Controller for permanent magnet synchronous motor and motor control system
A permanent magnet synchronous and control device technology, applied in the direction of motor generator control, electronic commutation motor control, motor control, etc., can solve problems such as setting errors, achieve the effects of suppressing imbalance and improving speed control accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
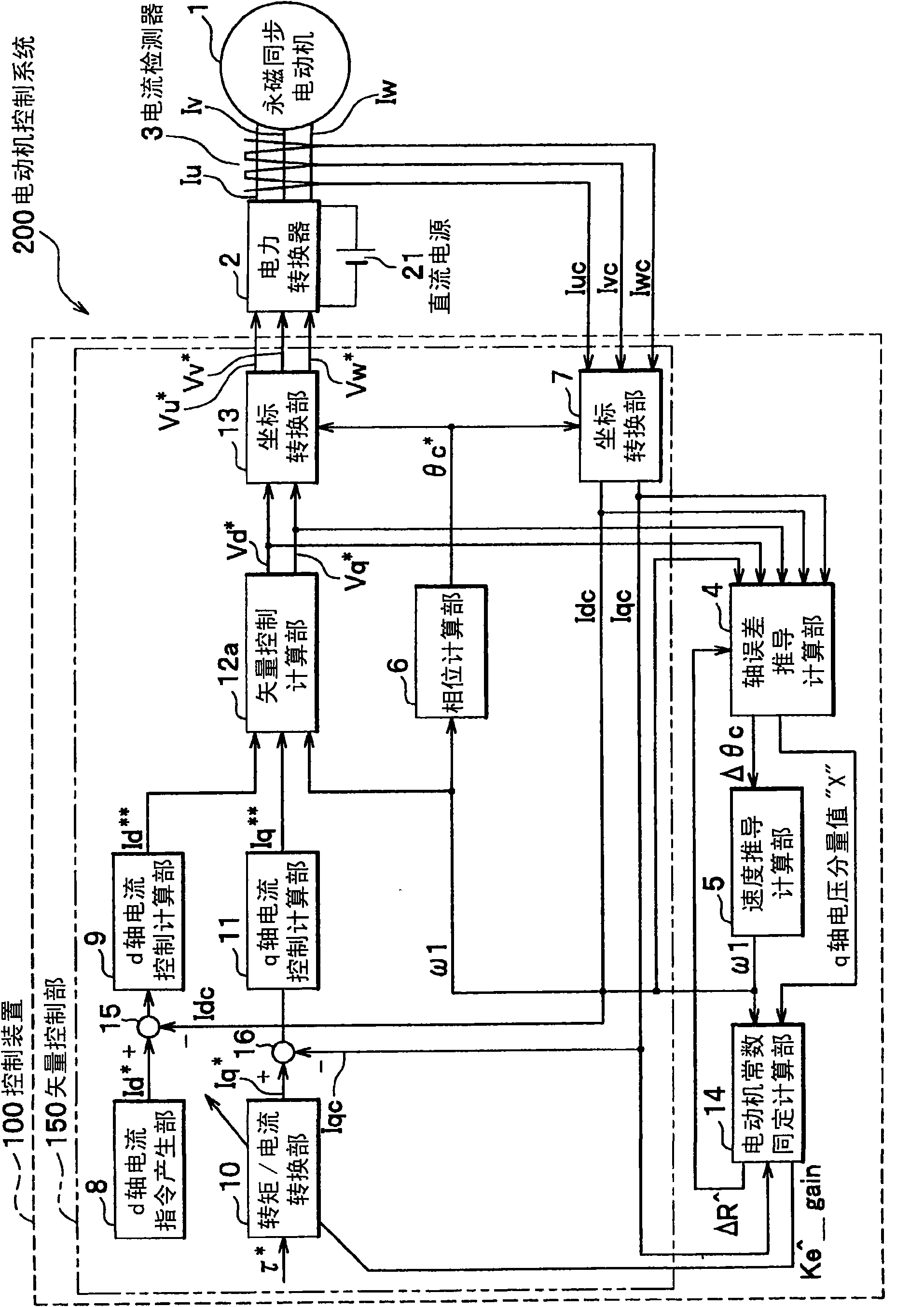
[0028] figure 1 It is an overall configuration diagram of the motor control system according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0029] figure 1 The motor control system 200 is composed of a permanent magnet synchronous motor 1, a power converter 2, a current detector 3, a DC power supply 21, and a control device 100. The vector control unit 150 of the control device 100 uses the torque command τ * Perform dq vector control as the target value.
