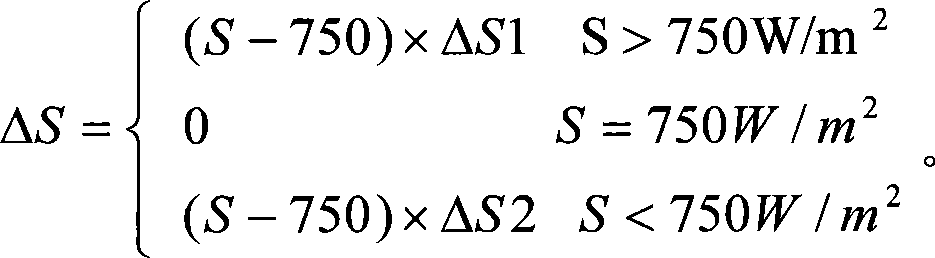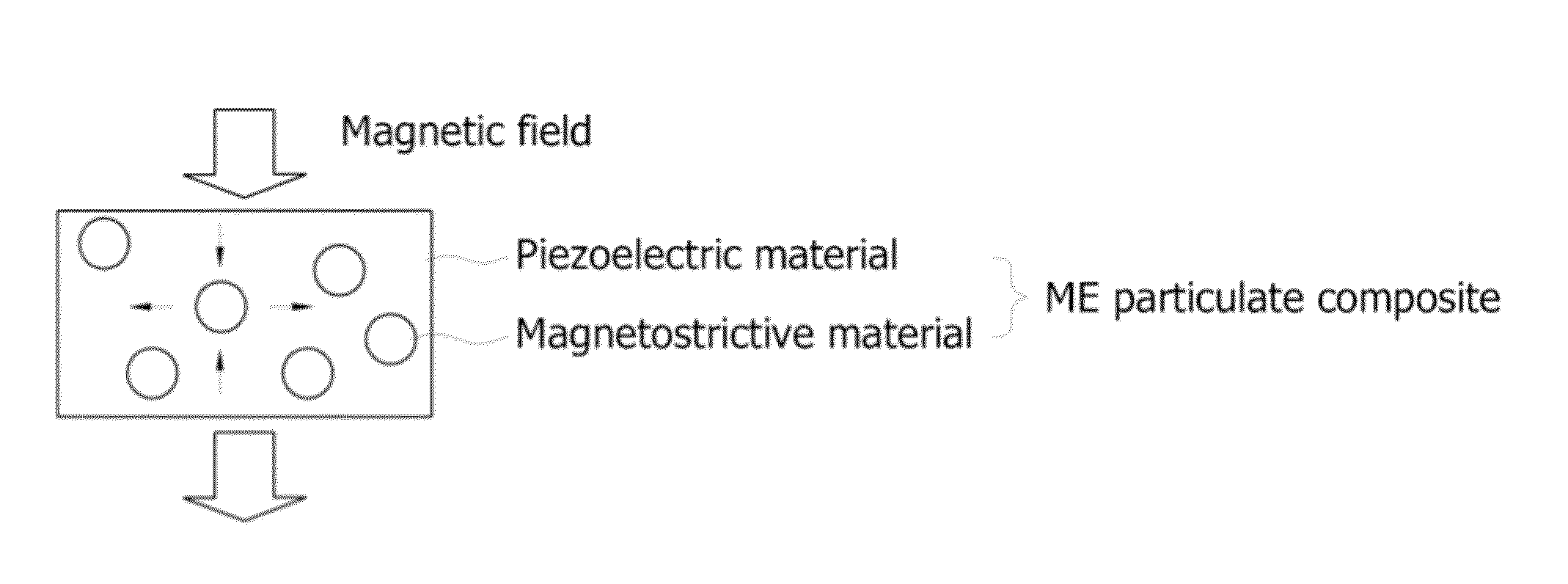Patents
Literature
125 results about "Voltage coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
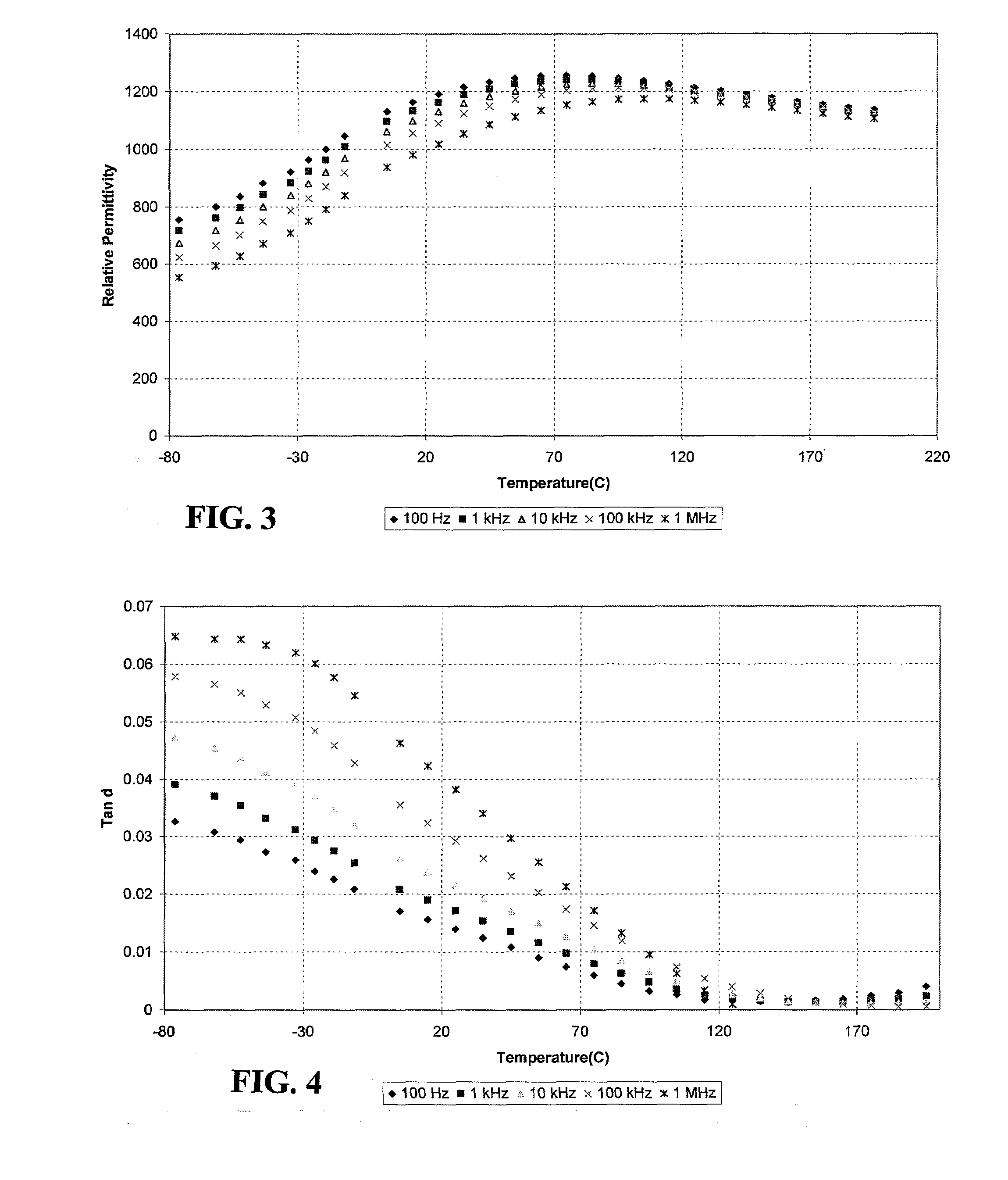
Voltage coefficient, measured in ppm/V, is negative for most materials. Voltage coefficient is generally measured between 10% and full rated voltage.
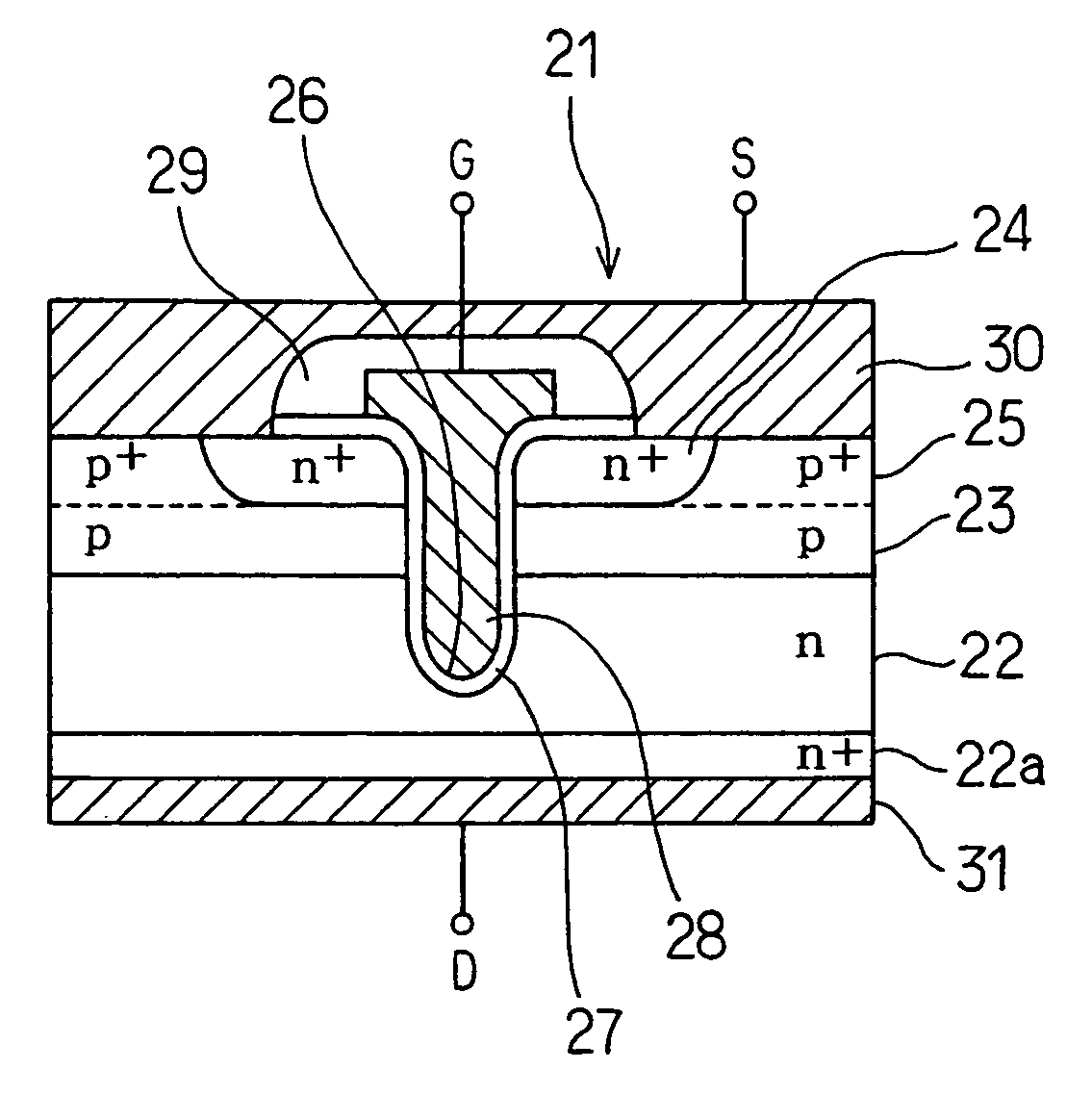
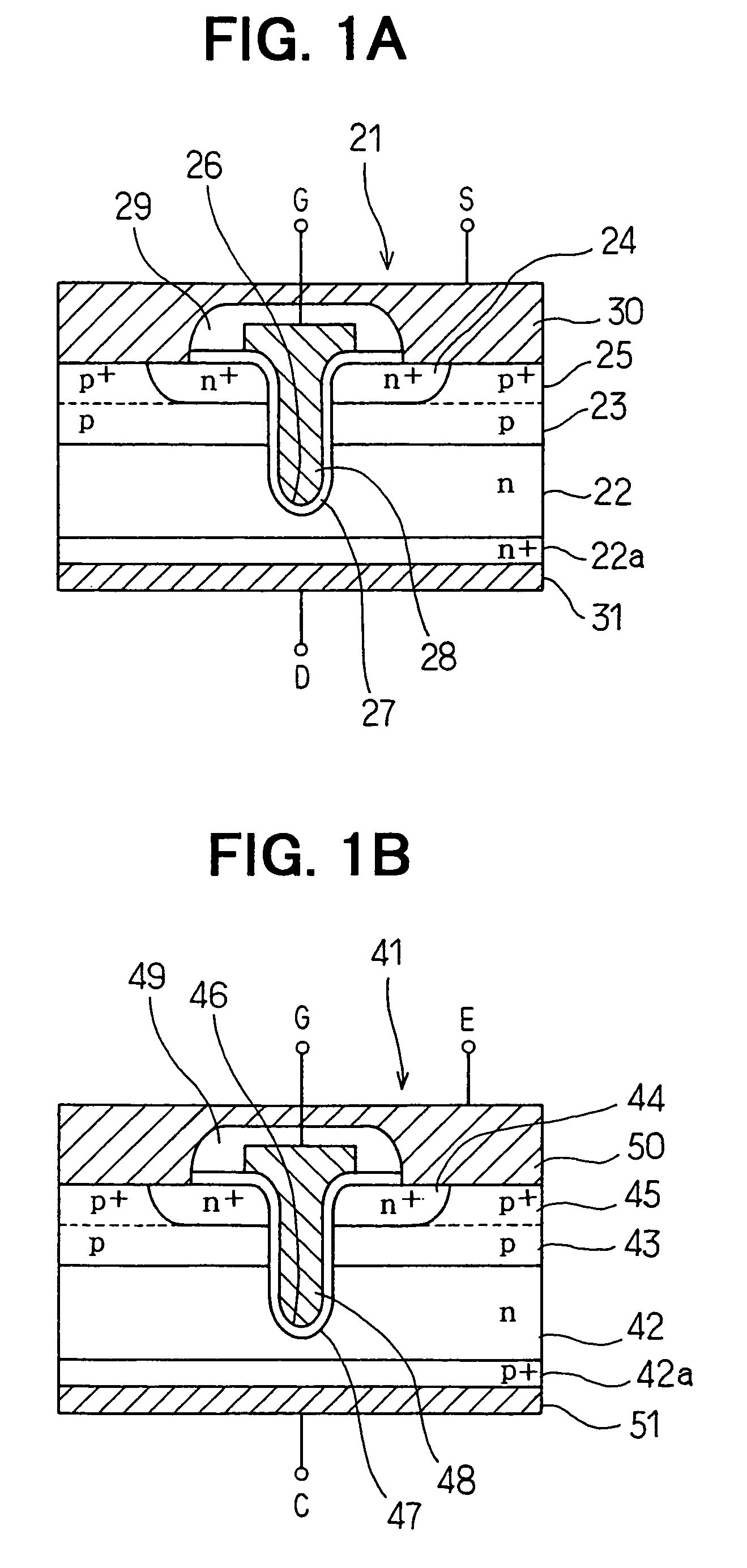
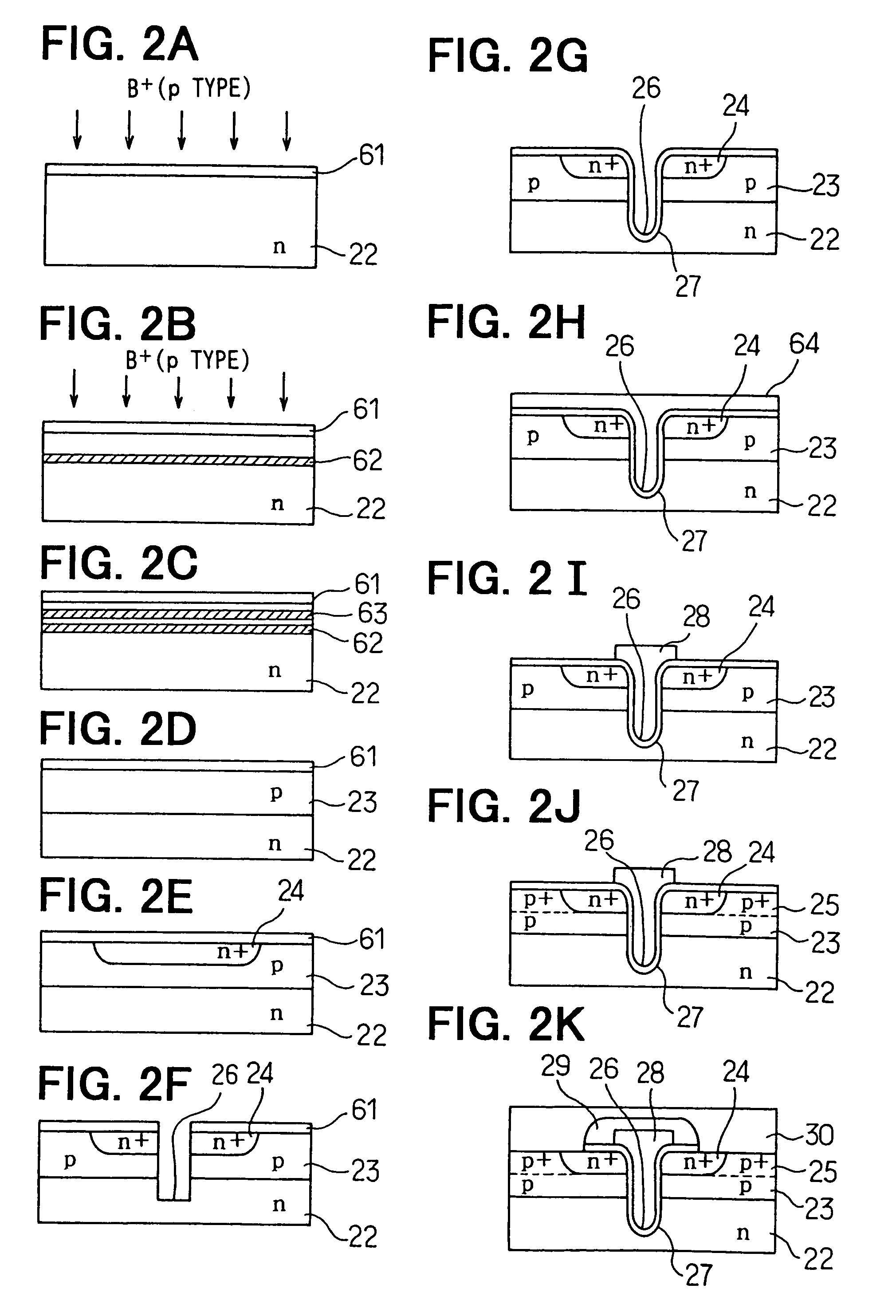
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS7037788B2Suppress mutationDeterioration of characteristicSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSub thresholdHigh acceleration
By improving profile of impurity concentration in a channel portion of an FET or an IGBT of a trench gate type, variation of threshold value is lessened, and a destruction caused by current concentration is prevented while suppressing deterioration of cut-off characteristics. An island of a base region of p-type is formed in a semiconductor substrate of n-type by carrying out high acceleration ion implantation twice followed by annealing, so that the impurity concentration profile in a channel portion changes gradually in a depth direction. Accordingly, it is possible to lessen variation of the threshold value and to reduce pinch resistance while at the same time improving sub-threshold voltage coefficient and conductance characteristics.
Owner:DENSO CORP
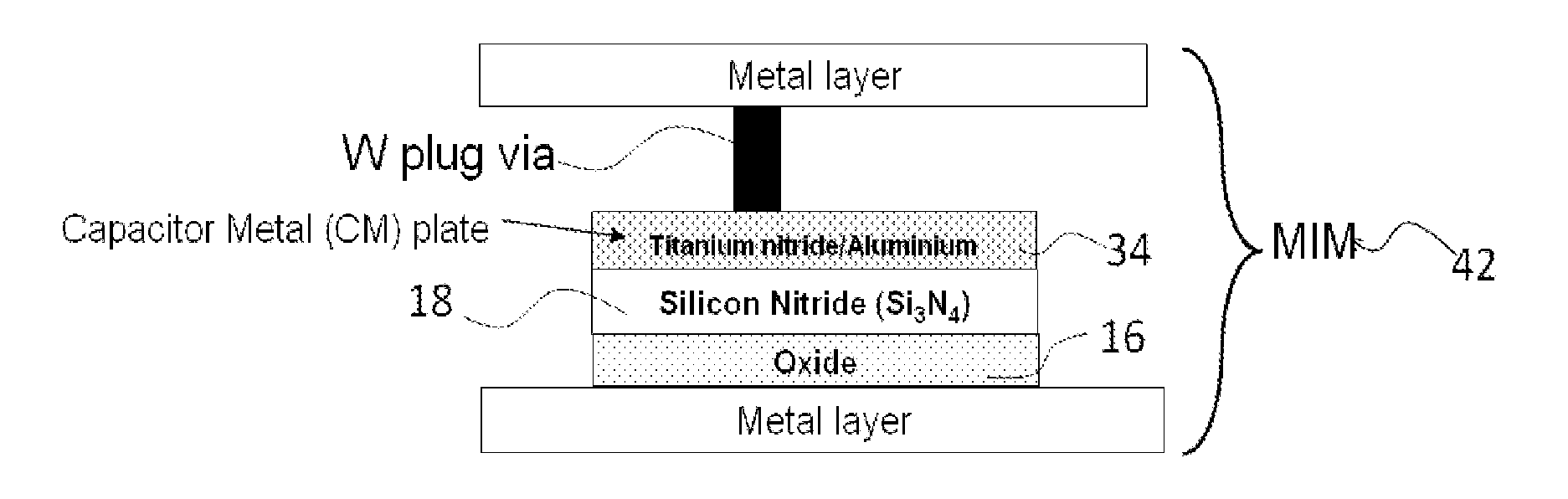
Ultra-low voltage coefficient capacitors
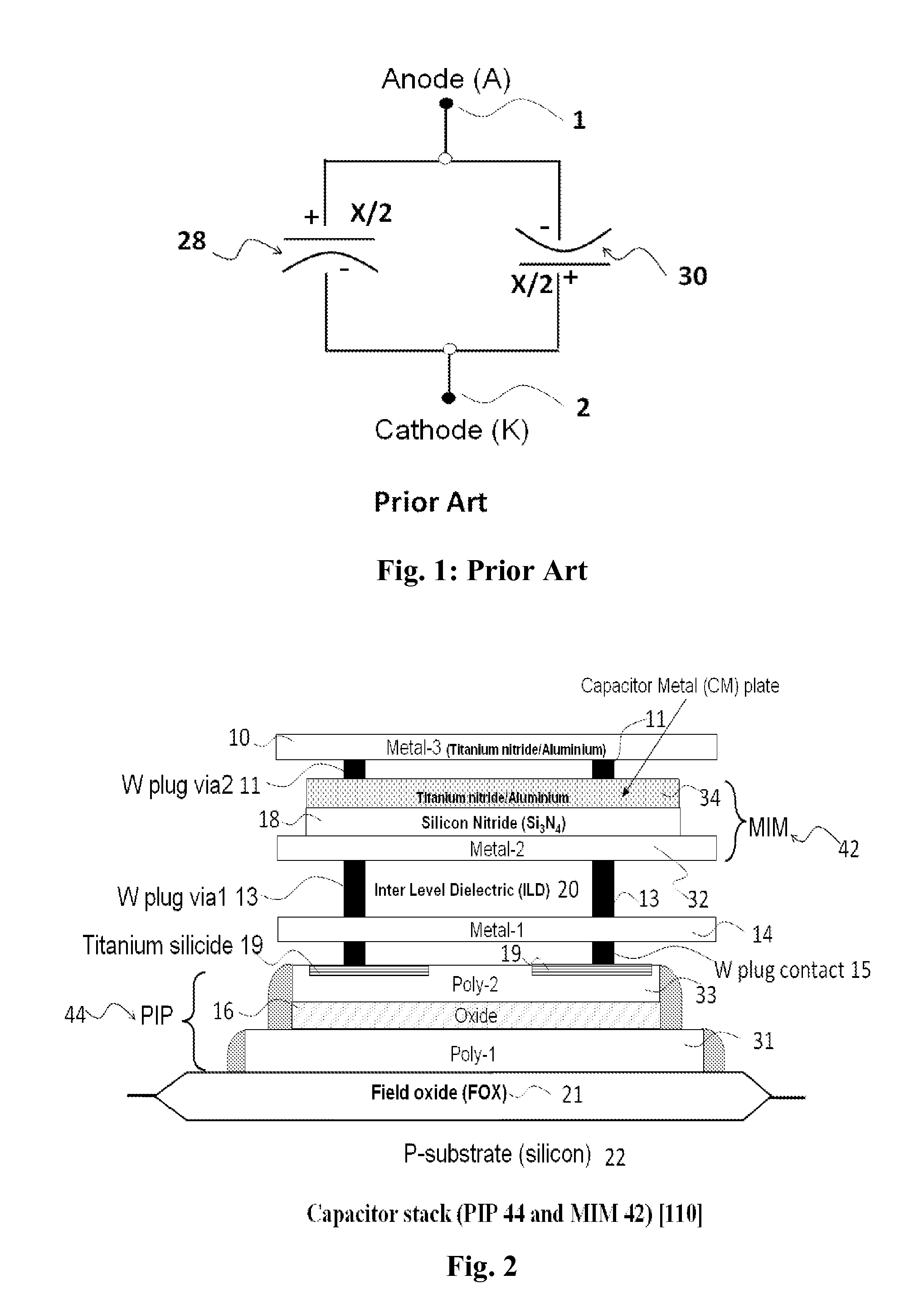
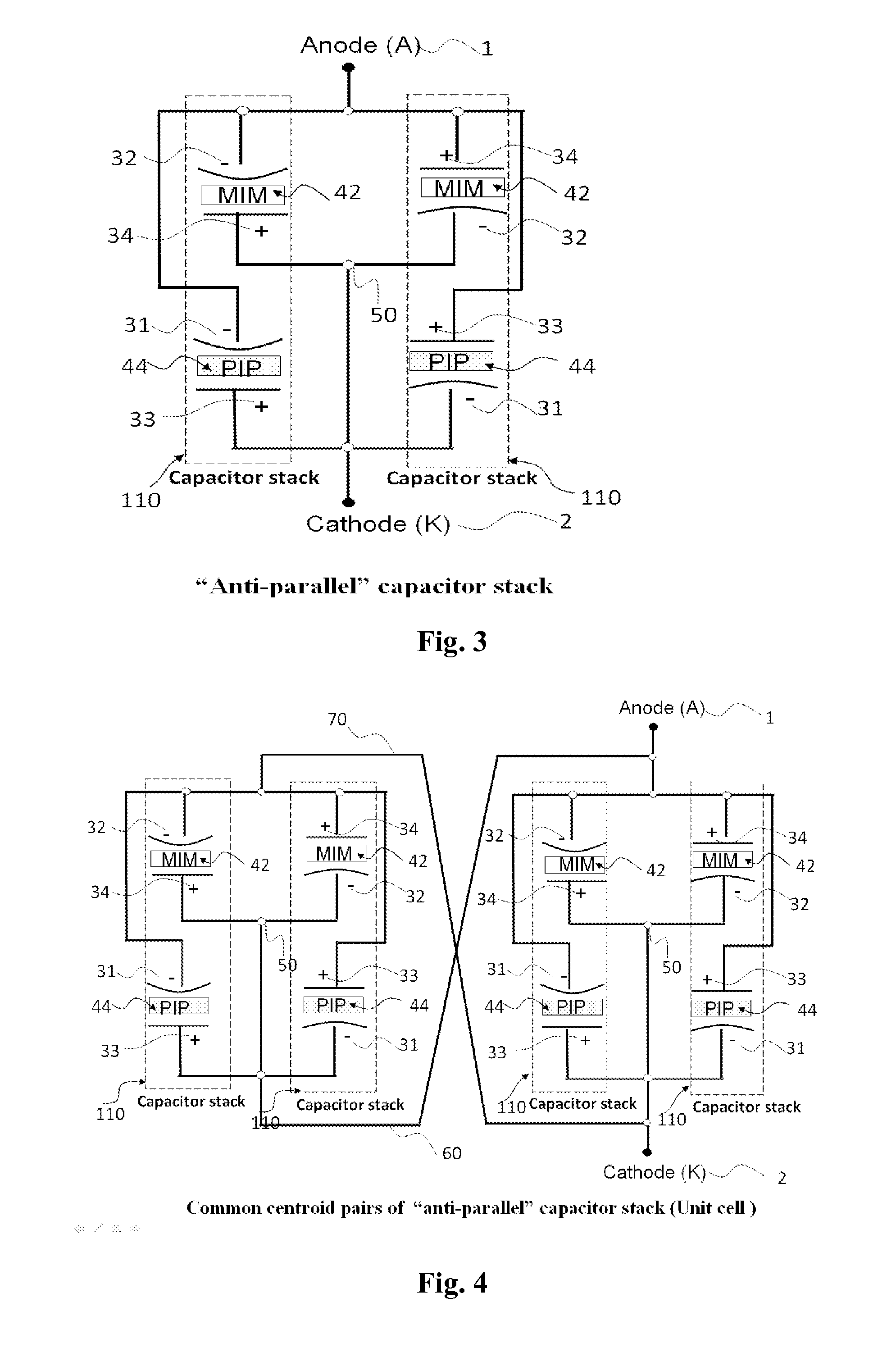
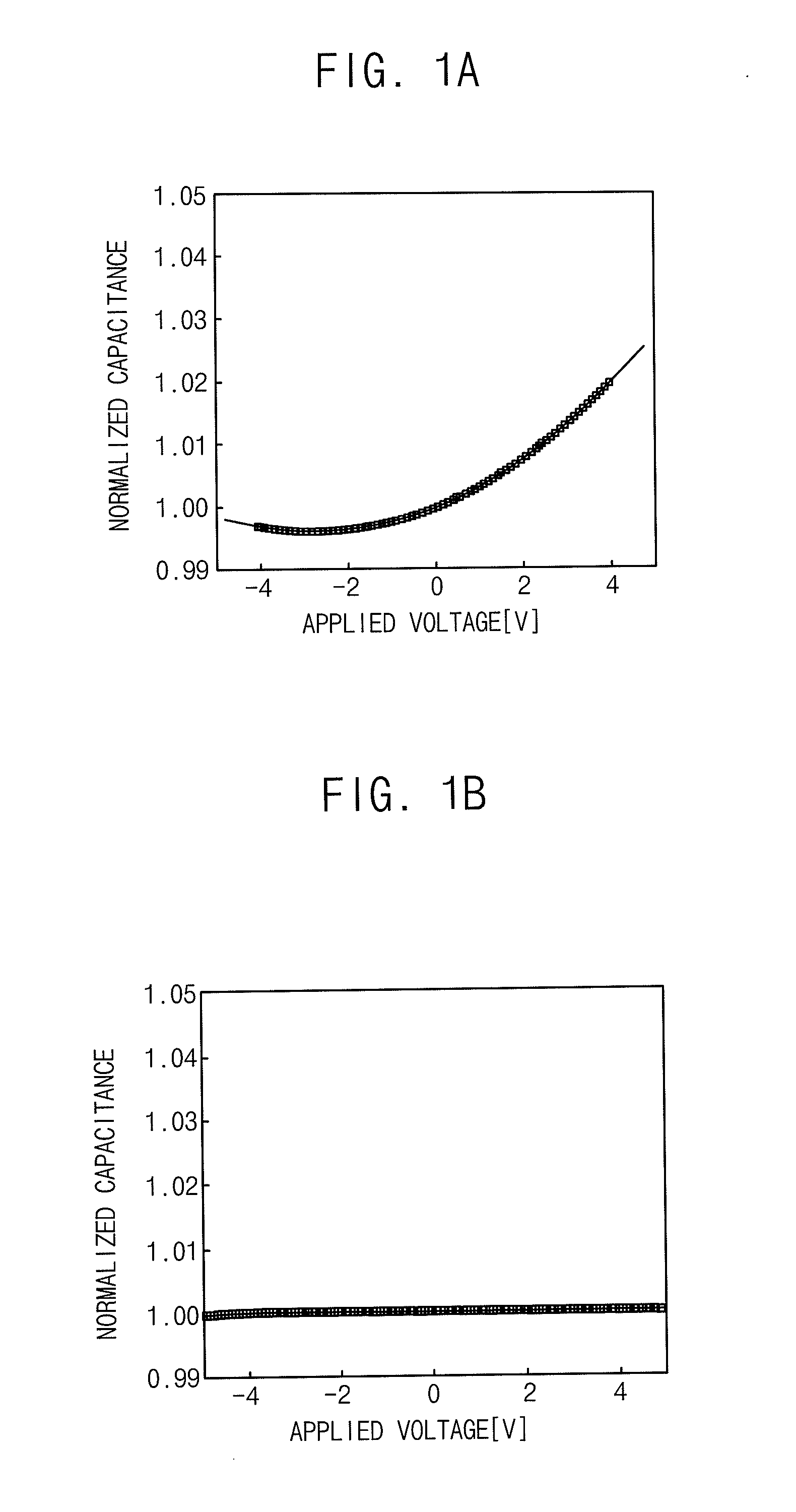
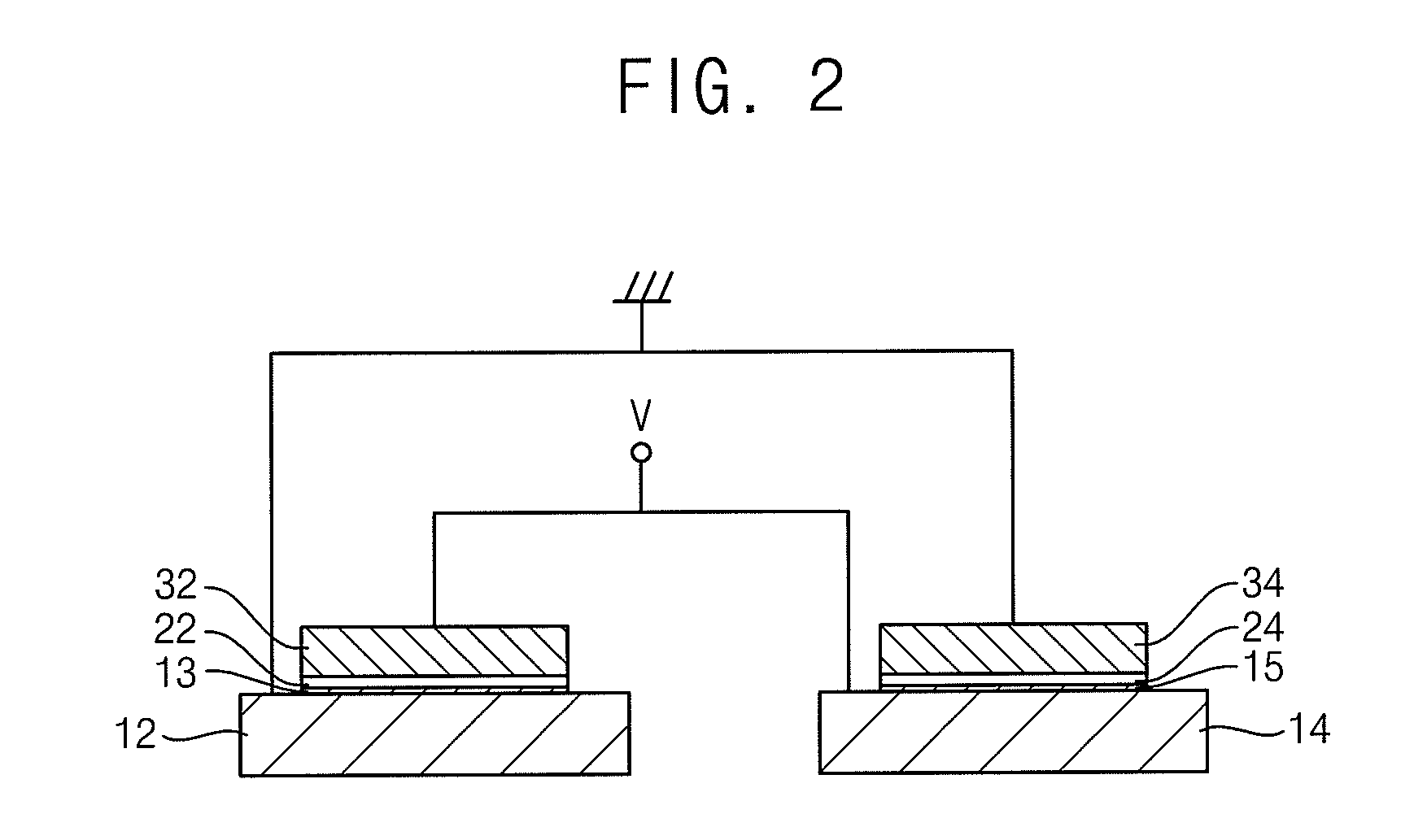
A capacitor has first and second conducting plates and a dielectric region between the plates, wherein the dielectric region comprises two dielectric materials for each of which the variation of capacitance with voltage can be approximated by a polynomial having a linear coefficient and a quadratic coefficient, and wherein the quadratic coefficients of the two dielectric materials are of opposite sign. The capacitor comprises for example a first capacitor (42) and a second capacitor (44) that one connected in an anti-parallel manner. The insulating layer (18) of the first capacitor comprises silicon nitride and the insulating layer (16) of the second capacitor comprises silicon dioxide
Owner:X FAB SEMICON FOUNDRIES
Voltage-variable photovoltaic system maximal power tracing control method adapting to weather status
InactiveCN101236446AMeet the needs of maximum power trackingImprove performancePhotovoltaic energy generationElectric variable regulationIlluminanceClosed loop
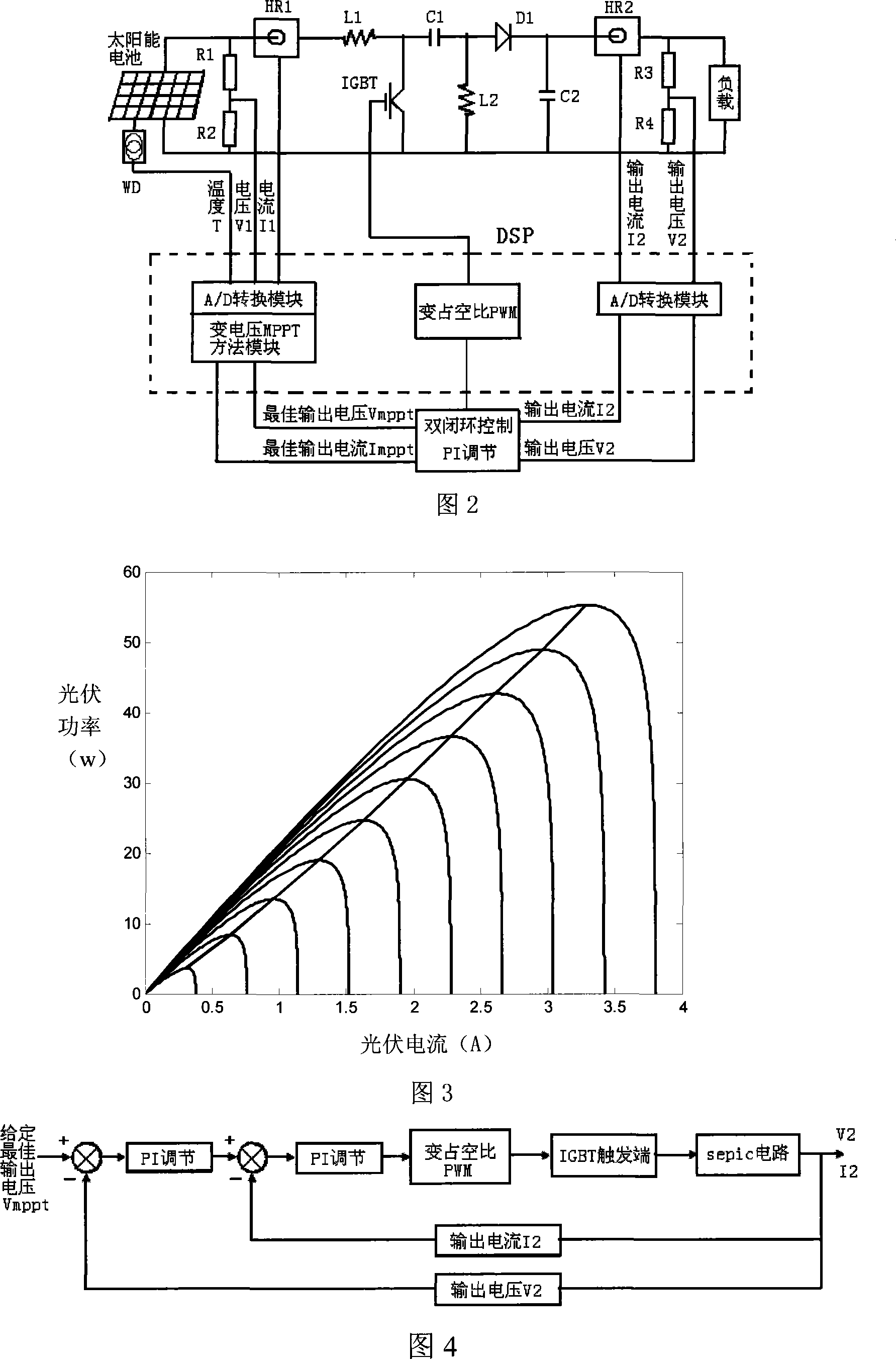
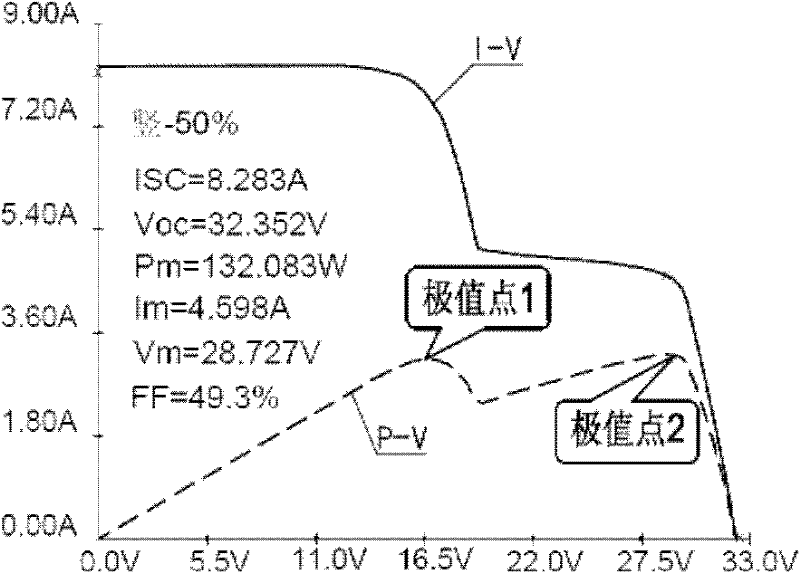
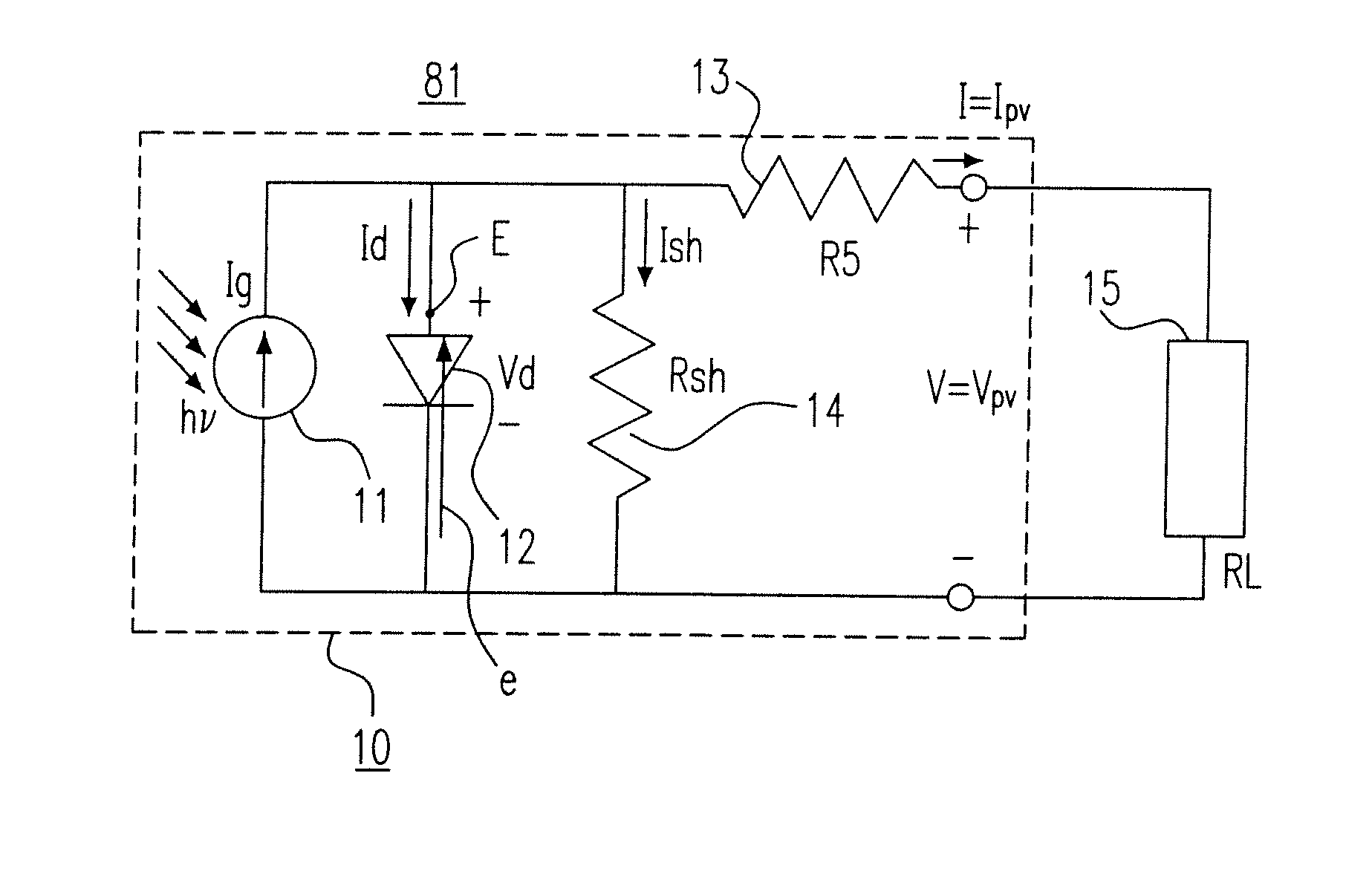
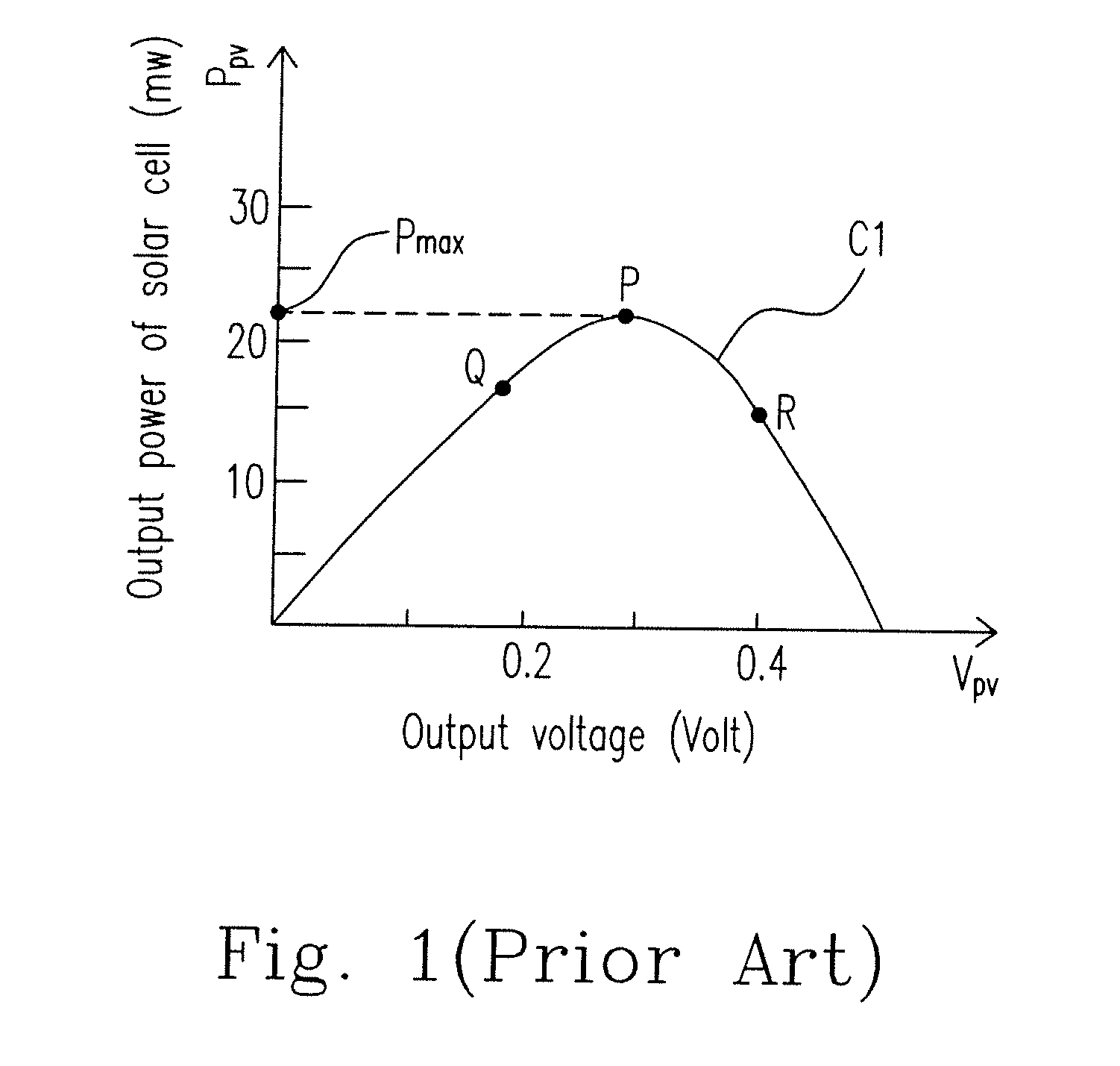
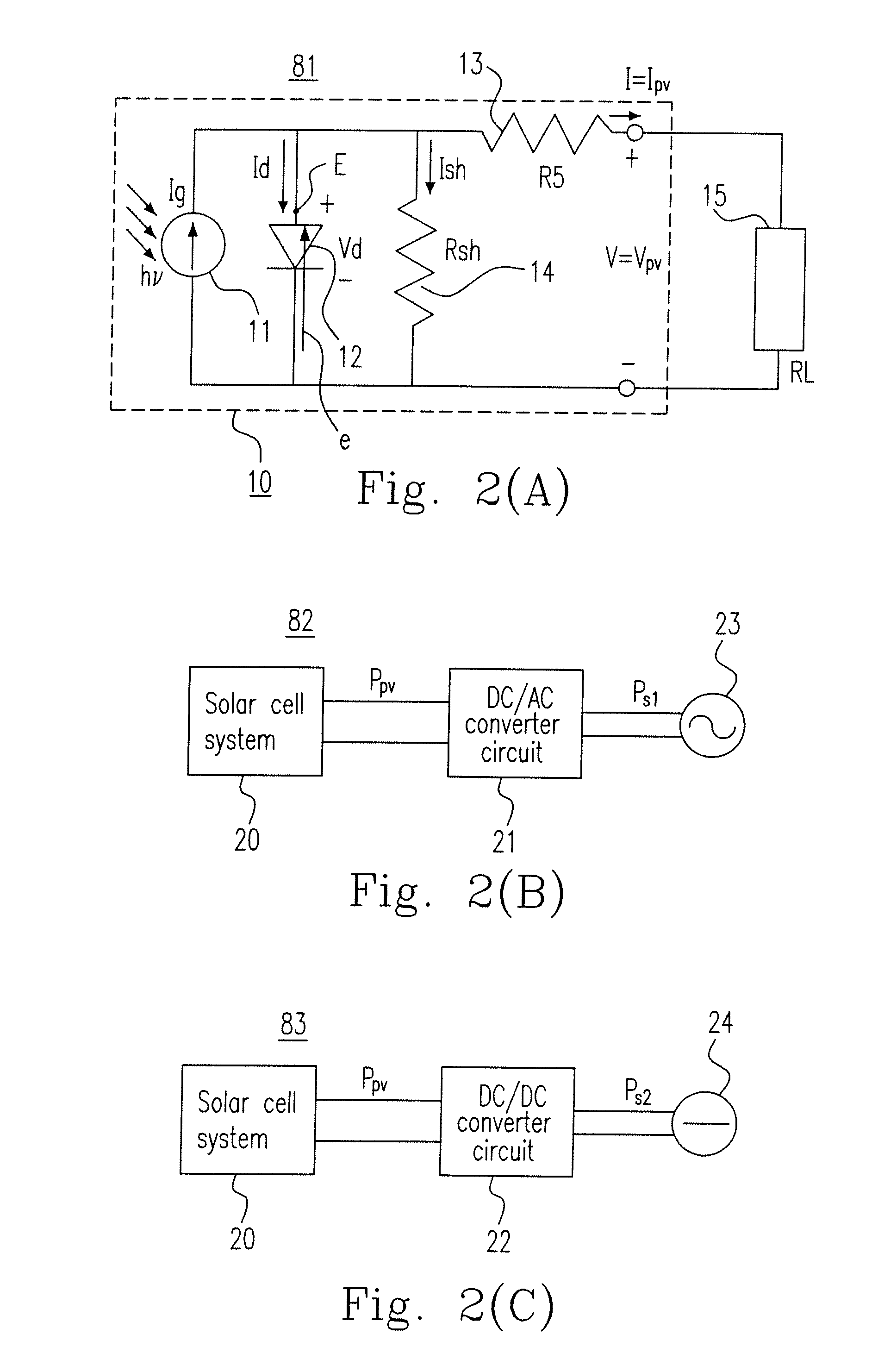
The invention provides a maximum power tracking control method of a voltage variable photovoltaic system which adapts to weather conditions, belonging to the photovoltaic power generation technical field; firstly, three data of voltage, current outputted by a photovoltaic battery and temperature of a photovoltaic battery plate at a moment are collected by a collection circuit, and an open circuit voltage value and an illuminating value at the moment are worked out based on the collected data; secondly, an approximate optimum output voltage value is obtained by a real optimized voltage coefficient multiplying the open circuit voltage value, and the temperature and the illumination are compensated, which obtain a real optimum output voltage value, and further a real optimum output current value is obtained; thirdly, an output value of a load end is compared with the real optimum output voltage value and the real optimum output current value, and a maximum power output is realized based on the proportional plus integral control on a fluctuating chopper circuit and a double closed loop of the voltage and the current. The maximum power tracking control method of the voltage variable photovoltaic system improves the output power of a photovoltaic power generation system and simultaneously ensures the operational stability and reliability of the system.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for the on-board functional diagnosis of a soot sensor in a motor vehicle and/or for the detection of further constituents in the soot
