Hollow/porous fibers and applications thereof
A fiber and blend technology, which is applied to hollow/porous fibers and their application fields, can solve the problems of difficult production of fibers, and achieve the effect of improving the ability of decomposition and improving efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0043] In another embodiment, there is provided a method for preparing a fiber described herein, comprising:
[0044] (a) adding polyvinyl acetate to polyacrylic acid to form a spinning mixture; and
[0045] (b) passing the spinning mixture directly through a die or spinneret to form fibers.
[0046] The die or spinneret used to form the fibers may have an annular configuration. For example, a spinneret having an annular orifice or hole through which the liquefied spinning mixture is passed under pressure can be used to form the walls of the hollow fiber structures described herein. In a specific embodiment, a coaxial central port in the spinneret can be used to introduce material to fill the core or lumen of the fiber with a target material, usually gas or liquid, that serves to expand the core of the fiber and Prevent it from flattening during spinning. Such a die or spinneret may be placed at the outlet of a conventional compounder or extruder, such as a twin screw extru...
Embodiment 1
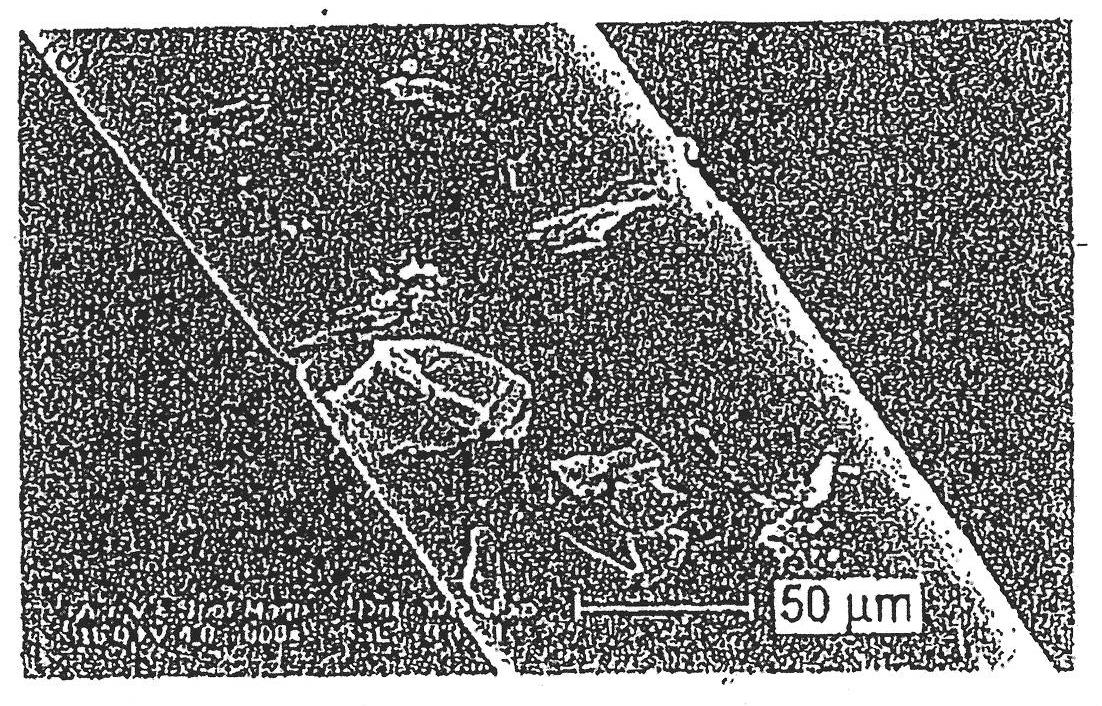
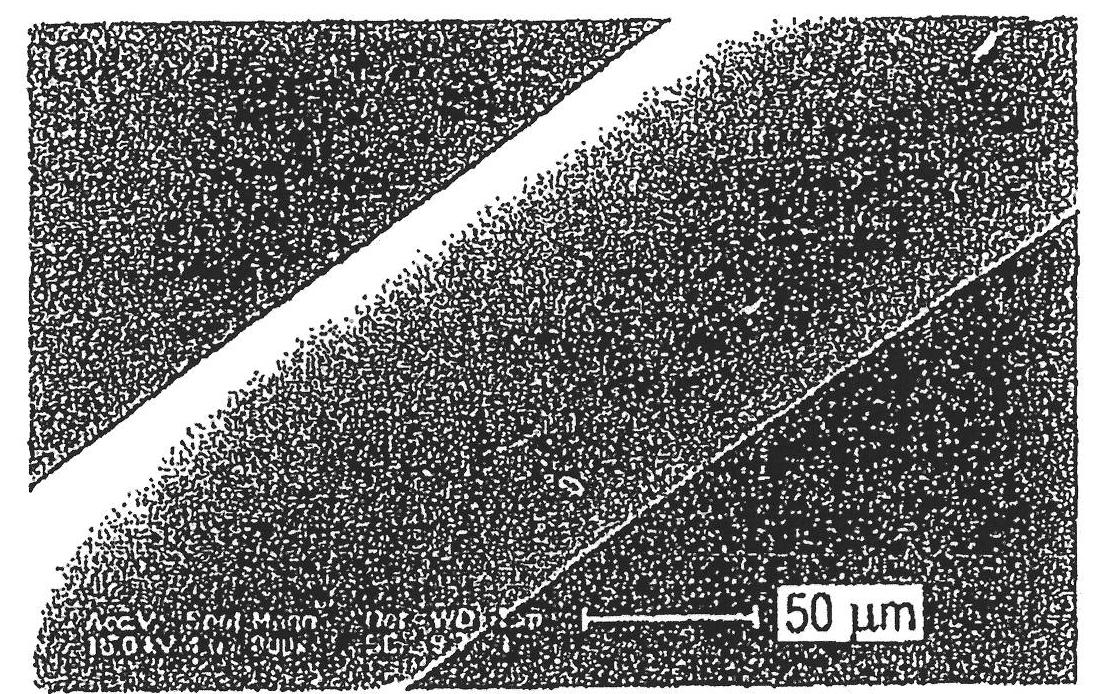
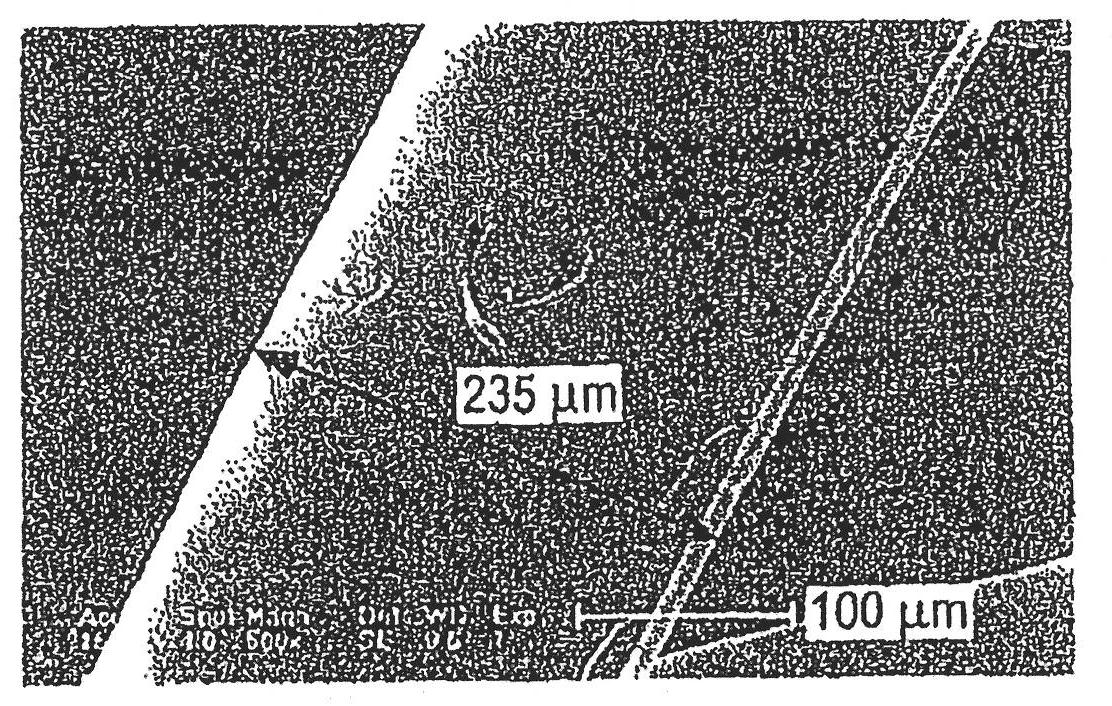
[0055] In a microblender, 1 gram of polyvinyl acetate was added to 1 gram of polyacrylic acid and heated and blended for 2 minutes at a temperature of 150° C. and a blending speed of 100 rpm. The resulting polymer melt was drawn directly from the die of the microblender and spun into fibers using a spin line and a spool with a take-up speed of 5 m / min. The obtained fibers were photographed under transmitted polarized light using an Olympus BX60 Petrographic optical microscope. Figure 4 A cross-section of the fiber is shown, and the microcellular structure of the fiber is also shown. A longitudinal view of the fiber is shown in Figure 2D middle.
Embodiment 2
[0057] A similar procedure to Example 1 was followed except varying the amount of each polymer added to the microblender to obtain a blend and fiber with 60 wt% polyvinyl acetate, 40 wt% polyacrylic acid. The melt-spun fibers were photographed as described in Example 1, and the resulting images are shown in Figure 5 with 6 middle. The microcellular nature of the fibers is clearly visible.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com