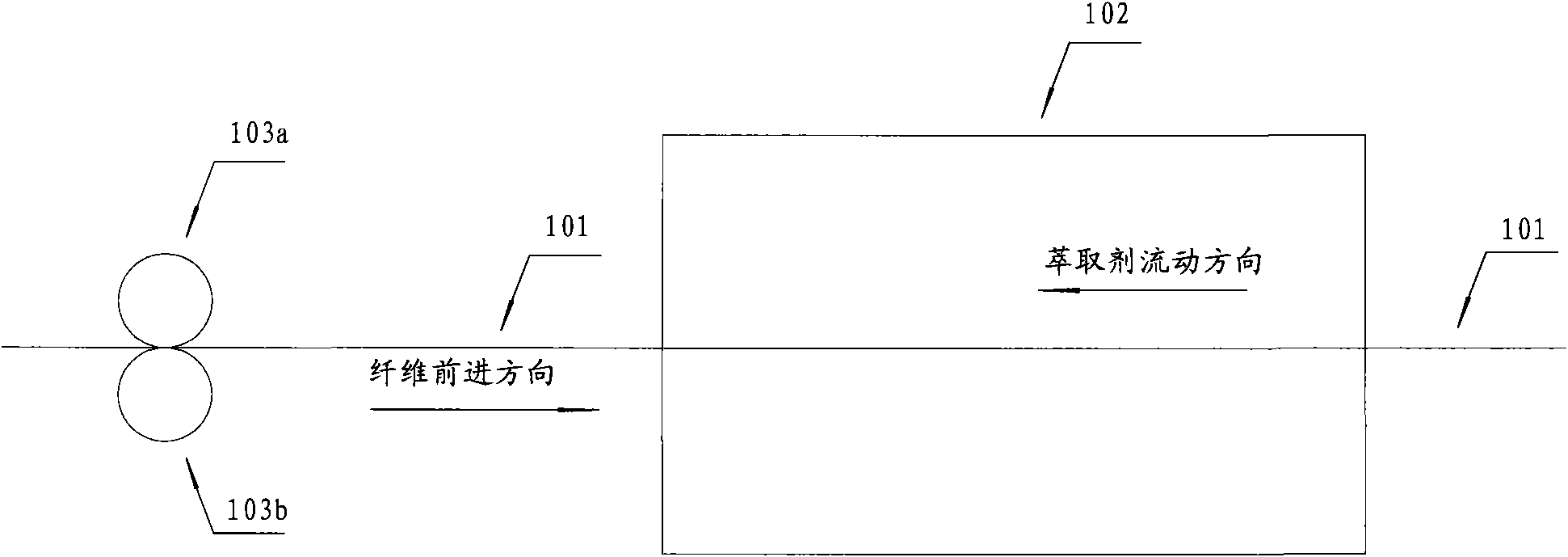Method and device for removing solvent from polyethylene fiber
A polyethylene fiber and solvent technology, applied in the field of polyethylene fibers, can solve the problems of poor first solvent removal effect, large consumption of extractant, and high cost of extractant recovery, so as to save extractant, improve performance, and improve The effect of extraction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
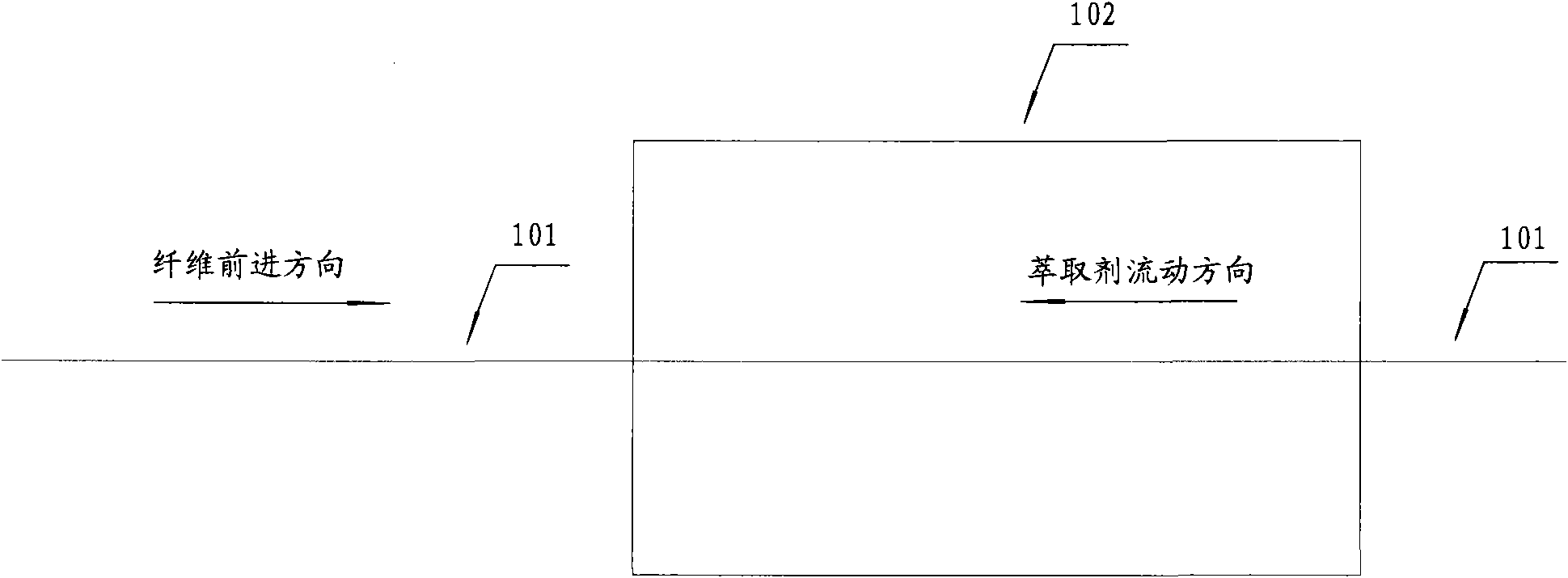
[0041] See figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of a method for removing solvent in polyethylene fiber in the prior art. The polyethylene fiber 101 advances in the direction shown in the figure, and the advancing direction is opposite to the flow direction of the extractant, and the polyethylene fiber 101 directly enters the extraction tank 102 without preprocessing. See figure 2 , figure 2 It is the first embodiment of the method for removing the solvent in the polyethylene fiber according to the present invention, compared to figure 1 The method for removing the solvent in the polyethylene fiber 101 shown in the prior art, in this embodiment, before the polyethylene fiber 101 enters the extraction tank 102, it first passes through a process of extruding the polyethylene fiber 101 to remove the solvent Some solvents.
[0042]In this embodiment, extruding the polyethylene fiber 101 is accomplished by a rubber roller 103a and a stainless steel roller 103b. Ther...
Embodiment 1