InactiveUS20110015824A1Inexpensively detectEasy to produceVehicle testingElectrical controlElectricityOn board
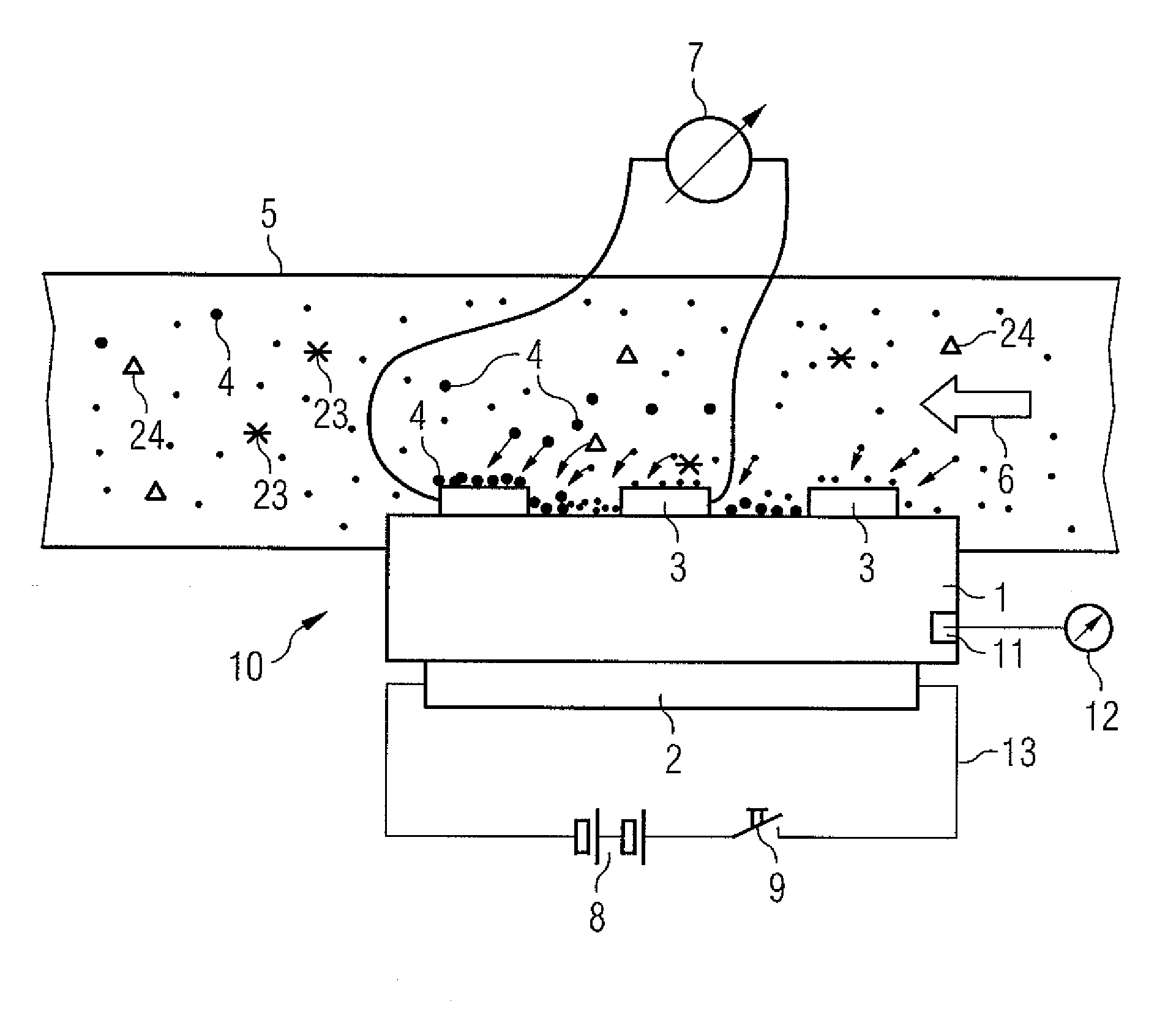
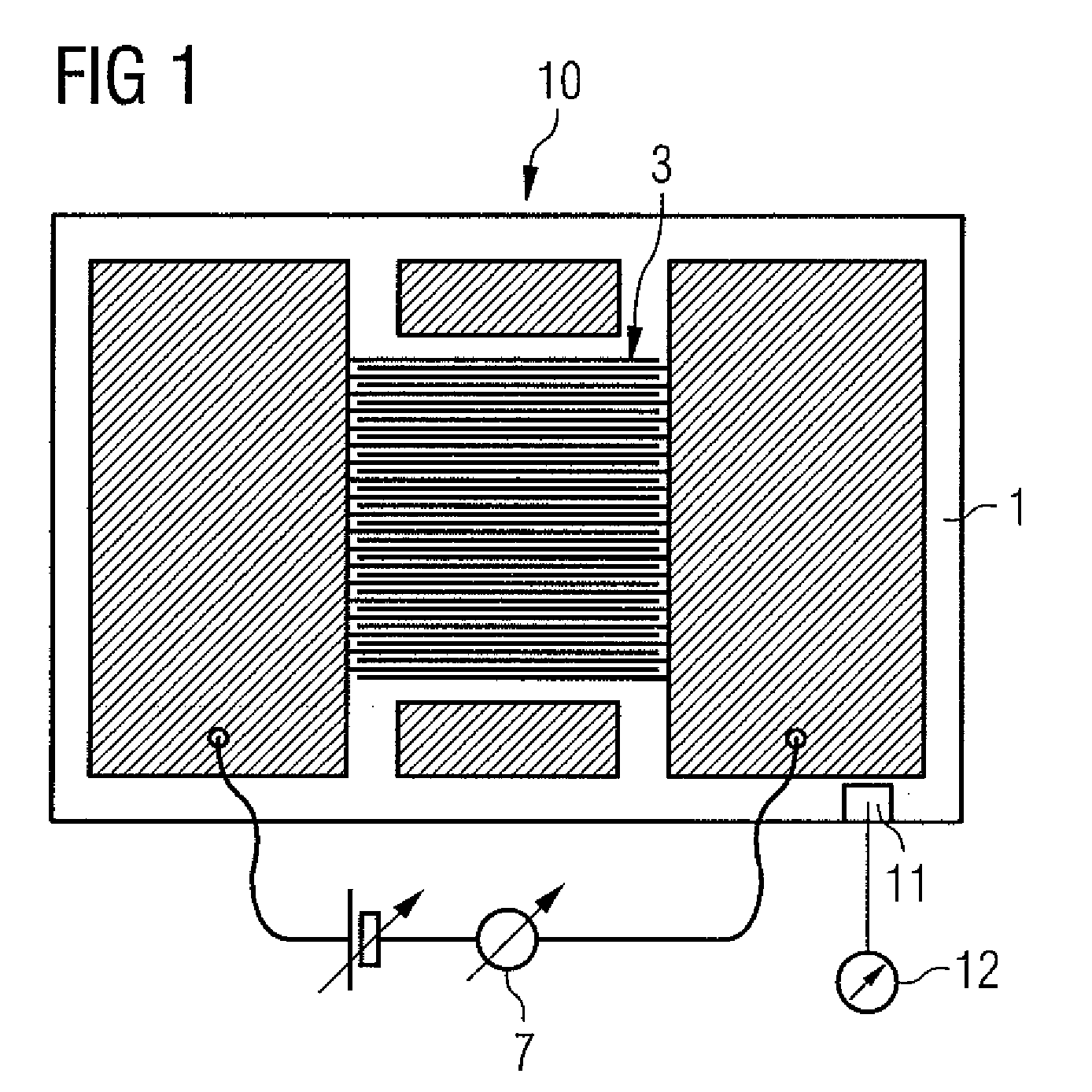
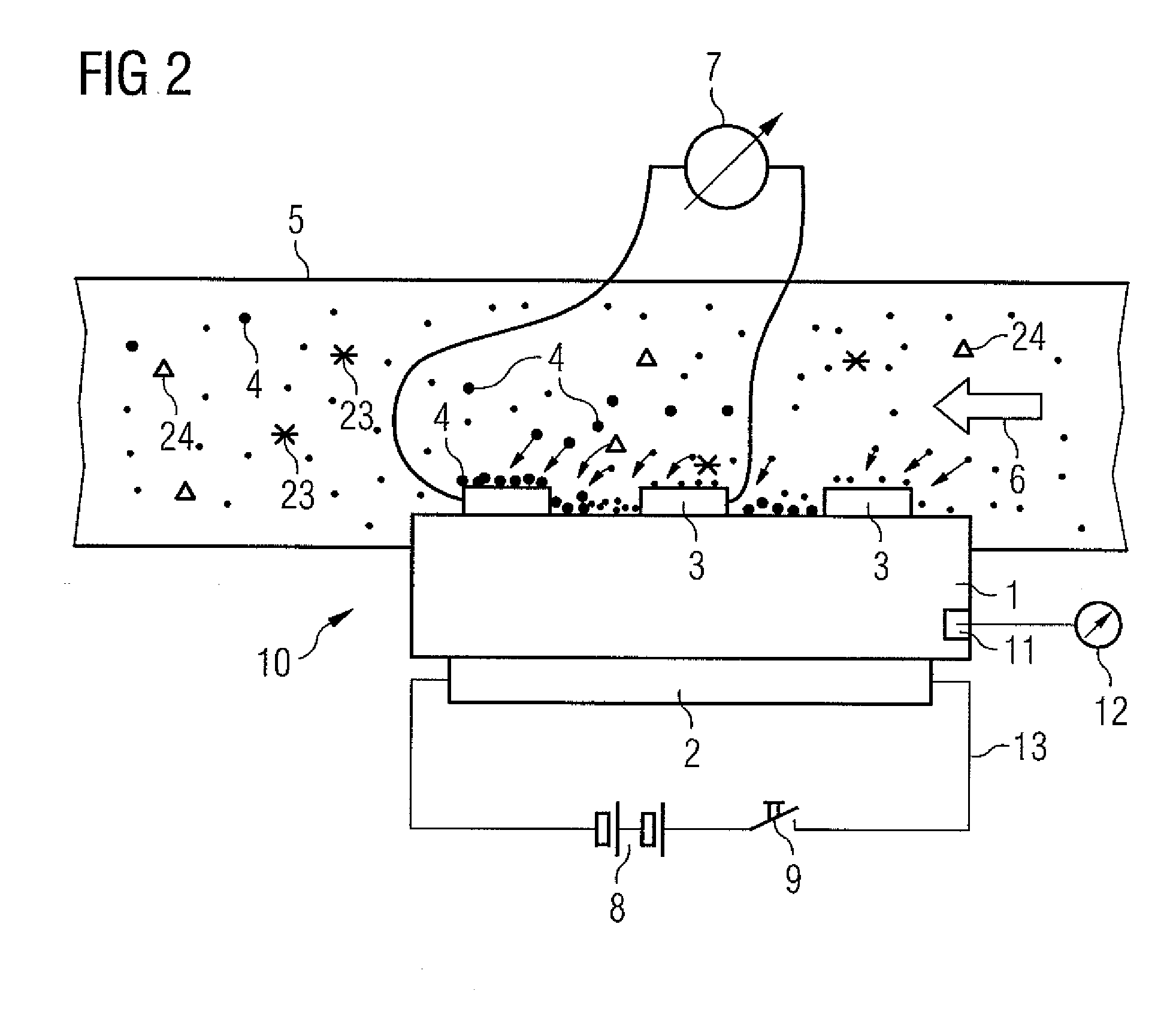
A method for the on-board functional diagnosis of a soot sensor and detection of further constituents in the soot in a motor vehicle having an internal combustion engine. The soot sensor is connected electrically to an evaluation circuit in the motor vehicle. A faulty soot sensor and / or further constituents in the soot can be detected in an inexpensive way. The evaluation circuit measures the voltage coefficient of the soot sensor and detects the defectiveness of the soot sensor and / or the presence of further constituents in the soot using the voltage coefficient of the soot sensor.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
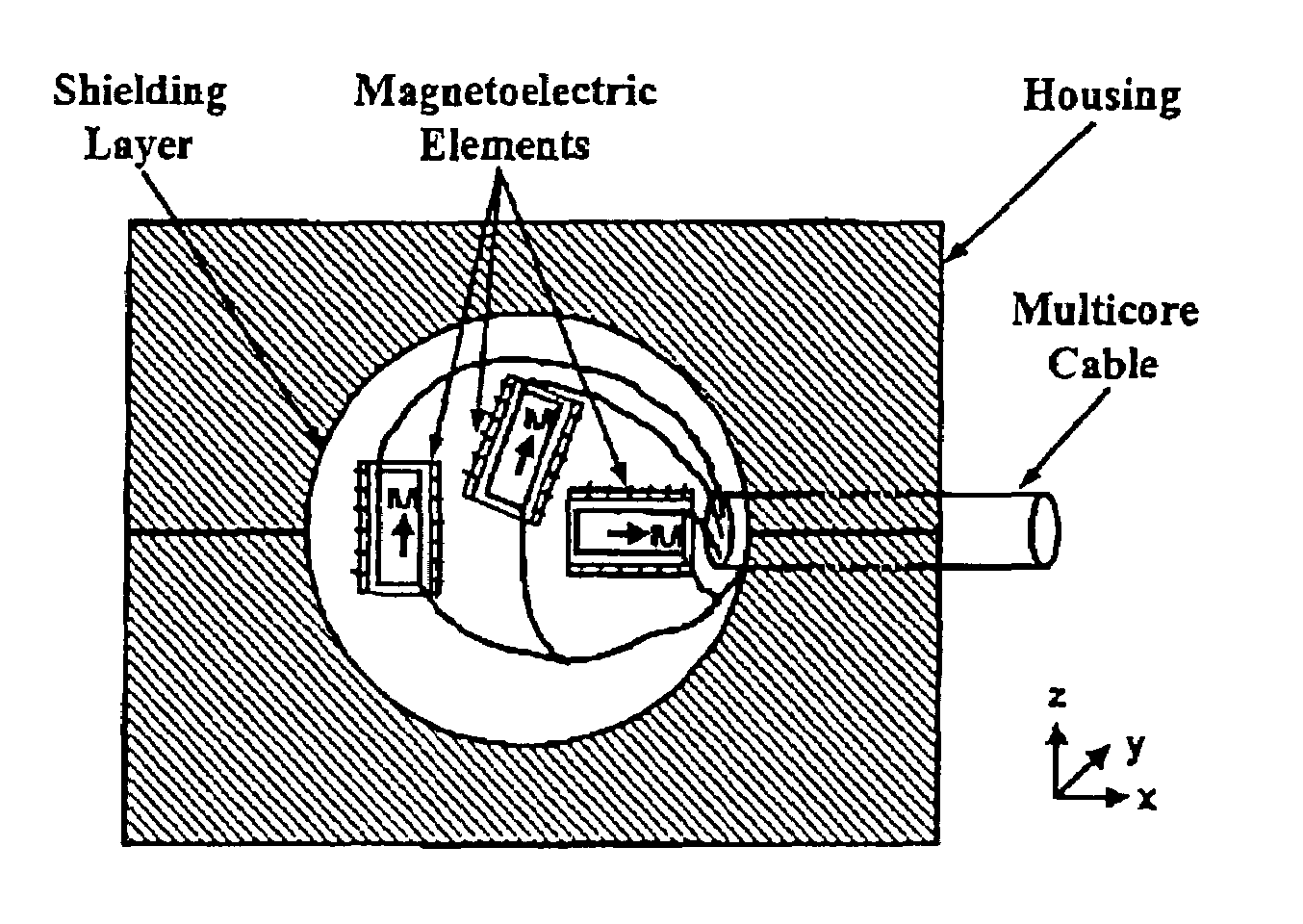
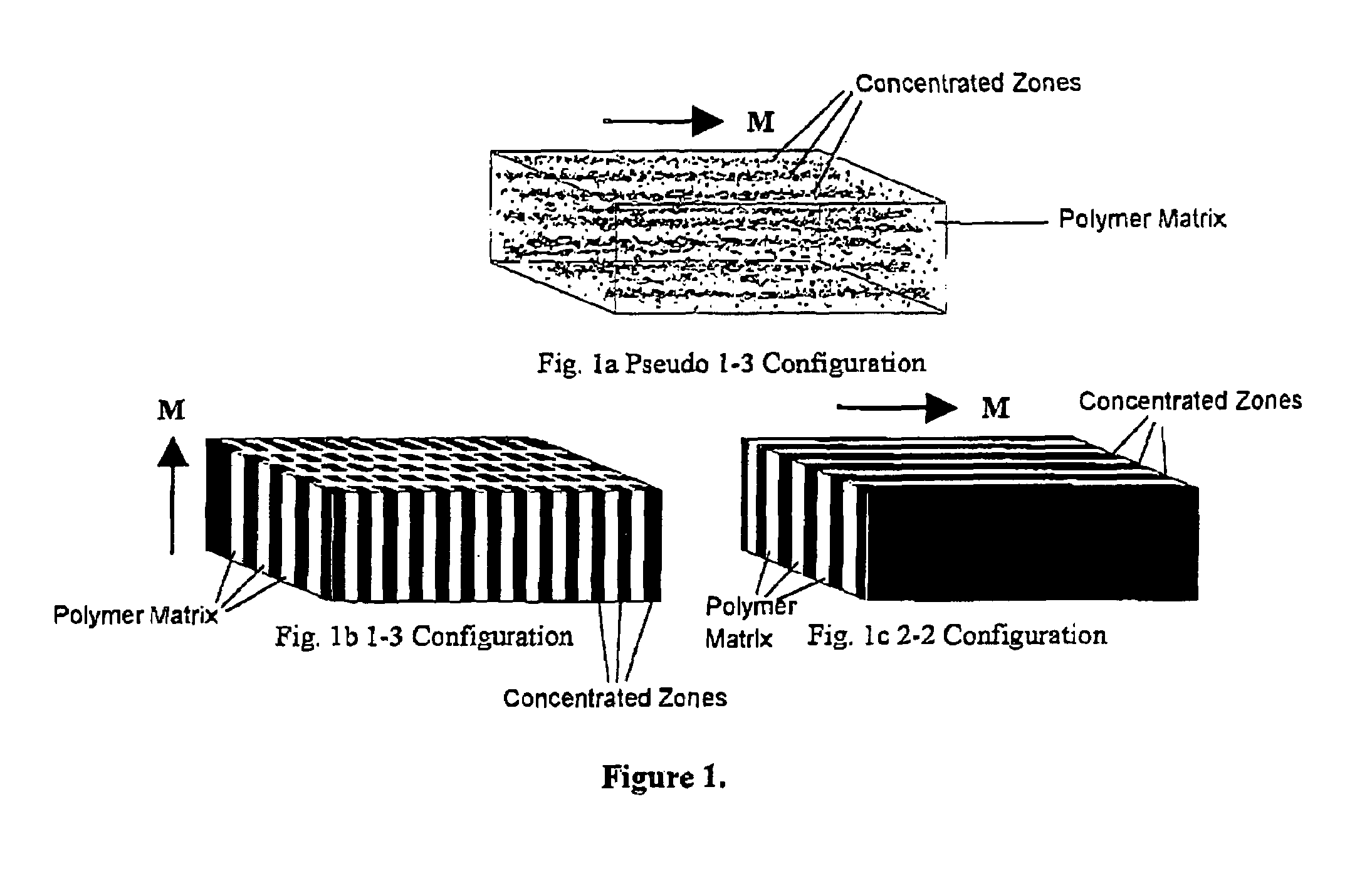
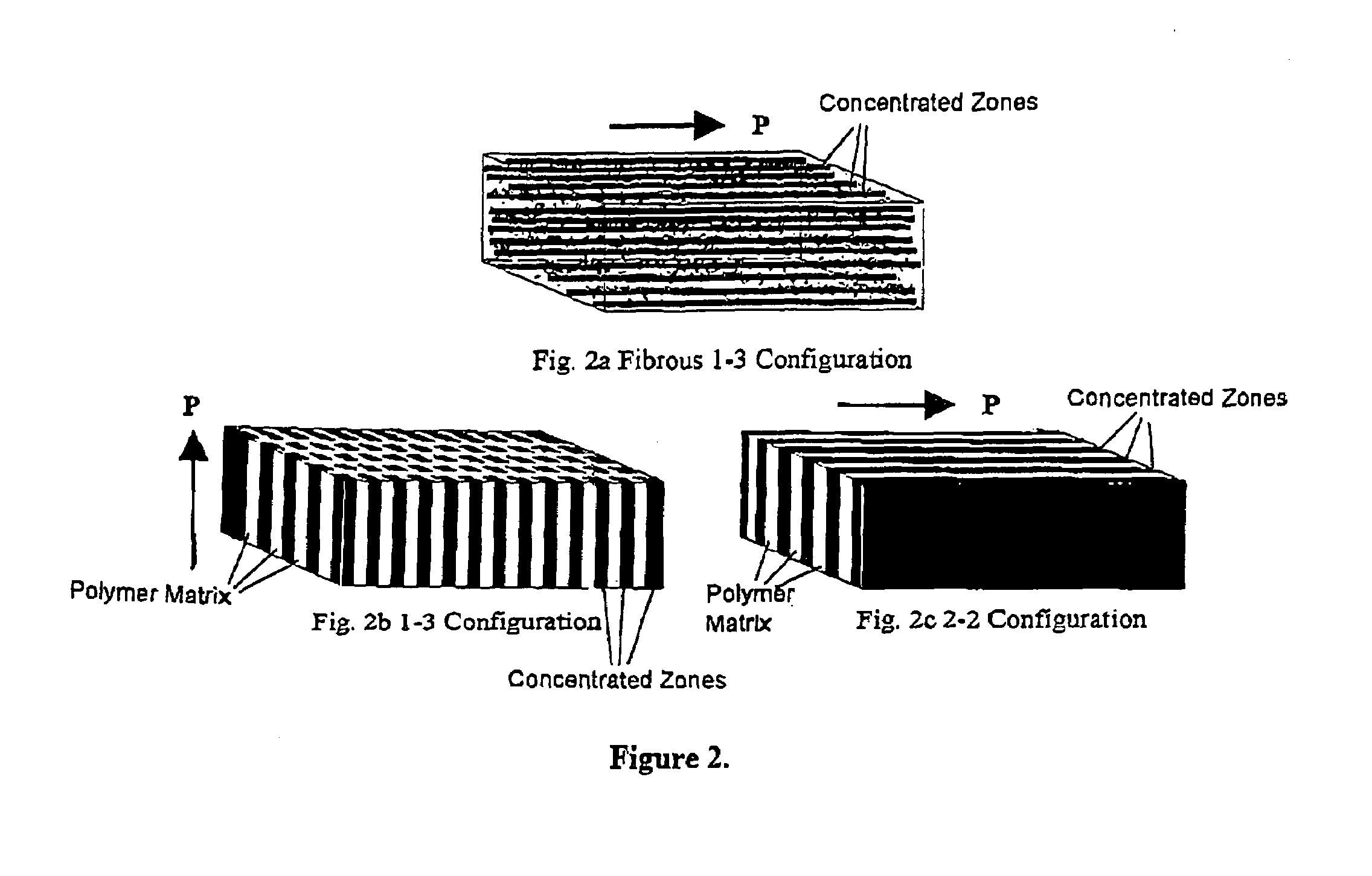
Magnetoelectric devices and methods of using same
ActiveUS20050218729A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDevice material selectionElectricityEddy current
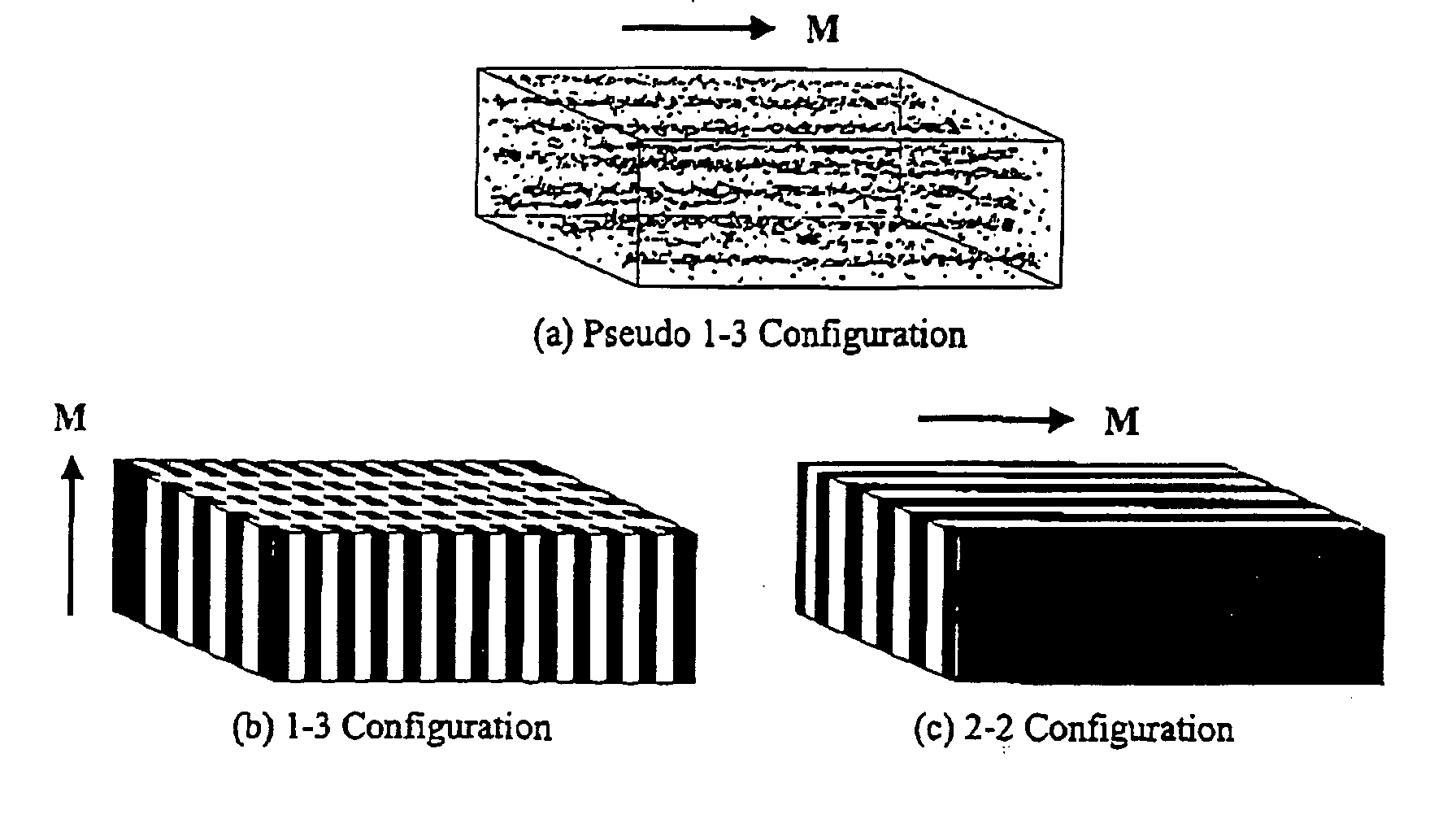
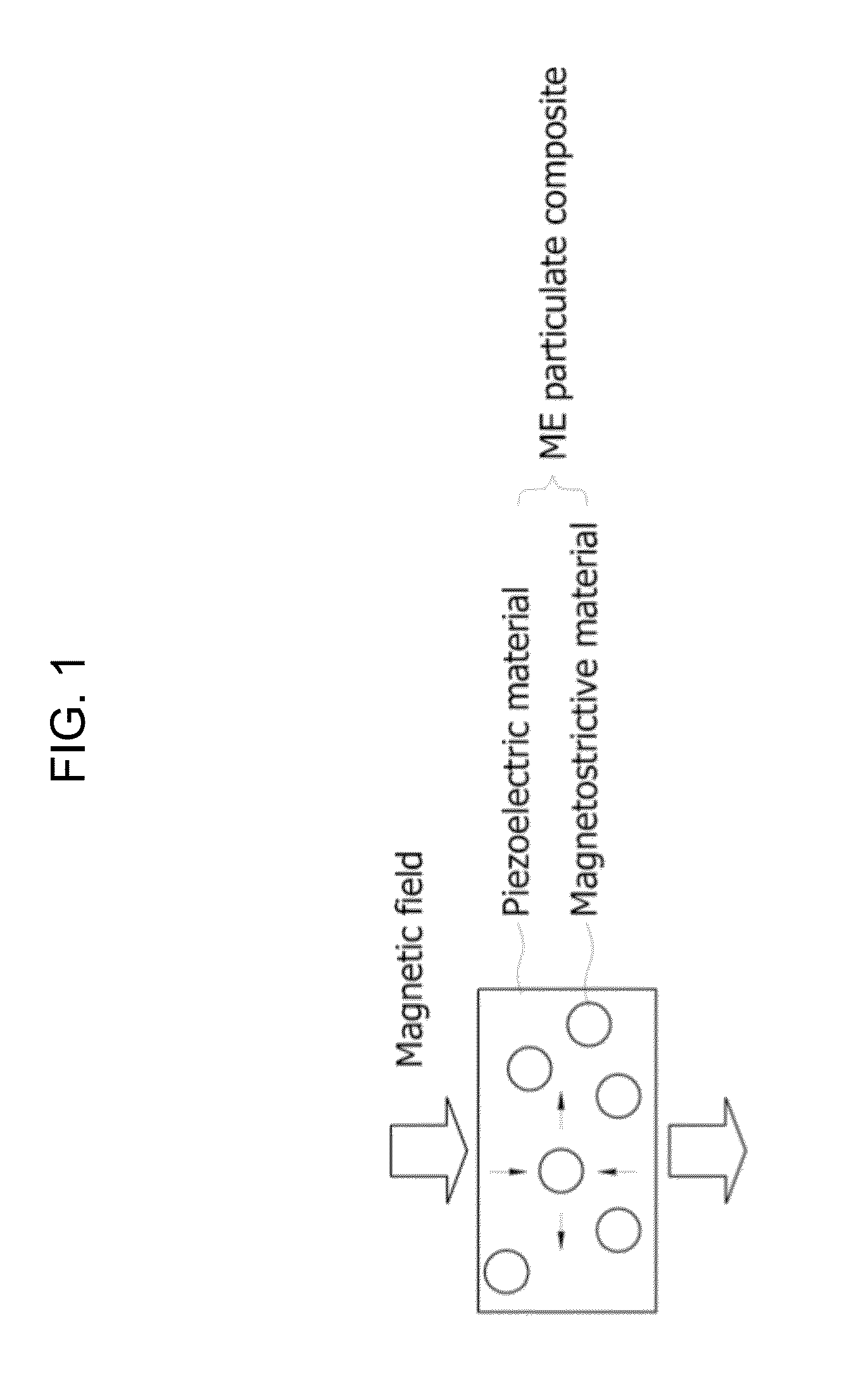
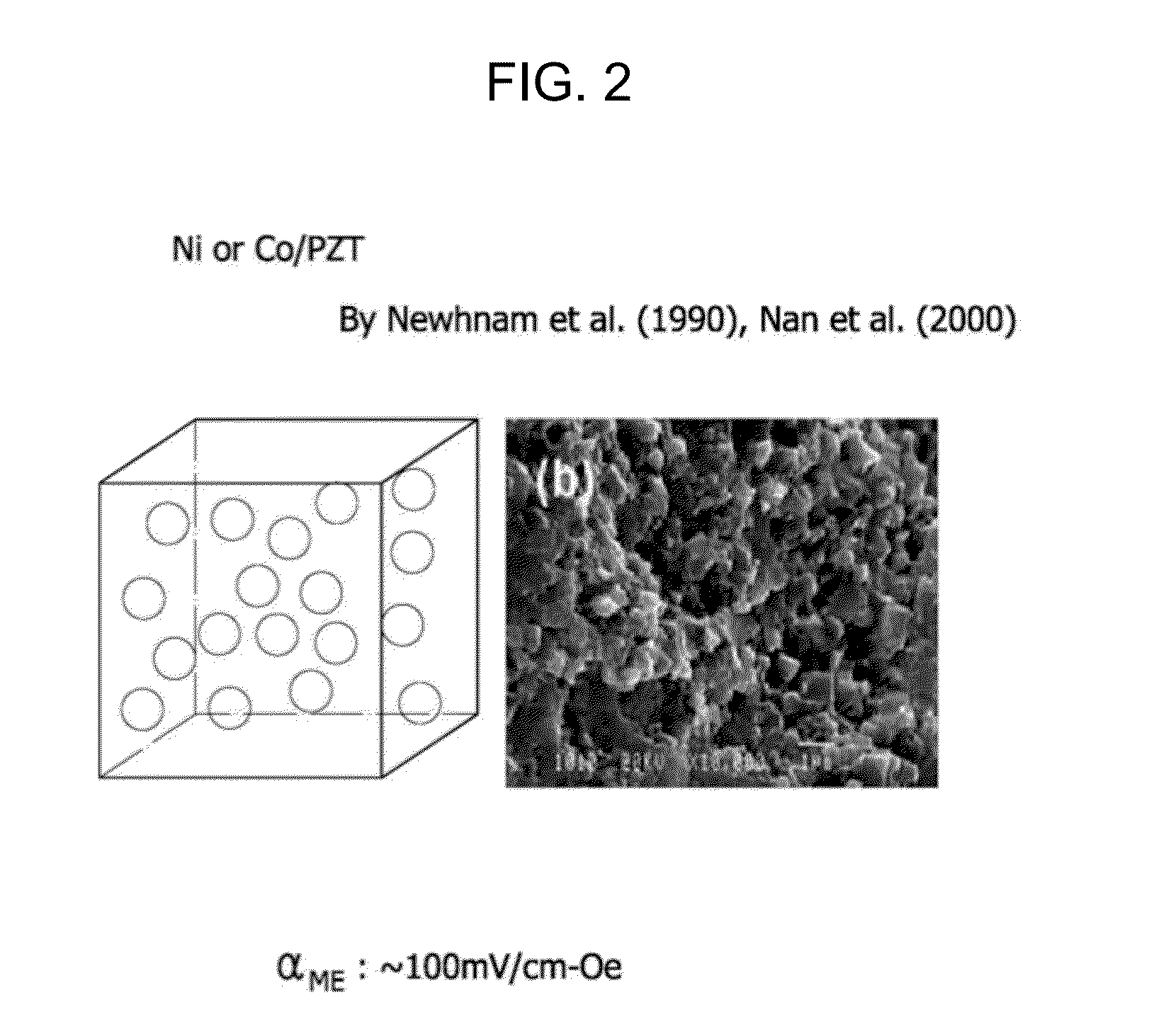
Existing magnetoelectric materials relying on the use of metallic or ceramic magnetostrictive materials and ceramic piezoelectric materials as their constituent phases may have three problems. First, the operational frequency may be limited to a few kilohertz due to the presence of eddy-current losses in the metallic magnetostrictive phase. Secondly, it may be difficult to machine and fabricate devices due to the mechanical brittleness of the ceramic and some metallic magnetostrictive phases as well as of the ceramic piezoelectric phase. Thirdly, it may be difficult to tailor and optimize the properties (i.e., magnetoelectric voltage coefficient αE, etc.) of the devices due to the limitation of the types of the constituent materials. This invention provides a magnetoelectric element including at least one set of alternative piezoelectric layer and magnetostrictive composite layer. The magnetostrictive composite layer includes at least one magnetostrictive material dispersed in first concentrated zones within a first polymer matrix, wherein all of said concentrated zones are orientated along a first direction. It is found that the conversion efficiency (i.e., αE) varies in accordance with applied magnetic control field Hcontrol in magnetoelectric devices made of such a magnetoelectric element.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Charge pump circuit for low current mismatching and low current change
InactiveCN102185473AReduce mismatchLittle changeApparatus without intermediate ac conversionLow noisePhase locked loop circuit
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
High-Temperature Dielectric Materials and Capacitors Made Therefrom
InactiveUS20080239627A1Reduce lossHigh dielectric constantFixed capacitor dielectricFixed capacitor terminalsCapacitanceLow voltage
A ceramic dielectric composition suitable for preparing capacitors for use in high-temperature service conditions is disclosed. The ceramic material and capacitors made from it exhibit unique and heretofore unrealizable properties including low variation in capacitance with voltage up to high fields, low variation in capacitance with temperature over a broad temperature range, retained high permittivity at temperatures up to 200° C. and beyond, low loss, low field-induced strain and adequate capacitance to retain performance at very low service temperatures. The material is based on sodium bismuth titanate (NBT) with selected additions of substituents and dopants to broaden and flatten its dielectric response, lower loss, lower strain, lower voltage coefficient and increase resistivity.
Owner:ALFRED UNIVERSITY +1
Magnetoelectric composites
