Method for measuring bicarbonate ion utilizing capability of plant
A bicarbonate ion and plant technology, applied in the field of ecological environment management, can solve the problems of inability to measure the photosynthesis of plant leaves, etc., and achieve the effect of less steps, simple calculation, and less plant materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
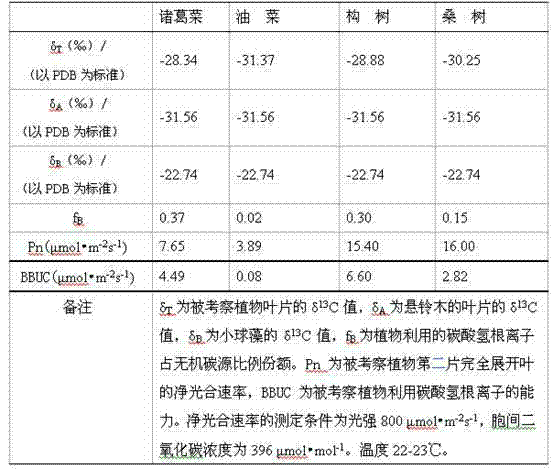
[0017] Embodiments of the present invention: it comprises the following steps, the first, measure respectively the stable carbon isotope composition δ of the leaves of the investigated plant and the reference plant 13 The value of C; second, the determination of the stable carbon isotopic composition of microalgae δ 13 C value; third, the δ of the plant leaves to be investigated 13 C value, δ of leaves of reference species 13 C value, δ of microalgae 13 The C value is brought into the two-terminal model to calculate the proportion of bicarbonate ion used by the investigated plant to the inorganic carbon source; fourth, measure the net photosynthetic rate of the investigated plant leaf; fifth, according to the net photosynthetic rate of the investigated plant leaf rate and the proportion of bicarbonate ions used by the investigated plants in the inorganic carbon source, and the ability of the investigated plants to utilize bicarbonate ions was obtained.
[0018] The detailed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com