[0030] The permanent magnet synchronous motor 1 is configured such that a rotor with built-in permanent magnets rotates inside a stator, and motor constants (R, Ld, Lq, Ke) define the axis of excitation (d axis) and torque axis (q axis). Voltage and current characteristics. The power converter 2 compares the voltage command value Vu * 、Vv * 、Vw * With the triangular wave, the output PWM modulates the three-phase AC voltage of the DC voltage. The current detector 3 detects the three-phase AC currents Iu, Iv, and ...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
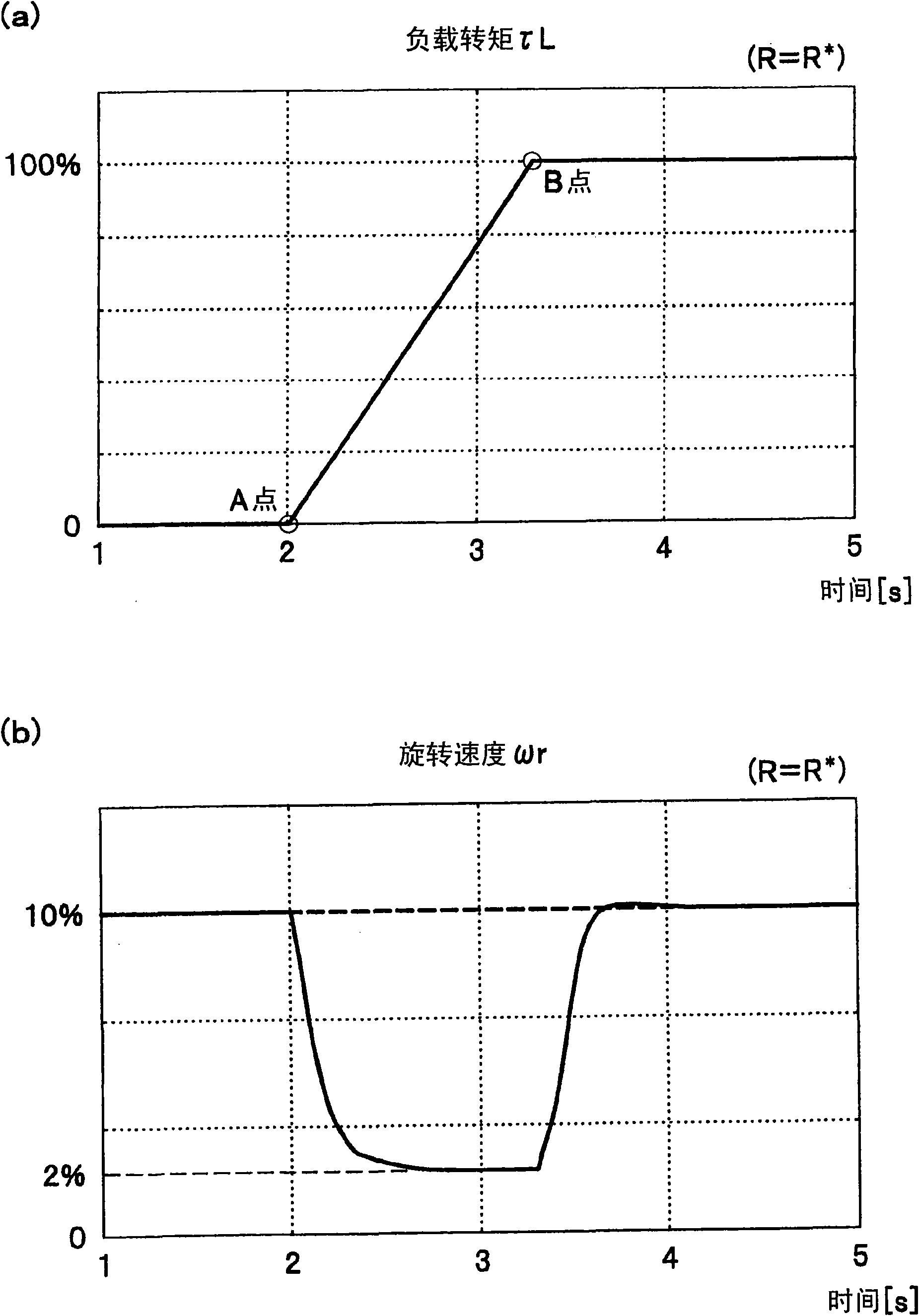
[0182] In the first embodiment, the output value (ΔR^, Ke^_gain) of the motor constant constant calculation section 14 is used to correct the motor constant of the torque / current conversion section 10 and the shaft error derivation calculation section 4, and the output value (ΔR^ , Ke^_gain), can also be applied to the set value of the vector control calculation unit 12.
[0183] Figure 12 Each constituent element of the overall configuration diagram is changed from the vector control calculation unit 12a to the vector control calculation unit 12b. That is, except that the motor control system 210 has the control device 110, the control device 110 has the vector control unit 152, and the vector control unit 152 has the vector control calculation unit 12b, and figure 1 same.
[0184] The vector control calculation unit 12b outputs the d-axis voltage command value Vd shown in the mathematical formula (28). * and the q-axis voltage command value Vq * .