ActiveUS20130252030A1High ME compositesHigh sensitivityDevice material selectionLaminationResonanceCrystal orientation
Disclosed is a magnetoelectric (ME) composite including both a piezoelectric material and a magnetostrictive material, wherein a piezoelectric single crystal material having high piezoelectric properties is used as the piezoelectric material, and a metal magnetostrictive material having high magnetostrictive properties is used as the magnetostrictive material, thus achieving an ME composite having a layered structure via adhesion. When the ME layered composite is manufactured such that a <011> crystal orientation of the piezoelectric single crystal material is set to a thickness direction, high ME voltage coefficient, which is at least doubled, compared to a conventional <001> crystal orientation, can be obtained, and such an effect is further maximized in the resonance of the composite.
Owner:KOREA INST OF MATERIALS SCI
Surface electrode silver paste for chip type resistor and preparation method for surface electrode silver paste
ActiveCN106683746AImprove solderabilityLow contact resistance characteristicsNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialMetal/alloy conductorsSilver pasteElectrical resistance and conductance
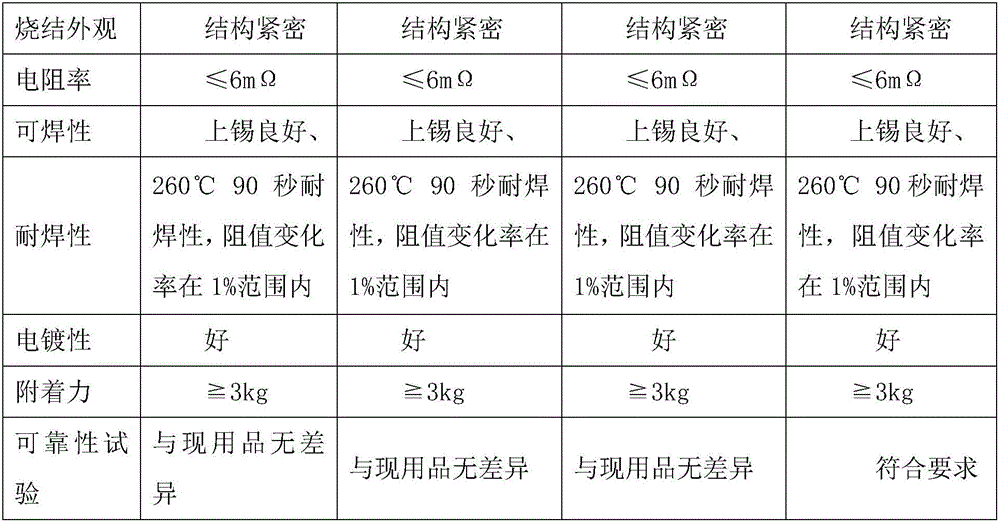
The invention discloses surface electrode silver paste for a chip type resistor. The surface electrode silver paste is prepared from the following raw materials based on weight percentages: 65-74% of silver powder with grain diameter of smaller than 5[mu]m, 0.5-5% of palladium powder, 0.5-5% of metal powder, 1-6% of glass powder, and 10-33% of organic carrier. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the surface electrode silver paste for the chip type resistor. The surface electrode silver paste for the chip type resistor can effectively solve the problems on the aspects of adhesive force, electroplating property, acid resistance, printing property and the like; the main technological goals of the products comprise resistance value precision, working voltage, temperature coefficient, voltage coefficient, stability and the like, and technologic indexes of the like products in Europe and America can be reached; and all the adopted materials can satisfy environment protection demands of foreign countries.
Owner:广东羚光新材料股份有限公司
Method for eliminating damage of hot marks by controlling operating point with set voltage range of photovoltaic module
ActiveCN102244139AEliminate Hot Spot DamageReduce security risksFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesOperating pointEngineering
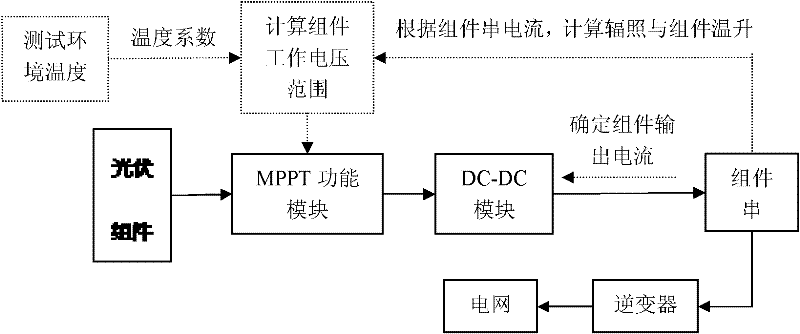
The invention relates to a method for eliminating damage of hot marks by controlling an operating point with a constant voltage range of a photovoltaic module. The method comprises the following steps that an output end of the module is connected in series with an MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) functional module and a DC-DC module sequentially; and the MPPT functional module searches the maximum power point of the module to track in a set operating voltage range. A method for setting the operating voltage range comprises the step of calculating an actual optimum operating voltage Vm when the module is not shielded by environment temperature Ta, irradiation strength R, a module temperature rise coefficient K caused by irradiation, a module temperature voltage coefficient Ct and a nominal rated optimal operating point voltage of the module at a temperature of 25 DEG C, which are obtained by measurement, according to a formula that Vm=Vmr-Ct(Ta+R*K-25), wherein the range of Vm+Vr to Vm-Vr is the set operating voltage range and Vr represents the maximum reverse bias voltage of the shielded module. In the method, the damage of the hot marks to the module can be eliminated in a mode of controlling the voltage of the operating point of the photovoltaic module. Meanwhile, in the mode, the design of the photovoltaic module without a bypass diode can be realized and the power loss caused by mismatching of electrical properties between the modules can also be reduced.
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD +1
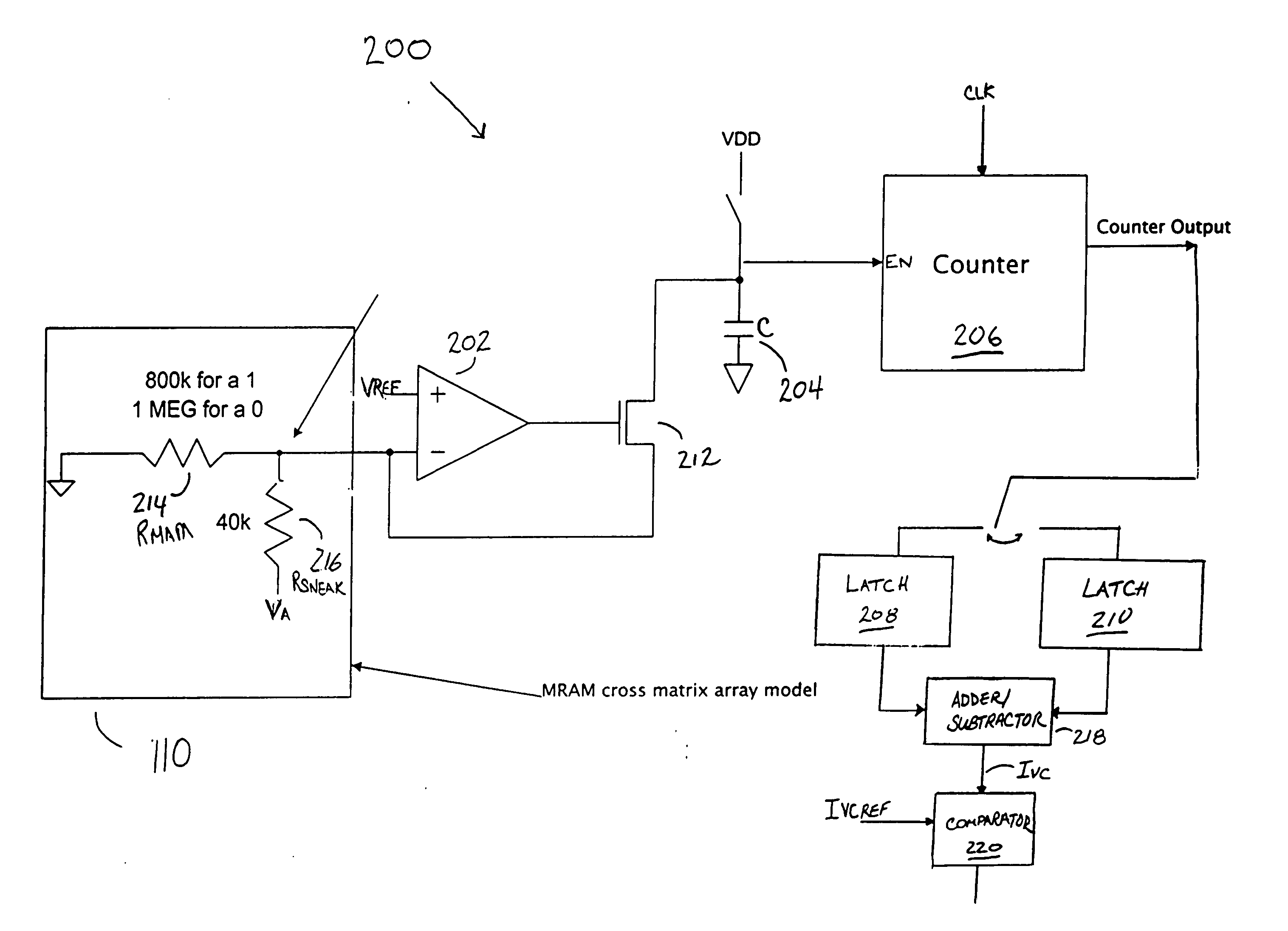