[0056] The polyethylene powder with a weight average molecular weight of 5 million, additives, and solvent paraffin oil are thoroughly mixed and dissolved, and then enter the twin-screw extruder. Then it enters the spinning box and is extruded into filaments through the spinneret. After cooling in the coagulation bath water tank, gel fibers are formed, and then pass through the above-mentioned rubber roller 103a and stainless steel roller 103b. The pressure between the rubber roller 103a and the stainless steel roller 103b is 15N, which is the pressure for 1000 polyethylene fibers. The extruded polyethylene fibers are extracted with solvent gasoline. The extraction equipment is an extraction tank made of stainless steel, and the extraction adopts three-stage countercurrent extraction, and the extraction temperature is 20°C. Water is added to the extraction equipment to form a water seal with a thickness of 5 cm. Then enter the drying box for drying treatment, the drying temp...
Embodiment 3
[0060] The polyethylene fibers prepared in Example 1 and Comparative Example 2 were tested for solvent content and mechanical properties respectively, and the specific data are shown in Table 1.
[0061] The performance comparison of the polyethylene fiber prepared by different embodiments of table 1
[0062] testing sample
Tensile Strength
(cN / dtex)
Tensile modulus
(cN / dtex)
Solvent content (weight
content)
Example 1
30
950
0.75%
Comparative Example 1
28
940
1.2%
[0063] From the above under the same test conditions, it can be seen that the solvent content in the final polyethylene fiber is significantly lower than that without pre-extrusion, and the mechanical properties are also improved. cN / dtex in Table 1 is the unit of specific stress, c stands for one percent, N stands for cattle, and dtex stands for dtex.
