Method for extracting regenerated carbon-containing fused magnesia from waste magnesia carbon bricks
A technology of fused magnesia and waste magnesia-carbon bricks, which is applied in the field of recycling waste magnesia-carbon bricks, can solve the problems of low added value, difficulty in cleaning, and hard surface debris, so as to increase particle volume density and improve resistance Erosion performance, the effect of eliminating false particles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
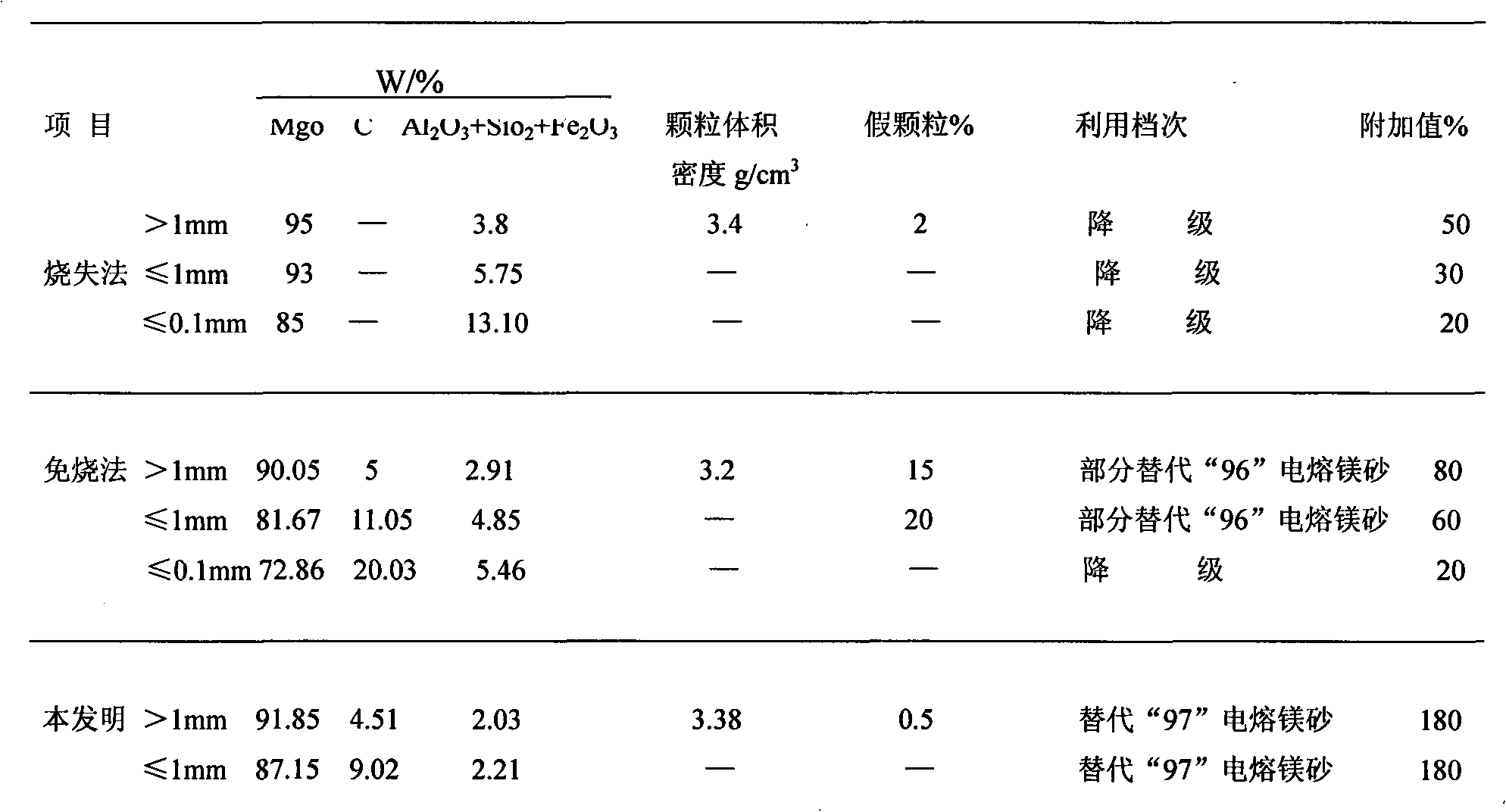
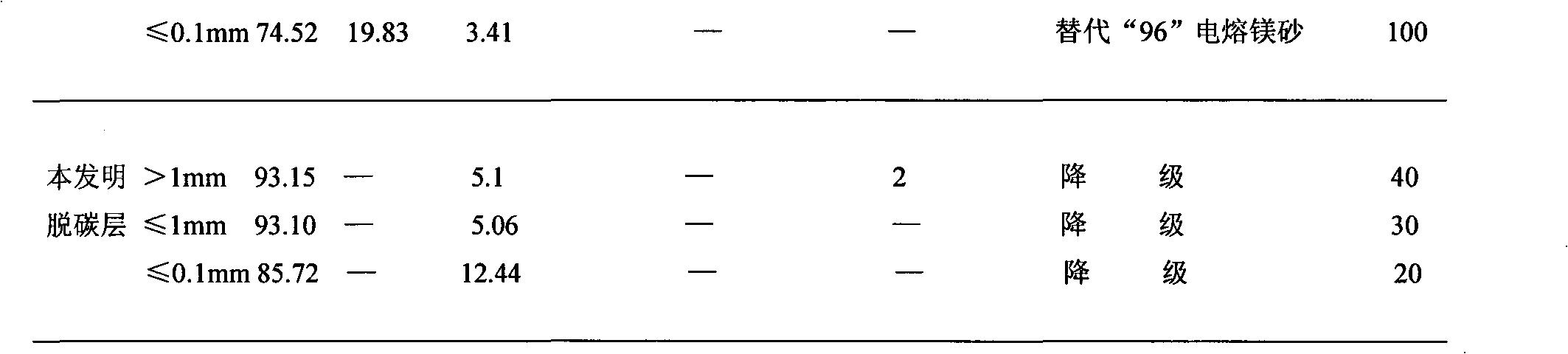
[0030] Remove the sundries on the surface of waste bricks and break them into pieces of about 150mm in size, with a volume of 30m 3 Calcined in the vertical kiln, the prepared fan model is 9-26 series, machine number is 8.0 NO High pressure centrifugal fan.
[0031]First, use about 150mm material blocks to install the cooling zone of the vertical kiln (accounting for about 1 / 3 of the kiln height), then in the calcination zone, use diesel to ignite, turn on the fan, and charge the material while blowing, and the temperature reaches 800 ℃-1000℃, graphite starts to oxidize, stop supplying fuel, rely on graphite oxidation in the material as fuel, charge at a speed of 90-110kg / min, fill the kiln at one time, and continue blasting for 80min-100min after loading, The temperature of the kiln in the calcining zone rises to 1350°C-1400°C, at this time, the flame is filled with the kiln roof, and the blast continues for 30-40 minutes. After the material is discharged, the second kiln i...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Remove the sundries on the surface of waste bricks and break them into pieces of about 150mm in size, with a volume of 30m 3 Calcined in the vertical kiln, the prepared fan model is 9-26 series, machine number is 8.0 NO High pressure centrifugal fan.