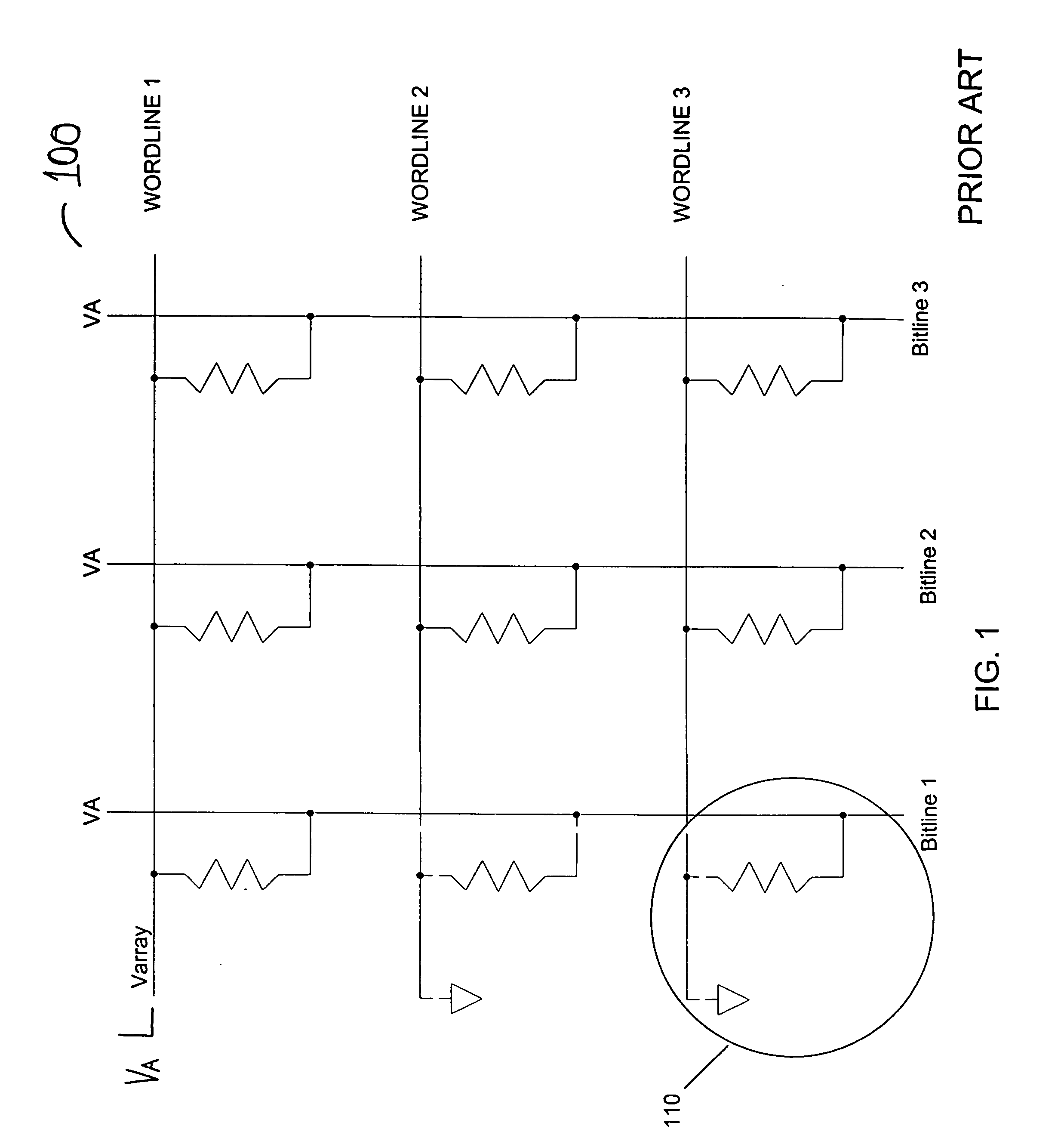
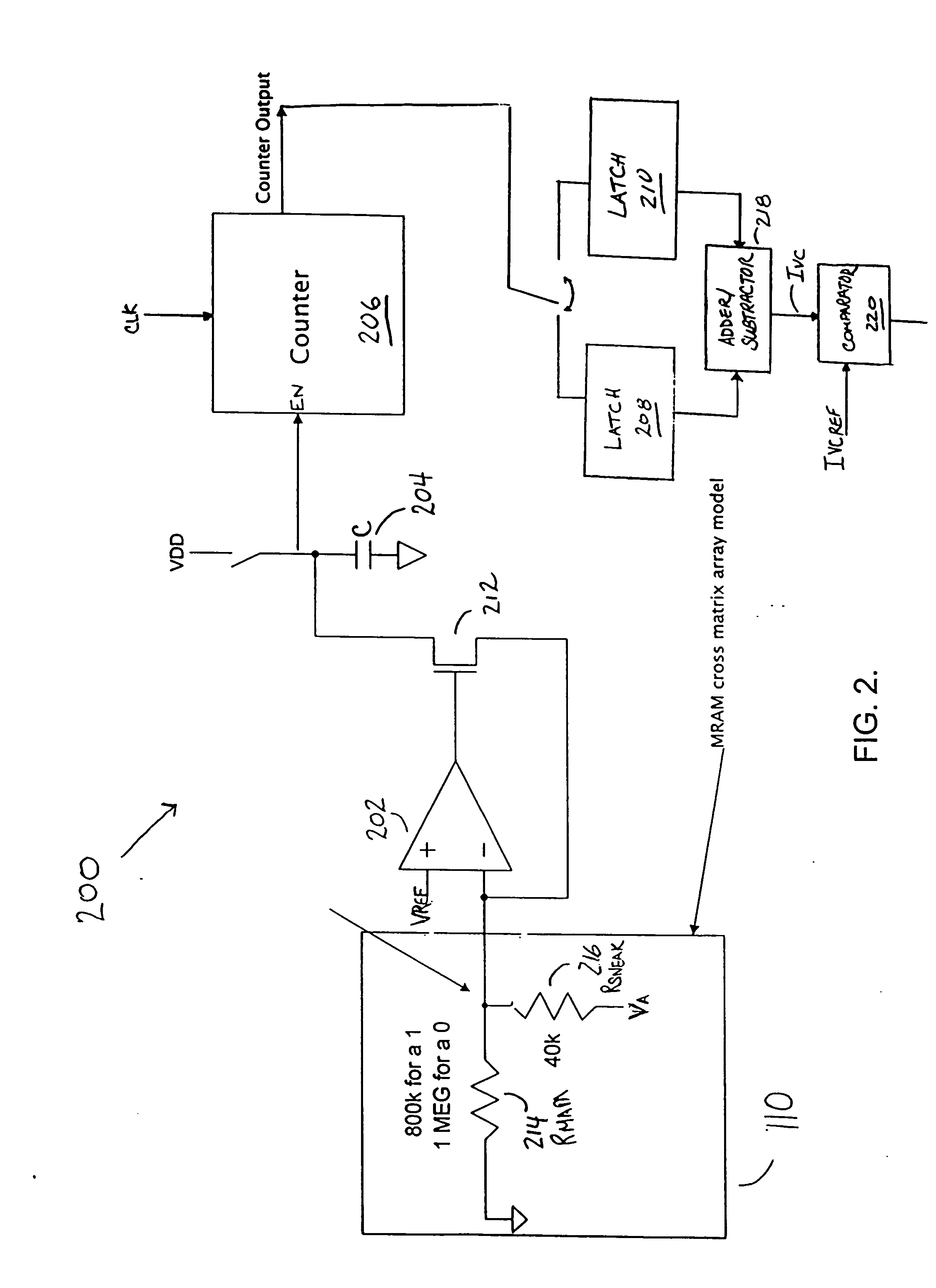
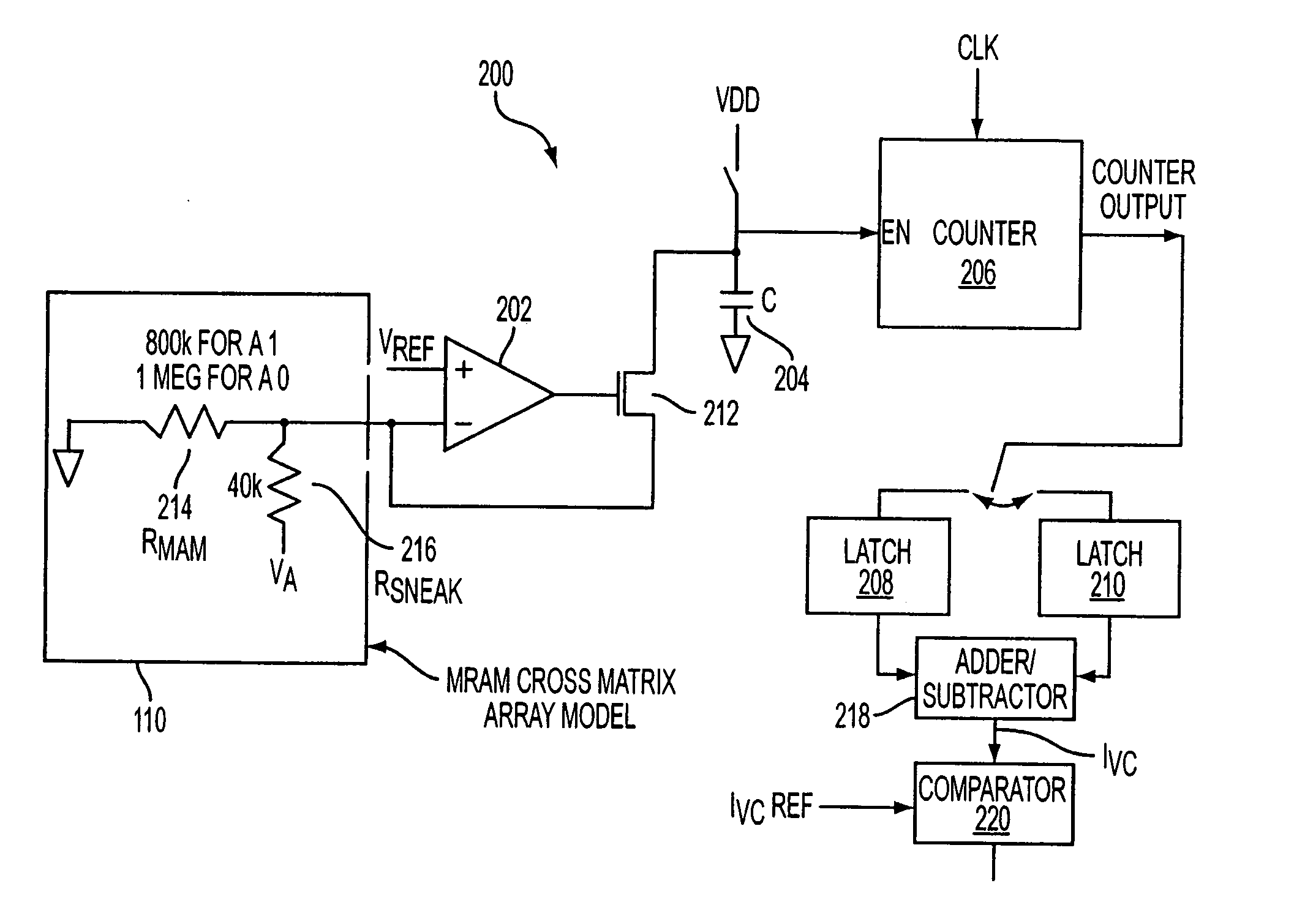
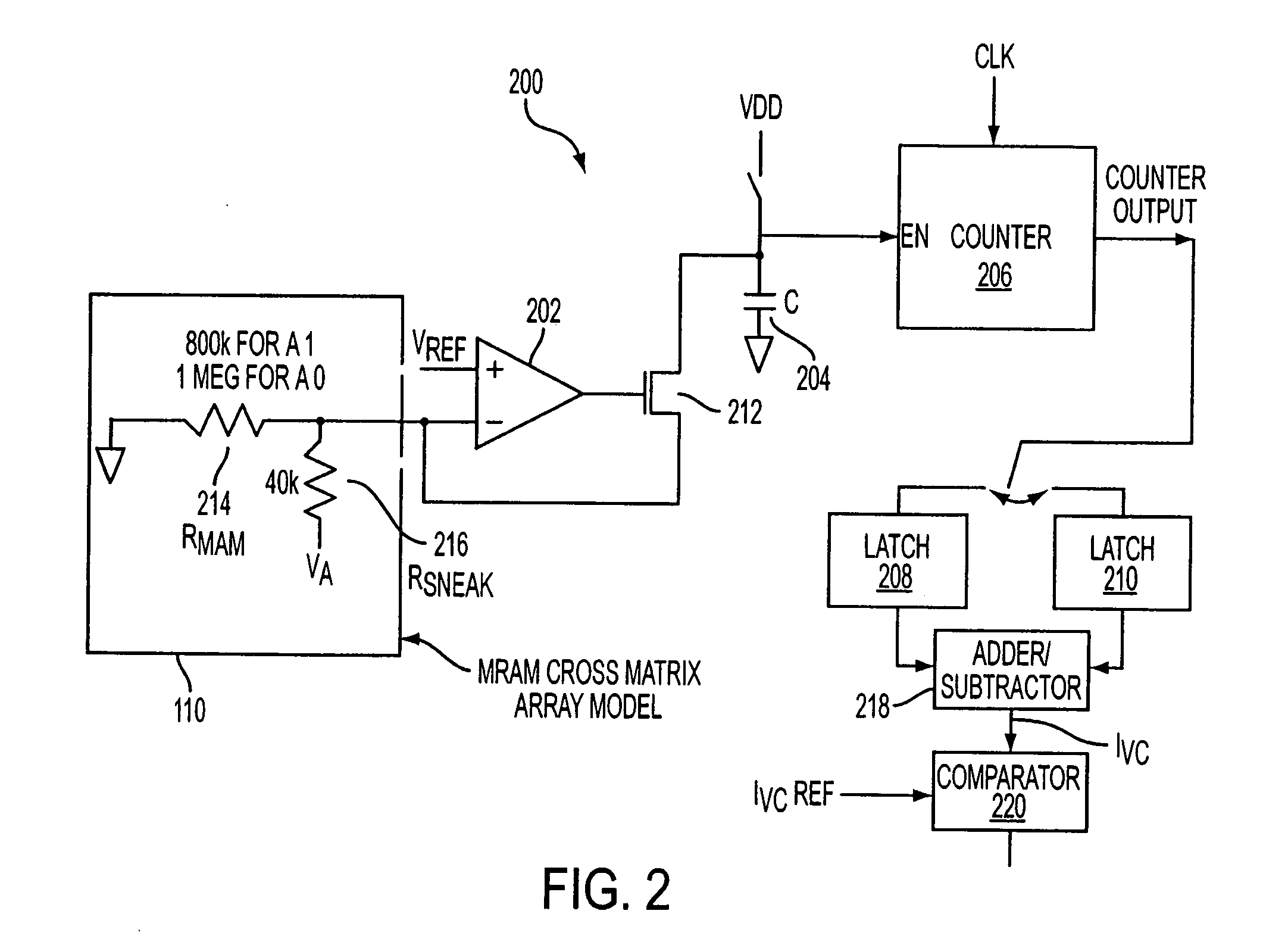
Sensing scheme for programmable resistance memory using voltage coefficient characteristics
A method and apparatus for sensing the resistance state of data in a resistance memory cell by using the voltage coefficient of the cell instead of only its resistance. A voltage potential is applied across the resistance memory cell allowing the voltage coefficient of the cell to be determined and subsequently used to determine the logic state of the cell.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
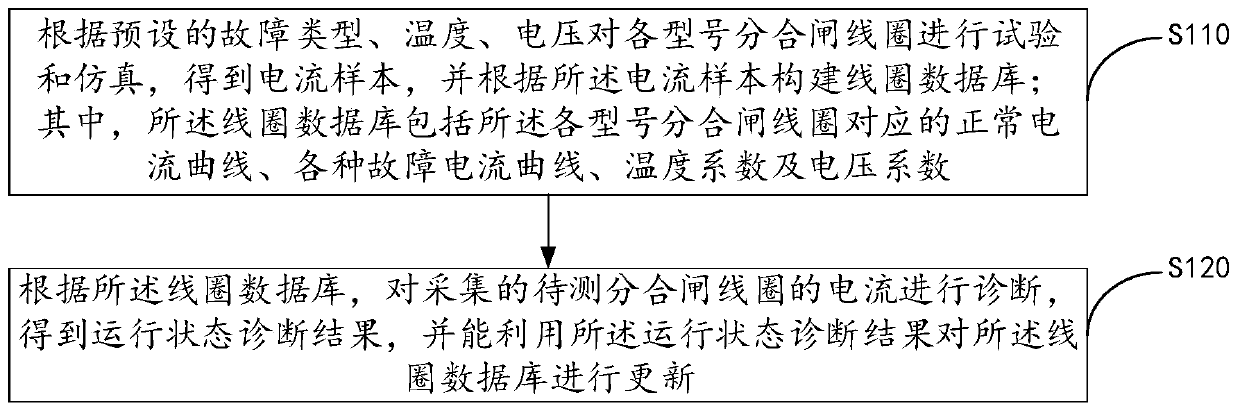
Method and device of diagnosing running state of circuit breaker mechanism
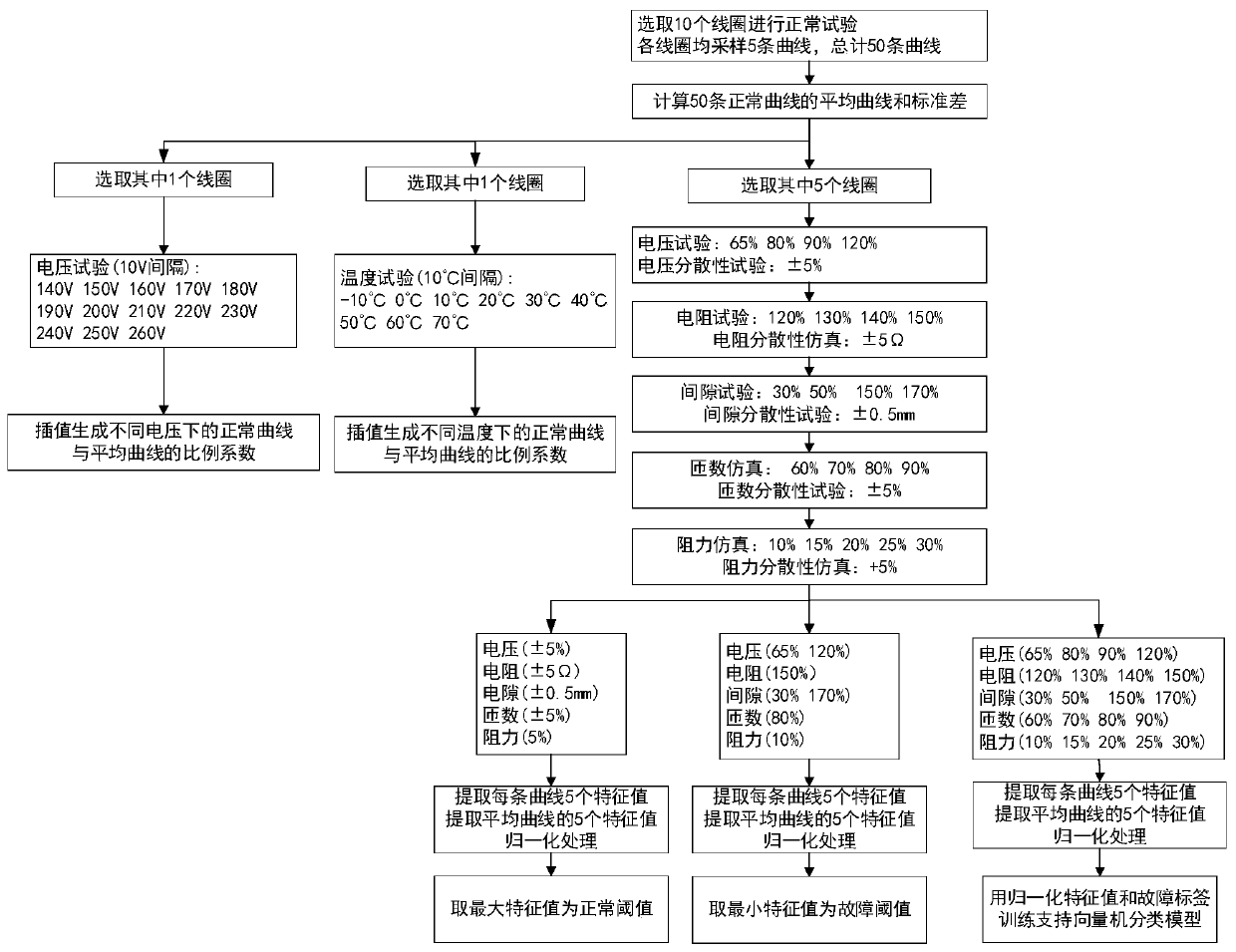
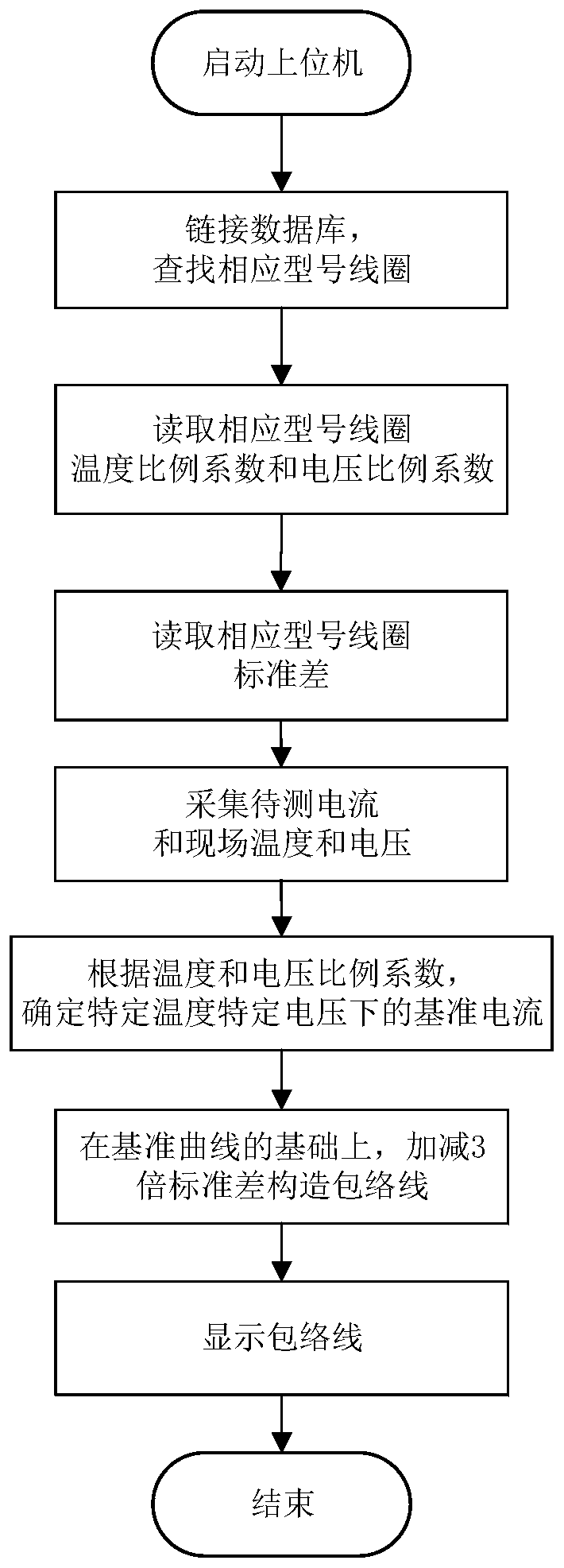
ActiveCN110007220AImprove applicabilityGuaranteed pertinenceCircuit interrupters testingCurrent sampleModel Number
The invention discloses a method and a device of diagnosing a running state of a circuit breaker mechanism. The method comprises steps of: testing and simulating opening and closing coils of all models according to preset fault types, temperature and voltage, so as to obtain a current sample, and constructing a coil database according to the current sample, wherein the coil database comprises normal current curves, various fault current curves, temperature coefficients and voltage coefficients of opening and closing coils of all models; and according to the coil database, diagnosing collectedcurrents of to-be-tested opening and closing coils, so as to obtain a running state diagnosis result. The coil database can be updated by using the running state diagnosis result, corresponding coil databases can be established for opening and closing coils of different models, so as to guarantee pertinence and accuracy of diagnosis; further, the fault type can be diagnosed, fault diagnosis is more accurate, and the coil database can be expanded and updated in real time so as to improve the applicability.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
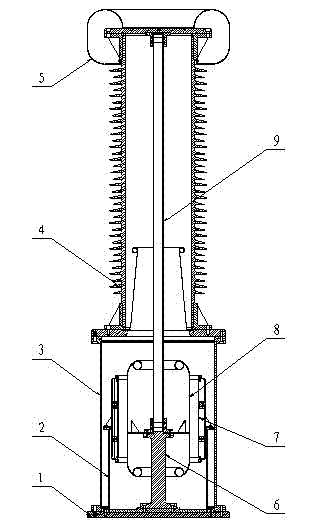
Extra-high voltage reference capacitor
ActiveCN101183121ASolve the problem of inconvenient transportationIncrease the voltage coefficientResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitorsPositive pressureLow voltage
The present invention is an ultra-high voltage standard capacitor, which is an upright structure in which both the high-voltage electrode and the low-voltage electrode are fixed in the pressure vessel tank at the bottom with an insulating support, and overcomes the influence of the increase of the voltage level of the standard capacitor on the increase of its voltage coefficient. problem; for the field test structure, the present invention divides the standard capacitor into three independently sealed air chambers, which solves the inconvenient transportation problem of large-scale test equipment, so as to be used for field test and detection. When the present invention is used for UHV standard capacitors The insulation level is extremely high, the short-term power frequency voltage withstand capacity can exceed 1600kV, the long-term rated working voltage exceeds 1200kV, and the voltage coefficient is better than 2×10-6. The invention can also be used in the production of standard capacitors with a rated working voltage of less than 1600kV voltage level.
Owner:WUHAN NARI LIABILITY OF STATE GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
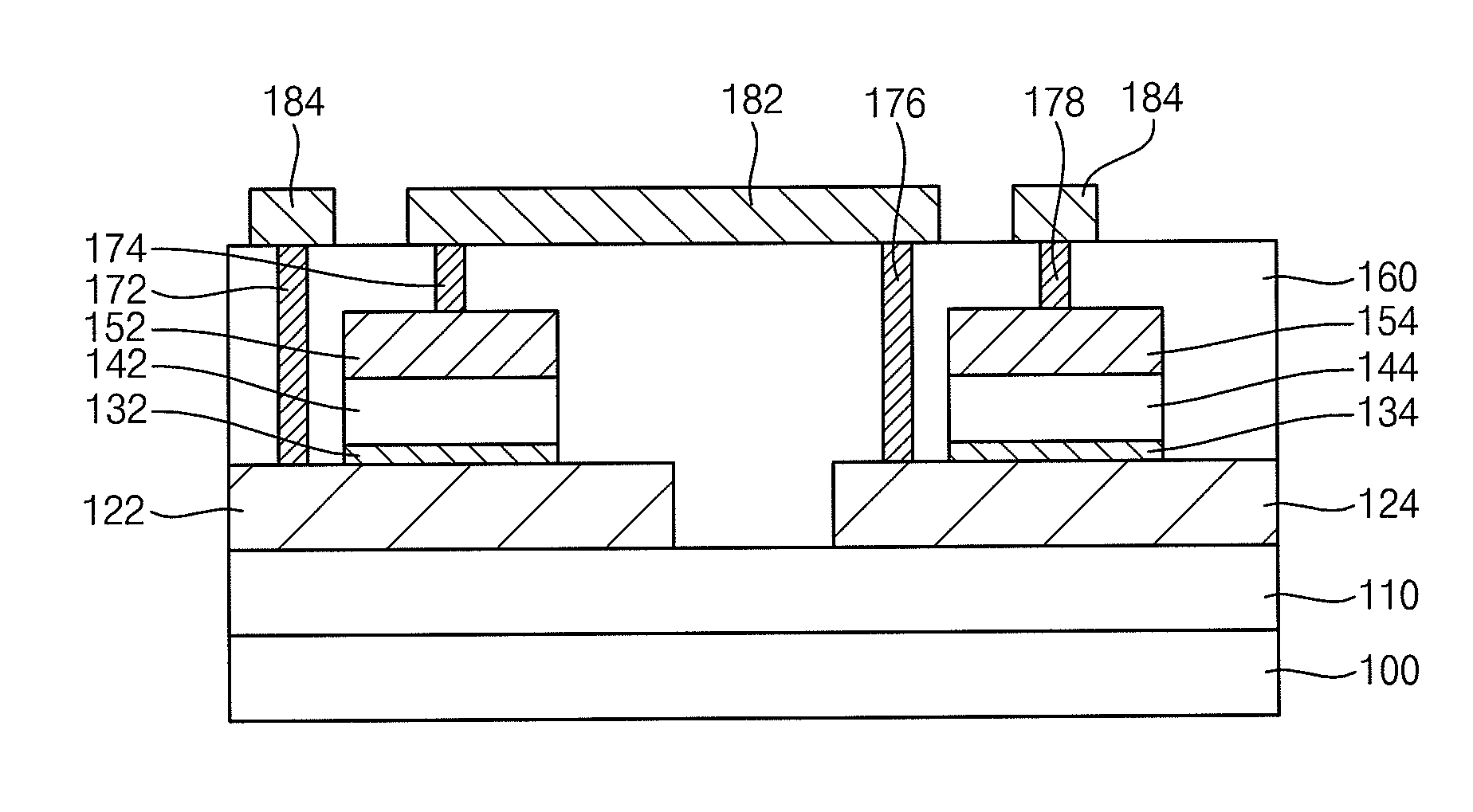
Capacitor Unit and Method of Forming the Same
A capacitor unit includes a first capacitor and a second capacitor. The first capacitor includes a first lower electrode, a first dielectric layer pattern and a first upper electrode sequentially stacked. The first capacitor includes a first control layer pattern for controlling a voltage coefficient of capacitance (VCC) of the first capacitor between the first lower electrode and the first dielectric layer pattern. The second capacitor includes a second lower electrode, a second dielectric layer pattern and a second upper electrode sequentially stacked. The second lower electrode is electrically connected to the first upper electrode, and the second upper electrode is electrically connected to the second lower electrode. The second capacitor includes a second control layer pattern for controlling a VCC of the second capacitor between the second lower electrode and the second dielectric layer pattern.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method For Estimating Maximum Power Of A Circuit And Apparatus Thereof