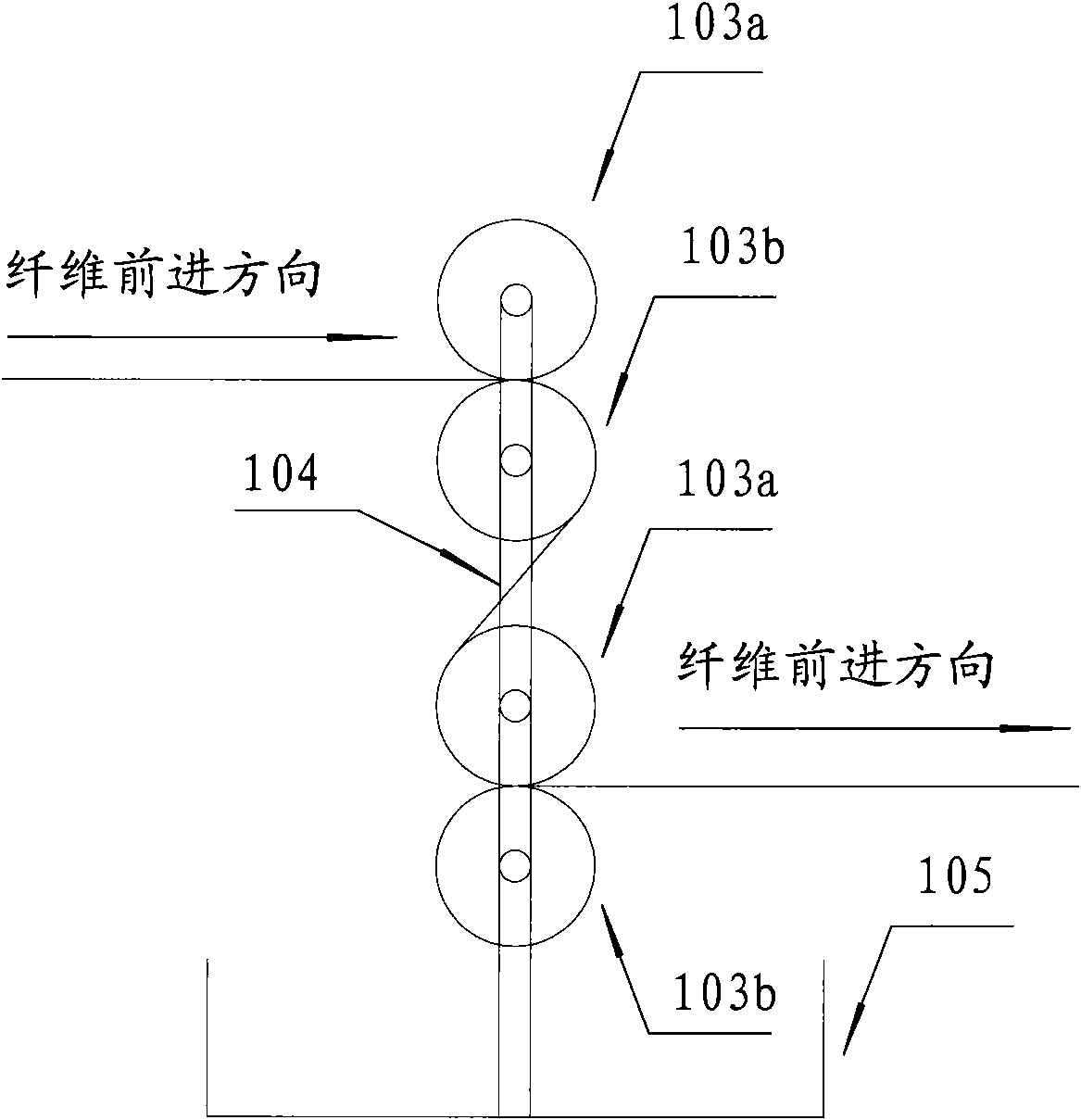
[0064] See image 3 , image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the first embodim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com