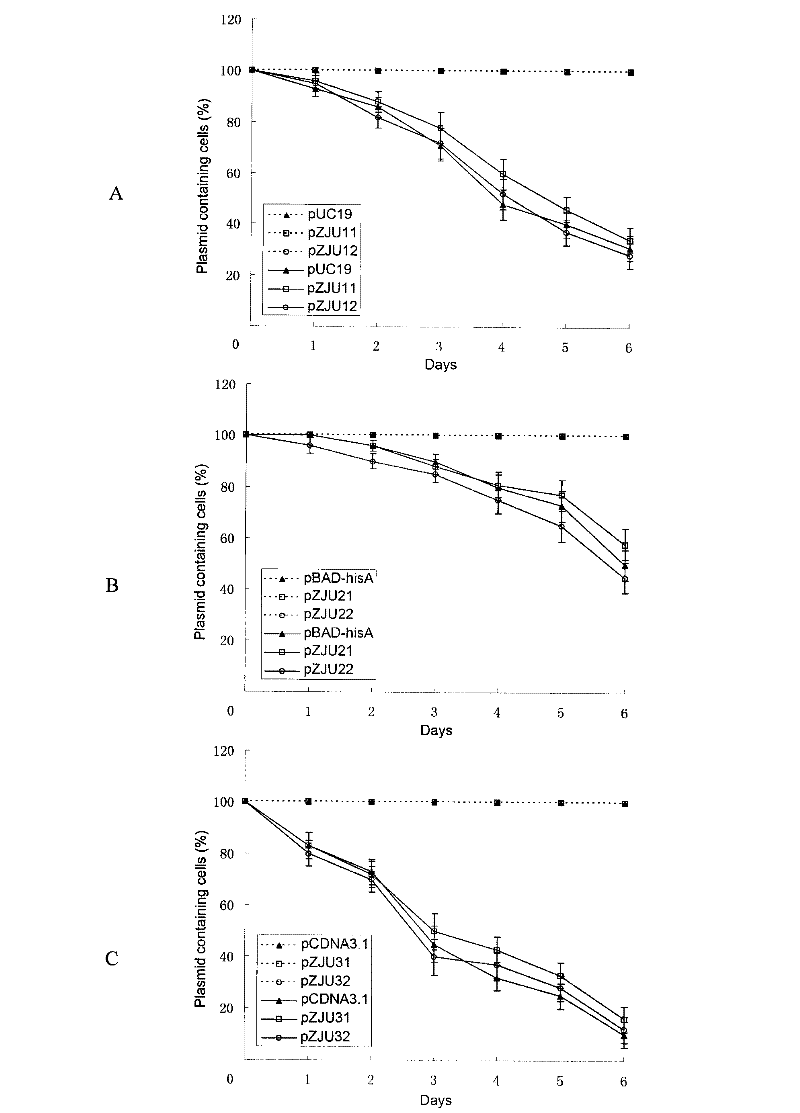
[0106] 0.1 μg of pUC19, pZJU11, pZJU12, pBAD-hisA, pZJU21, pZJU22, pCDNA3.1+, pZJU31, pZJU32 plasmids were respectively transformed into BW25113ΔQAPRTase, and the bacterial solution after recovery culture was spread on the plate. Among them, pUC19, pBAD-hisA and pCDNA3.1+ were coated on LB plates (containing 50 μg / mL Amp), and the other six plasmids were coated on M9 plates. After culturing at 37°C until a single colony appeared, the transformation efficiency was counted. see results figure 1 , when the antibiotic resistance gene on the plasmid was replaced with the QAPRTase gene of bacterial origin, its transformation efficiency was not inferior to that of the original plasmid. When the antibiotic resistance gene on the plasmid was rep...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com