ActiveUS20120016529A1Mechanical power/torque controlLevel controlOpen-circuit voltageVoltage coefficient
The present invention provides a method for adjusting a maximum power of a circuit having a first voltage output and a first power. The method includes the following steps: (a) obtaining a voltage coefficient by measuring the first power of the circuit and calculating an open-circuit voltage of the first voltage output; (b) estimating an estimated power based on the voltage coefficient; and (c) repeating the steps (a) to (b) for a specific number of times, in which the specific number of times is determined based on a variation of the estimated power during a time period.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Formation method of silicon oxide film and metal-insulator-metal capacitor
ActiveCN101736314AImprove electrical performanceIncrease deposition powerSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingMetal-insulator-metalCapacitance
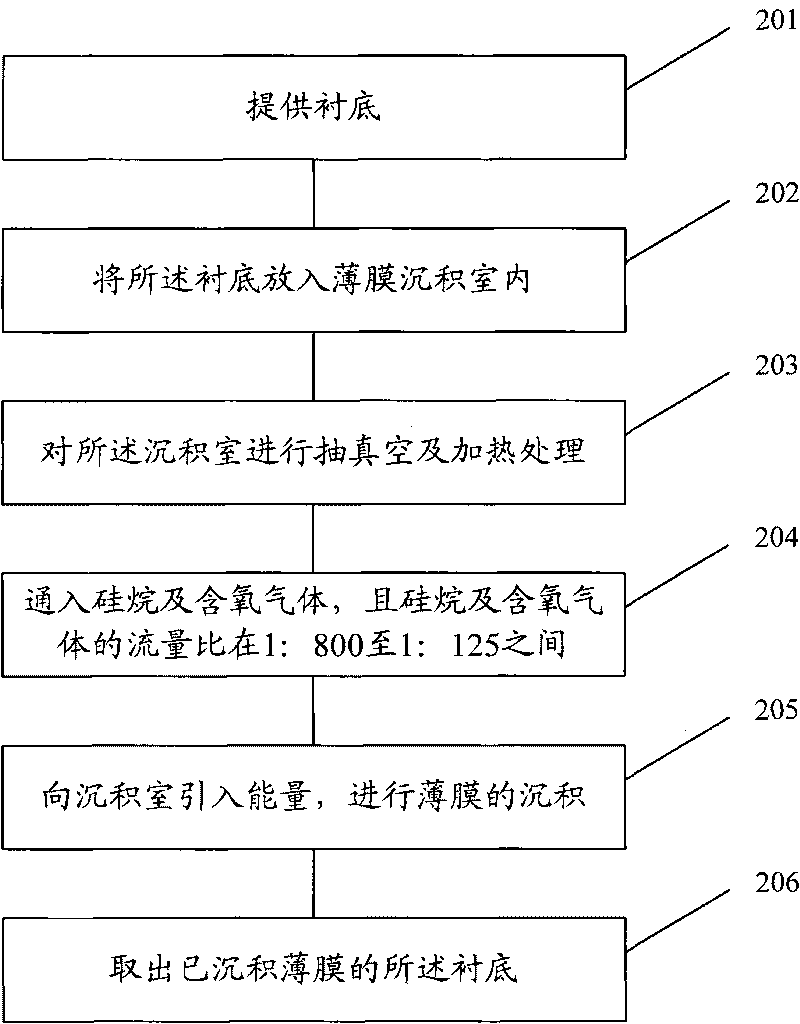
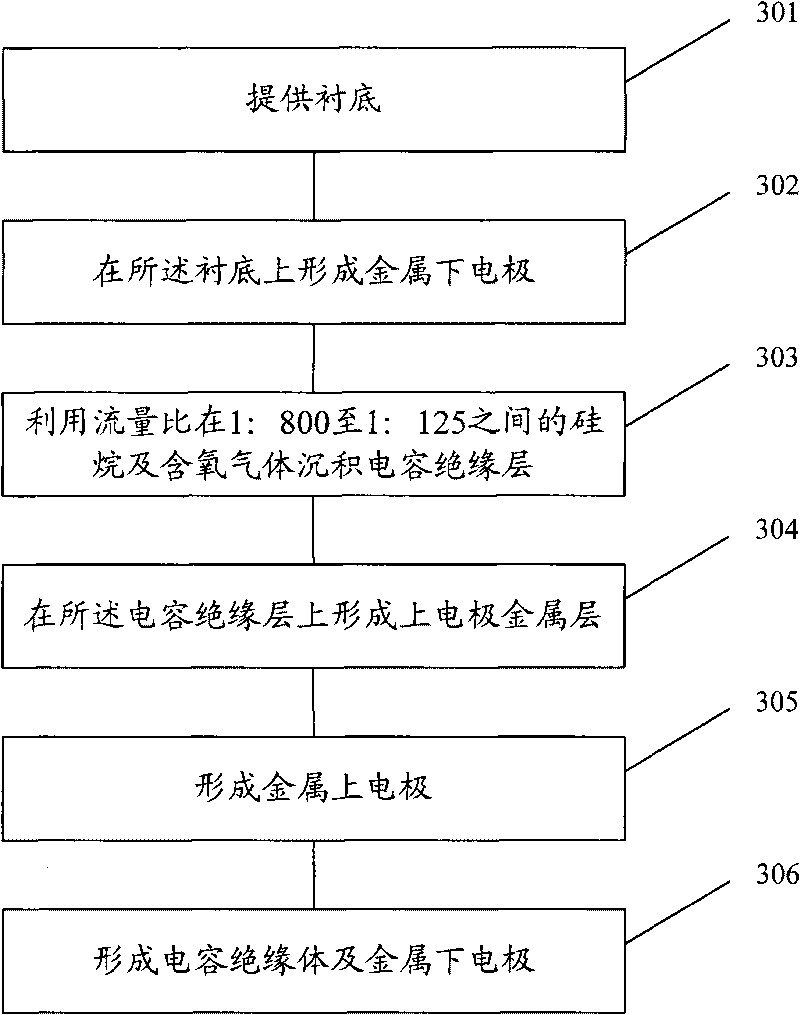
The invention discloses a formation method of a silicon oxide film, comprising the following steps of: providing a substrate, placing the substrate into a film deposition chamber, vacuumizing the deposition chamber, heating the deposition chamber, introducing silicane and oxygenous gas to the deposition chamber, wherein the flow ratio of silicane to oxygenous gas is between 1:800 and 1:125, introducing energy to the deposition chamber to deposit the film, and taking out the substrate with the deposited film. The invention also discloses a corresponding formation method of a metal-insulator-metal capacitor. The metal-insulator-metal capacitor formed by using the silicon oxide film method reduces and stabilizes a voltage coefficient of capacitance and a temperature coefficient of capacitance of the capacitor, improves the dynamic characteristics of the capacitor and enhances the electrical property stability of the capacitor.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP
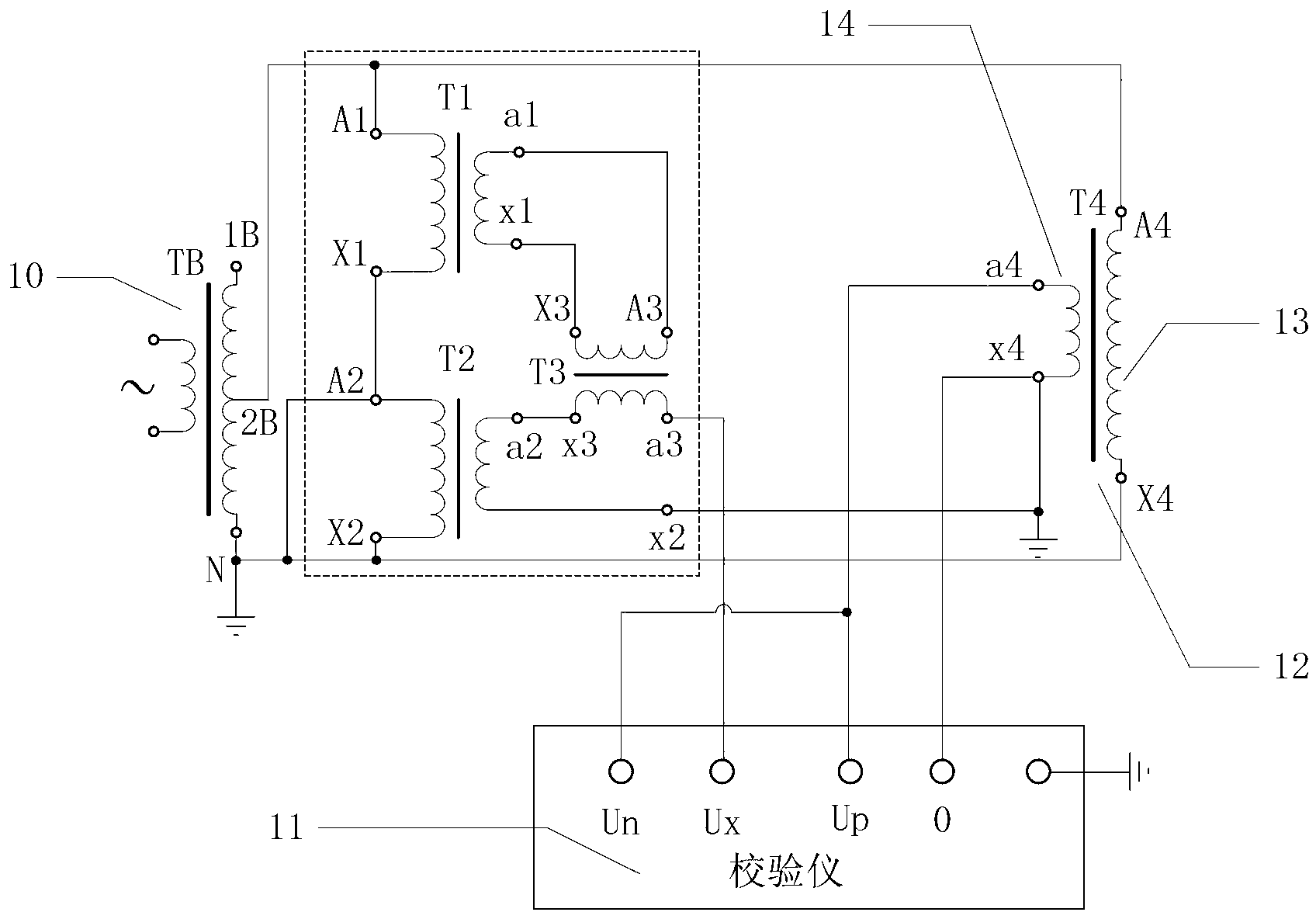
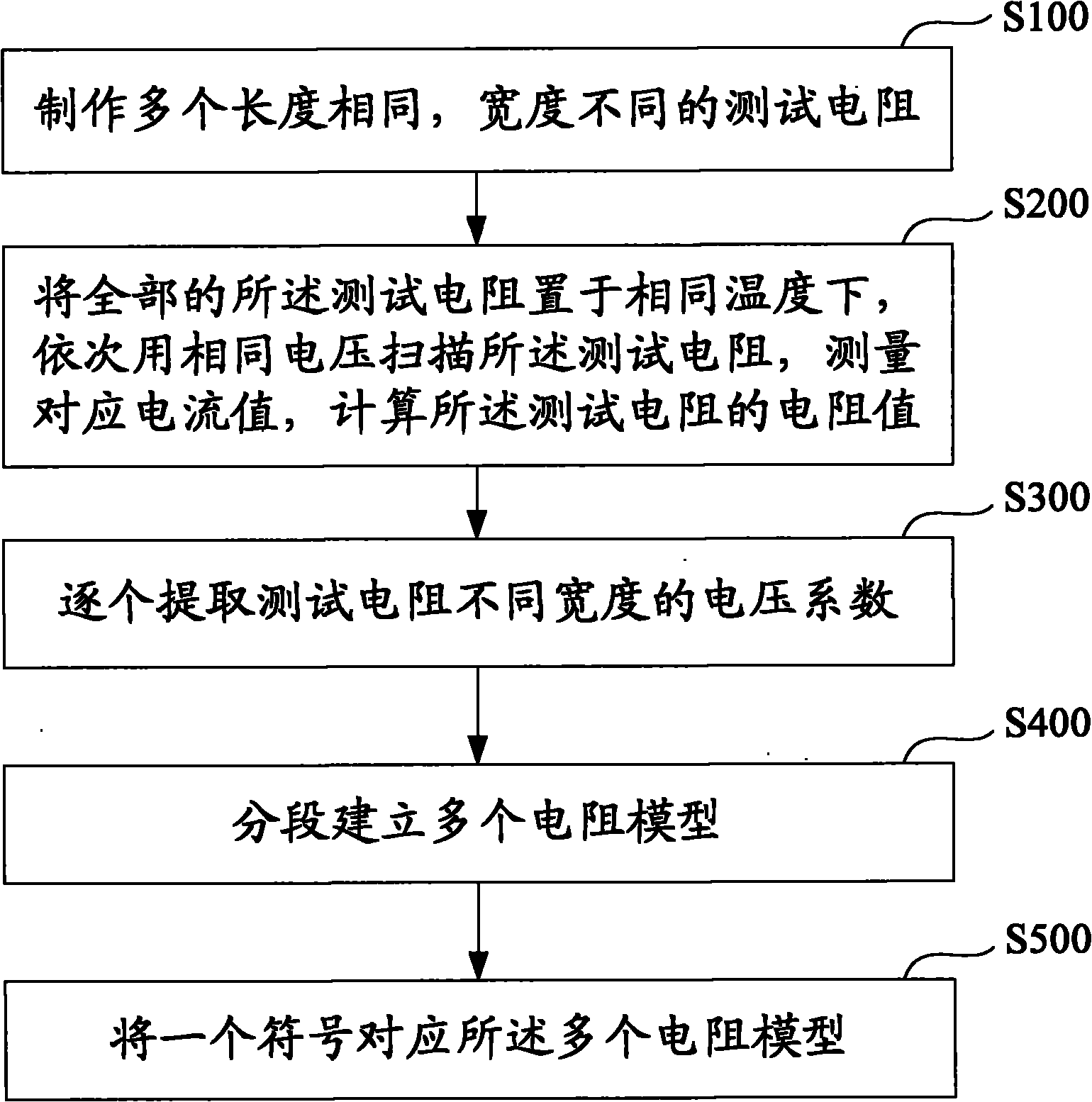
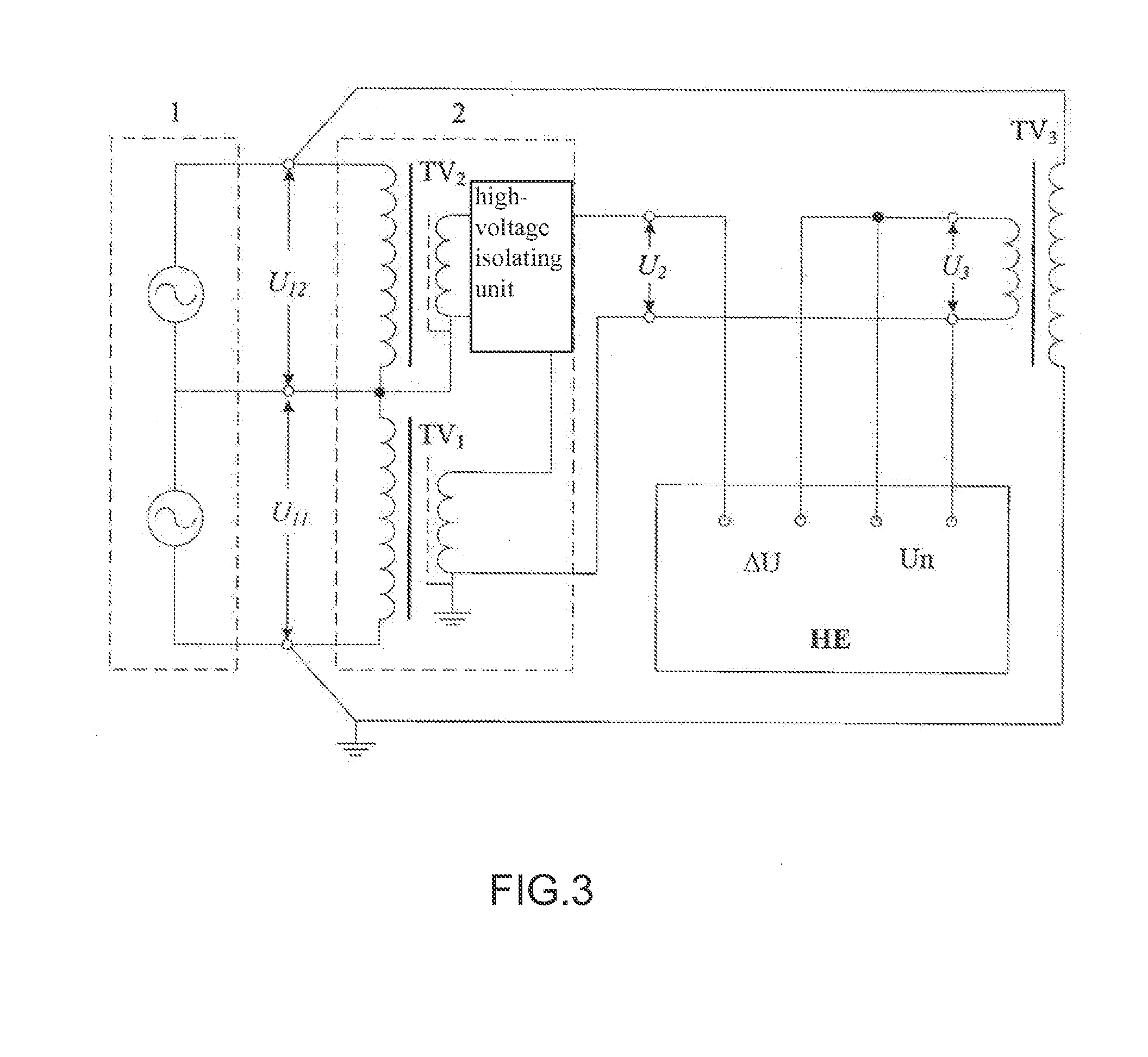
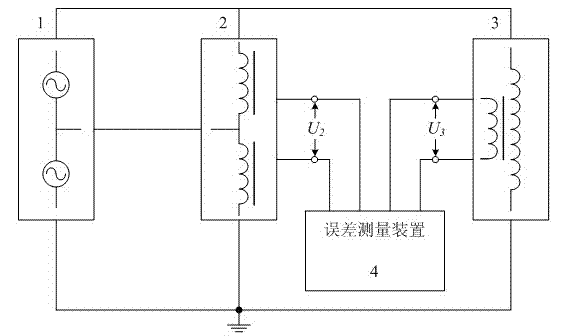
Circuit and method for measuring voltage transformer voltage coefficient
ActiveCN103267958AAvoid influenceEfficient implementationElectrical measurementsUltra high pressureSingle stage
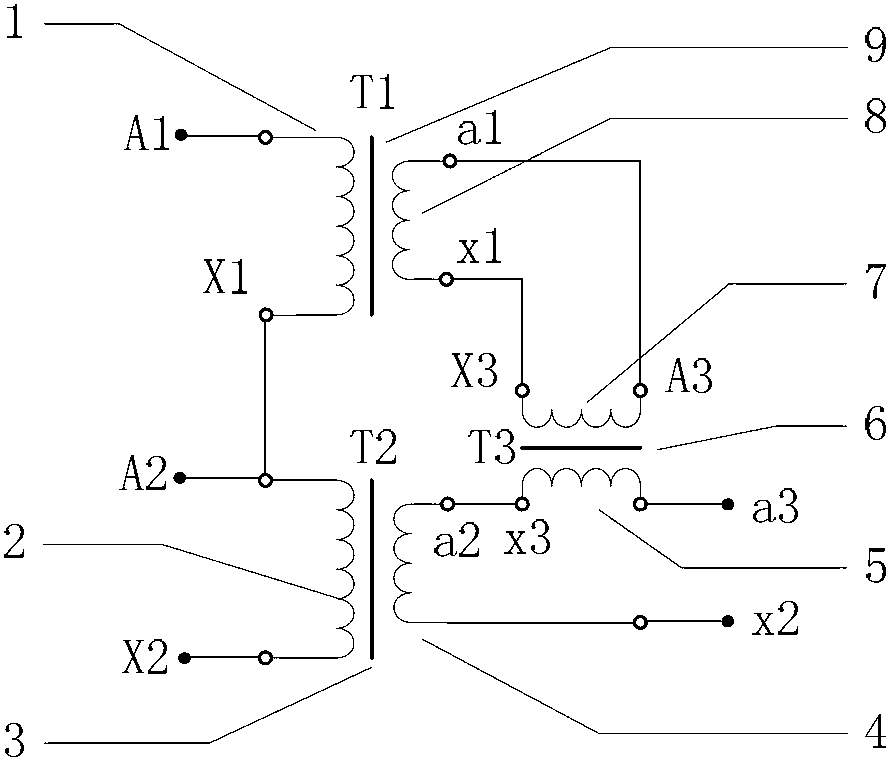
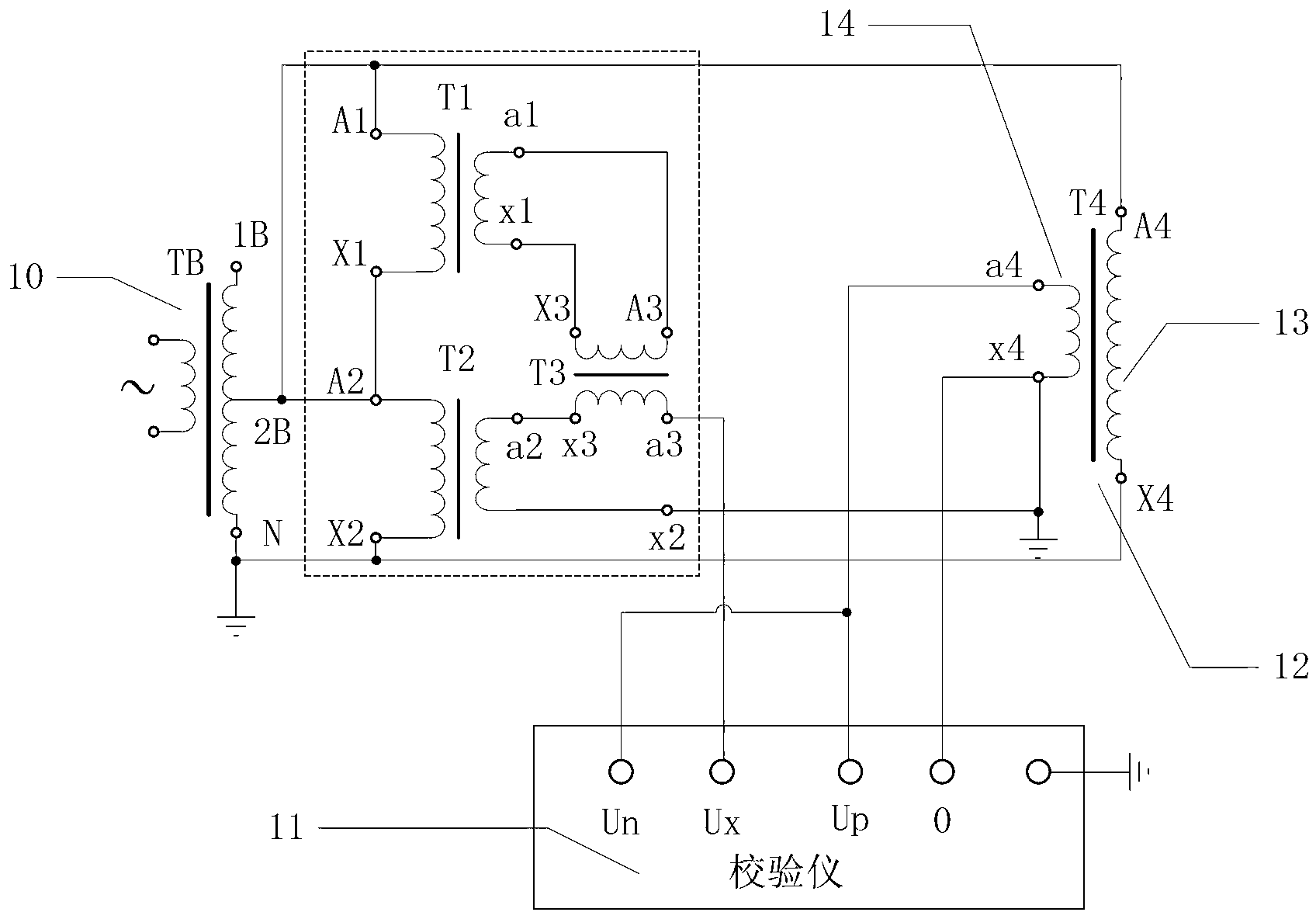
The invention relates to a circuit for measuring a voltage transformer voltage coefficient, and further relates to a method for measuring the voltage transformer voltage coefficient through the circuit. The circuit for measuring the voltage transformer voltage coefficient comprises a first single-stage voltage transformer (T1), a second single-stage voltage transformer (T2) and a passive linear circuit composed of an isolation transformer (T3). Both the rated transformation ratio of the first single-stage voltage transformer (T1) and the rated transformation ratio of the second single-stage voltage transformer (T2) are equal to K; the rated transformation ratio of the isolation transformer (T3) is equal to 1; a primary low-voltage terminal (X1) of the first single-stage voltage transformer (T1) is connected with a primary high-voltage terminal A2 of the second single-stage voltage transformer (T2); a secondary high-voltage terminal a1 of the first single-stage voltage transformer (T1) is connected with a primary high-voltage terminal A3 of the isolation transformer (T3); a secondary low-voltage terminal x1 of the first single-stage voltage transformer (T1) is connected with a primary low-voltage terminal X3 of the isolation transformer (T3); a secondary low-voltage terminal x3 of the isolation transformer (T3) is connected with a secondary high-voltage terminal a2 of the second single-stage voltage transformer (T2). According to the circuit and method for measuring the voltage transformer voltage coefficient, the effect of shielding errors of a voltage transformer on a series addition line can be overcome, and power frequency voltage addition can be effectively used in a 220 kV high-voltage interval and can even be used in a 330kV-1000kV extra-high-voltage interval.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Magnetoelectric devices and methods of using same
