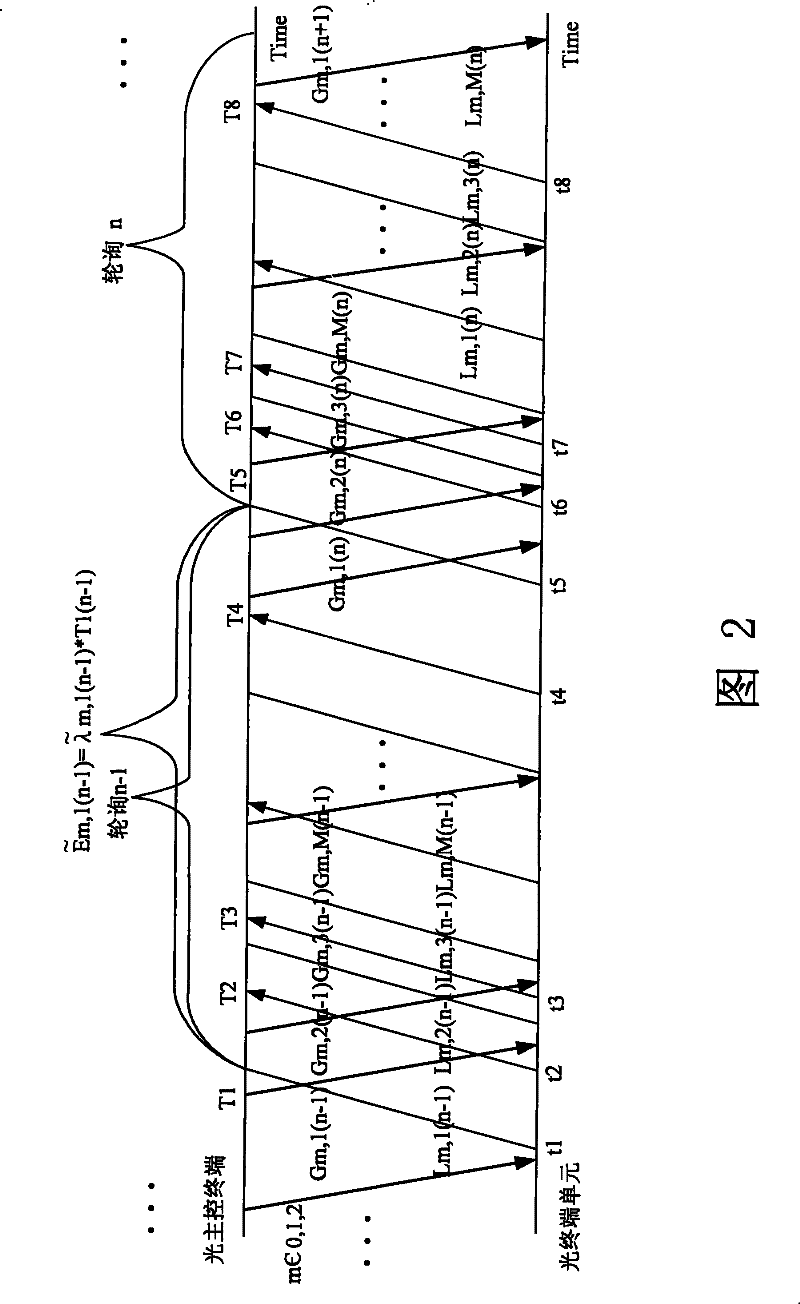
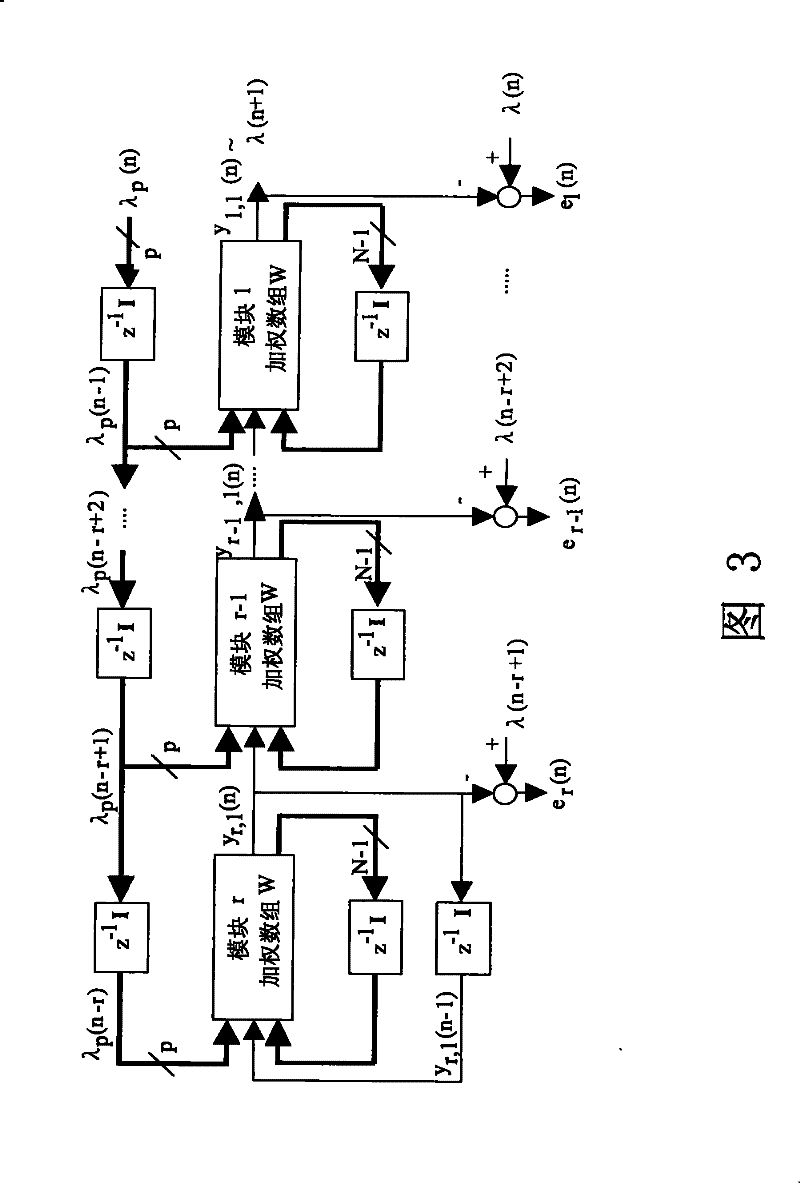
Method for allocating dynamic bandwidth of ether passive optical network
An optical fiber network, passive technology, applied in the field of dynamic bandwidth assignment, can solve the problems of increasing the polling time, reducing the completion transmission rate, poor bandwidth utilization rate, etc., so as to improve the bandwidth utilization efficiency and reduce the packet loss rate. , the effect of improving the transmission efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
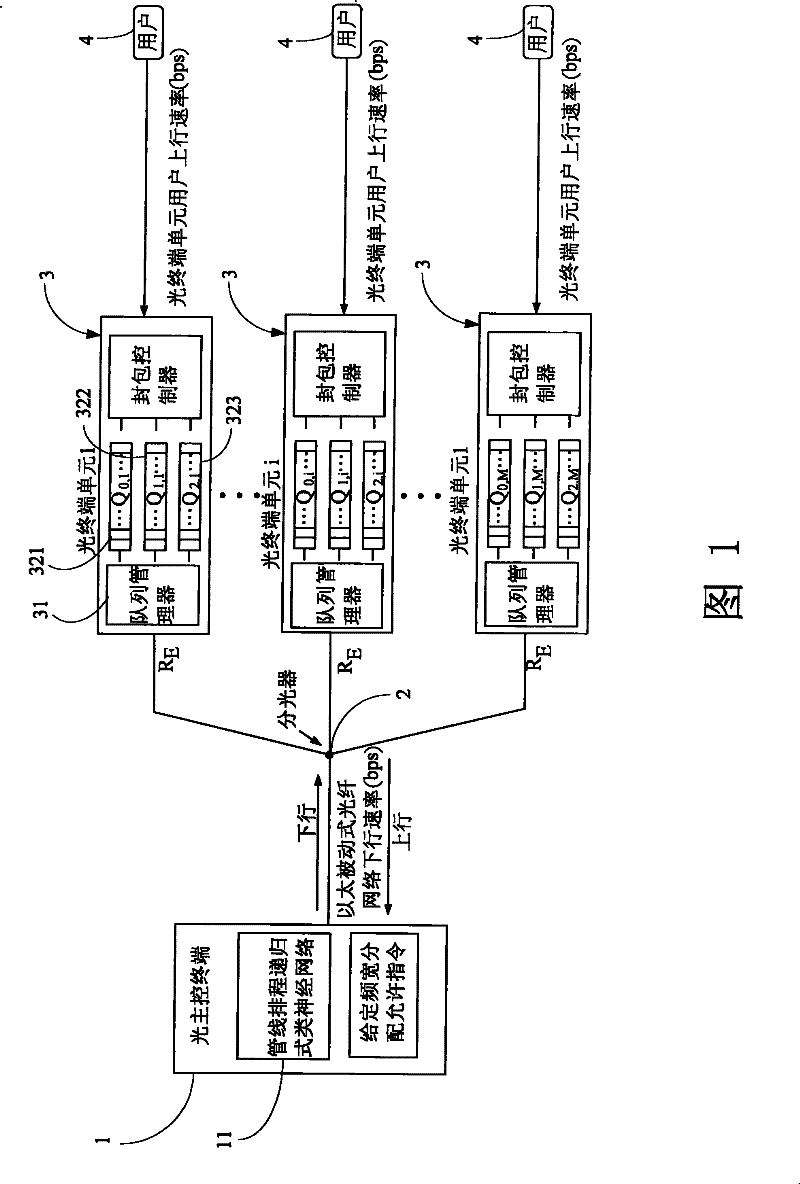
[0042] see figure 1 , is the Ethernet passive optical fiber network system architecture diagram of the dynamic bandwidth assignment method of the Ethernet passive optical fiber network of the present invention, which includes:
[0043] The optical main control terminal 1 is connected with the optical splitter 2, and the downlink packet is broadcast to several optical terminal units 3 through the optical splitter 2. In addition, the optical main control terminal 1 has a pipeline scheduling recursive neural network 11, Allocate permission commands with a given bandwidth;
[0044] The optical splitter 2 is connected with the optical main control terminal 1 and several optical terminal units 3, and is a single-point to multi-point optical splitter (splitter);
[0045] Several optical terminal units 3 are connected to the optical splitter 2 and several clients 4, and each optical terminal unit receives its own packets according to its Logic Link Identifier (LLID), and discards oth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com