[0185] (mathematica...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
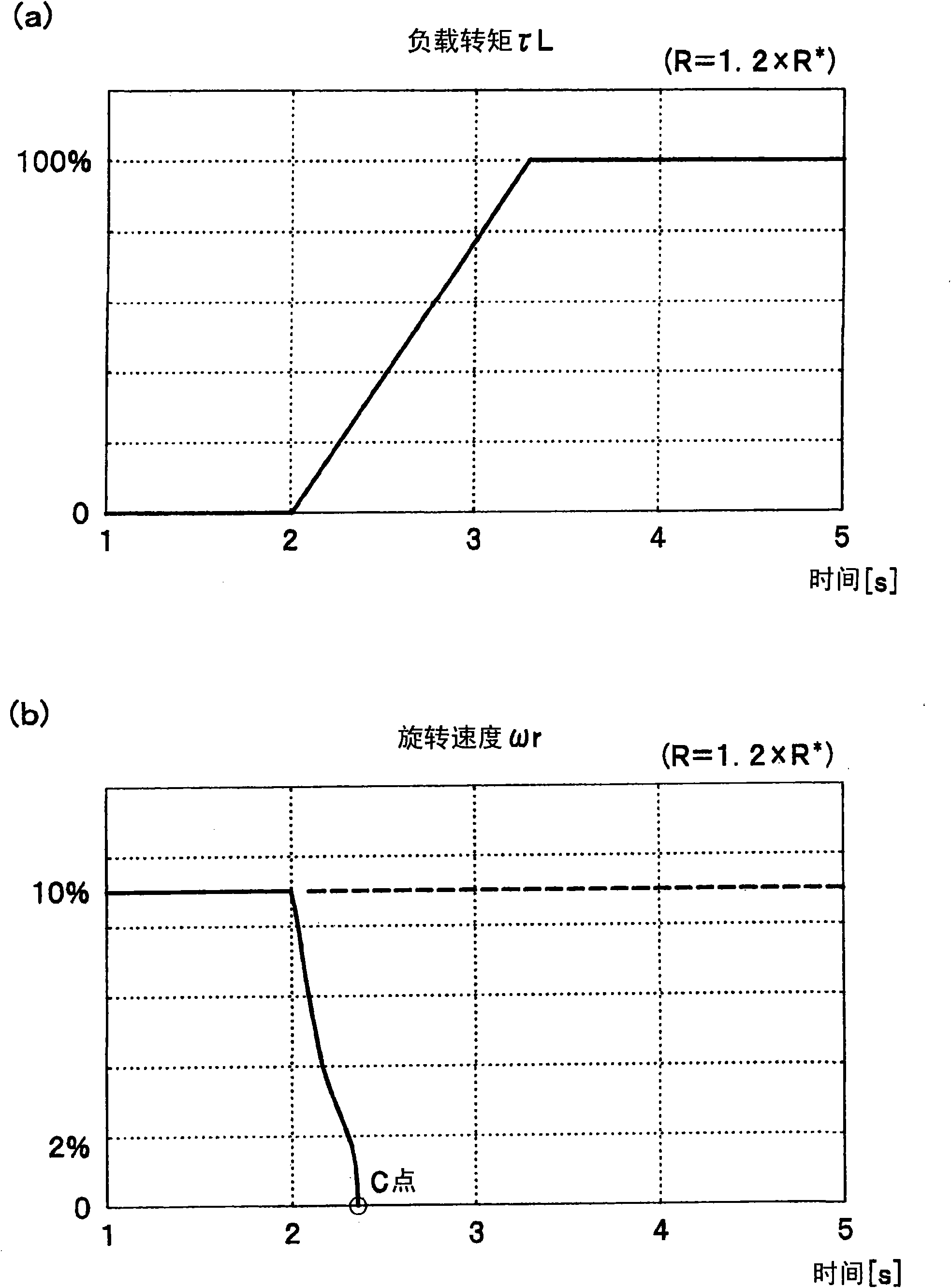
[0189] In the first embodiment, the output value (ΔR^, Ke^_gain) of the motor constant constant calculation section 14 is used to correct the motor constant of the torque / current conversion section 10 and the shaft error derivation calculation section 4, but the output value is used ΔR^ can also be applied to the calculation of the control gains of the d-axis current control calculation unit 9 and the q-axis current control calculation unit 11 .
[0190] exist Figure 13 In the overall structure diagram, except that the motor control system 220 has the control device 120, the control device 120 has the vector control unit 154, and the vector control unit 154 has the d-axis current control calculation unit 9a and the q-axis current control calculation unit 11a, the others are similar to figure 1 same.
[0191] As shown in the mathematical formula (29), if the control gain (Kp_d, Kp_q) of the d-axis current control calculation part 9a and the q-axis current control calculation ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com