ActiveUS7199495B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDevice material selectionElectricityEddy current
The operational frequency of existing magnetoelectric materials having metallic or ceramic magnetostrictive materials and ceramic piezoelectric materials may be limited to a few kilohertz due to the presence of eddy-current losses in the metallic magnetostrictive phase. Further, these materials may be difficult to machine and fabricate due to their brittleness. Additionally, it may be difficult to tailor and optimize the properties (i.e., magnetoelectric voltage coefficient αE, etc.) of the devices. This invention provides a magnetoelectric element including at least one set of alternative piezoelectric layer and magnetostrictive composite layer. The magnetostrictive composite layer includes at least one magnetostrictive material dispersed in first concentrated zones within a first polymer matrix, wherein all of said concentrated zones are orientated along a first direction. It is found that the conversion efficiency (i.e., αE) varies in accordance with applied magnetic control field Hcontrol.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
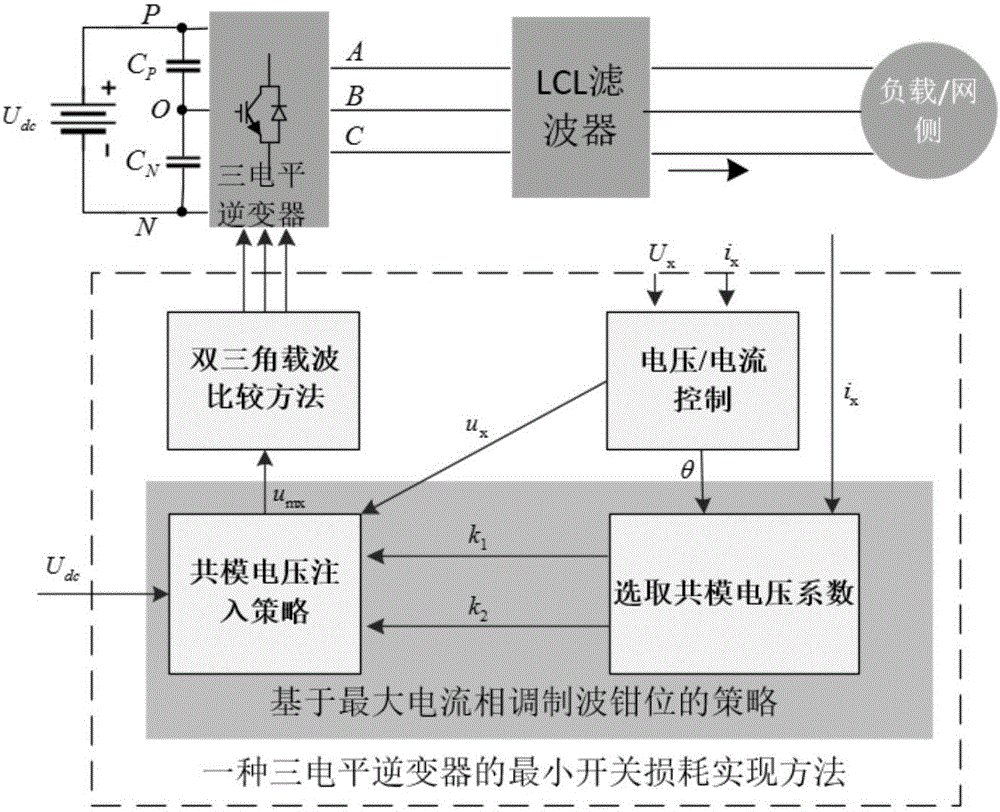
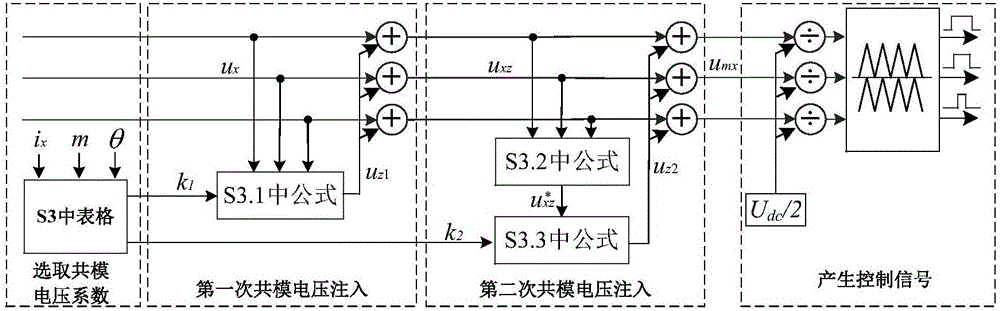
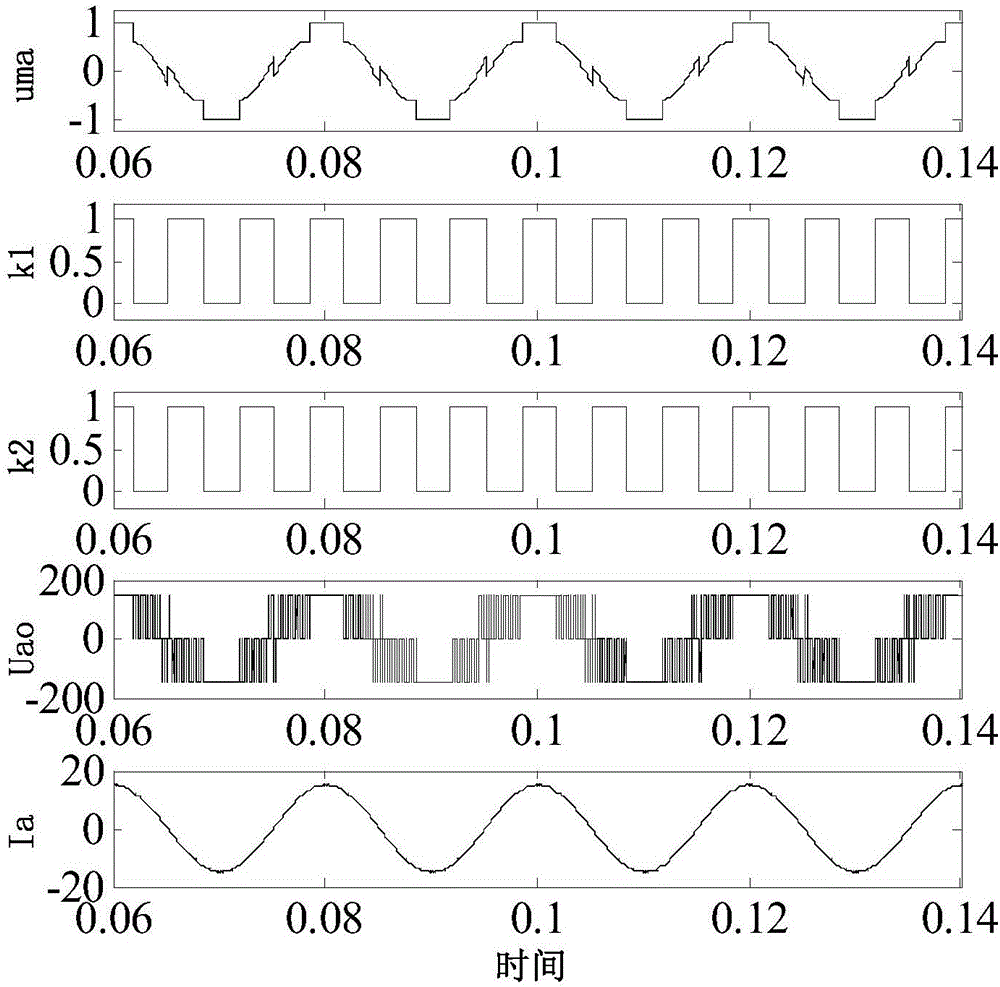
Least switching loss implementation method of three-level inverter
InactiveCN106533236AEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionVoltage vectorCarrier signal
The present invention discloses a least switching loss implementation method of a three-level inverter. According to the data of alternating current side voltage, the alternating current side current and the direct current side total voltage collected by a sensor and the region whether the current relation and the voltage vectors are located, a common-mode voltage coefficient k1 and a common-mode voltage coefficient k2 are selected, the equivalent modulation wave based on the maximum current phase modulation wave clamping is calculated, and the IGBT driving signals are generated through adoption of the double-triangle carrier comparison method. Through combination of the strategy of the maximum current phase modulation wave clamping and the double-triangle carrier comparison method, the least switching loss method is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
On-chip oscillator circuit capable of eliminating control logic delay
ActiveCN104143968ASimple structureEliminate frequencyElectric pulse generator circuitsCapacitanceLow voltage
The invention discloses an on-chip oscillator circuit capable of eliminating control logic delay. The on-chip oscillator circuit mainly comprises a first reference voltage, a second reference voltage, a first charging and discharging current, a first charging and discharging switching group, a first charging and discharging capacitor, a first comparator and a control logic part, wherein the branch of the first charging and discharging capacitor is connected with a first switch tube in series, the first switch tube is in the open state, and the voltage of a starting signal and a power voltage are in positive correlation. According to the on-chip oscillator circuit capable of eliminating control logic delay, influences caused by control logic delay to a clock frequency voltage coefficient and a temperature coefficient can be eliminated, the circuit is especially suitable for the occasion with high clock frequency and big changes of a clock frequency range, the implementation cost is low, and the circuit is simple in structure and easy to implement.
