Method for monitoring misalignment of physically cross-coupling feeding machine shafts
An orthogonal coupling and feeding technology, applied in the field of numerical control, can solve the problems of high cost, increased cost, and inability to use infrared sensors, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost and high benefit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples.
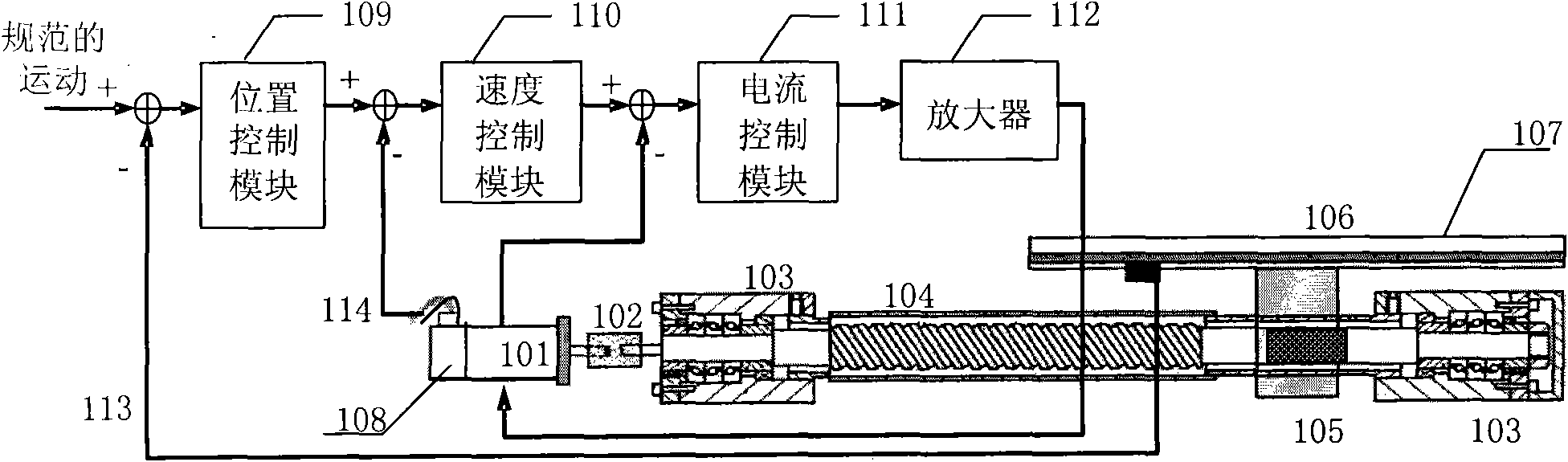
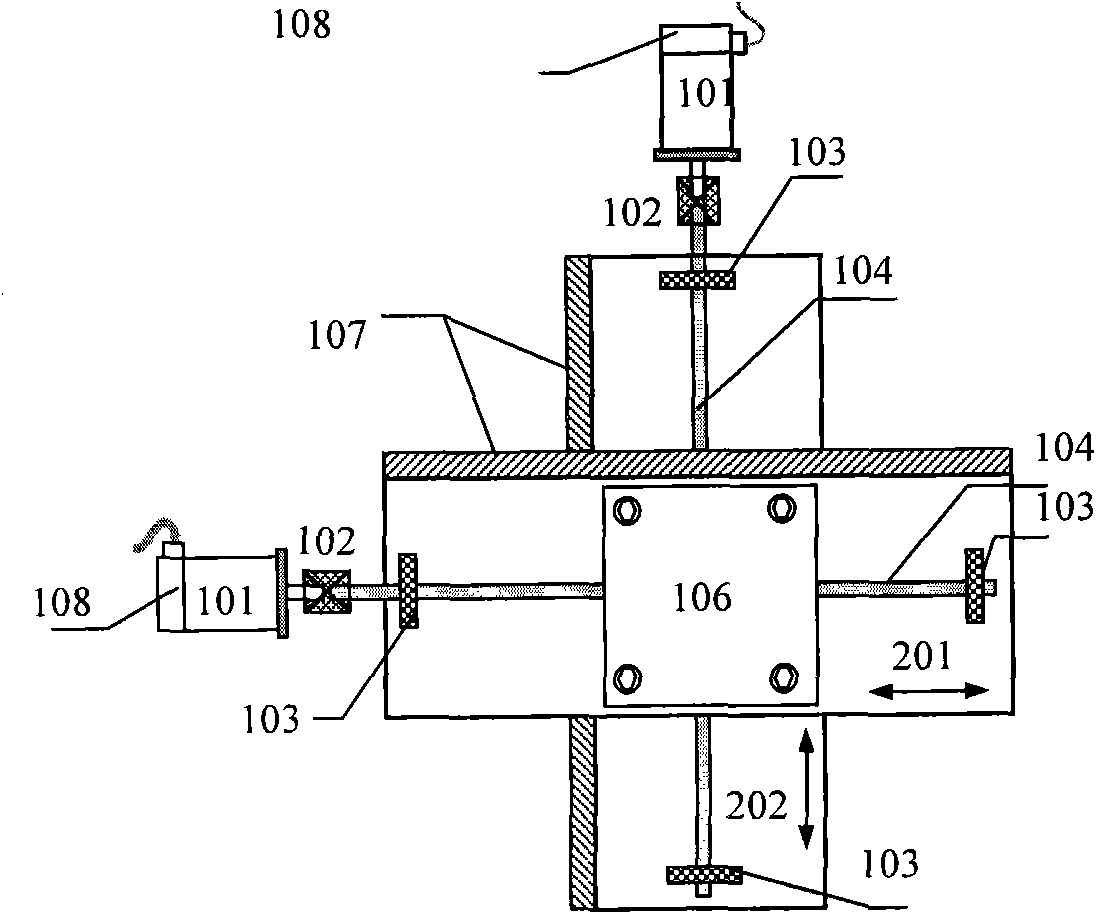
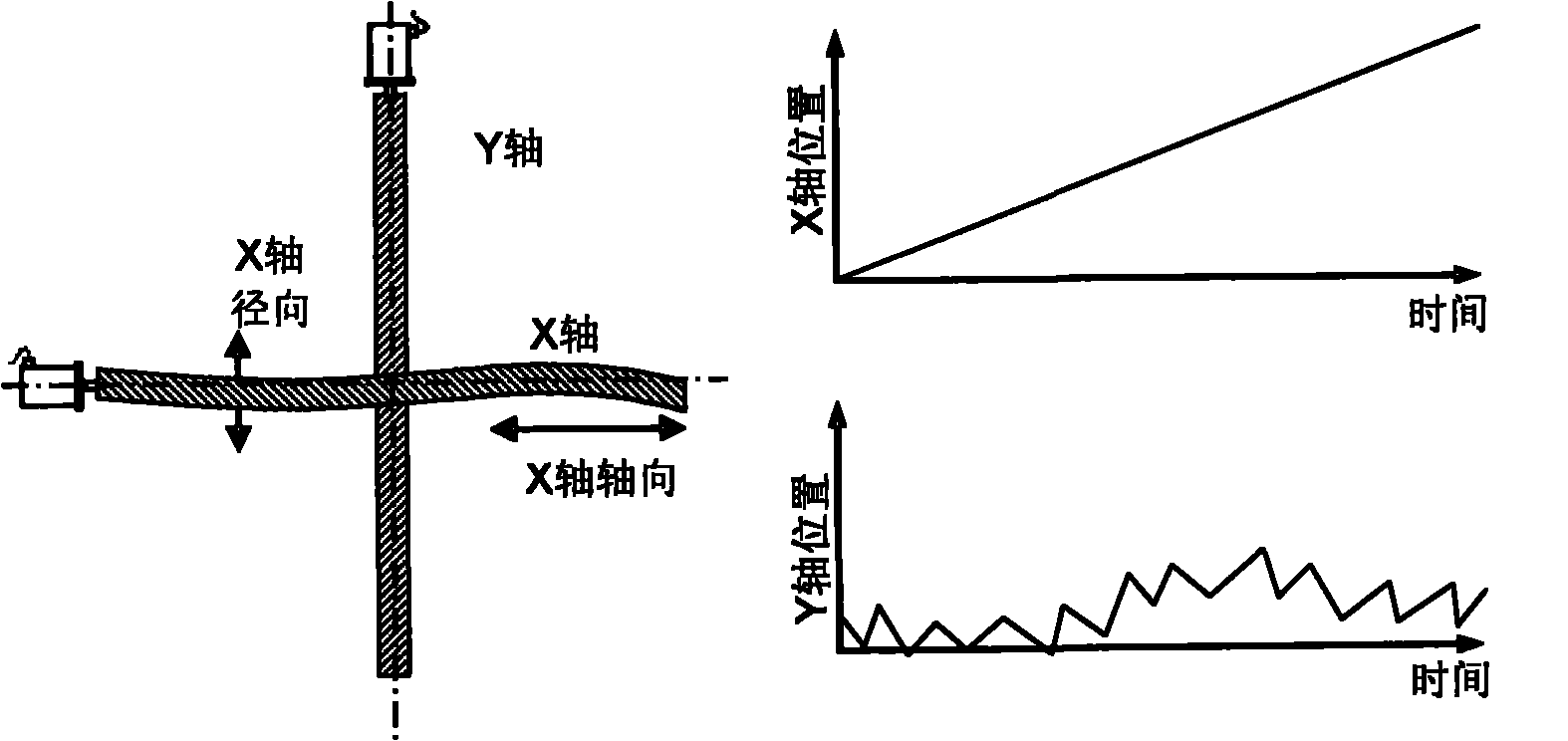
[0042] The main idea of the present invention is: utilizing the characteristic that the axes of the feed machine of orthogonal coupling are perpendicular to each other in physics, when one of the axes moves, if the axis is misaligned, there will also be movement in the radial direction of the axis, so that the other The shaft will also move accordingly. Therefore, by analyzing the DMS position signal of the physically orthogonally coupled feed mechanical shaft, the vibration and displacement in the radial direction of the feed mechanical shaft can be sensed, thereby realizing the misalignment of the feed mechanical shaft. monitor. image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the principle of the method for monitoring the misalignment of physically orthogonal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com