[0037] First, use about 150mm material blocks to install the cooling zone of the vertical kiln (accounting for about 1 / 3 of the kiln height), then in the calcination zone, use diesel to ignite, turn on the fan, and charge the material while blowing, and the temperature reaches 800 ℃-1000℃, the graphite starts to oxidize, stop supplying fuel, rely on the graphite oxidation in the material as fuel, charge the material at a speed of 100kg / min, and fill the kiln at one time. The temperature of the kiln rises to 1350°C-1400°C. At this time, the flame fills the kiln roof, and the blasting continues for 35 minutes. When the kiln temperature in the calcination zone drops to 600°C-650°C, the blasting is stopped, and the cooling z...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Remove the sundries on the surface of waste bricks and break them into pieces of about 150mm in size, with a volume of 30m 3 Calcined in the vertical kiln, the prepared fan model is 9-26 series, machine number is 8.0 NO High pressure centrifugal fan.
[0040] First, use about 150mm material blocks to install the cooling zone of the vertical kiln (accounting for about 1 / 3 of the kiln height), then in the calcination zone, use diesel to ignite, turn on the fan, and charge the material while blowing, and the temperature reaches 800 ℃-1000℃, the graphite starts to oxidize, stop supplying fuel, rely on the graphite oxidation in the material as fuel, charge the material at a speed of 110kg / min, fill the kiln at one time, continue blasting for 100min after loading, and calcine in the belt The temperature of the kiln rises to 1350°C-1400°C. At this time, the flame fills the kiln roof, and the blasting continues for 40 minutes. When the kiln temperature in the calcination zone ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com