Owner:CHIPSEA TECH SHENZHEN CO LTD
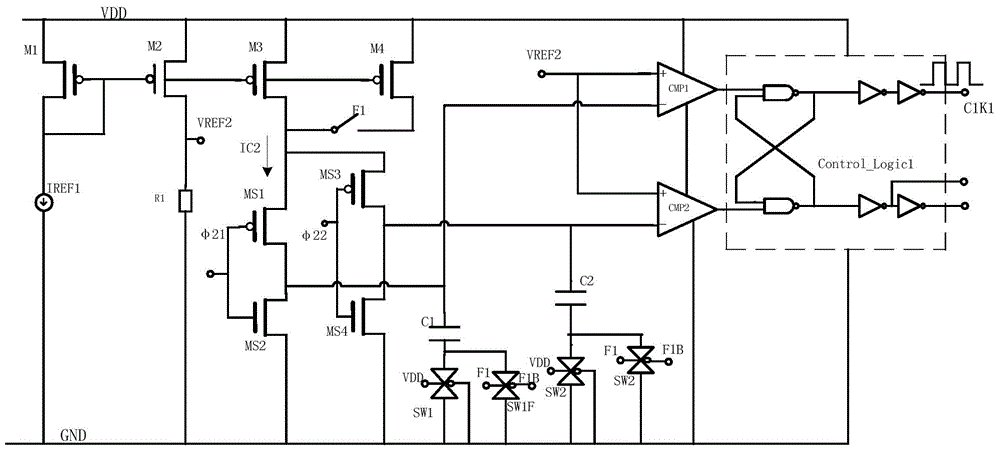
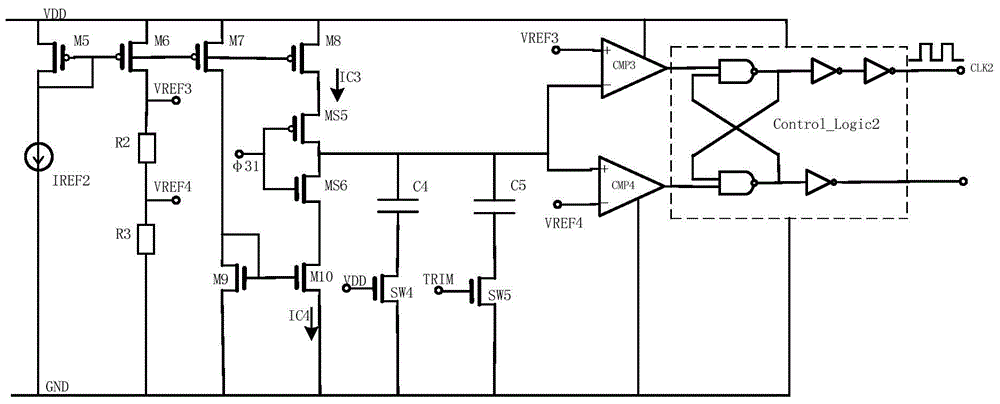
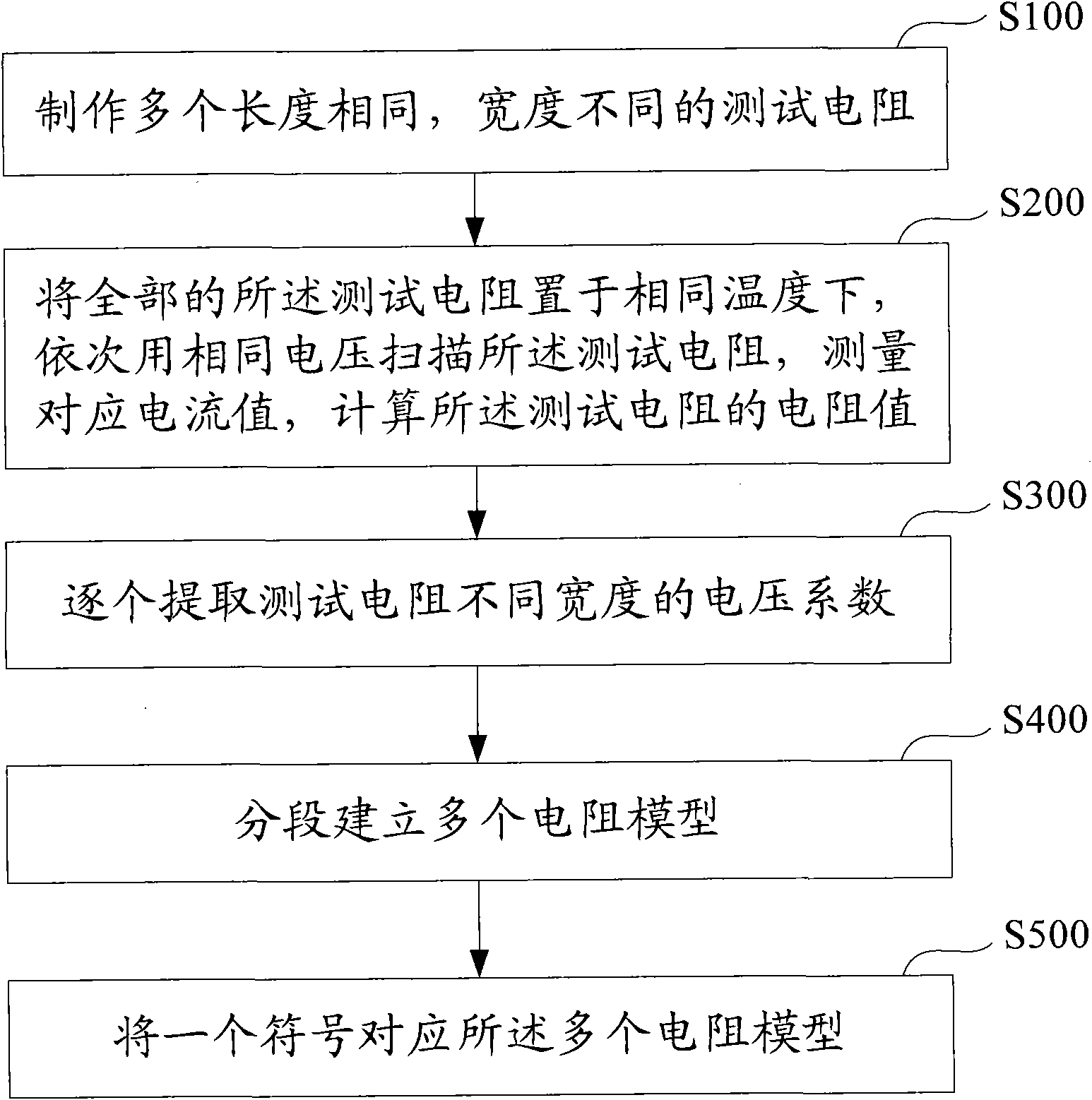
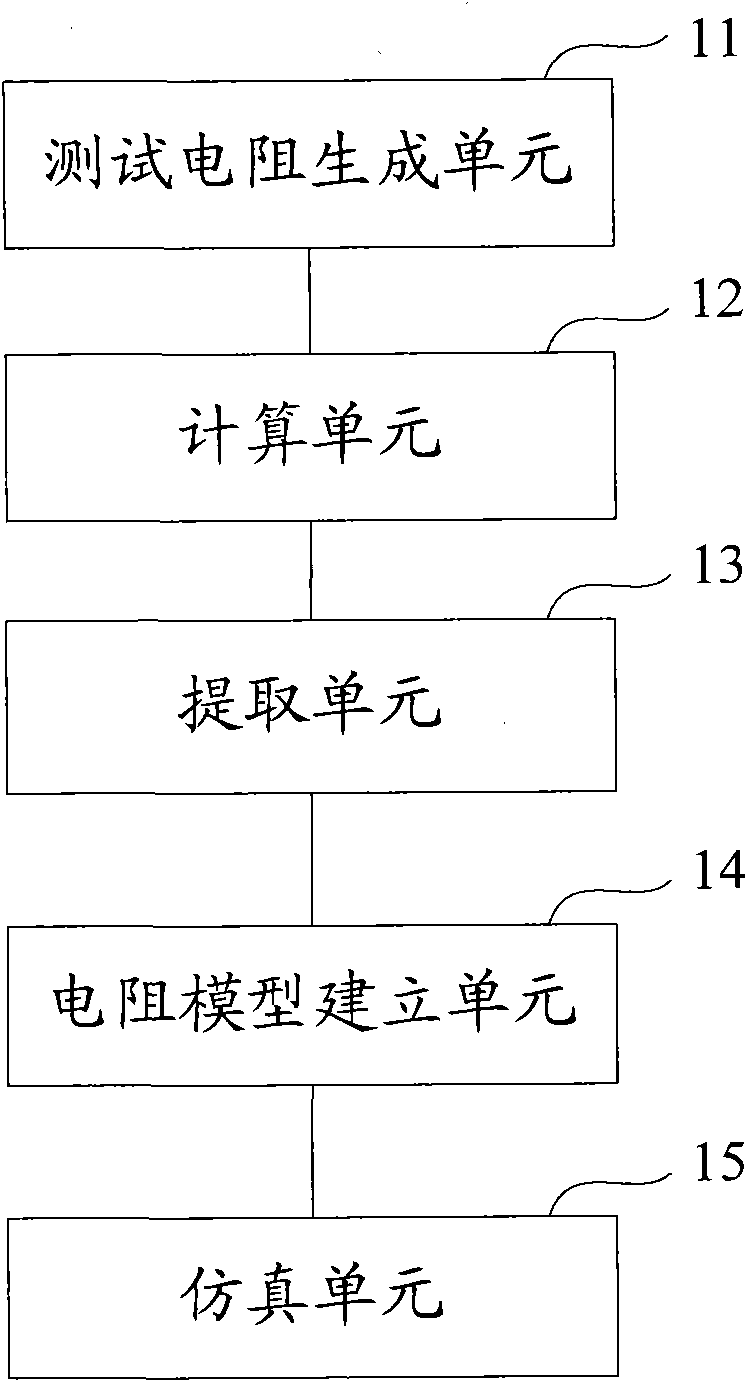
Method and system for establishing diffused resistor voltage coefficient extraction and simulation model
ActiveCN101894177AEasy to useResistance/reactance/impedenceSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical resistance and conductanceSimulation
Owner:BCD (SHANGHAI) MICRO ELECTRONICS LTD
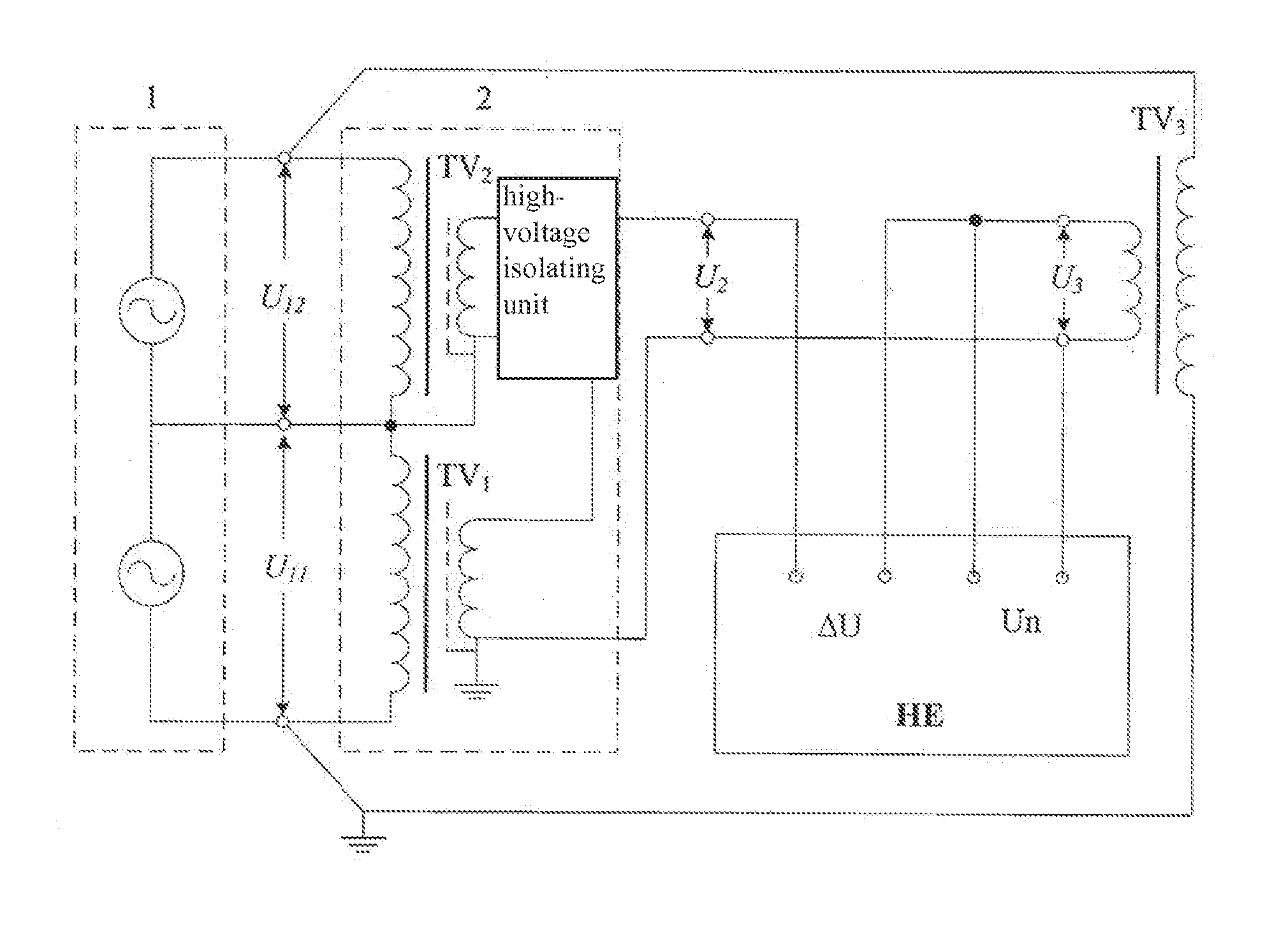
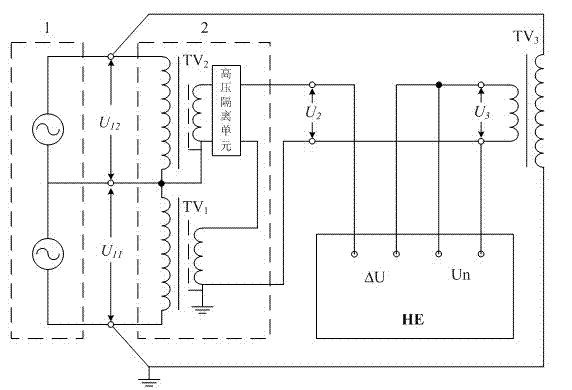
Method and Apparatus for Calibrating Voltage Transformer Serial Addition
A series summation-calibrating device based on a semi-insulating voltage transformer includes a symmetrical high voltage test power supply, a three-port serial voltage transformer, a semi-insulating voltage transformer and an error measuring apparatus. The present invention is characterized by: a complete set of equipment for measuring the traceability of power frequency voltage ratio can be manufactured; calibrating the line according to the serial addition based on the semi-insulating voltage transformer; measuring the relative error between the three-port serial voltage transformer and the semi-insulating voltage transformer; and mathematically processing the measuring result to obtain the voltage coefficient curve of the semi-insulating voltage transformer error. The method is easy to operate without being restricted by voltage level, and can establish, from a low voltage of 10V to a high voltage of 1,000V, a standard power frequency voltage ratio measurement system serving as a measurement standard at the national or provincial / ministerial level.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
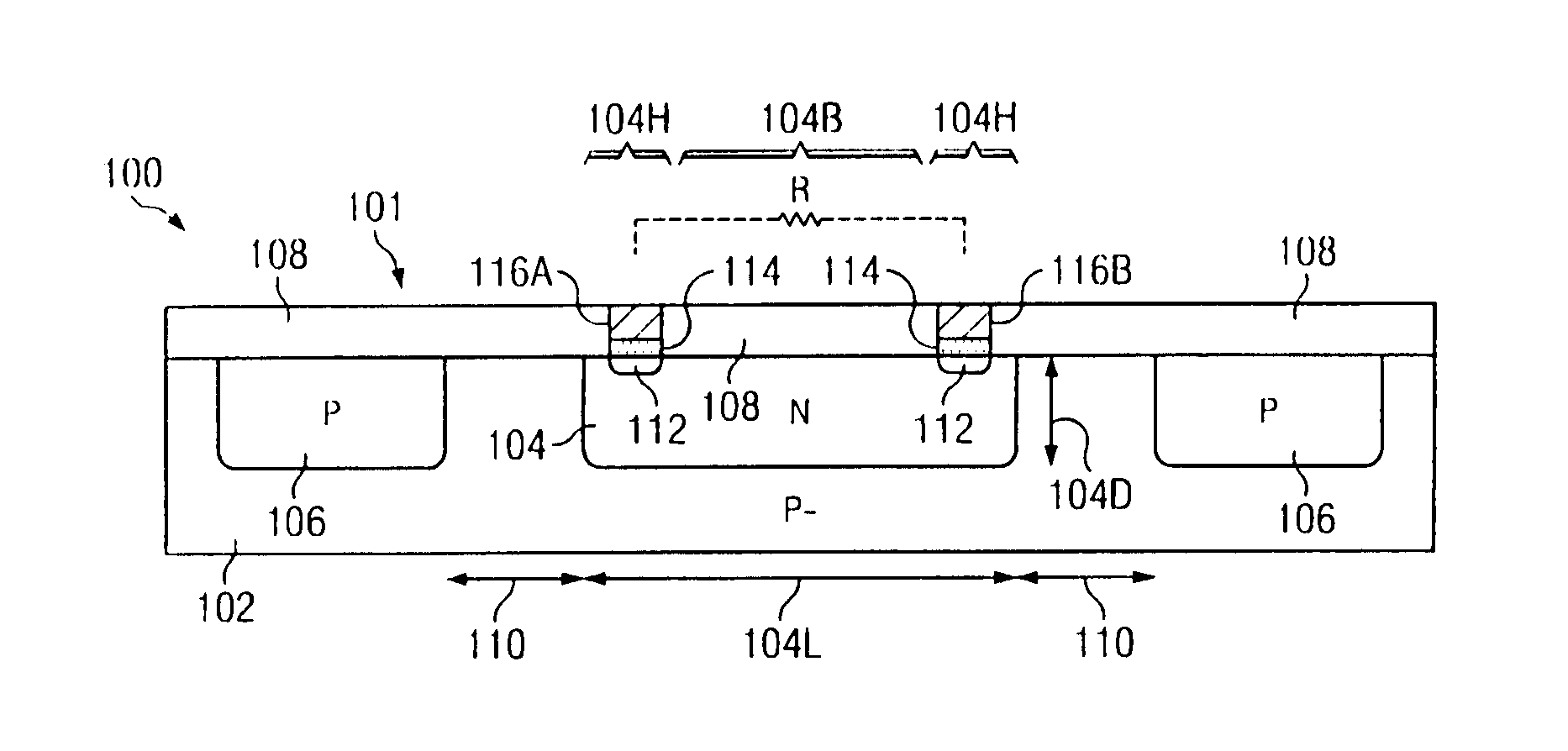
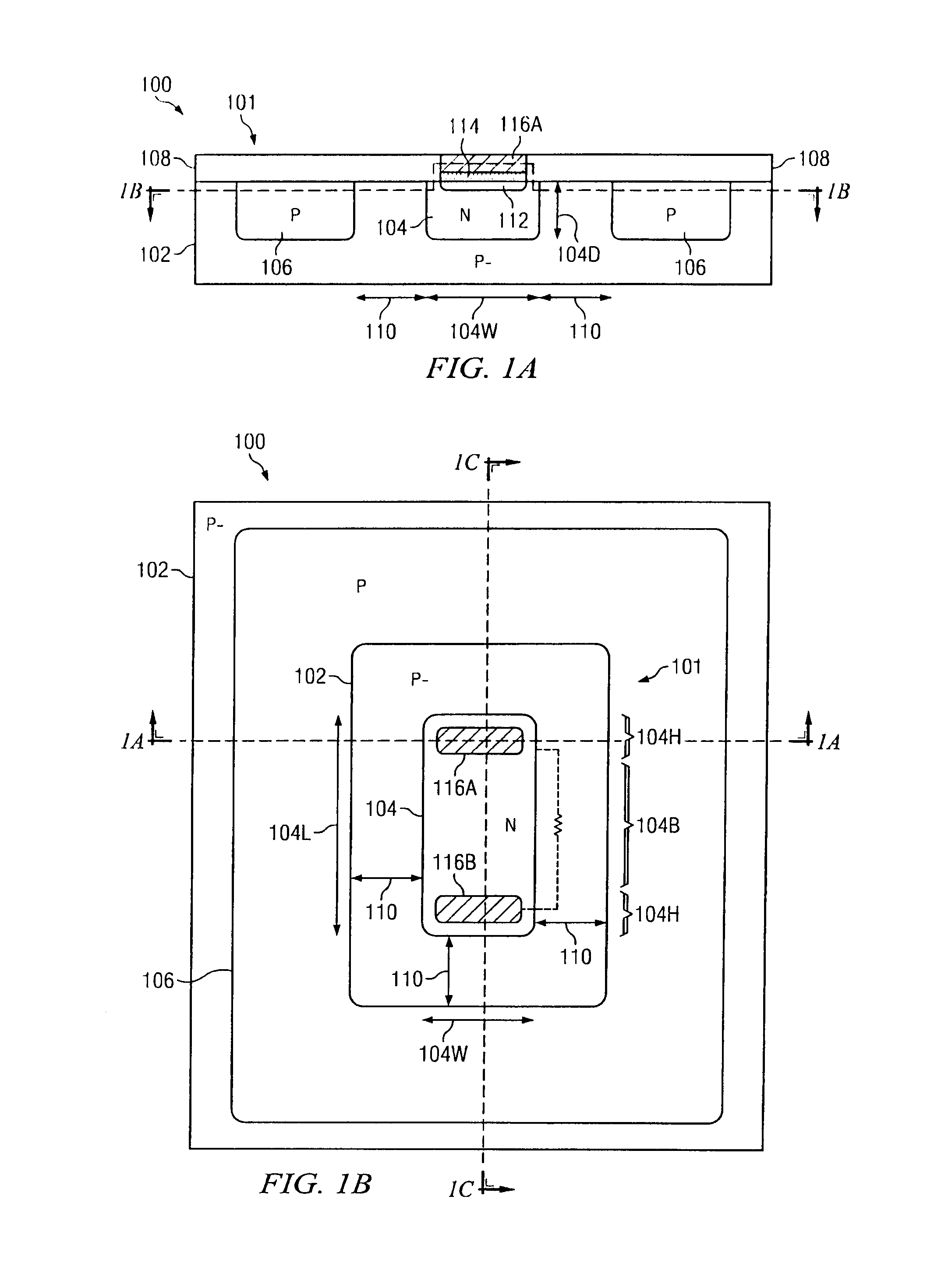
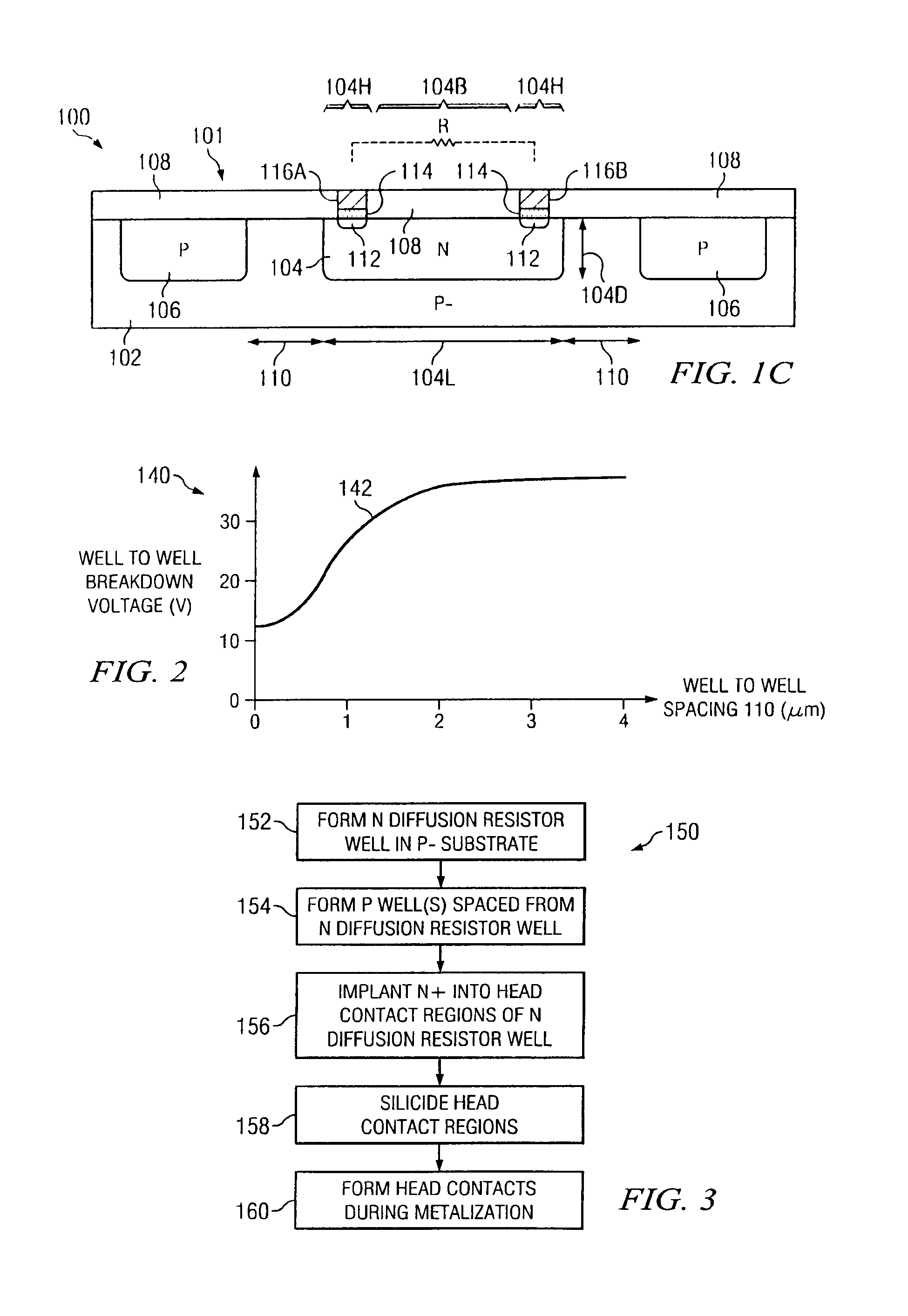
Diffusion resistor with reduced voltage coefficient of resistance and increased breakdown voltage using CMOS wells
ActiveUS20140070361A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove breakdown voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSMaterials science
Integrated circuits and manufacturing methods are presented for creating diffusion resistors (101, 103) in which the diffusion resistor well is spaced from oppositely doped wells to mitigate diffusion resistor well depletion under high biasing so as to provide reduced voltage coefficient of resistivity and increased breakdown voltage for high-voltage applications.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
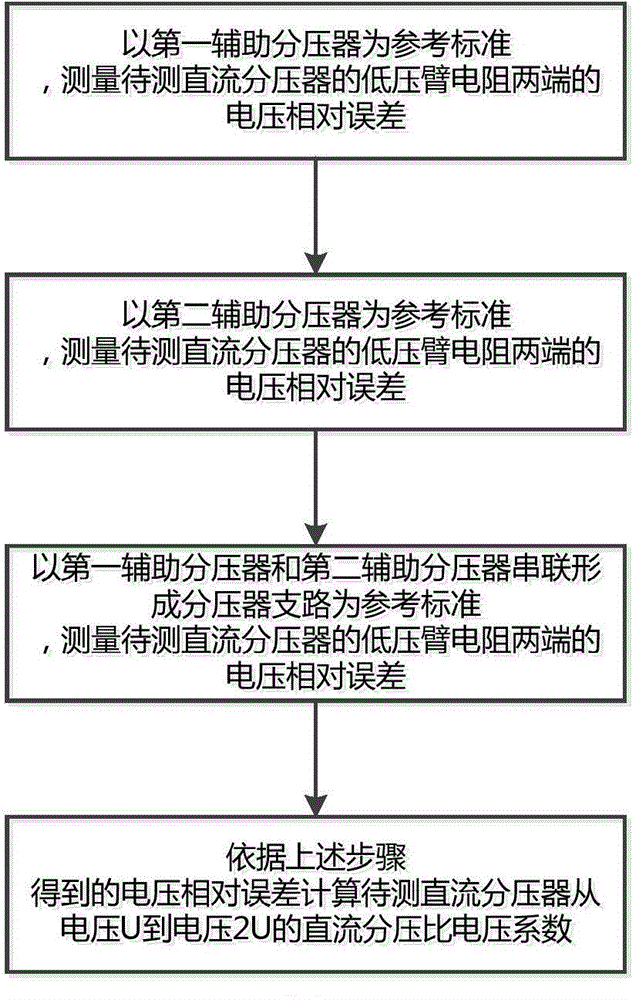
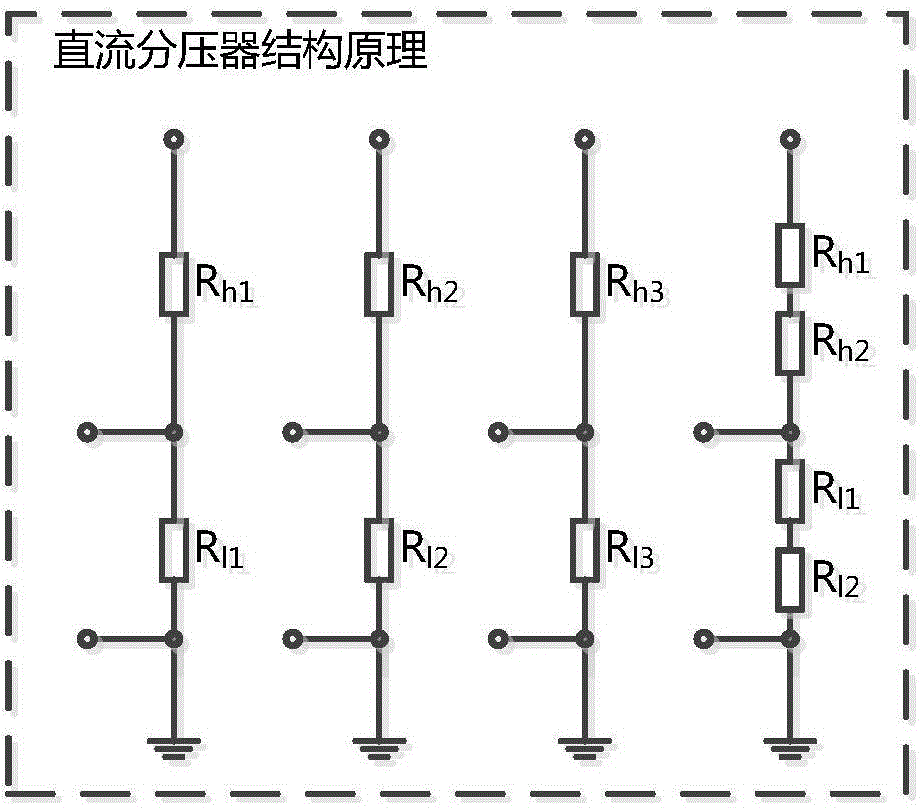
Stand-off ratio voltage coefficient detection method based on separable direct current voltage divider
ActiveCN104360141ARaise the level of measurement uncertaintyEliminate errorsCurrent/voltage measurementLow voltageEngineering
The invention provides a stand-off ratio voltage coefficient detection method based on a separable direct current voltage divider. The method comprises the steps of 1, measuring the relative error of the voltage of a low-voltage arm resistor of a direct current voltage divider to be measured with a first auxiliary voltage divider as the reference standard; 2, measuring the relative error of the voltage of the low-voltage arm resistor of the direct current voltage divider to be measured with a second auxiliary voltage divider as the reference standard; 3, measuring the relative error of the voltage of the low-voltage arm resistor of the direct current voltage divider to be measured with a voltage divider subcircuit formed by series connection of the first auxiliary voltage divider and the second auxiliary voltage divider as the reference standard; 4, calculating the stand-off ratio voltage coefficient of the direct current voltage divider to be measured. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that detection is easier and more convenient, a detection result is more accurate, and the influence of the difference in low-voltage arm resistors of auxiliary voltage dividers on calculation of the stand-off ratio voltage coefficient of the direct current voltage divider to be measured existing during a direct voltage addition test is avoided.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
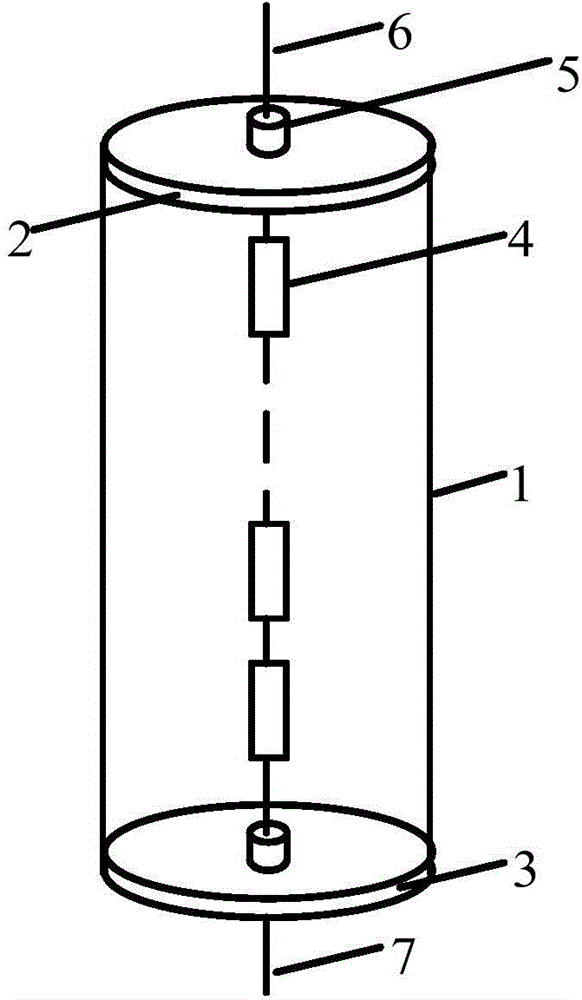
Standard capacitor installed by separated type coaxial structure
InactiveCN102901879AAvoid changeReduce installation errorsFixed capacitor electrodesResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitanceLow voltage
The invention provides a standard capacitor installed by a separated type coaxial structure. The standard capacitor is characterized in that the standard capacitor comprises a bottom plate, a casing component, an electrode component, a high voltage bushing, a conducting rod and a grading ring, the electrode component comprises an electrode fixing platform, a supporting insulator, a high voltage electrode, a low voltage electrode and a shield component, the casing component and the electrode fixing platform are installed at the center of the bottom plate, the low voltage electrode and shield component are fixed on a flange of the electrode fixing platform, the supporting insulator is disposed at the center of a base plate of the electrode fixing platform, the high voltage electrode is mounted at the center of the supporting insulator, and the high voltage bushing is installed at the center of the casing component. According to the standard capacitor installed by the separated type coaxial structure, the separated type structure is utilized, the low voltage electrode and the shield component are separated from a barrel wall, the change of capacitance caused by the deformation of the barrel wall is avoided, temperature coefficient and pressure coefficient are reduced, simultaneously, each part on the installing platform is positioned and processed along a central axis, the coaxiality of high and low voltage electrode assembly can be effectively guaranteed, and the voltage coefficient is reduced.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Calibration circuit applied to signal chain analog gain and calibration method thereof
InactiveCN108551343AReduced area requirementsAvoid overheadAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingVoltage generatorDigital analog converter
The invention discloses a calibration method for a calibration circuit applied to a signal chain analog gain. The calibration circuit is disposed on the auxiliary path of an amplifier in a signal transmission device and is composed of a first Poly resistor, a second Poly resistor and a calibration voltage generator of a reference voltage Vref; the calibration voltage generator is a digital analogconverter consisting of a string of common resistors and a switch array, and the output of the calibration voltage generator is connected to the substrates of the two Poly resistors for voltage regulation. By applying the calibration circuit and calibration method thereof provided by the invention, the calibration circuit is capable of realizing the calibration of ultra-high precision analog gainby using the voltage coefficient characteristic of the Poly resistor, and the calibration process is not in the signal main path, thereby avoiding the performance impact on the PGA main path, greatlyreducing the area requirement of the calibration circuit, and avoiding the overhead and cost of the unit resistance for calibrating and the chip area occupied by the calibration switch. In addition, the calibration circuit is capable of avoiding the influence of introducing the dynamic performance of the PGA and increasing the voltage linearity of the PGA.
Owner:3PEAK INC
Sensing scheme for programmable resistance memory using voltage coefficient characteristics
A method and apparatus for sensing the resistance state of data in a resistance memory cell by using the voltage coefficient of the cell instead of only its resistance. A voltage potential is applied across the resistance memory cell allowing the voltage coefficient of the cell to be determined and subsequently used to determine the logic state of the cell.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
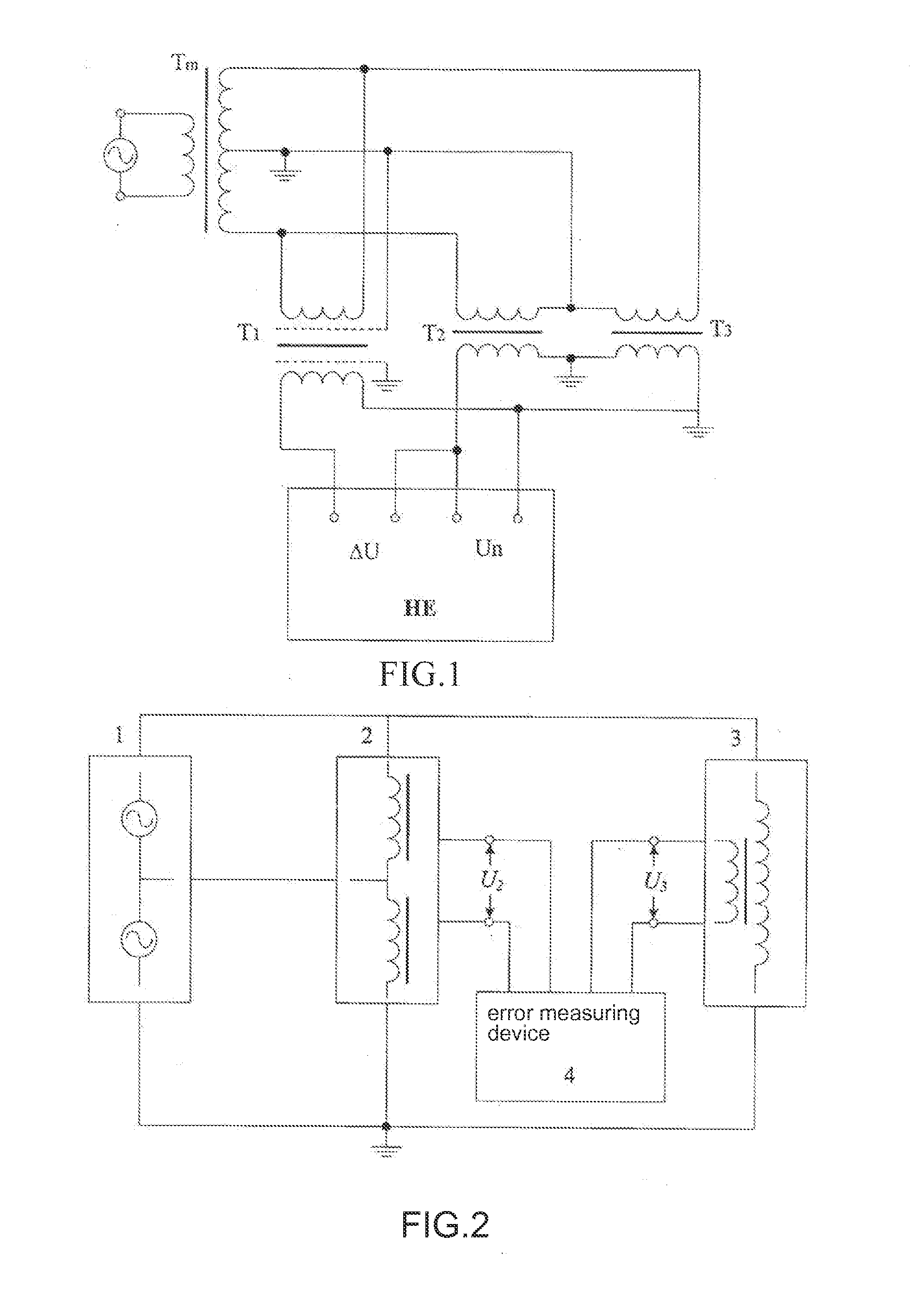
Series addition checking method and device of voltage transformer
InactiveCN102353919AEliminate the effects ofImprove accuracyTransformers testingTransformerLow voltage
The invention provides a series addition checking method and a device based on a semi-insulating voltage transformer. The device comprises a symmetrical high-voltage testing power supply, a three-port series voltage transformer, the semi-insulating voltage transformer and an error measuring device. According to the characteristics of the series addition checking method and the device based on the semi-insulating voltage transformer, complete equipment for tracing a source of a mains-frequency voltage proportional quantity value can be manufactured, and according to a series addition checking line based on the semi-insulating voltage transformer, through measuring a relative error between the three-port series voltage transformer and the semi-insulating voltage transformer and carrying out a mathematical treatment on a measurement result, a voltage coefficient curve of the error of the semi-insulating voltage transformer can be obtained. The method is convenient to operate and is not limited by a voltage class, and a mains-frequency voltage proportional standard quantity value system from a low voltage of 10 V to a high voltage of 1000 kV can be established and is used as a national or provincial measurement standard.
Owner:STATE GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
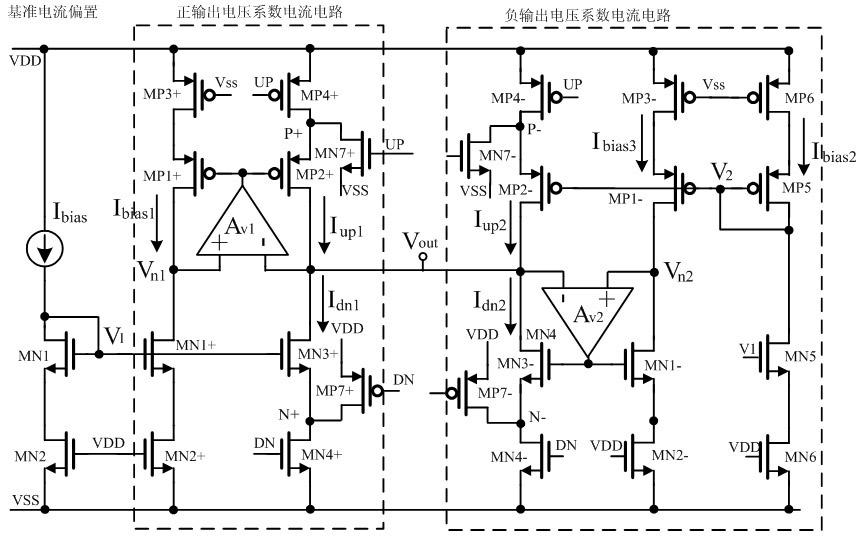
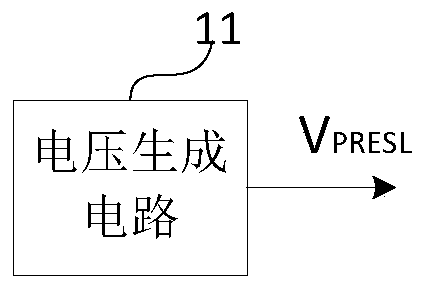
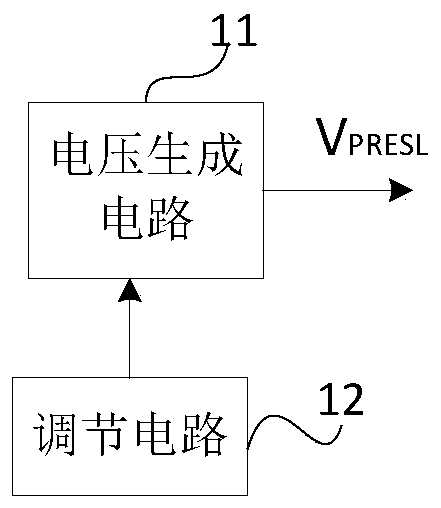
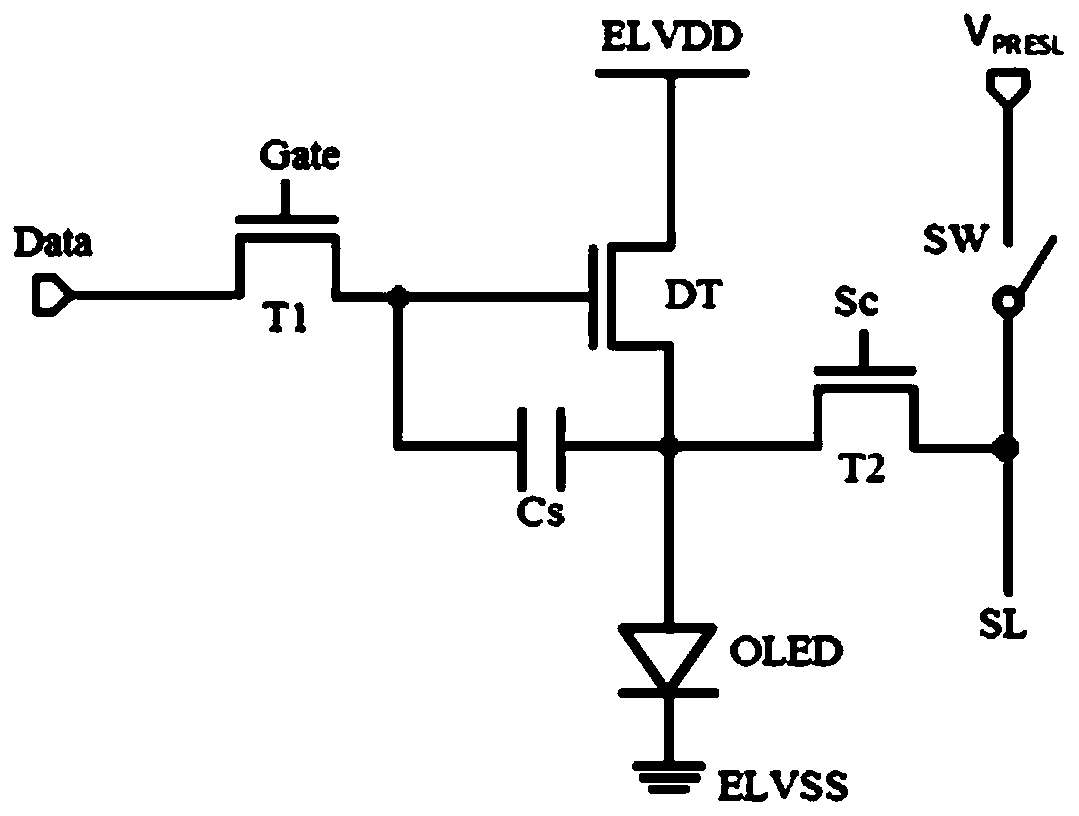
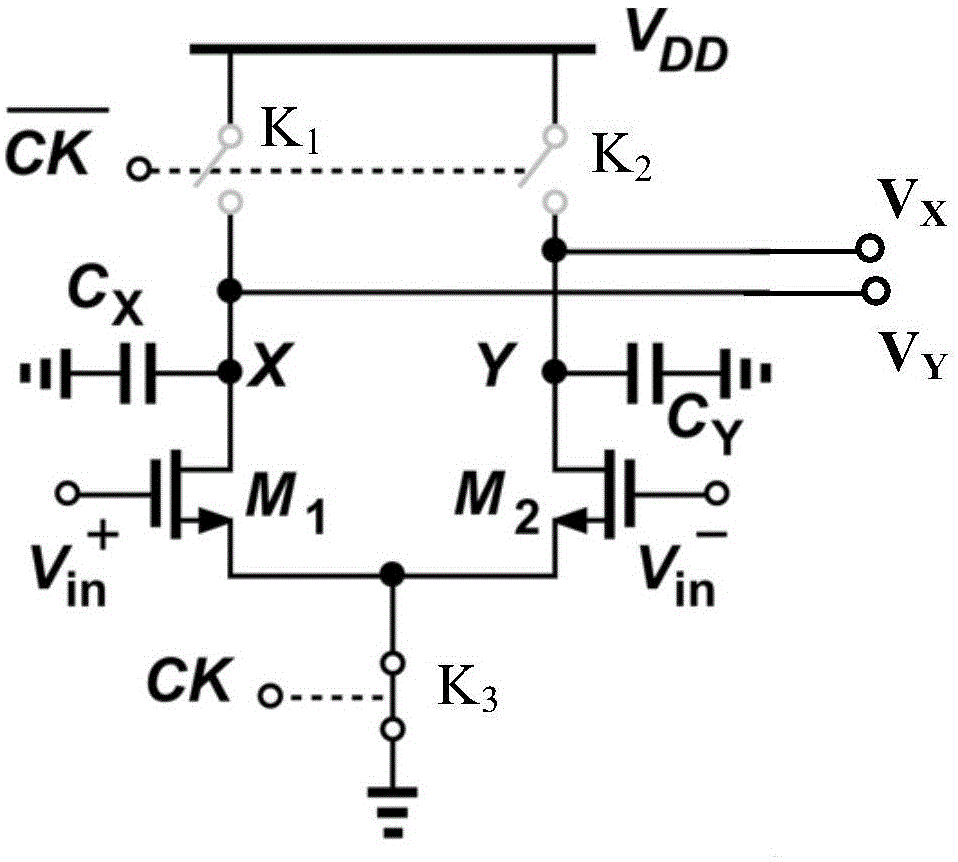
Set voltage generation unit, set voltage generation method, and display device
ActiveCN109830210AEliminate compensation errorsGood compensation display effectStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceVoltage fluctuation
The invention provides a set voltage generation unit, a set voltage generation method and a display device. The setting voltage generation unit comprises a voltage generation circuit; and the voltagegeneration circuit is used for generating a setting voltage according to the gamma main voltage, so that the ratio of the variation of the setting voltage to the variation of the gamma main voltage isa voltage coefficient K, and the K is a positive number smaller than or equal to 1. Compensation errors caused by gamma main voltage fluctuation can be eliminated, and a good compensation display effect is guaranteed.
Owner:HEFEI XINSHENG OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD +1
Differential amplification circuit and assembly line analog to digital converter (ADC) with differential amplification circuit
ActiveCN105099451AImprove linearityImproved ability to follow input voltageAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAssembly lineEngineering
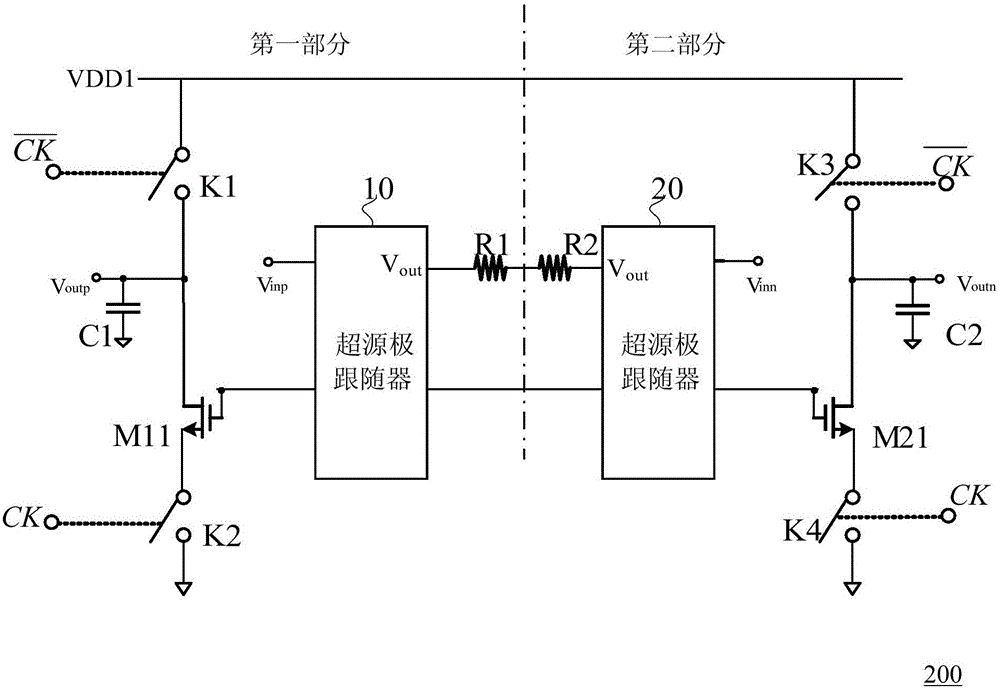
The invention provides a differential amplification circuit and an assembly line ADC with the differential amplification circuit. The differential amplification circuit comprises super-source followers, output voltage of each super-source follower is strictly equivalent to input voltage of the same, low output resistance can be realized, the capability that the output voltage follows the input voltage is improved, the output voltage is converted into current via resistors, the voltage and temperature coefficients of theresistors are both very low, namely, the linearity of theresistors is higher, and thus, the linearity of the differential amplification circuit is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com